Transfer function model of sloshing force effect of liquid propellant and its application
-
摘要:
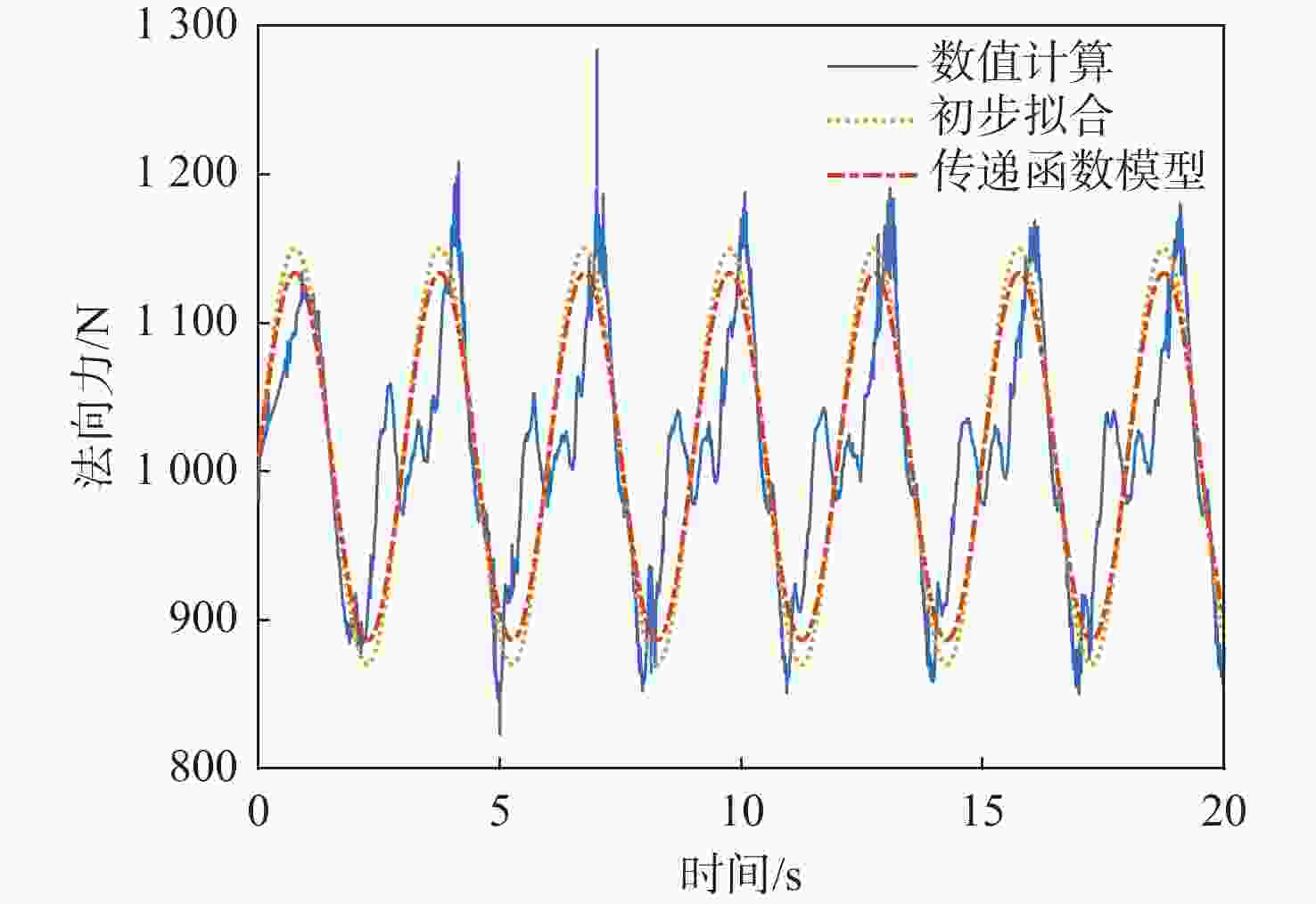
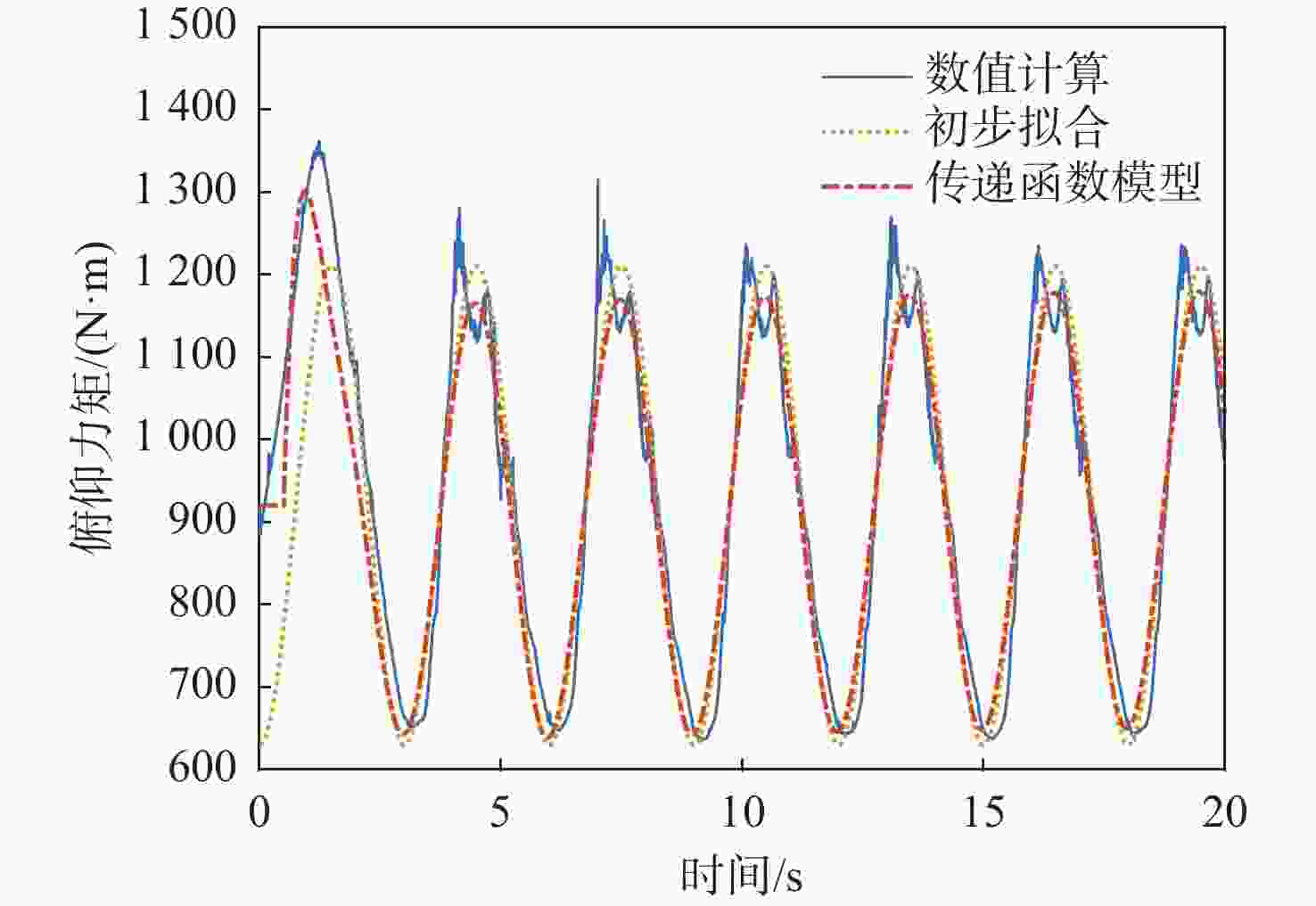
面向液体推进剂小幅晃动引发运载器不良耦合运动的预测和控制需要,基于液体晃动数值计算结果,开展晃动力效应的传递函数模型辨识研究。对返回阶段水平飞行运载器内置的平放煤油贮箱示例,根据其飞行阶段关注的转动运动范围,建立力效应传递函数描述模型,在此基础上,进行晃动抑制设计,以期增加晃动阻尼并削弱晃动对飞行的影响。结果表明:传递函数辨识结果能够捕获液体推进剂晃动力效应,可以用于运载器飞行特性预测和晃动抑制设计。
Abstract:To predict and regulate the space vehicle’s undesirable coupling motion produced by tiny amplitude sloshing of liquid propellant, a transfer function model identification study is carried out based on the findings of numerical calculations. For an example of a horizontally placed kerosene tank in a vehicle, during the level flight in the re-entry phase, a force effect transfer function description model is established with the range of rotational motion of interest, based on which a sloshing suppression design is carried out to increase sloshing damping and weaken the impact of sloshing on flight. The findings show that the transfer function can capture the impacts of the liquid propellant sloshing force, which can be utilized to anticipate space vehicle flight characteristics and design sloshing suppression.
-
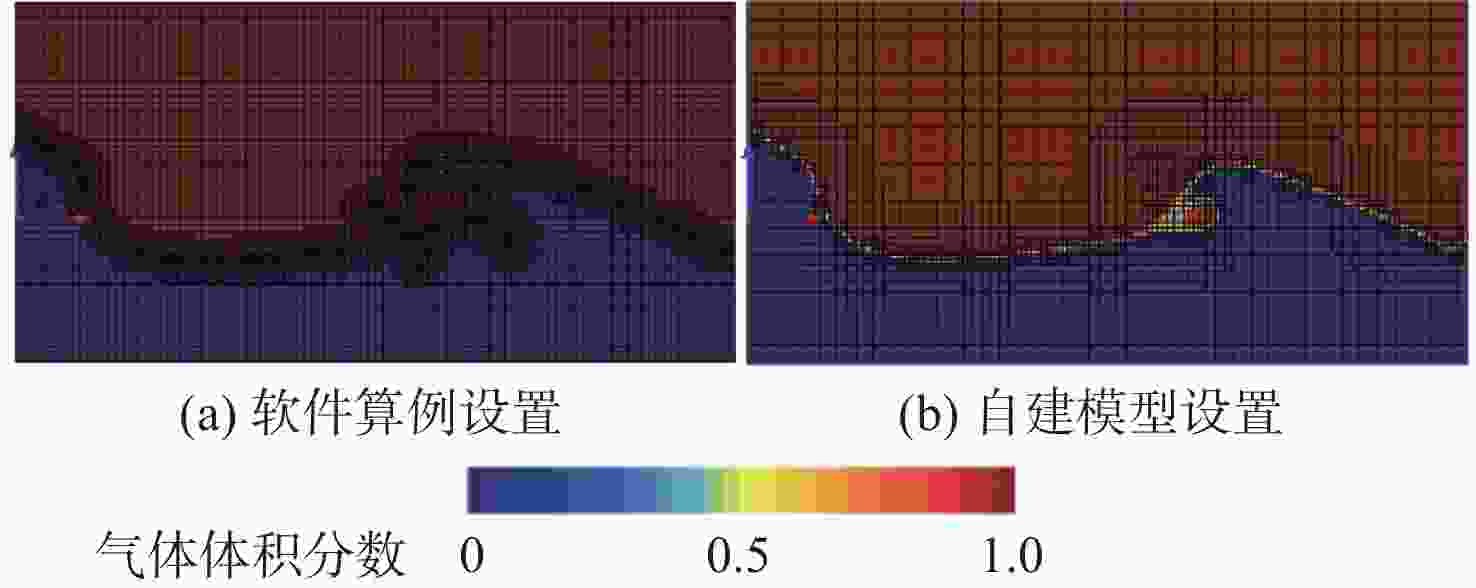
表 1 数值计算模型参数设置
Table 1. Model parameter settings for numerical calculation
模型参数 软件算例设置 自建模型设置 网格生成器 表面重构
切割体网格单元生成表面重构
切割体网格单元生成网格基础尺寸/m 0.005 0.1 空间模型 三维 三维 时间模型 隐式非稳态 隐式非稳态 材料模型 多相流(水+空气)、VOF(分离流) 多相流(水+空气)、VOF(分离流) 湍流模型 K-Epsilon Spalart-Allmaras 自适应设置 自适应网格、自适应时间步 自适应网格、自适应时间步 求解器设置 一阶时间离散、时间步触发自适应 二阶时间离散、时间步触发自适应 内部迭代步数 15 50 表 2 滚转运动输入与输出系数
Table 2. Input and output coefficients of rolling motion
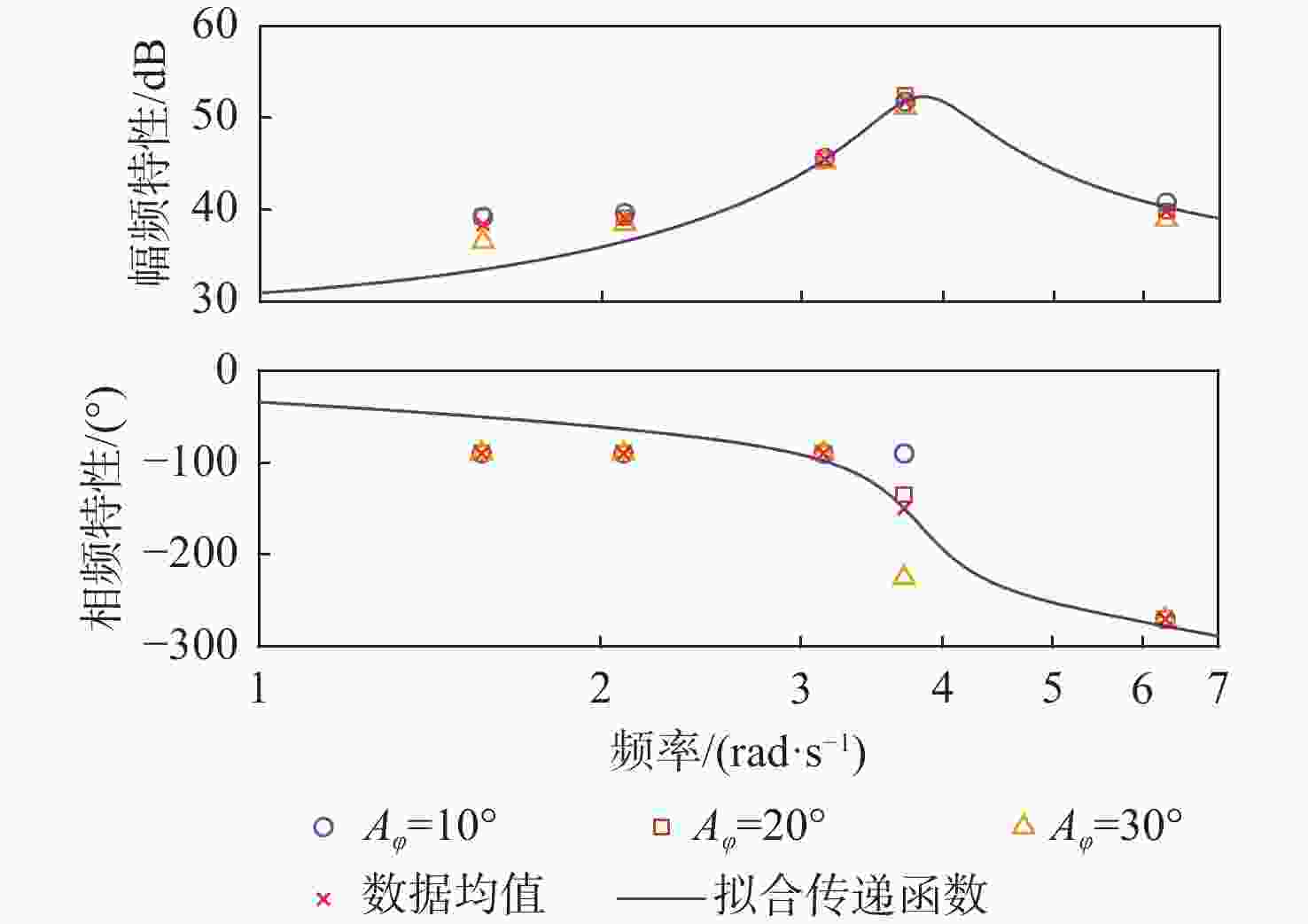
滚转输入参数 滚转输出参数 Aφ/(°) ωp/(rad·s−1) Ap/rad $ A_{F_y} $/N $ \varphi_{F_y} $/(°) $ A_{M_x} $/(N·m) $ \varphi_{M_x} $/(°) $A_{M_{\textit{z}}} $/(N·m) $ \varphi_{M_{\textit{z}}} $/(°) 10 1.57 0.27 25 0 50 0 24 180 2.09 0.37 35 0 50 0 35 180 3.14 0.55 105 0 50 0 115 180 3.70 0.65 250 0 47 0 290 180 6.28 1.10 120 −180 51 0 148 0 20 1.57 0.55 50 0 100 0 48 180 2.09 0.73 66 0 101 0 68 180 3.14 1.10 210 0 99 0 235 180 3.70 1.29 540 −45 95 0 660 135 6.28 2.19 215 −180 98 0 265 0 30 1.57 0.82 55 0 150 0 55 180 2.09 1.10 92 0 150 0 96 180 3.14 1.64 300 0 140 0 345 180 3.70 1.94 700 −135 160 0 750 45 6.28 3.29 290 −180 145 0 355 0 表 3 俯仰运动输入与输出系数
Table 3. Input and output coefficients of pitching motion
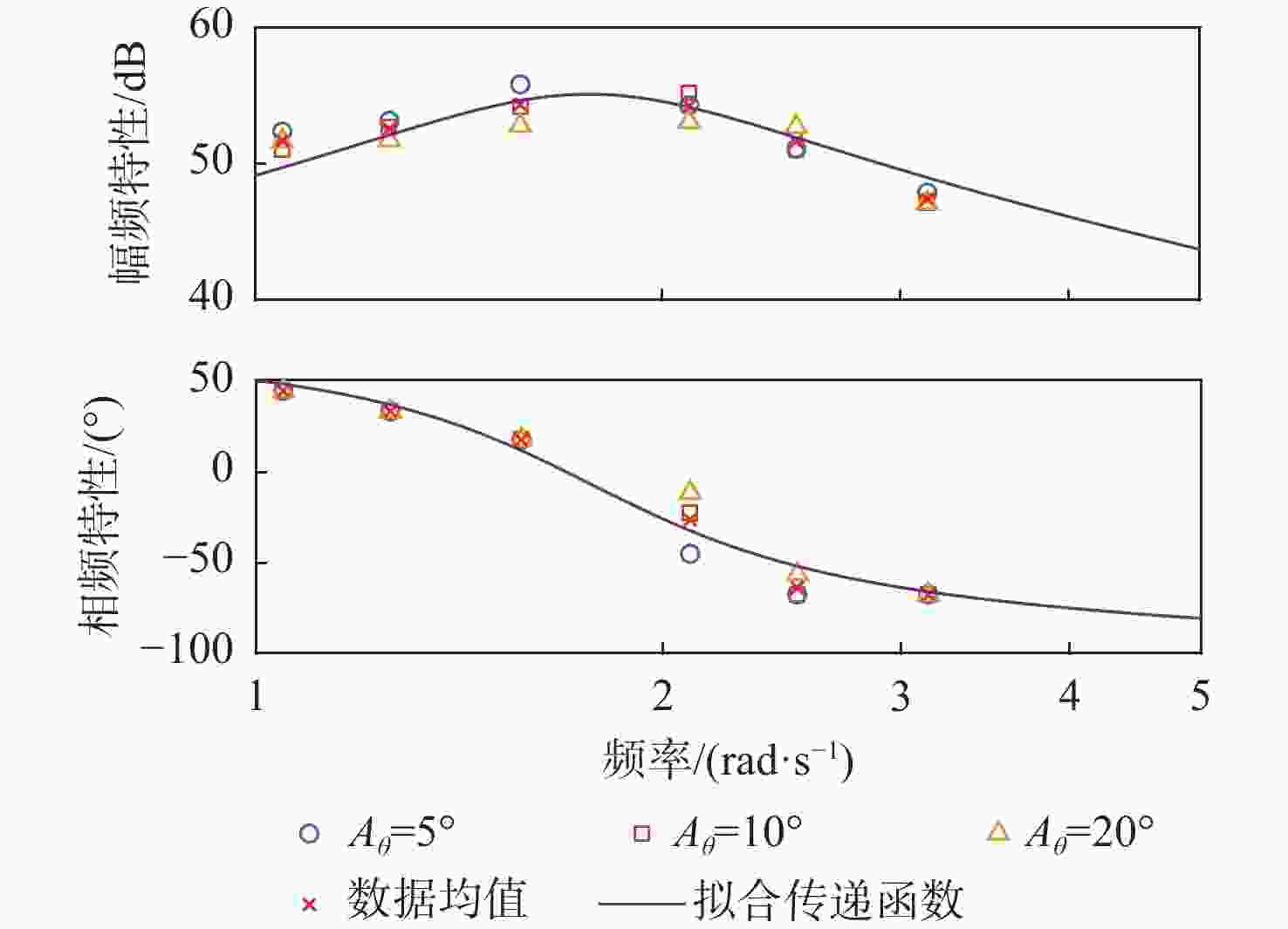
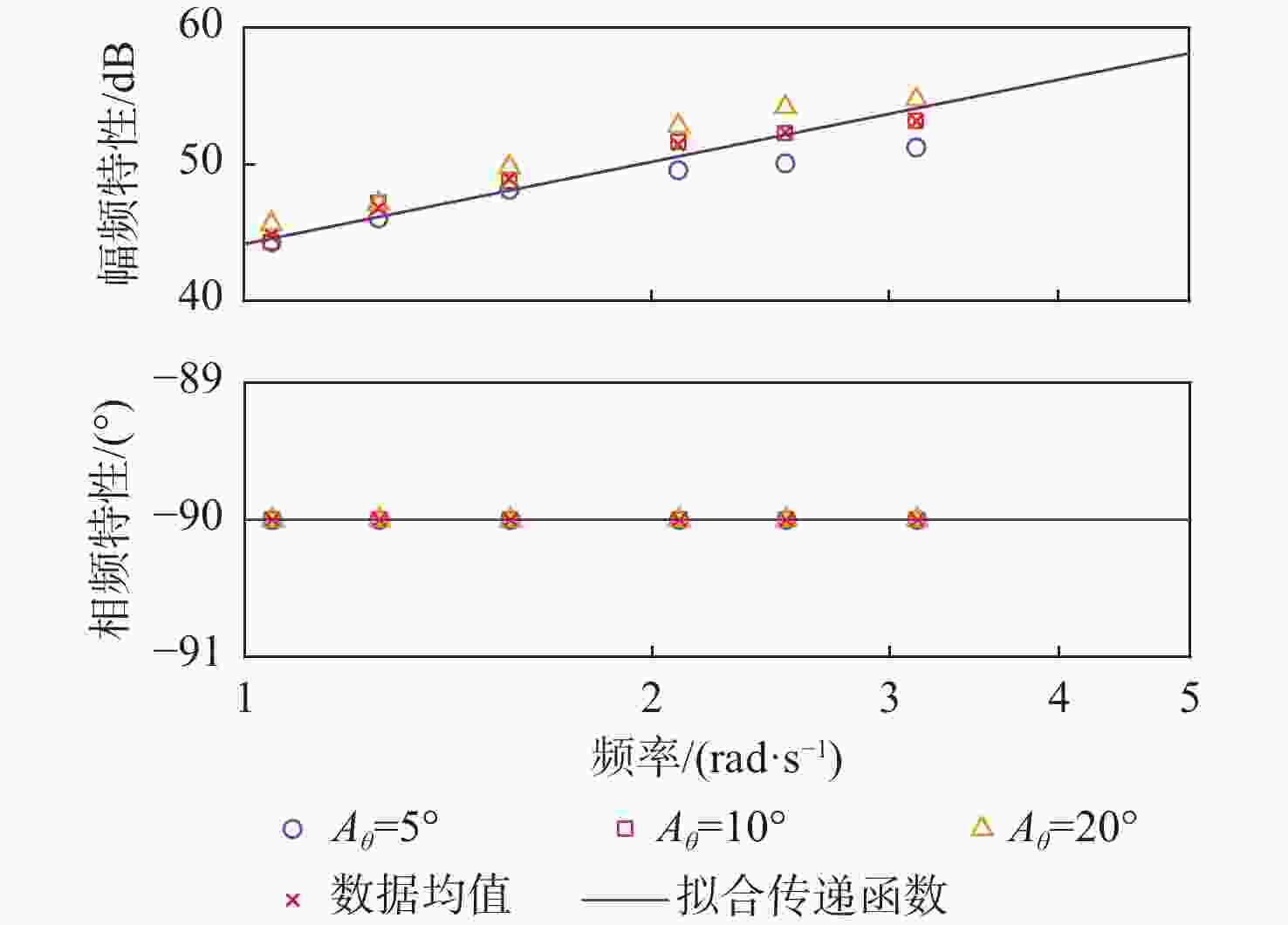
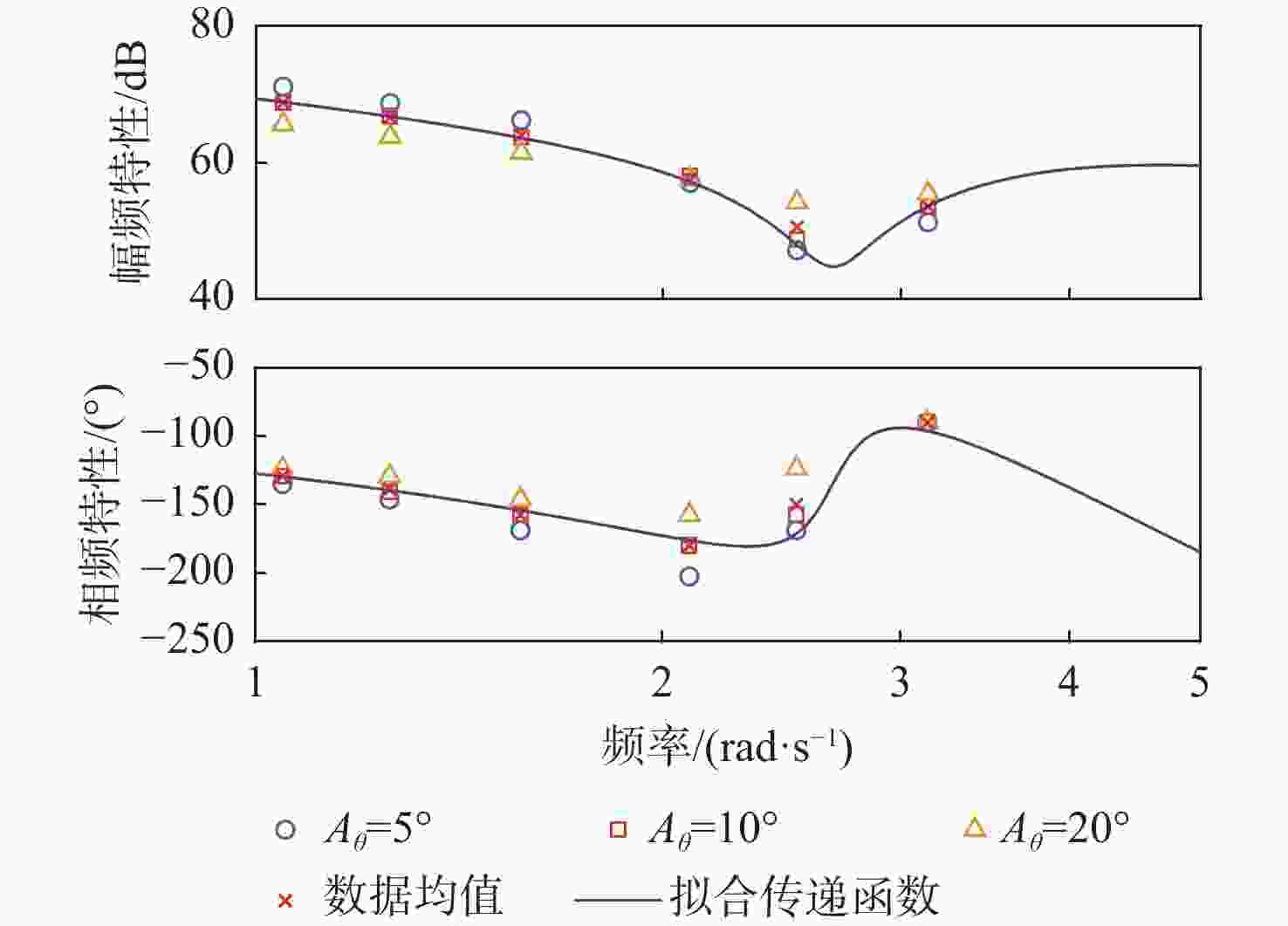
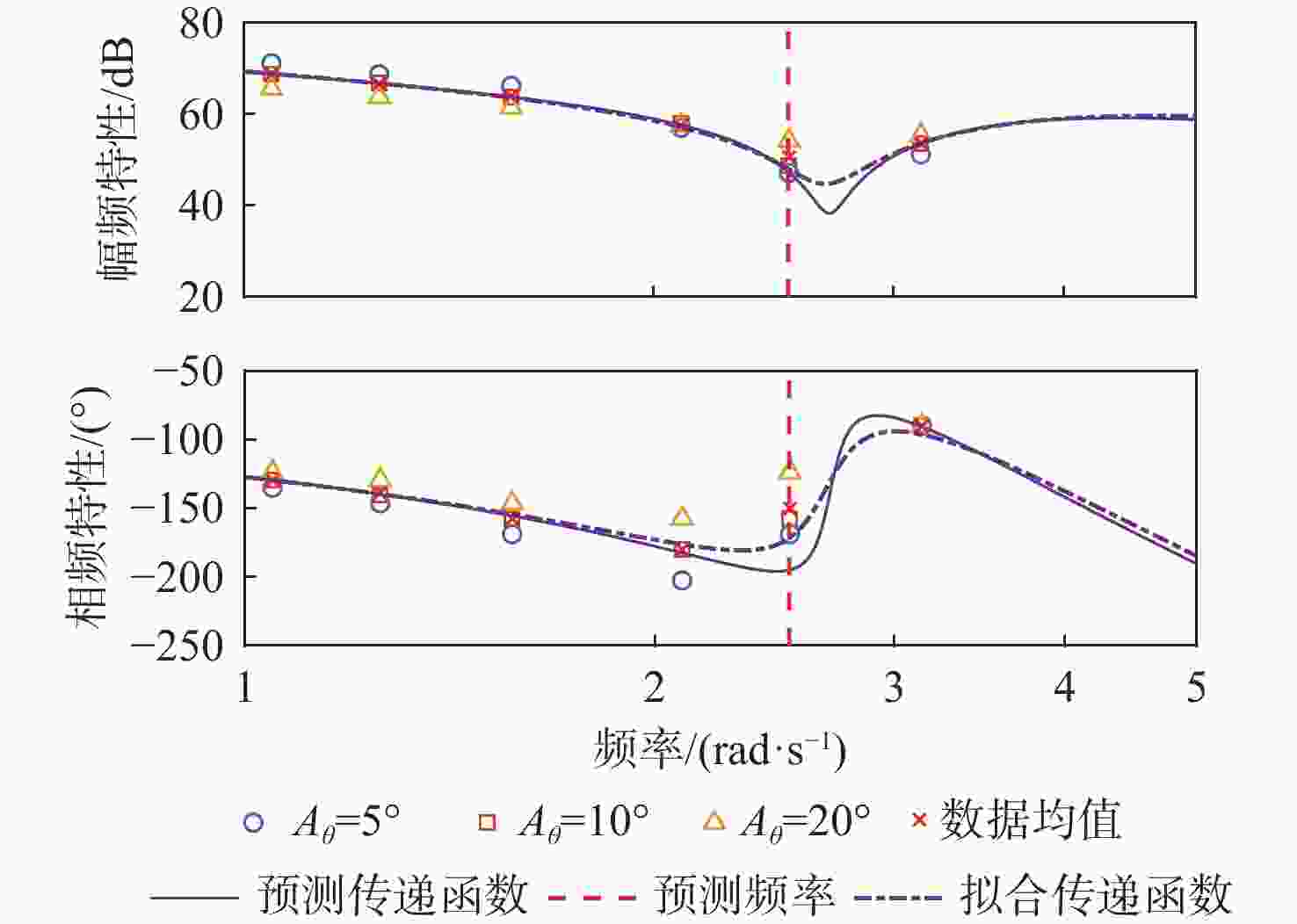
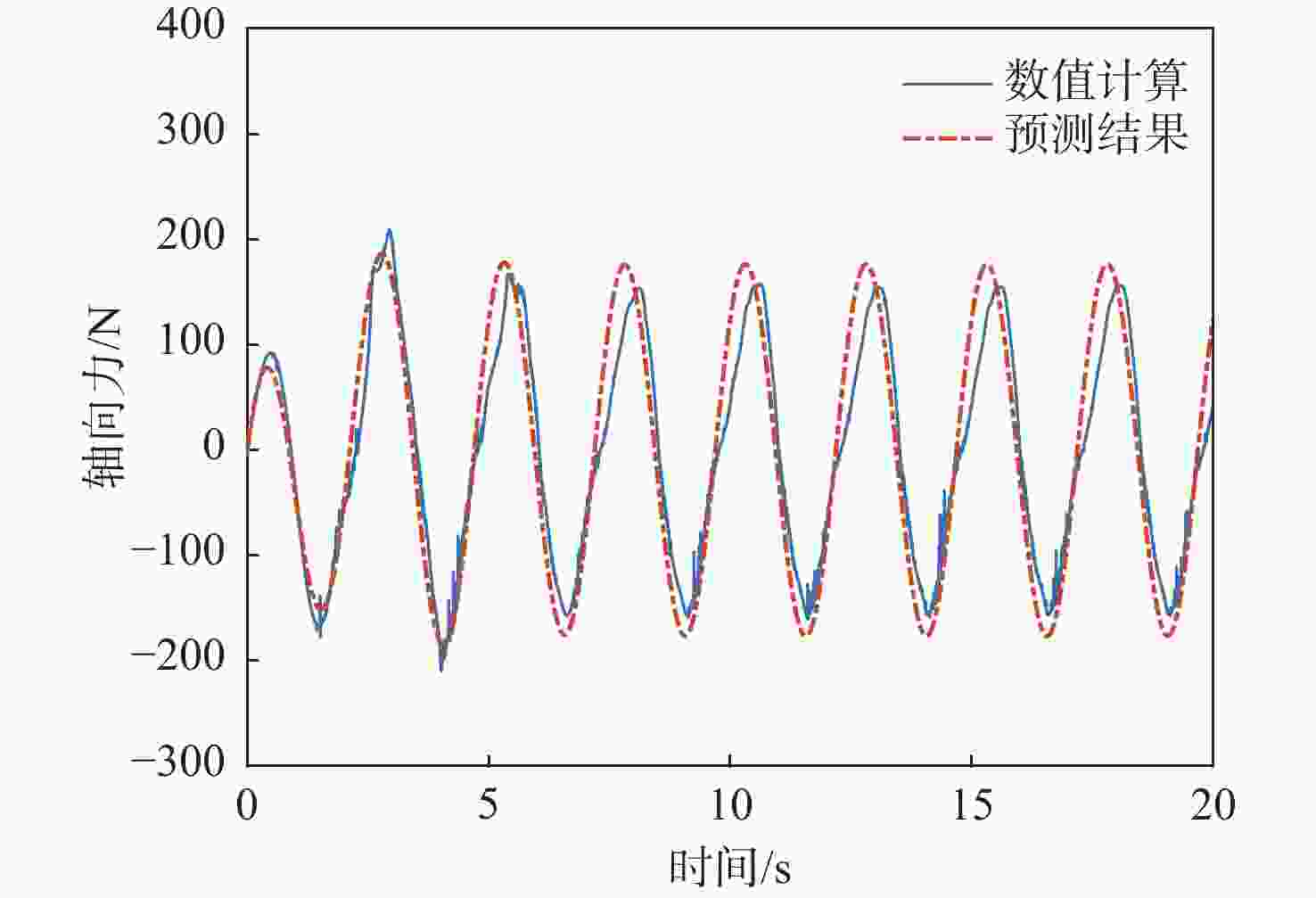
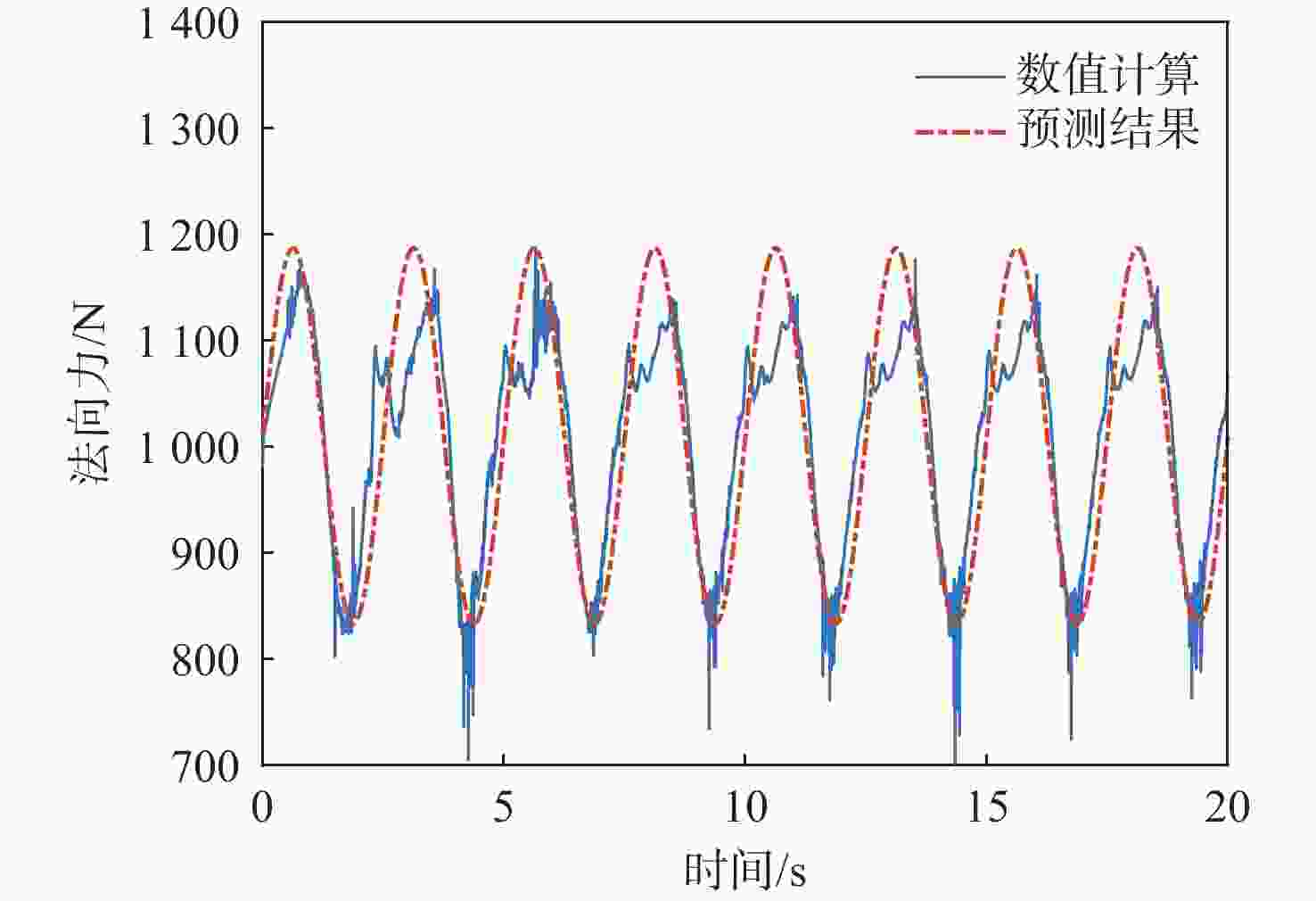
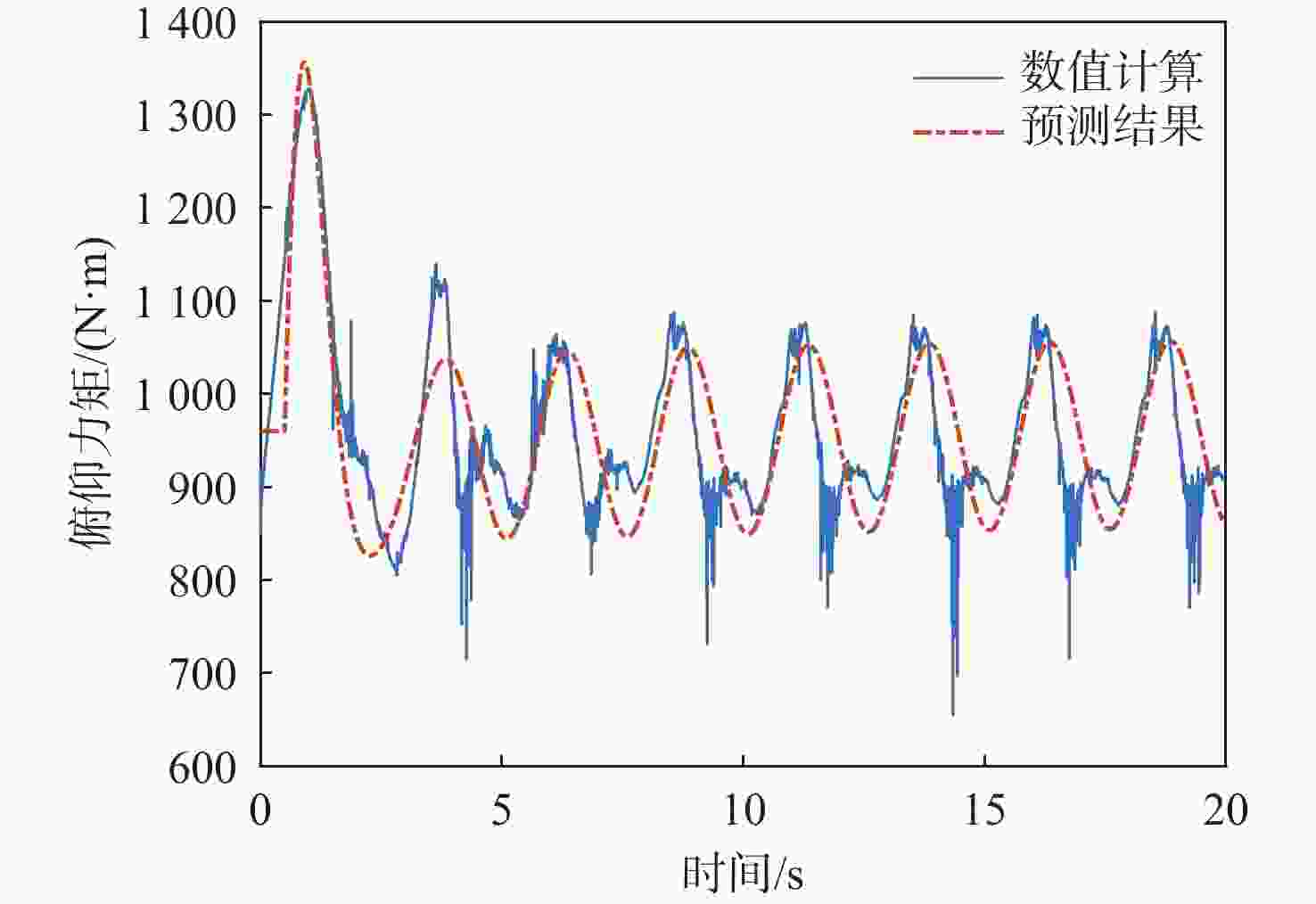
俯仰输入参数 俯仰输出参数 Aθ/(°) ωq/(rad·s−1) Aq/rad $A_{F_x} $/N $ \varphi_{F_x} $/(°) $A_{F_{\textit{z}}} $/N $ \varphi_{F_{\textit{z}}} $/(°) $A_{M_y} $/(N·m) $ \varphi_{M_y} $/(°) 5 1.05 0.09 38 135 15 0 330 −45 1.26 0.11 50 123.75 22 0 300 −56.25 1.57 0.14 85 108 35 0 280 −78.75 2.09 0.18 95 45 55 0 130 −112.5 2.51 0.22 79 22.5 70 0 50 −78.75 3.14 0.27 68 22.5 100 0 100 0 10 1.05 0.18 65 135 30 0 500 −39.38 1.26 0.22 95 123.75 50 0 480 −50.63 1.57 0.27 140 108 75 0 420 −67.5 2.09 0.37 210 67.5 140 0 290 −90 2.51 0.44 156 22.5 160 0 120 −67.5 3.14 0.55 125 22.5 250 0 260 0 20 1.05 0.37 140 135 70 0 700 −33.75 1.26 0.44 170 123.75 100 0 680 −39.38 1.57 0.55 240 108 170 0 650 −56.25 2.09 0.73 330 78.75 320 0 550 −67.5 2.51 0.88 380 33.75 450 0 450 −33.75 3.14 1.10 250 22.5 600 0 650 0 表 4 转动角速度-力效应拟合传递函数模型与评价
Table 4. Transfer function model and fitting evaluation of rotational rate to force effect
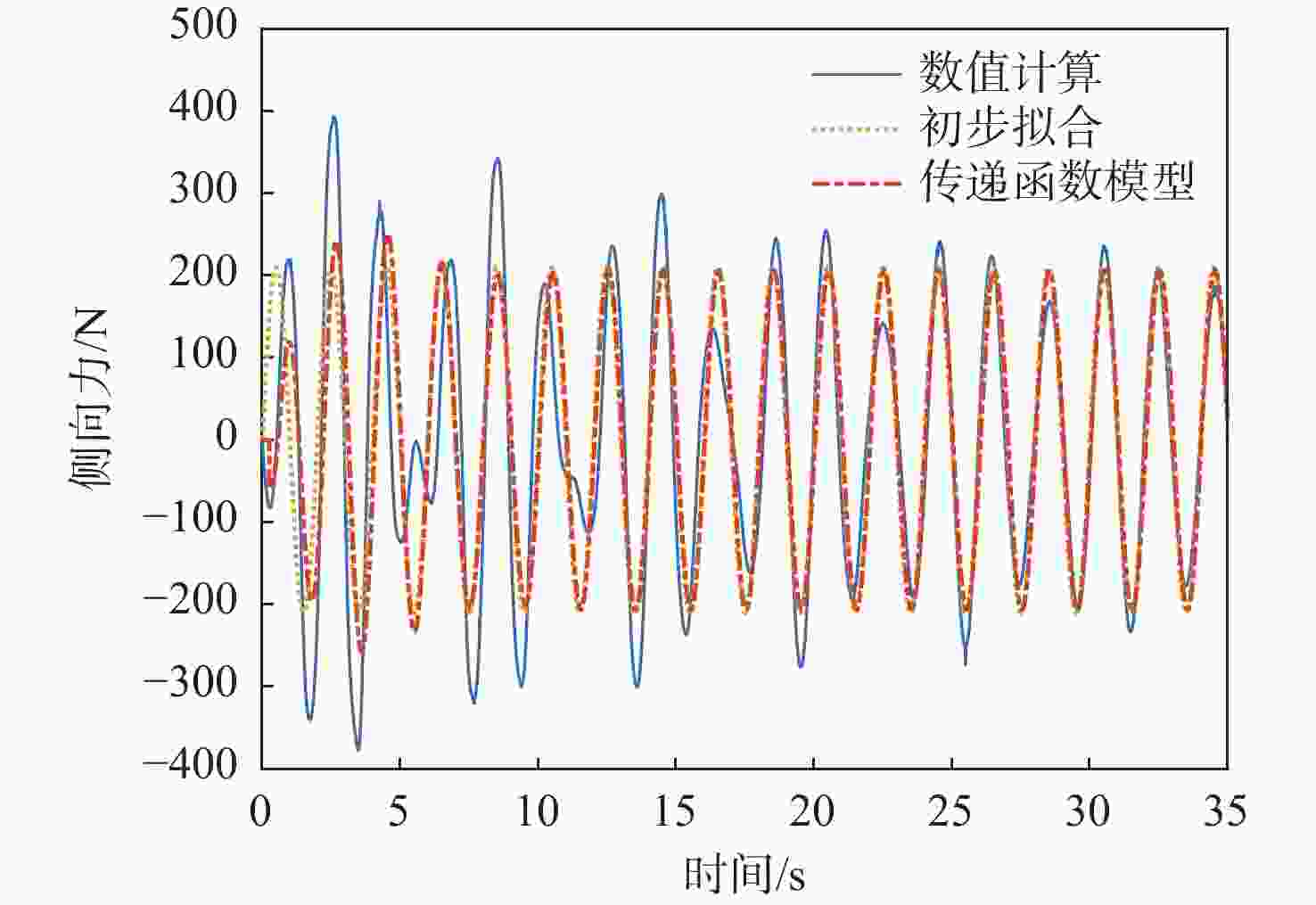
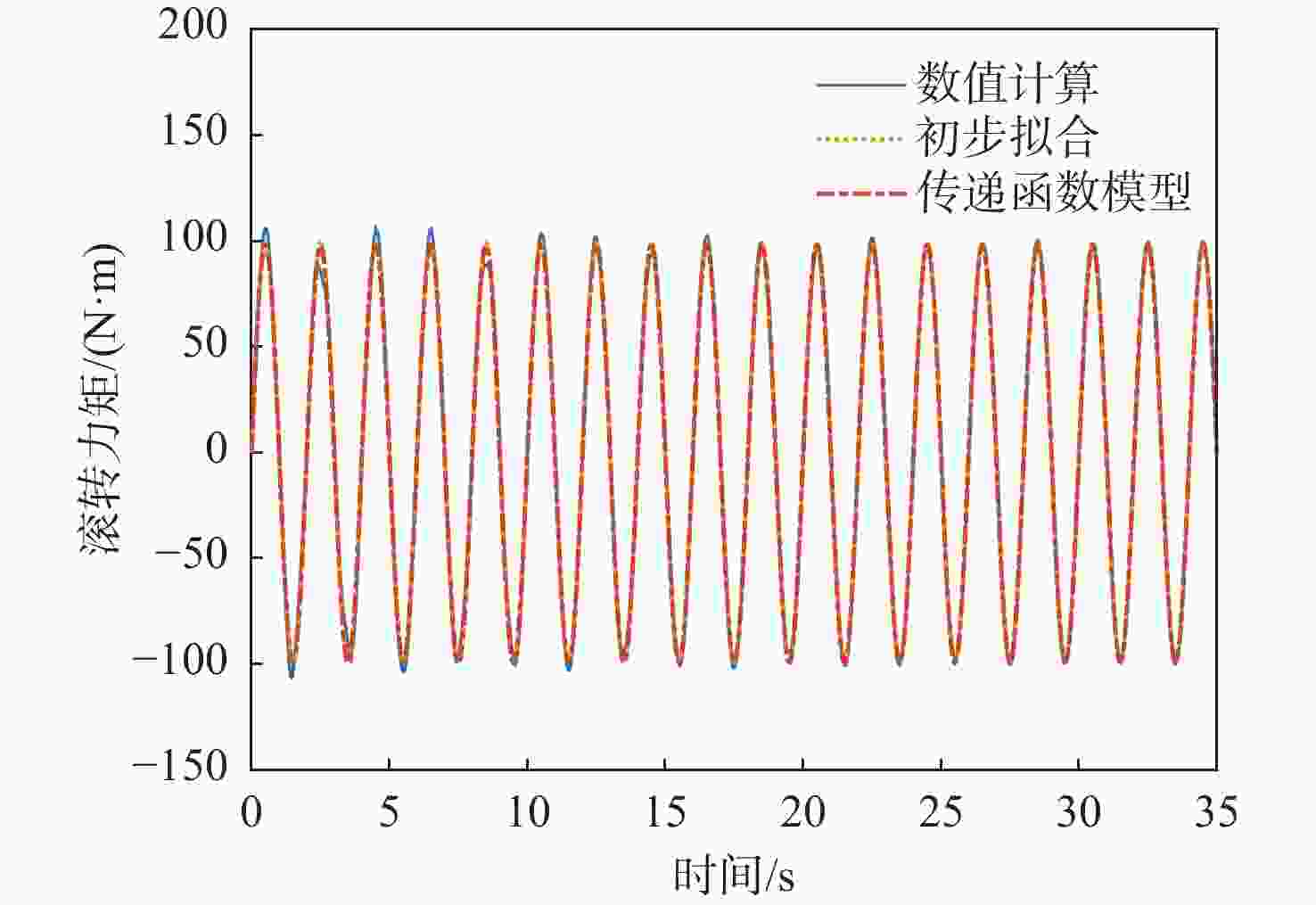
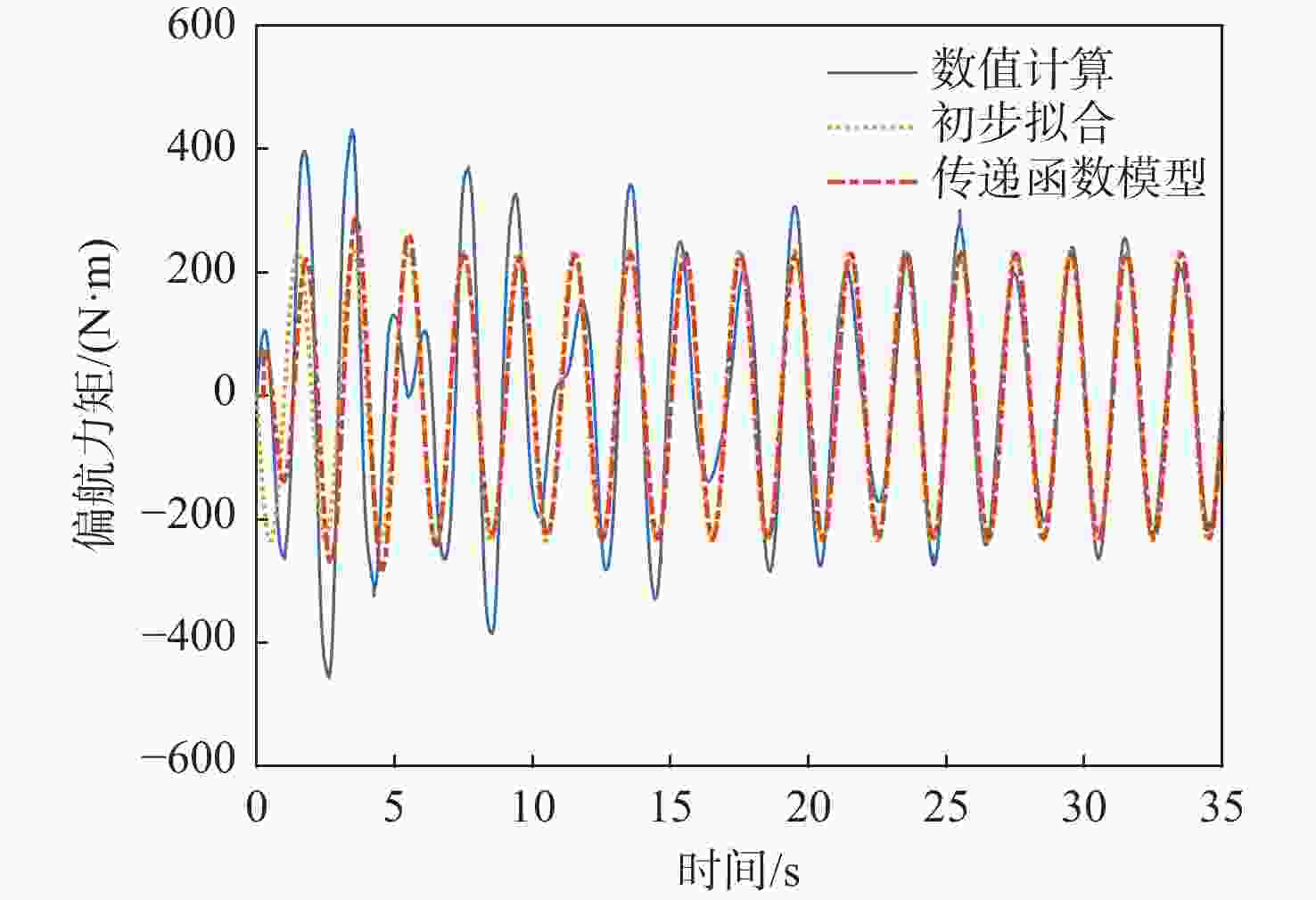
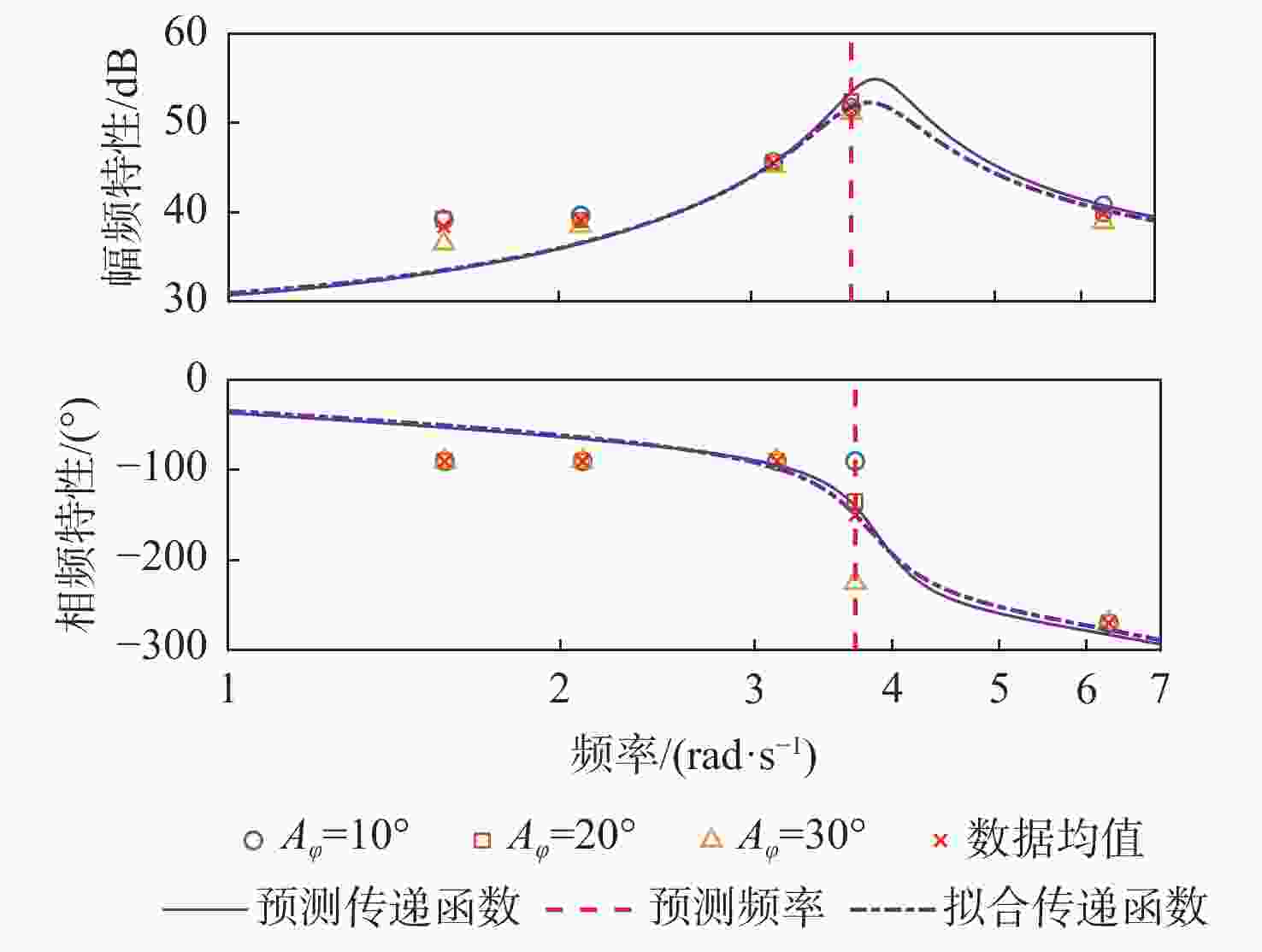
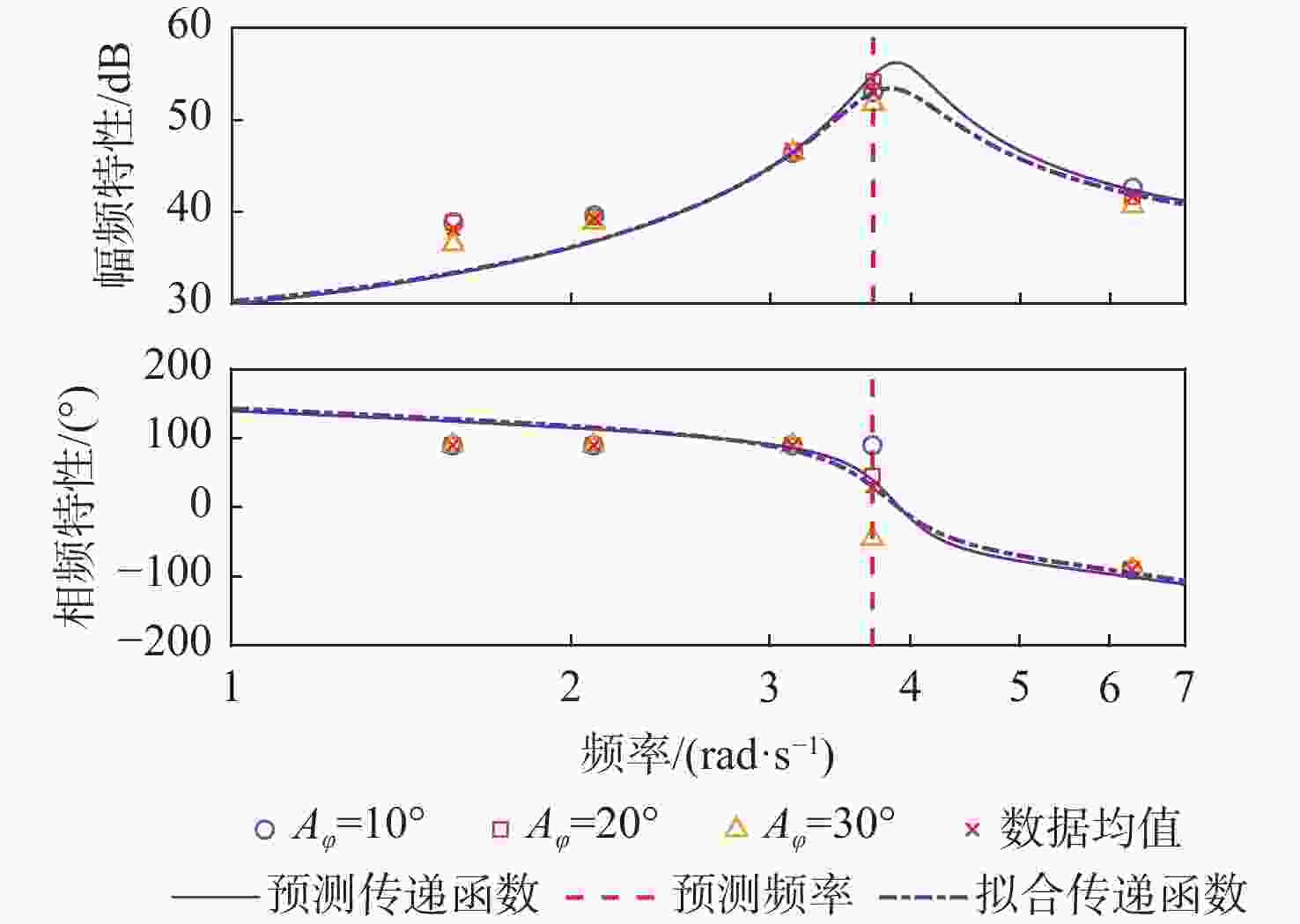
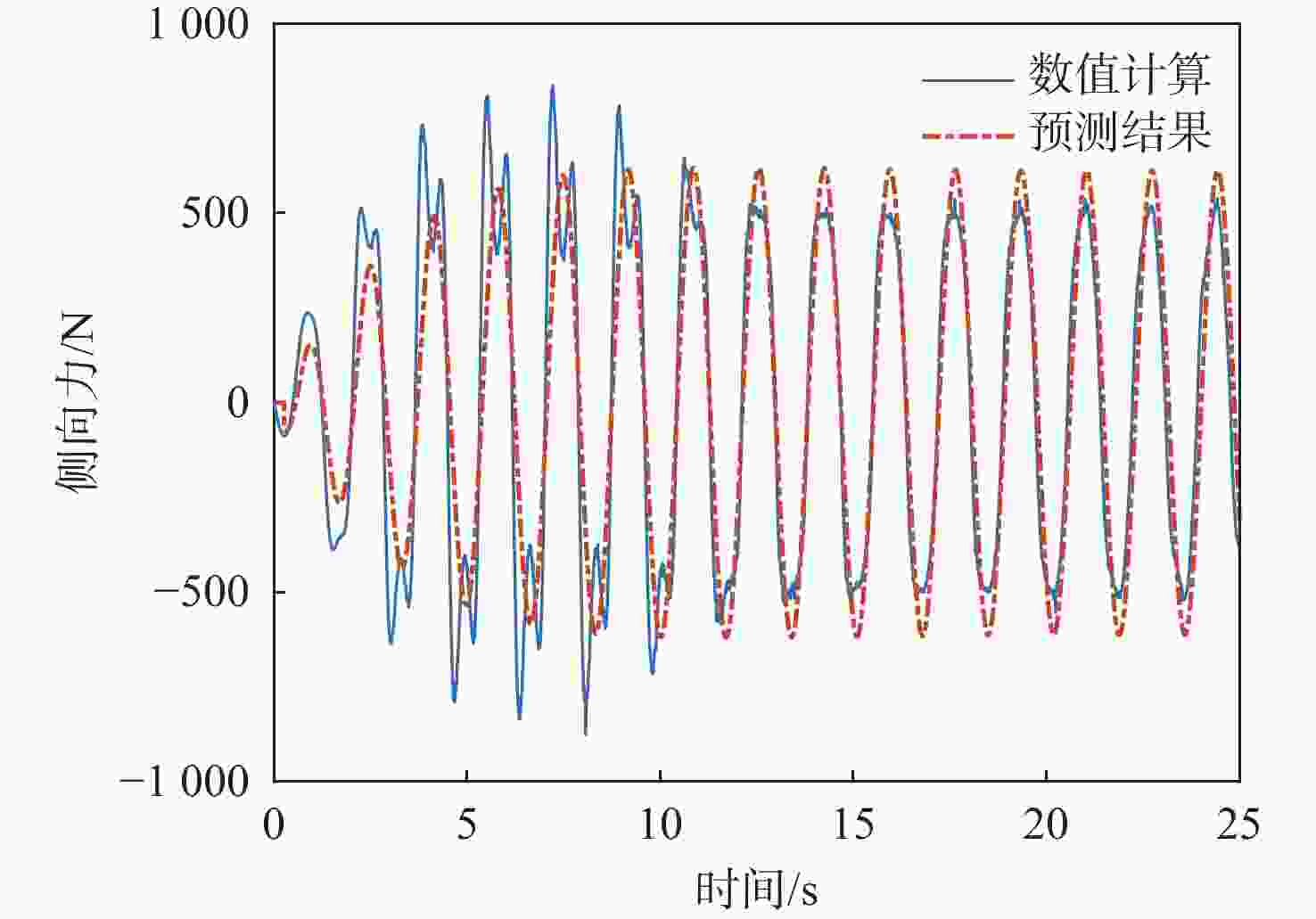
信号通道 传递函数 拟合度/% 幅频分散度/% p-Fy $ {G_{{F_y}}}\left( s \right) = {{\text{e}}^{ - 0.25s}}\dfrac{{ - 52.31{s^2} - 136.3s + 408.6}}{{{s^2} + 0.812\;6s + 14.64}} $ 80.2 1.93 p-Mx $ {G_{{M_x}}}\left( s \right) = \dfrac{{0.688\;3{s^2} + 281.1s + 574.4}}{{{s^2} + 1.998s + 0.053\;94}} $ 98.3 0.66 p-Mz $ {G_{{M_{\textit{z}}}}}\left( s \right) = {{\text{e}}^{ - 0.25s}}\dfrac{{68.11{s^2} + 142.9s - 349.6}}{{{s^2} + 0.807\;9s + 14.53}} $ 83.4 1.88 q-Fx $ {G_{{F_x}}}\left( s \right) = \dfrac{{ - 11.27{s^2} + 693.5s + 102.1}}{{{s^2} + 1.223s + 3.123}} $ 78.6 1.69 q-Fz $ {G_{{F_{\textit{z}}}}}\left( s \right) = {{ - 161}}{\text{.5}}s $ 72.7 2.55 q-My $ {G_{{M_y}}}\left( s \right) = {{\text{e}}^{ - 0.5s}}\dfrac{{5\;604{s^2} + 1\;777s + 4.001 \times {{10}^4}}}{{{s^3} + 3.446{s^2} + 12.44s + 1.095}} $ 91.8 3.92 表 5 滚转角速度-力效应预测传递函数模型与评价
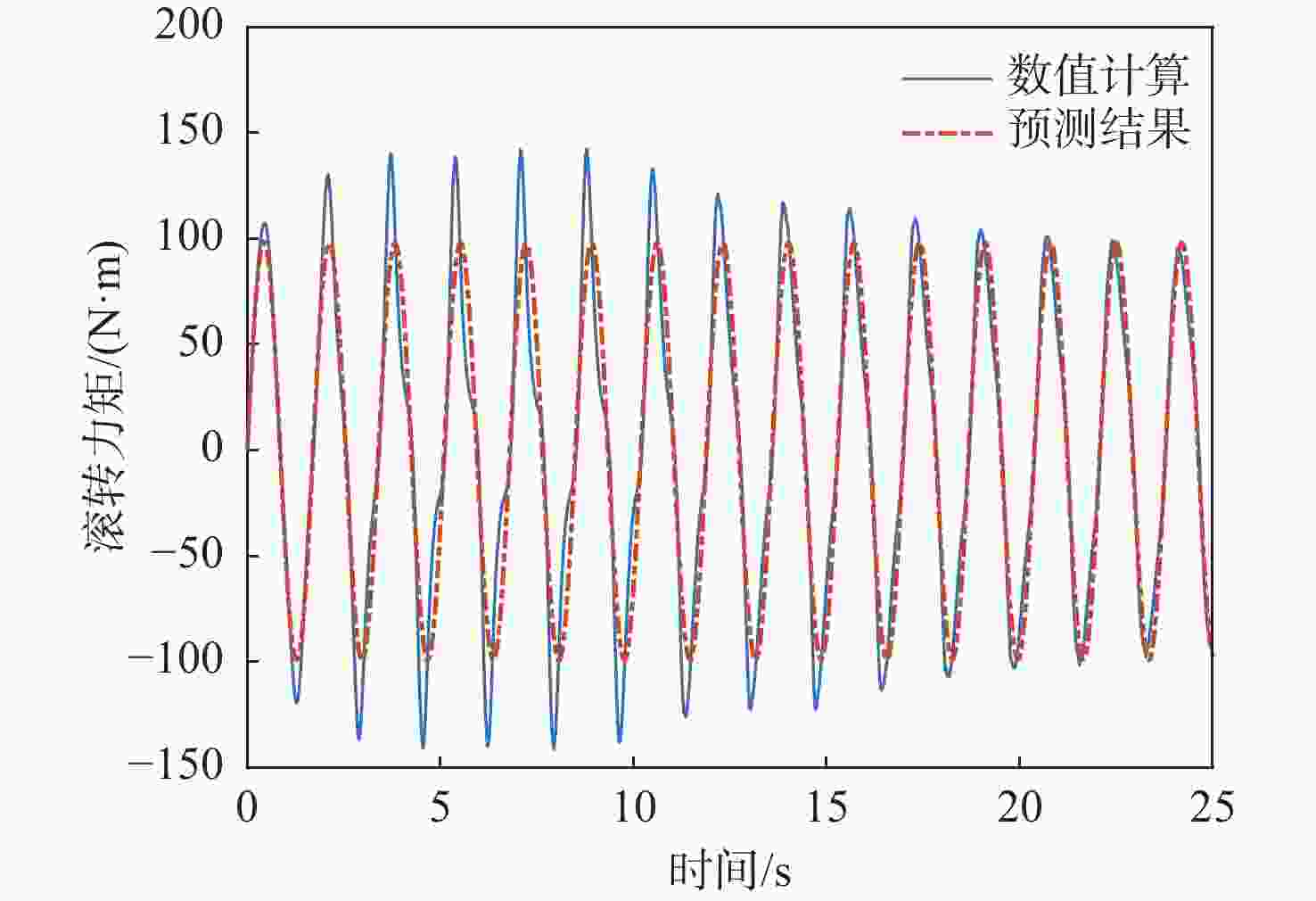
Table 5. Predictive transfer function model and evaluation of roll rate to force effect
信号
通道传递函数 拟合度/% 幅频
分散度/%p-Fy $ {G_{{F_y}}}\left( s \right) = {{\text{e}}^{ - 0.25s}}\dfrac{{ - 53.36{s^2} - 162.4s + 399.9}}{{{s^2} + 0.626\;8s + 15.07}} $ 64.3 2.10 p-Mx $ {G_{{M_x}}}\left( s \right) = \dfrac{{0.643\;9{s^2} + 281.1s + 552.1}}{{{s^2} + 1.921s + 0.053\;19}} $ 98.3 0.42 p-Mz $ {G_{{M_{\textit{z}}}}}\left( s \right) = {{\text{e}}^{ - 0.25s}}\dfrac{{69.31{s^2} + 174.1s - 334.6}}{{{s^2} + 0.607\;5s + 14.96}} $ 70.5 1.78 表 6 俯仰角速度-力效应预测传递函数模型与评价
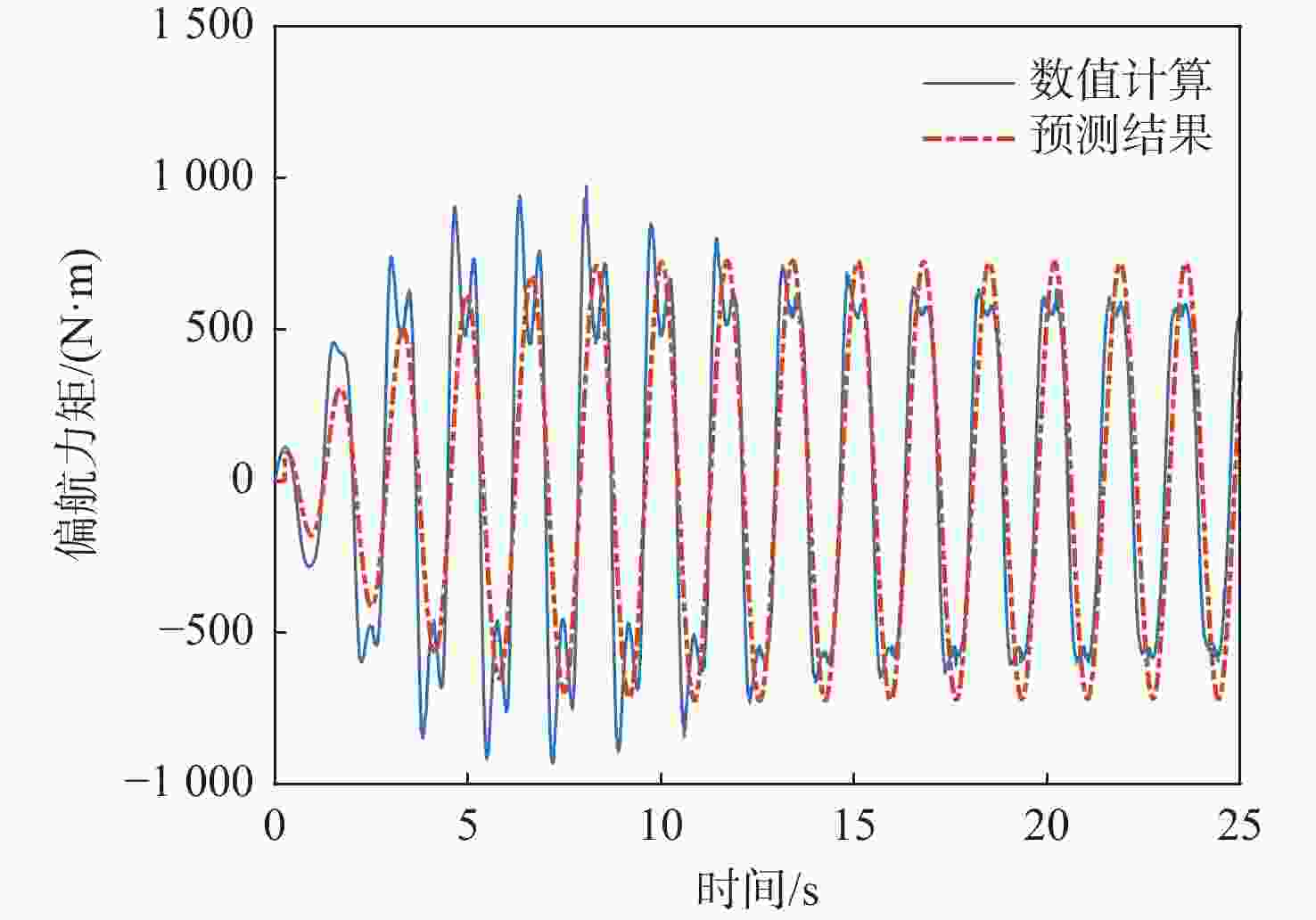
Table 6. Predictive transfer function model and evaluation of pitch rate to force effect
信号
通道传递函数 拟合度/% 幅频
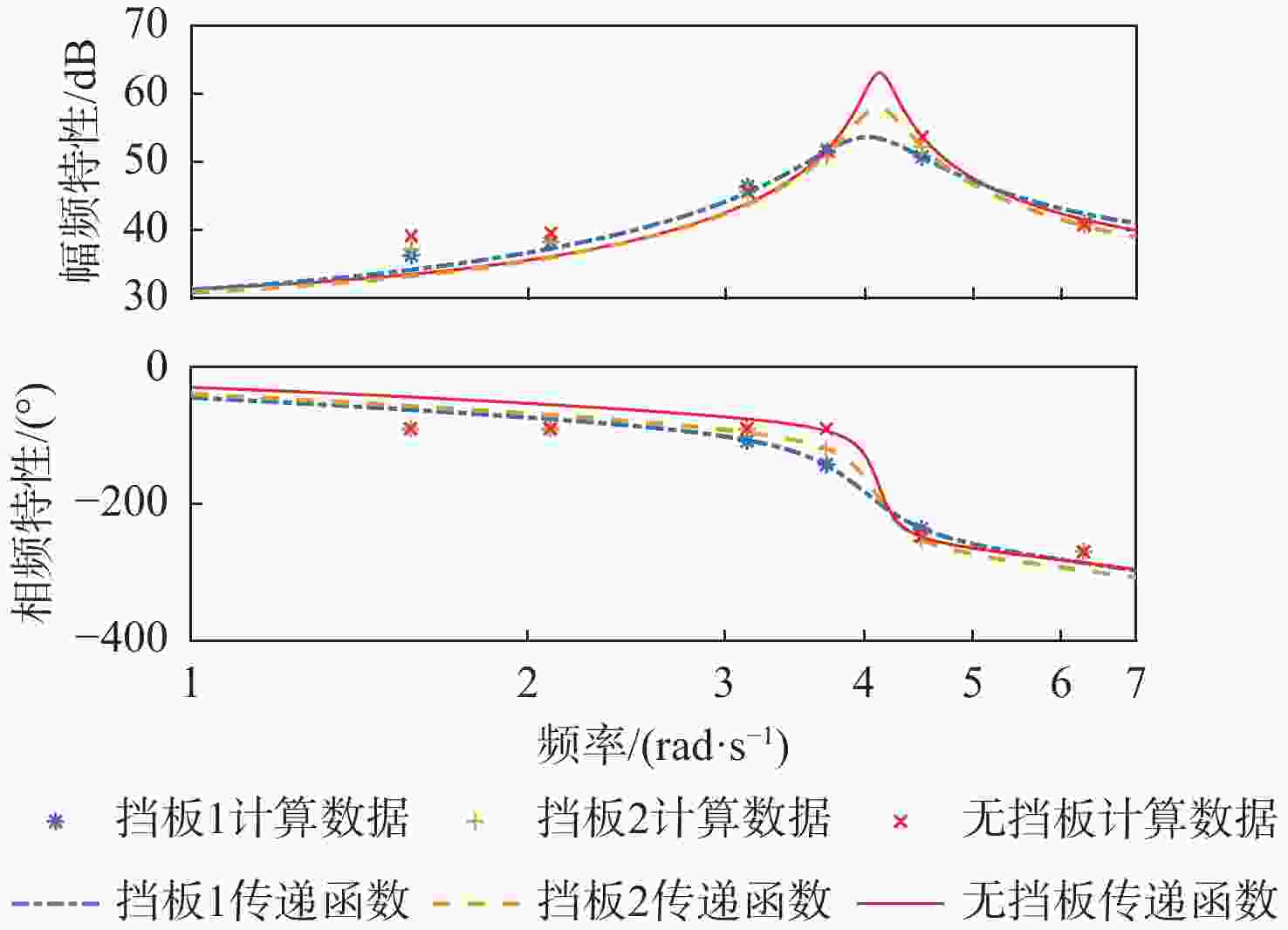
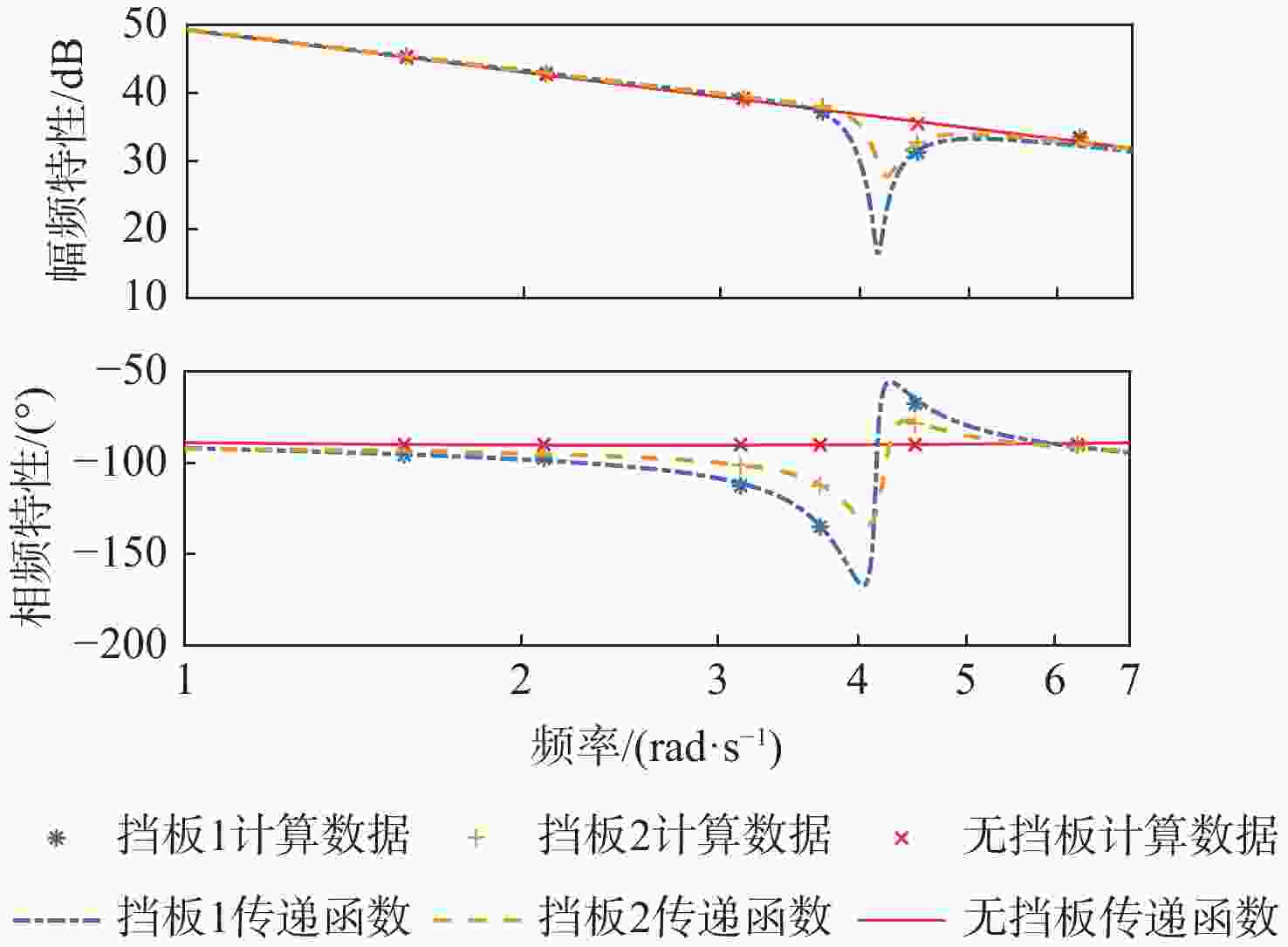
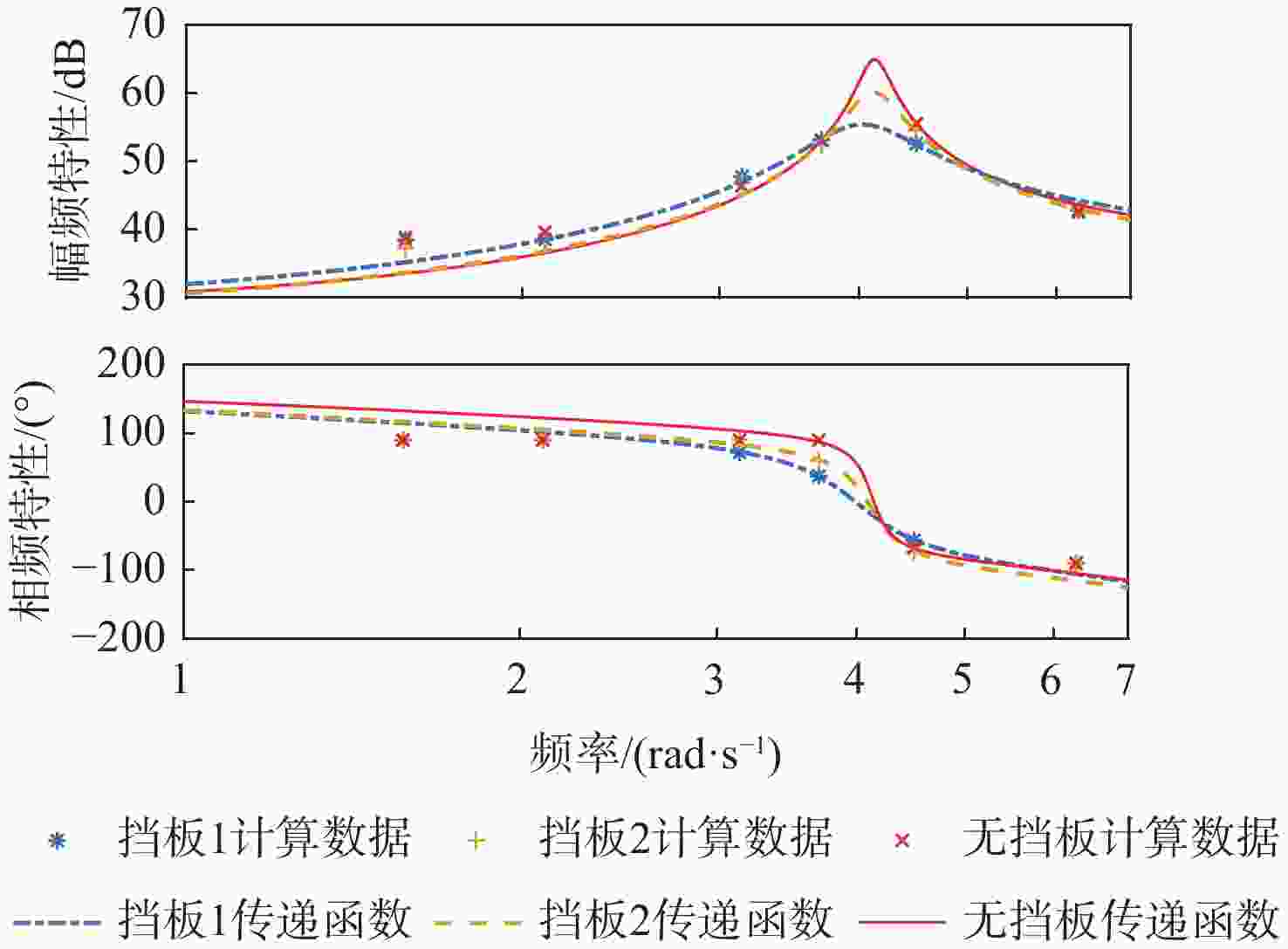
分散度/%q-Fx $ {G_{{F_x}}}\left( s \right) = \dfrac{{8.038{s^2} + 743.1s + 100.7}}{{{s^2} + 1.328s + 3.087}} $ 81.0 1.66 q-Fz $ {G_{{F_{\textit{z}}}}}\left( s \right) = {{ - 160}}{\text{.4}}s $ 69.8 2.27 q-My $ {G_{{M_y}}}\left( s \right) = {{\text{e}}^{ - 0.5s}}\dfrac{{4835{s^2} + 676.1s + 3.5 \times {{10}^4}}}{{{s^3} + 2.826{s^2} + 11.21s + 1.116}} $ 96.1 3.24 表 7 不同挡板传递函数幅频峰值特性
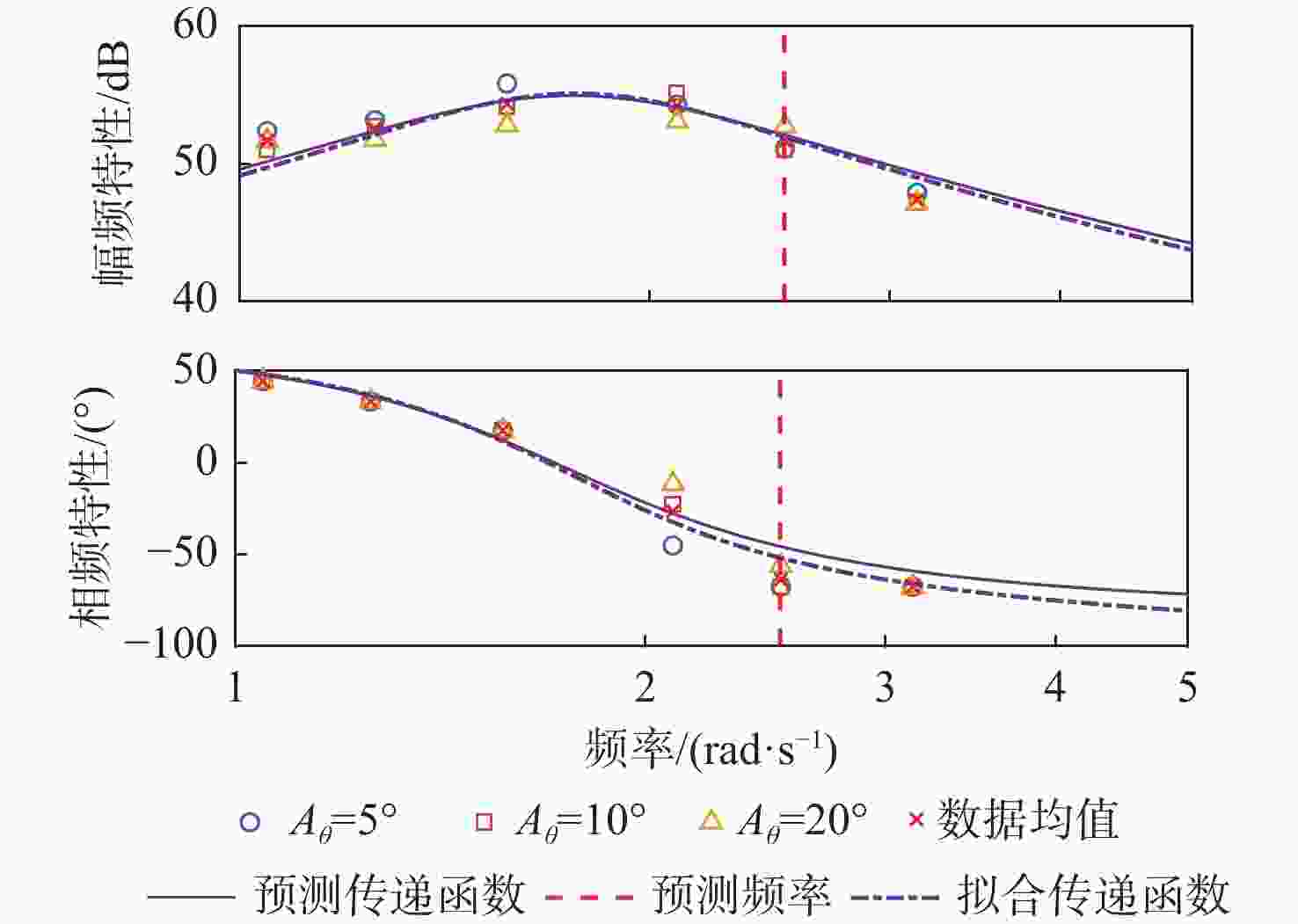
Table 7. Amplitude frequency peak characteristics of transfer function with different baffle settings
挡板设置 侧向力幅
值峰值/dB侧向力峰
值频率/(rad·s−1)偏航力矩
幅值峰值/dB偏航力矩
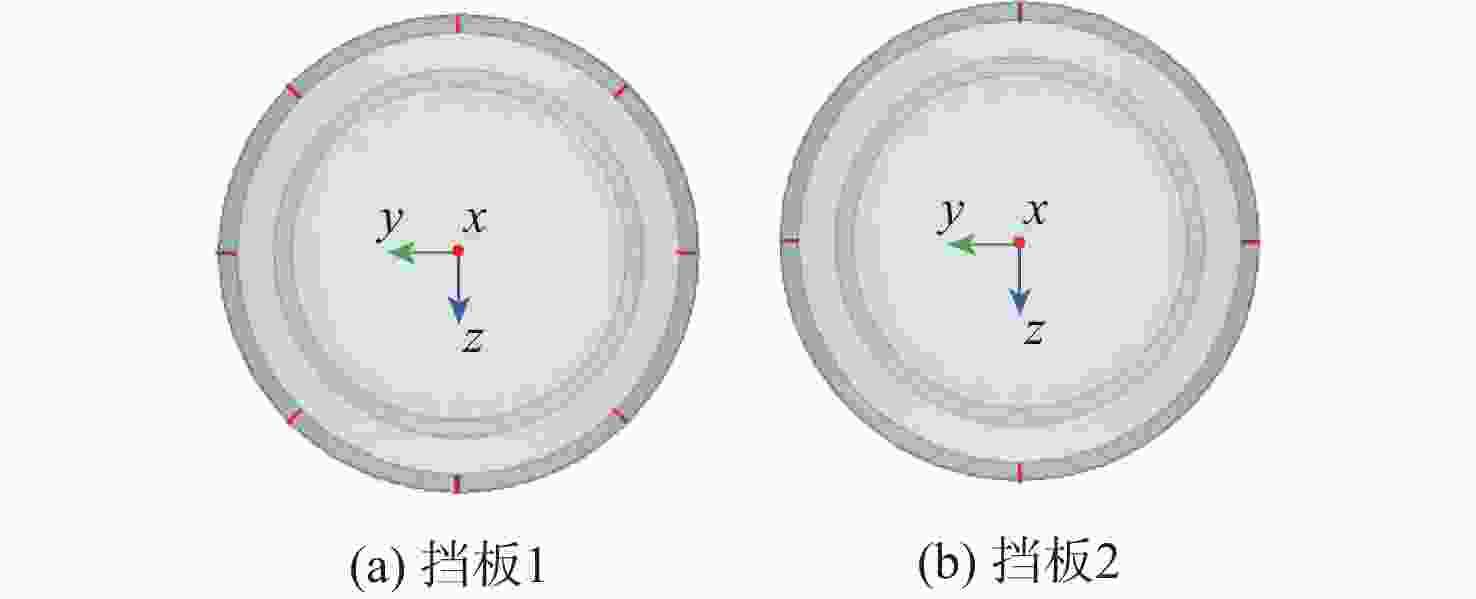
峰值频率/(rad·s−1)无挡板 63.1 4.1 64.9 4.1 挡板2 57.9 4.1 60.1 4.1 挡板1 53.6 4.0 55.3 4.0 -
[1] 胡平信, 刘国球. 液体火箭发动机的技术发展与展望[J]. 导弹与航天运载技术, 1998(2): 1-10.HU P X, LIU G Q. Technological development and prospect for liquid rocket engines[J]. Missiles and Space Vehicles, 1998(2): 1-10(in Chinese). [2] 尹立中, 王本利, 邹经湘. 航天器液体晃动与液固耦合动力学研究概述[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 1999, 31(2): 118-122. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0367-6234.1999.02.031YIN L Z, WANG B L, ZOU J X. Introduction to investigation of liquid sloshing and liquid-solid coupled dynamics of spacecraft[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 1999, 31(2): 118-122(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0367-6234.1999.02.031 [3] RUBEN A M. Prevention of coupled structure-propulsion instability (POGO): NASA SP-8055[R]. Washington, D. C. : NASA, 1970. [4] ABRAMSON H N. The dynamic behavior of liquids in moving containers: NASA SP-106[R]. Washington, D. C. : NASA, 1966. [5] 李俊峰, 周宏, 王为, 等. 充液航天器液体晃动及液固耦合动力学研究进展[C]//动力学与控制及航天应用. 北京: 中国宇航出版社, 2008: 64-88.LI J F, ZHOU H, WANG W, et al. Research progress on liquid sloshing and liquid-solid coupling dynamics of liquid-filled spacecraft[C]//Dynamics, Control and Aerospace Applications. Beijing: China Astronautic Publishing House, 2008: 64-88(in Chinese). [6] 李青. 充液挠性系统动力学分析及在航天工程中的应用研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2010.LI Q. Dynamicanalysis of liquid-filled flexible systems and its application studies on aerospace engineering[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2010(in Chinese). [7] 李青, 马兴瑞, 王天舒. 非轴对称贮箱液体晃动的等效力学模型[J]. 宇航学报, 2011, 32(2): 242-249.LI Q, MA X R, WANG T S. Equivalent mechanical model for liquid sloshing in non-axisymmetric tanks[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2011, 32(2): 242-249(in Chinese). [8] 丁文镜, 吴学森. 辨识液体晃动力学参数的频域法[J]. 宇航学报, 1991, 12(3): 68-75.DING W J, WU X S. Frequency domain method of identifying mechanical parameters of sloshing liquid[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 1991, 12(3): 68-75(in Chinese). [9] 丁文镜, 曾庆长. 晃动液体单摆模型动力学参数的频域辨识[J]. 振动工程学报, 1992, 5(3): 211-218.DING W J, ZENG Q C. Identification in frequency domain for dynamic parameters of pendulum model of sloshing liquid[J]. Journal of Vibration Engineering, 1992, 5(3): 211-218(in Chinese). [10] 夏益霖. 液体晃动等效力学模型的参数识别[J]. 应用力学学报, 1991, 8(4): 27-35.XIA Y L. Parameters estimation for liquid sloshing equivalent mechanical models[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics, 1991, 8(4): 27-35(in Chinese). [11] 陈青全. 卫星贮箱液体晃动等效力学模型参数辨识[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学, 2014.CHEN Q Q. Parameter identification of liquid sloshing equivalent mechanical model in satellite tank[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2014(in Chinese). [12] 李超. 球形贮箱内液体晃动实验及等效力学模型参数辨识研究[D]. 柳州: 广西科技大学, 2021.LI C. Liquid sloshing experiment and equivalent mechanical model parameter identification research in spherical tank[D]. Liuzhou: Guangxi University of Science and Technology, 2021(in Chinese). [13] SNYDER H A. Effect of rotation on sloshing in low-gravity[J]. Cryogenics, 2004, 44(6-8): 525-536. doi: 10.1016/j.cryogenics.2004.02.011 [14] SALTARI F, TRAINI A, GAMBIOLI F, et al. A linearized reduced-order model approach for sloshing to be used for aerospace design[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2021, 108: 106369. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2020.106369 [15] 王佐, 吴文军, 姜丙超, 等. 球形贮箱内液体横向晃动问题的系统辨识与参数化等效建模[J]. 广西科技大学学报, 2022, 33(3): 1-7.WANG Z, WU W J, JIANG B C, et al. System identification and parametric equivalent modeling of liquid lateral sloshing in spherical tanks[J]. Journal of Guangxi University of Science and Technology, 2022, 33(3): 1-7(in Chinese). [16] 苟兴宇, 王本利, 马兴瑞, 等. 航天工程中的贮箱类液固耦合动力学建模及耦合机理研究[J]. 强度与环境, 1998, 25(1): 9-16.GOU X Y, WANG B L, MA X R, et al. Dynamic modelling of liquid-solid coupling system with container in spacecraft engineering and investigating of its coupling mechanism[J]. Structure & Environment Engineering, 1998, 25(1): 9-16(in Chinese). [17] 苟兴宇, 李铁寿, 马兴瑞, 等. 液固耦合系统中液体的有限幅晃动力及晃动力矩[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2001, 22(5): 465-476. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0887.2001.05.004GOU X Y, LI T S, MA X R, et al. Forces and moments of the liquid finite amplitude sloshing in a liquid-solid coupled system[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2001, 22(5): 465-476(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0887.2001.05.004 [18] 岳宝增. 液体大幅晃动动力学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2011.YUE B Z. Dynamics of liquid sloshing[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2011(in Chinese). [19] BERRY R L, TEGART J R. Experimental study of transient liquid motion in orbiting spacecraft (final report): NAS8-30690[R]. Washington, D. C. : NASA, 1976. [20] 黄华, 杨雷, 张熇, 等. 航天器贮箱大幅液体晃动三维质心面等效模型研究[J]. 宇航学报, 2010, 31(1): 55-59.HUANG H, YNAG L, ZHANG H, et al. Research on 3D constraint surface model for large amplitude liquid sloshing on spacecraft tank[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2010, 31(1): 55-59(in Chinese). [21] 刘峰, 岳宝增, 唐勇. 多充液贮腔航天器耦合动力学与姿态控制[J]. 宇航学报, 2020, 41(1): 19-26. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2020.01.003LIU F, YUE B Z, TANG Y. Dynamics modeling and attitude control of spacecraft with multiple propellant tanks[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2020, 41(1): 19-26(in Chinese). doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2020.01.003 [22] VREEBURG J P B. Dynamics and control of a spacecraft with a moving pulsating ball in a spherical cavity[J]. Acta Astronautica, 1997, 40(2): 257-274. [23] 邓明乐, 岳宝增, 黄华. 液体大幅晃动类等效力学模型研究[J]. 宇航学报, 2016, 37(6): 631-638.DENG M L, YUE B Z, HUANG H. Study on the equivalent mechanical model for large amplitude slosh[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2016, 37(6): 631-638(in Chinese). [24] 孙梓煜, 岳宝增, 刘峰, 等. 充液柔性航天器刚-液-柔耦合动力学研究的凯恩方法[J]. 宇航学报, 2021, 42(5): 552-561. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2021.05.002SUN Z Y, YUE B Z, LIU F, et al. Study on rigid-liquid-flex coupling dynamics for spacecraft by Kane’s method[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2021, 42(5): 552-561(in Chinese). doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2021.05.002 [25] 刘峰, 岳宝增, 马伯乐, 等. 燃料消耗下充液航天器等效动力学建模与分析[J]. 力学学报, 2020, 52(5): 1454-1464. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-20-027LIU F, YUE B Z, MA B L, et al. Equivalent dynamics modeling and analysis of liquid-filled spacecraft with fuel consumption[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2020, 52(5): 1454-1464(in Chinese). doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-20-027 [26] JUI J J, SUID M H, MUSA Z, et al. Identification of liquid slosh behavior using continuous-time Hammerstein model based sine cosine algorithm[C]//Proceedings of the 11th National Technical Seminar on Unmanned System Technology 2019. Berlin: Springer, 2021: 345-356. [27] ASTLEFORD W J, CHU W H, DODGE F T. Propellant dynamic problems in space shuttle vehicles: NASA-CR-111802[R]. Washington, D. C. : NASA, 1970. [28] KANA D D, KO W L, FRANCIS P H, et al. Coupling between structure and liquids in a parallel stage space shuttle design: NAS1-9890[R]. Washington, D. C. : NASA, 1972. [29] HIMENO T, WATANABE T, NONAKA S, et al. Sloshing prediction in the propellant tanks of VTVL rocket vehicle[C]//Proceedings of the 41st AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference & Exhibit. Reston: AIAA, 2005. [30] AOKI K, NAKAMURA T, IGARASHI I, et al. Experimental investigation of baffle effectiveness on nonlinear propellant sloshing in RLV[C]//Proceedings of the 43rd AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference & Exhibit. Reston: AIAA, 2007: 5556. [31] 尕永婧, 王浩苏, 张青松, 等. 垂直着陆过程推进剂流动行为特性及影响分析[J]. 深空探测学报(中英文), 2021, 8(1): 42-50.GA Y J, WANG H S, ZHANG Q S, et al. Propellant flow characteristics in tank and related impact analysis during the vertical landing stage[J]. Journal of Deep Space Exploration, 2021, 8(1): 42-50(in Chinese). [32] 罗盟, 陈士强, 李大鹏, 等. 星舰动力特点及再入过程推进剂流动仿真研究[J]. 南京航空航天大学学报, 2021, 53(S1): 9-16.LUO M, CHEN S Q, LI D P, et al. Characteristics of starship propulsion system and numerical simulation of propellant flow during reentry[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics, 2021, 53(S1): 9-16(in Chinese). [33] 钱翼稷. 空气动力学[M]. 北京: 北京航空航天大学出版社, 2004.QIAN Y J. Aerodynamics[M]. Beijing: Beihang University Press, 2004(in Chinese). [34] 王照林, 刘延柱. 充液系统动力学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2002.WANG Z L, LIU Y Z. Dynamics of liquid-filled system[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2002(in Chinese). [35] SIEMENS. Simcenter STAR-CCM+ CFD software[EB/OL]. (2023-09-15)[2023-09-25]. https://plm.sw.siemens.com/zh-CN/simcenter/fluids-thermal-simulation/star-ccm/. [36] 夏益霖. 液体推进剂贮箱的防晃设计[J]. 导弹与航天运载技术, 1995(6): 29-38.XIA Y L. Design of sloshing suppression for liquid propellant tanks[J]. Missiles and Space Vehicles, 1995(6): 29-38(in Chinese). [37] 万水, 朱德懋, 张福祥. 液体防晃研究进展[J]. 弹道学报, 1996, 8(3): 95-99.WAN S, ZHU D M, ZHANG F X. Research progress of liquid sloshing prevention[J]. Journal of Ballistics, 1996, 8(3): 95-99(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: