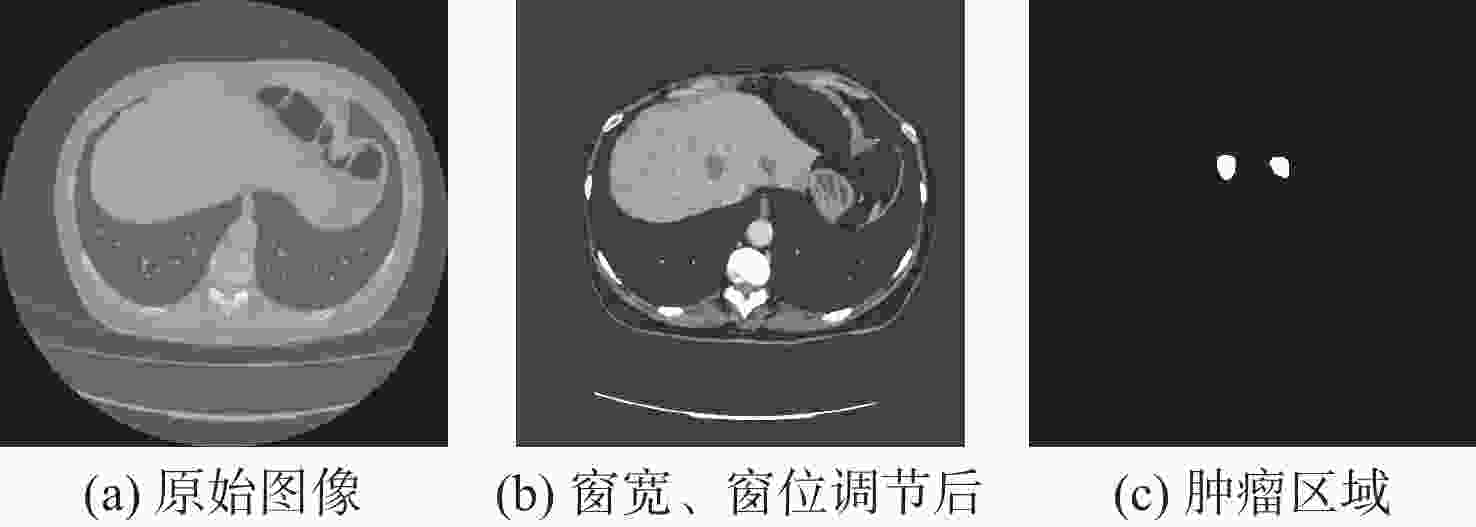
-
摘要:
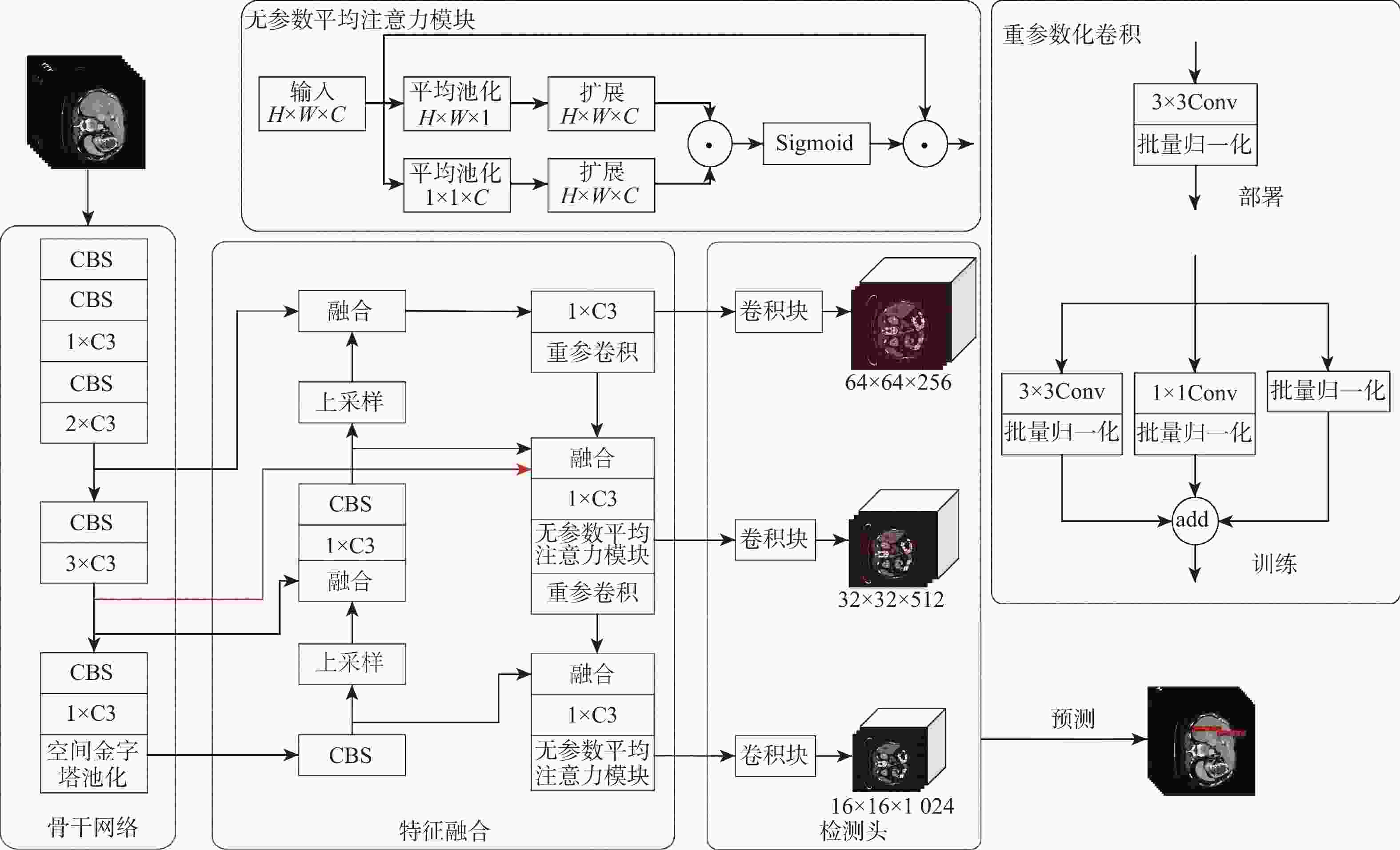
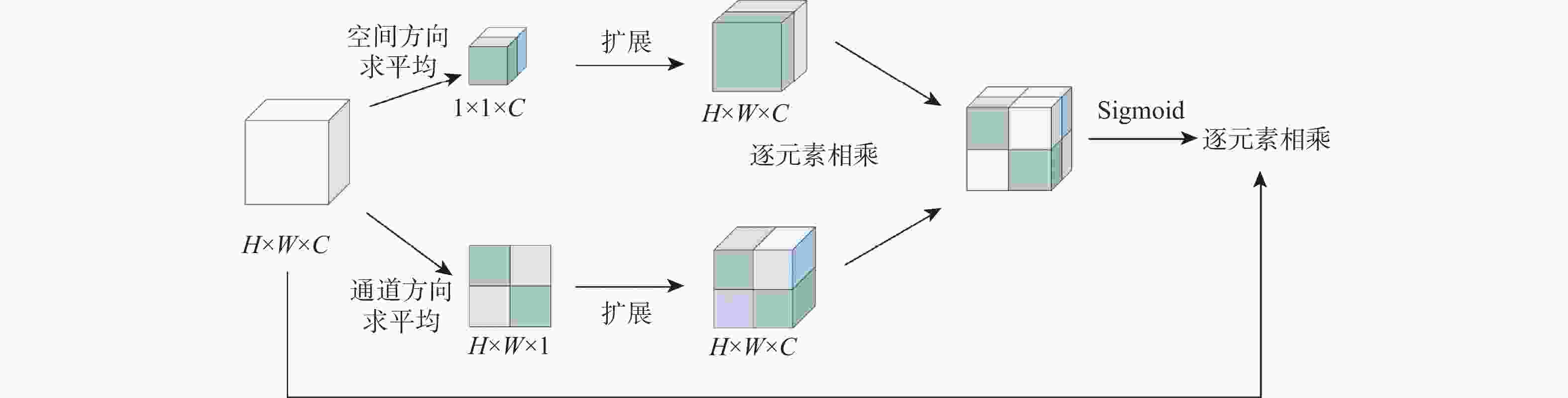
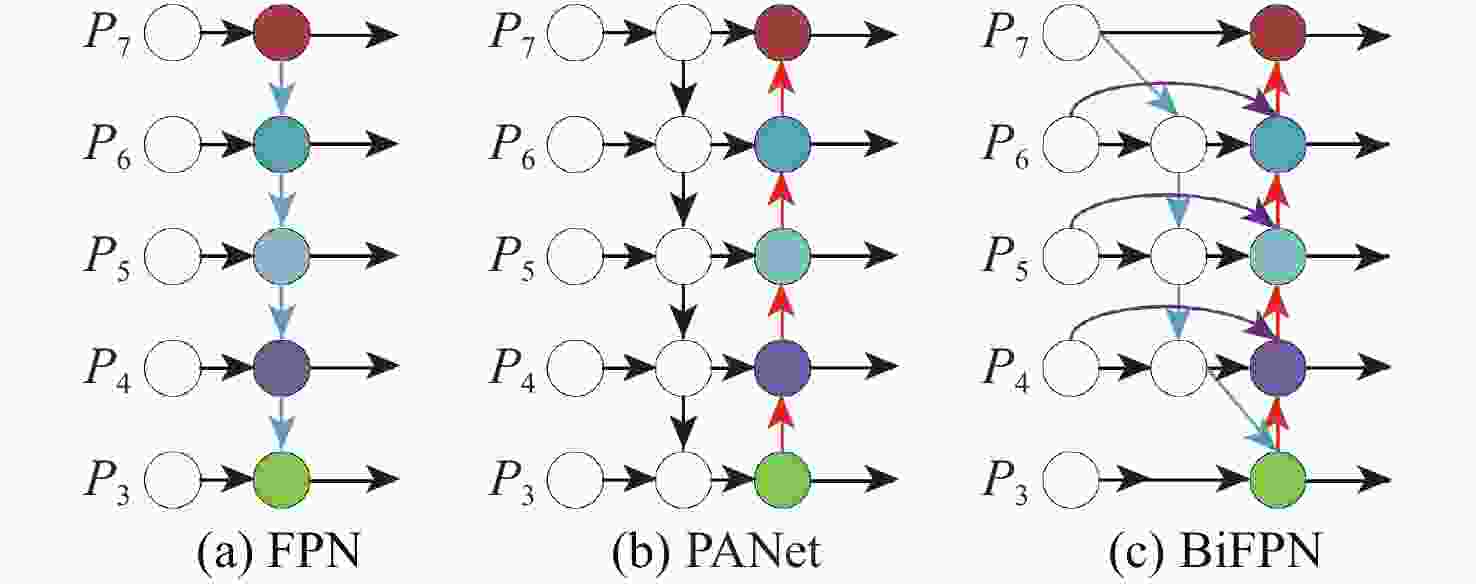
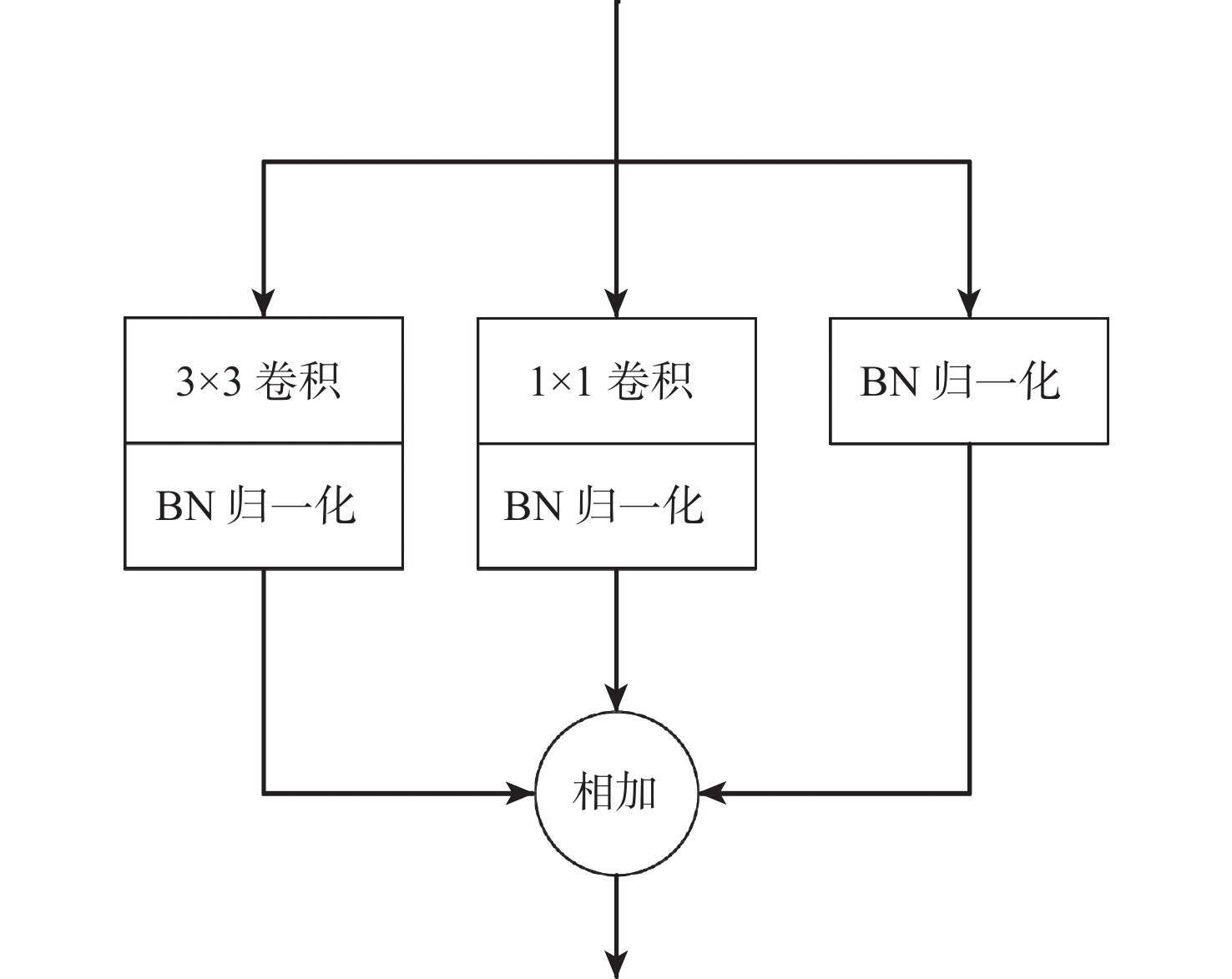
针对肝脏肿瘤检测中多尺度特征表达能力不足的问题,提出一种融合重参数化卷积、加权双向特征金字塔和注意力机制的肝脏肿瘤CT图像检测方法。使用数据增强改善样本量较少的问题,提高模型的泛化能力;使用加权双向特征金字塔网络融合图像的浅层与深层特征,提高多尺度特征的提取能力;在特征融合中引入无参数平均注意力模块,关注肝脏肿瘤的关键特征;使用重参数化卷积和边界框(SIoU)损失函数提高肿瘤的检测和定位能力。实验结果表明:所提方法在LT3DM和LiTS2017数据集上的平均精度均值(mAP)分别达到了92.9%和92.2%,比YOLOv5模型提高了2.3%和1.8%,相较于主流检测模型,所提方法具有更好的肝脏肿瘤检测能力。
Abstract:To address the problem of insufficient multi-scale feature representation in liver tumor detection, we propose a liver tumor CT image detection method that integrates reparameterized convolution, weighted bidirectional feature pyramid, and attention mechanism. Firstly, data augmentation is used to improve the problem of small sample size and enhance the generalization ability of the model. Secondly, to enhance the ability to extract multi-scale features, the weighted bidirectional feature pyramid network is utilized to merge the image's shallow and deep features. Then, a parameter-free attention mechanism is introduced in feature fusion to focus on the key features of liver tumors. Finally, reparameterized convolution and shapeaware intersection over union (SIoU) loss functions are used to improve tumor detection and localization accuracy. The mean average precision(mAP)of this method on LT3DM and LiTS2017 datasets reached 92.9% and 92.2%, respectively, which is 2.3% and 1.8% higher than that of the YOLOv5 model. The experimental results indicate that this method has a greater ability to detect liver tumors than standard detection models.
-
表 1 多种注意力机制对比
Table 1. Comparison of multiple attention mechanisms
表 2 LT3DM数据增强对比实验
Table 2. LT3DM data enhancement comparison experiment
% 数据增强方式 准确率 召回率 F1 mAP 无数据增强 93.0 85.9 89.31 89.8 Mosaic+左右翻转 94.1 87.7 90.79 92.4 Mosaic+左右翻转+复制粘贴 94.6 88.3 91.34 92.9 表 3 损失函数选取实验
Table 3. Loss Function Selection Experiment
% 表 4 注意力机制选取实验
Table 4. Experiment on selecting attention mechanisms
模型与注意力机制 精确率/% 召回率/% F1/% mAP/% 参数量 浮点运算速度/109 s−1 Base 92.8 88.2 90.44 91.8 7.170559 ×10616.3 Base+SE 94.5 88.0 91.13 92.6 7.172095 ×10616.3 Base+CBAM 94.0 88.6 91.22 92.7 7.212533 ×10616.3 Base+Coordatt 94.8 88.0 91.27 92.8 7.202887 ×10616.3 Base+EMA 93.8 88.2 90.91 92.5 7.170587 ×10616.3 Base+ECA 94.5 87.7 90.97 92.7 7.170565 ×10616.3 Base+PfAAM 94.6 88.3 91.34 92.9 7.170559 ×10616.3 表 5 消融实验
Table 5. Ablation experiments
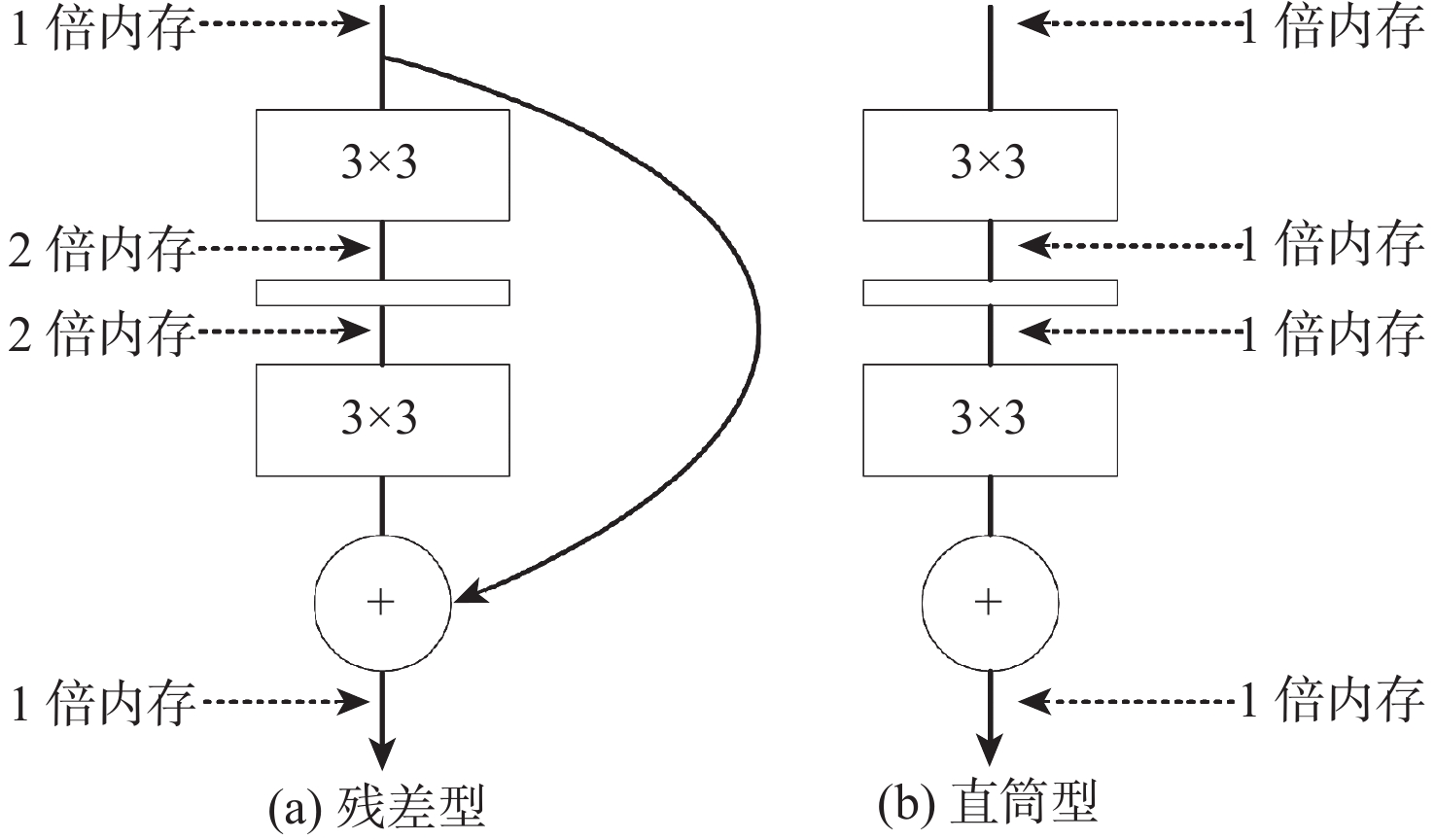
模型 精确率/% 召回率/% F1/% mAP/% 参数量 浮点运算速度/109 s−1 Baseline 93.6 85.7 89.4 90.6 7.022×106 15.9 Baseline+SIoU 93.1 86.4 89.6 91.3 7.022×106 15.9 Baseline+Repconv 93.5 87.3 90.3 91.6 7.105×106 16.1 Baseline+BiFPN 93.2 87.9 90.5 91.6 7.088×106 16.2 Baseline+PfAAM 94.6 86.4 90.3 91.2 7.022×106 15.9 Baseline+Repconv+BiFPN 92.8 88.2 90.4 91.8 7.171×106 16.3 Baseline+Repconv+PfAAM 93.3 87.1 90.1 91.8 7.105×106 16.1 Baseline+SIoU+Repconv+BiFPN+PfAAM 94.6 88.3 91.3 92.9 7.171×106 16.3 表 6 不同模型在LT3DM上的检测性能对比
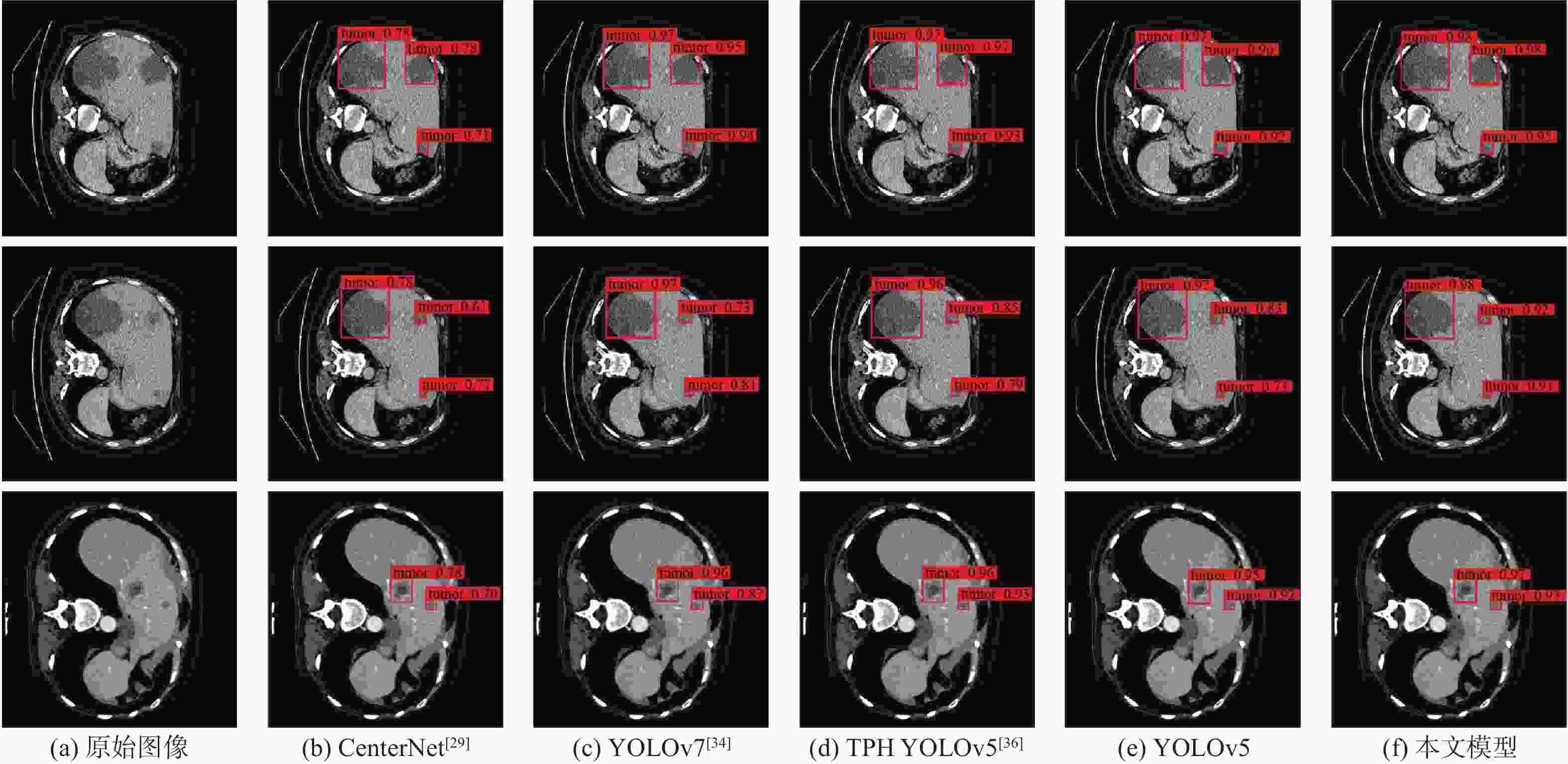
Table 6. Comparative experiments on LT3DM datasets in different models
模型 P/% R/% F1/% mAP/% 参数量 浮点运
算速度/
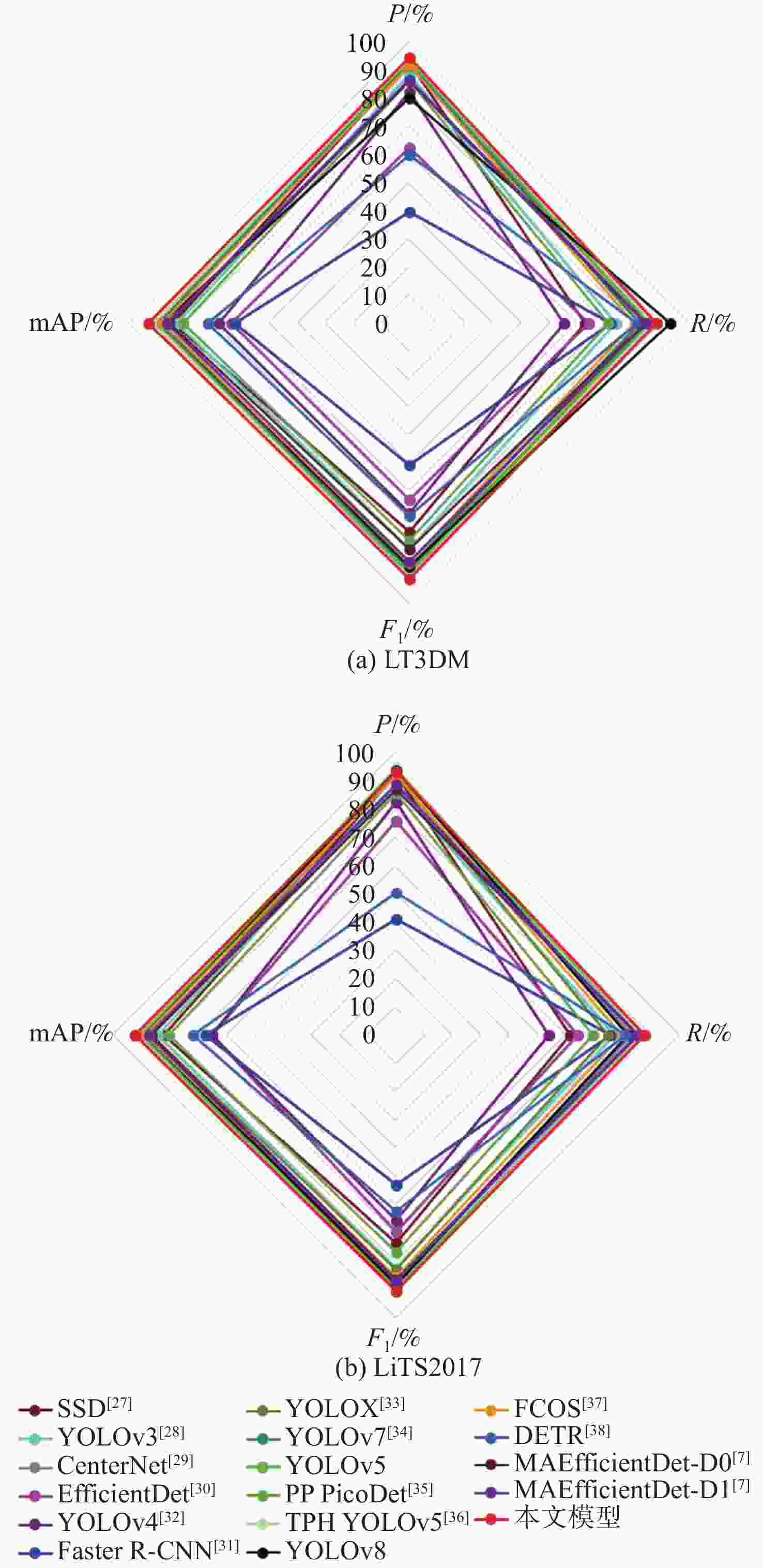
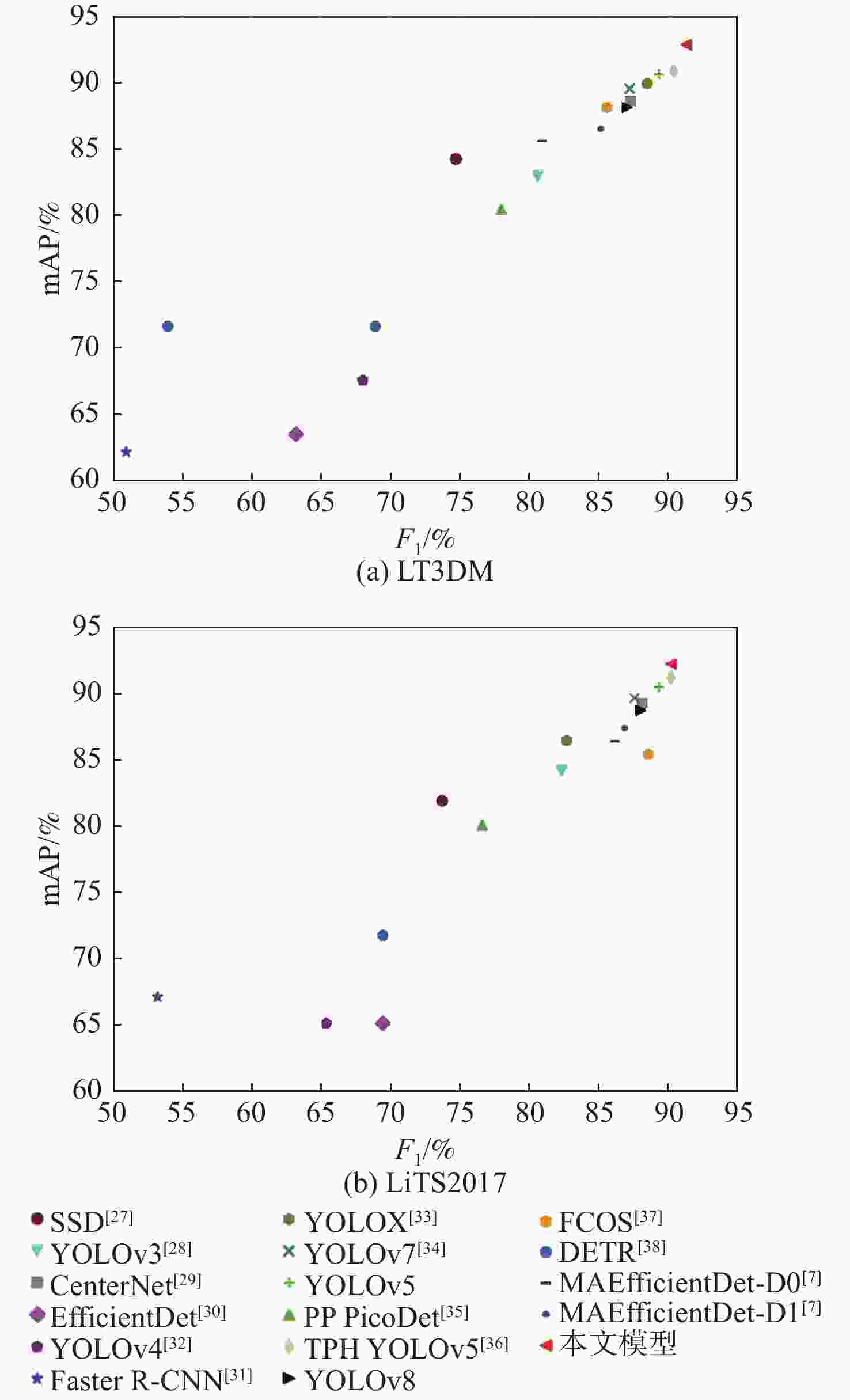
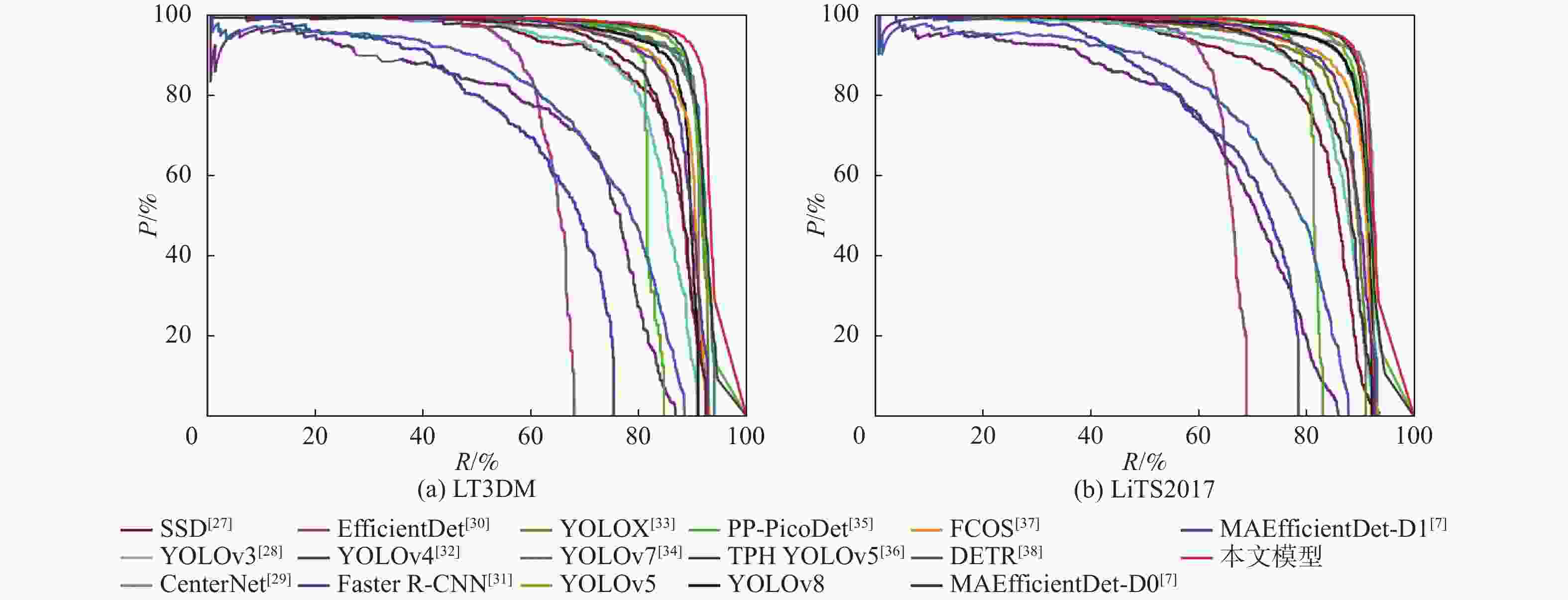
109 s−1SSD512(VGG) [27] 93.1 62.5 74.7 84.3 23.75×106 87.55 YOLOv3[28] 88.7 73.9 80.6 82.9 61.52×106 49.68 CenterNet[29] 92.8 82.5 87.3 88.6 32.66×106 35.09 EfficientDet[30] 62.5 63.9 63.2 63.5 3.83×106 2.37 YOLOv4[32] 82.4 55.2 68.0 67.6 63.94×106 45.41 Faster R-CNN(Res50) [31] 39.4 71.8 50.9 62.2 28.28×106 241.71 YOLOX[33] 91.5 85.8 88.5 89.9 8.94×106 8.56 YOLOv7[34] 92.8 82.2 87.2 89.6 6.22×106 33.01 YOLOv5 93.6 85.7 89.4 90.6 7.02×106 15.90 PP PicoDet[35] 86.1 71.2 77.9 80.5 1.18×106 4.59 TPH YOLOv5[36] 94.2 86.9 90.4 90.9 40.82×106 36.26 YOLOv8 80.1 93.3 87.0 88.1 11.13×106 9.10 FCOS[37] 91.9 80.1 85.6 88.1 32.11×106 51.56 DETR[38] 59.8 81.3 68.9 71.7 36.74×106 23.81 MAEfficientDet-D0[7] 86.2 84.1 80.9 85.6 4.34×106 2.83 MAEfficientDet-D1[7] 86.8 84.8 85.1 86.5 7.08×106 6.81 本文模型 94.6 88.3 91.3 92.9 7.17×106 16.30 表 7 不同模型在LiTS2017上的检测性能对比
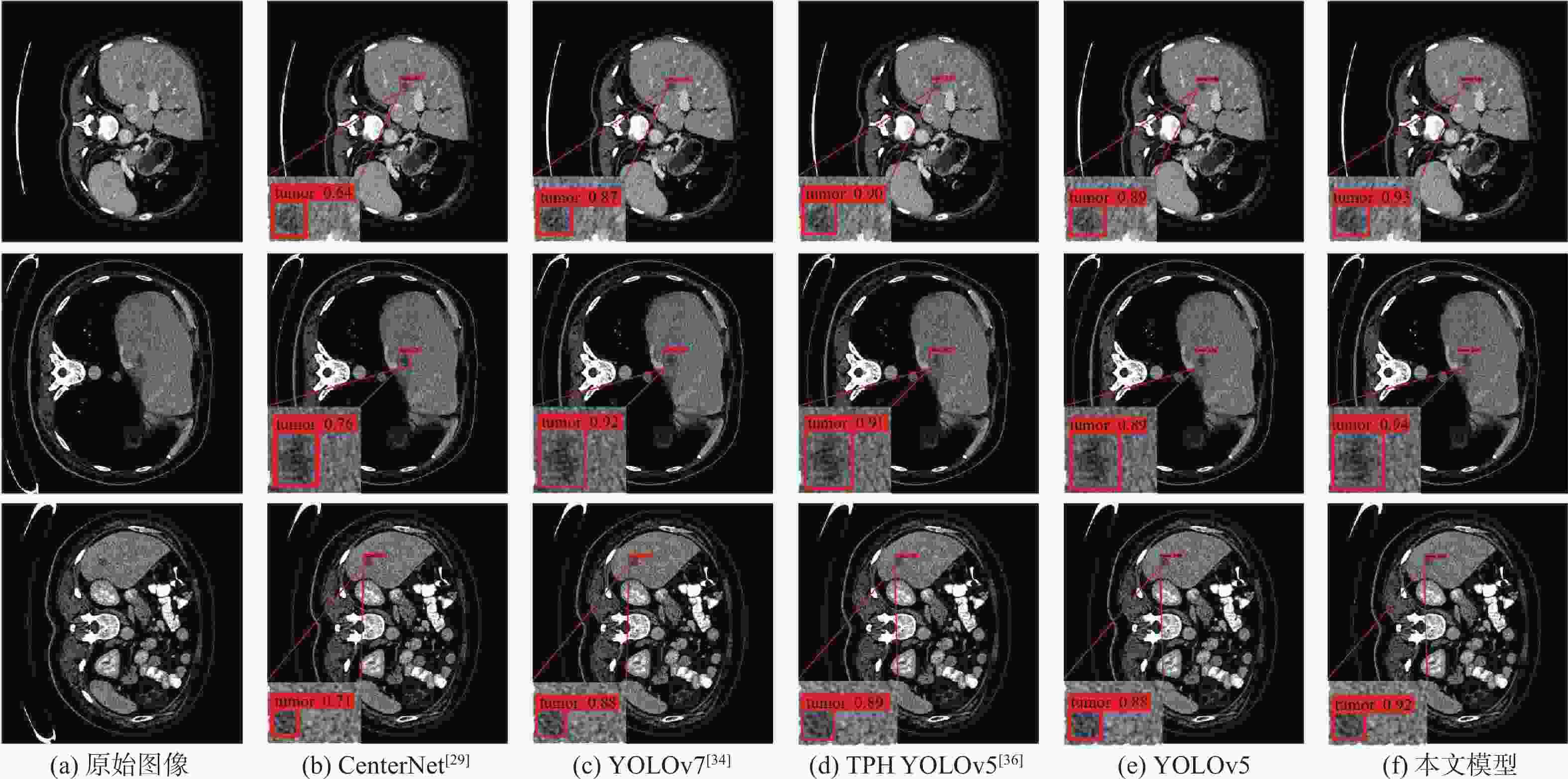
Table 7. Comparison experiments of LiTS2017 dataset in different models
模型 P/% R/% F1/% mAP/% 参数量 浮点运
算速度/
109 s−1SSD512(VGG) [27] 92.3 61.3 73.7 81.9 23.7×106 87.55 YOLOv3[28] 88.3 77.1 82.3 84.2 61.5×106 49.68 CenterNet[29] 93.4 83.4 88.1 89.3 32.6×106 35.09 EfficientDet[30] 75.8 64.1 69.4 65.1 3.83×106 2.37 YOLOv4[32] 82.6 54.0 65.3 65.1 63.9×106 45.41 FasterR-CNN(Res50) [31] 41.0 75.6 53.2 67.1 28.2×106 241.71 YOLOX[33] 92.2 75.0 82.7 86.4 8.94×106 8.56 YOLOv7[34] 93.8 82.2 87.6 89.7 6.22×106 33.01 YOLOv5 92.8 86.3 89.4 90.4 7.02×106 15.90 PP PicoDet[35] 85.4 69.5 76.6 80.1 1.18×106 4.59 TPH YOLOv5[36] 94.4 86.3 90.2 91.2 40.8×106 36.26 YOLOv8 93.7 82.0 88.0 88.7 11.1×106 9.10 FCOS[37] 91.7 80.0 85.4 88.6 32.1×106 51.56 DETR[38] 60.6 81.2 69.4 71.8 36.7×106 23.81 MAEfficientDet-D0[7] 87.0 85.5 86.2 86.3 4.34×106 2.83 MAEfficientDet-D1[7] 88.5 85.2 86.8 87.4 7.08×106 6.81 本文模型 93.1 87.9 90.4 92.2 7.17×106 16.30 -
[1] GUO X Y, WANG F S, TEODORO G, et al. Liver steatosis segmentation with deep learning methods[C]//Proceedings of the 16th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 24-27. [2] LIANG D, TONG R F, WU J, et al. Multi-stream scale-insensitive convolutional and recurrent neural networks for liver tumor detection in dynamic ct images[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 794-798. [3] TAO Q Y, GE Z Y, CAI J F, et al. Improving deep lesion detection using 3D contextual and spatial attention[C]//Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention. Berlin: Springer, 2019: 185-193. [4] ZHANG Z L, LI Y F, WU W, et al. Tumor detection using deep learning method in automated breast ultrasound[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2021, 68: 102677. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2021.102677 [5] 刘雅楠, 李靖宇, 许东滨, 等. 基于边缘几何特征的乳腺X线图像中微小肿瘤检测方法[J]. 影像科学与光化学, 2022, 40(3): 590-595. doi: 10.7517/issn.1674-0475.211118LIU Y N, LI J Y, XU D B, et al. The detection of micro tumor in breast X-ray image based on edge geometric features[J]. Imaging Science and Photochemistry, 2022, 40(3): 590-595(in Chinese). doi: 10.7517/issn.1674-0475.211118 [6] 马金林, 毛凯绩, 马自萍, 等. 基于ConA-FPN的肝脏肿瘤检测算法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2023, 59(2): 161-169.MA J L, MAO K J, MA Z P, et al. ConA-FPN based algorithm for liver tumor detection[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2023, 59(2): 161-169(in Chinese). [7] 马金林, 欧阳轲, 马自萍, 等. 多尺度自适应融合的肝脏肿瘤检测[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2023, 28(1): 260-276. doi: 10.11834/jig.220423MA J L, OUYANG K, MA Z P, et al. Multiscale adaptive fusion network based algorithm for liver tumor detection[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2023, 28(1): 260-276(in Chinese). doi: 10.11834/jig.220423 [8] YAN R, ZHANG R Y, BAI J Q, et al. STMS-YOLOv5: a lightweight algorithm for gear surface defect detection[J]. Sensors, 2023, 23(13): 5992. [9] BILIC P, CHRIST P, LI H B, et al. The liver tumor segmentation benchmark (LiTS)[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2023, 84: 102680. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2022.102680 [10] LIN T Y, DOLLÁR P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 936-944. [11] LIU S, QI L, QIN H F, et al. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 8759-8768. [12] YU H, WANG J G, HAN Y X, et al. Research on an intelligent identification method for wind turbine blade damage based on CBAM-BiFPN-YOLOV8[J]. Processes, 2024, 12(1): 205. [13] SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[EB/OL]. (2015-04-10)[2023-09-30]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1556. [14] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 770-778. [15] HUANG G, LIU Z, VAN DER MAATEN L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 2261-2269. [16] HU J, SHEN L, SUN G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 7132-7141. [17] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: convolutional block attention module[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich: ECCV, 2018: 3-19. [18] HOU Q B, ZHOU D Q, FENG J S. Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 13708-13717. [19] LI X, ZHONG Z S, WU J L, et al. Expectation-maximization attention networks for semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 9166-9175. [20] WANG Q L, WU B G, ZHU P F, et al. ECA-net: efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 11531-11539. [21] KÖRBER N. Parameter-free average attention improves convolutional neural network performance (almost) free of charge[EB/OL]. (2022-10-14)[2023-09-30]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.07828. [22] DING X H, ZHANG X Y, MA N N, et al. RepVGG: making VGG-style ConvNets great again[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 13728-13737. [23] WANG A R, LIANG G H, WANG X, et al. Application of the YOLOv6 combining CBAM and CIoU in forest fire and smoke detection[J]. Forests, 2023, 14(11): 2261. [24] IRCAD FRANCE. 3Dircadb[EB/OL]. (2020-07-16)[2023-09-30]. https://www.ircad.fr/research/data-sets/liver-segmentation-3dircadb01. [25] TONG Z J, CHEN Y H, XU Z W, et al. Wise-IoU: bounding box regression loss with dynamic focusing mechanism[EB/OL]. (2023-04-08)[2023-09-30]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.10051. [26] ZHANG Y F, REN W Q, ZHANG Z, et al. Focal and efficient IOU loss for accurate bounding box regression[J]. Neurocomputing, 2022, 506: 146-157. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2022.07.042 [27] LIU W, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: single shot MultiBox detector[C]//Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 21-37. [28] ZHANG Y, SHEN Y L, ZHANG J. An improved tiny-yolov3 pedestrian detection algorithm[J]. Optik, 2019, 183: 17-23. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2019.02.038 [29] ZHOU X Y, WANG D Q, KRÄHENBÜHL P. Objects as points[EB/OL]. (2019-04-25)[2023-09-30]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.07850. [30] TAN M X, PANG R M, LE Q V. EfficientDet: scalable and efficient object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 10778-10787. [31] REN S Q, HE K M, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1137-1149. [32] BOCHKOVSKIY A, WANG C Y, LIAO H Y M, et al. Yolov4: optimal speed and accuracy of object detection[EB/OL]. (2020-04-23)[2023-09-30]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.10934. [33] GE Z, LIU S T, WANG F, et al. Yolox: exceeding yolo series in 2021[EB/OL]. (2020-04-23)[2023-09-30]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.08430. [34] WANG C Y, BOCHKOVSKIY A, LIAO H M. YOLOv7: trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2023: 7464-7475. [35] YU G H, CHANG Q Y, LV W Y, et al. PP-PicoDet: a better real-time object detector on mobile devices[EB/OL]. (2021-11-01)[2023-09-30]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.00902#:~:text=Through%20these%20optimizations%2C%20we%20create%20a%20new%20family,accuracy%20and%20latency%20compared%20to%20other%20popular%20models. [36] ZHU X K, LYU S C, WANG X, et al. TPH-YOLOv5: improved YOLOv5 based on transformer prediction head for object detection on drone-captured scenarios[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 2778-2788. [37] TIAN Z, SHEN C H, CHEN H, et al. FCOS: fully convolutional one-stage object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 9626-9635. [38] CARION N, MASSA F, SYNNAEVE G, et al. End-to-end object detection with transformers[C]//Proceedings of the Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2020: 213-229. -






 下载:
下载: