-
摘要:
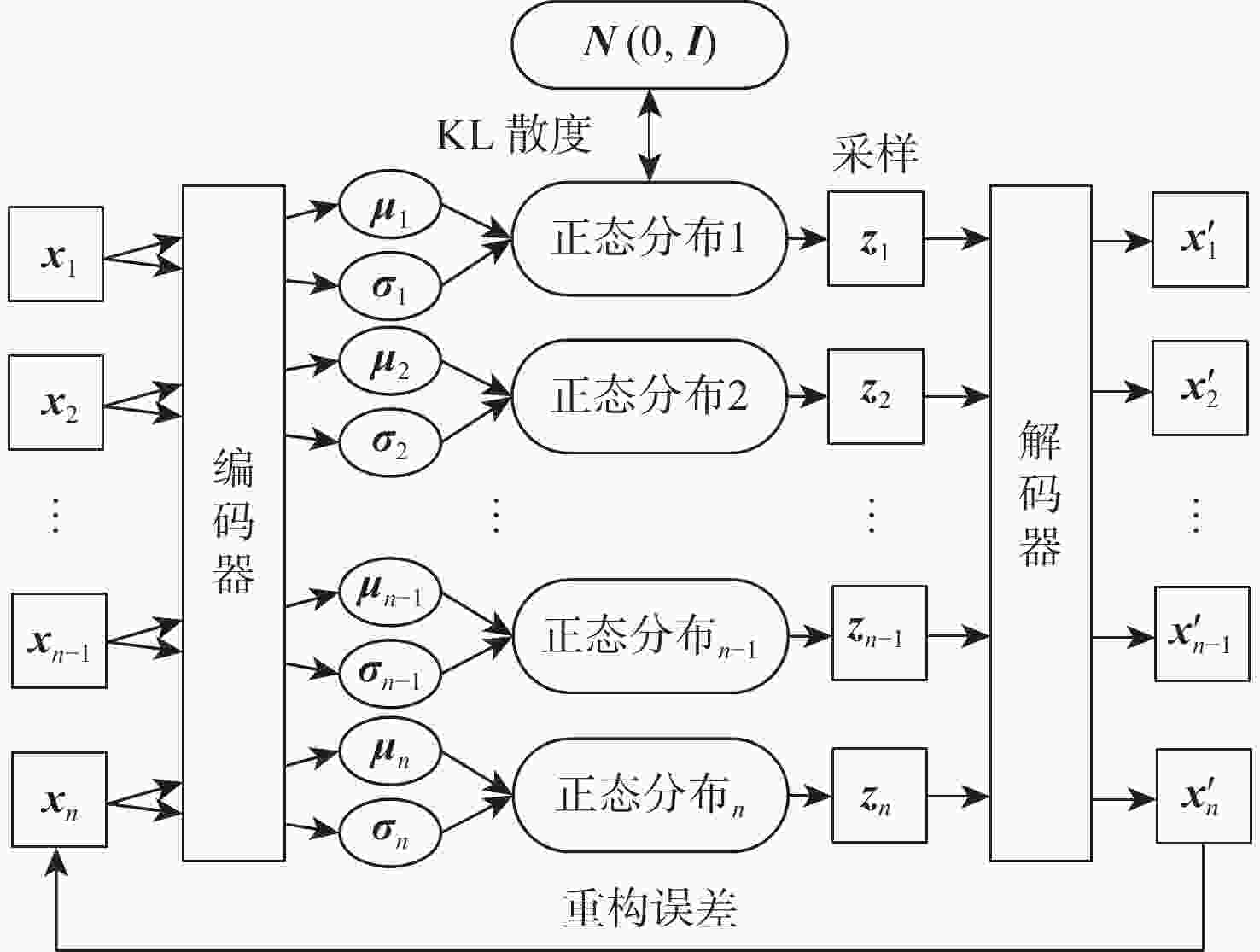
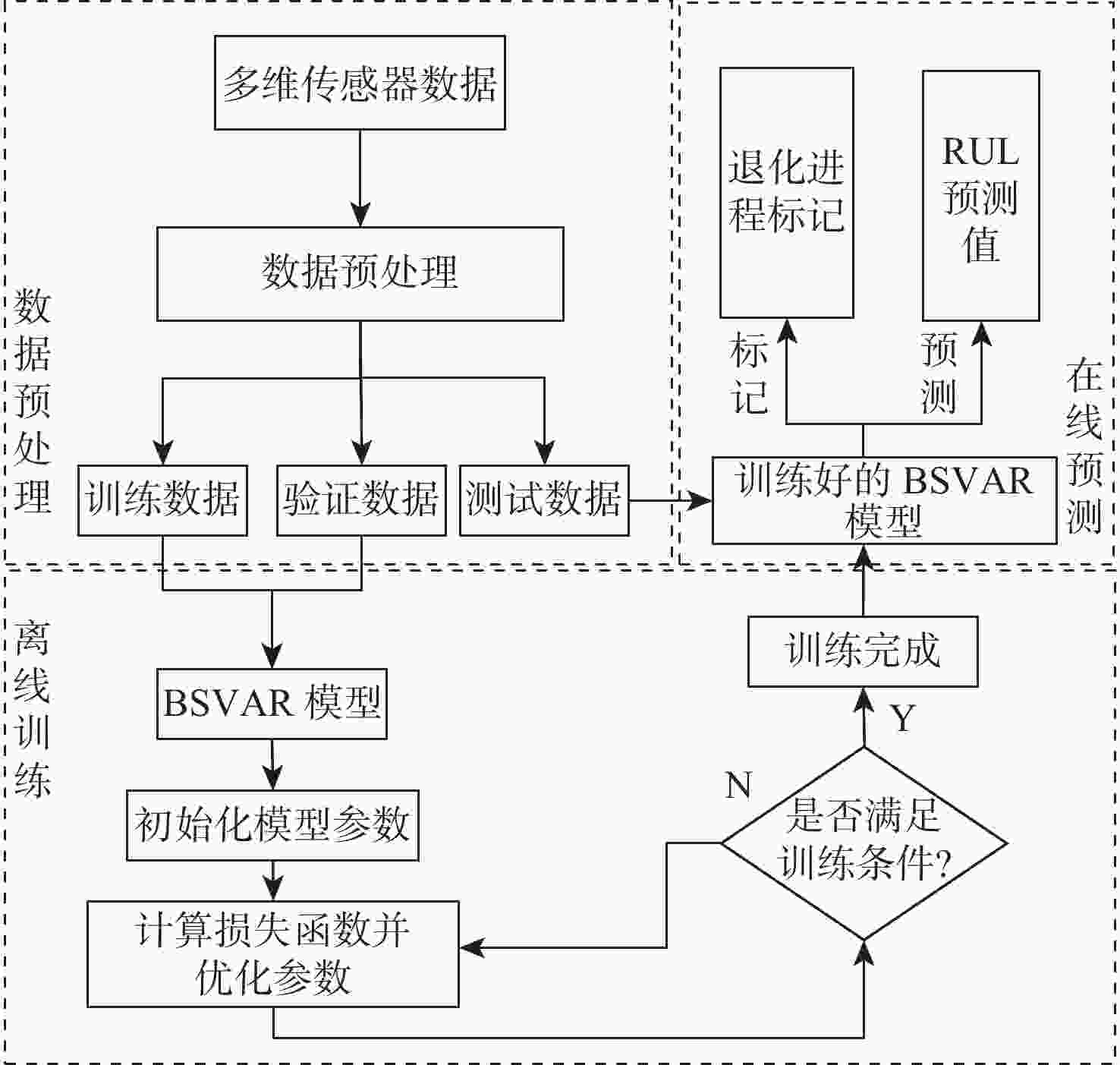
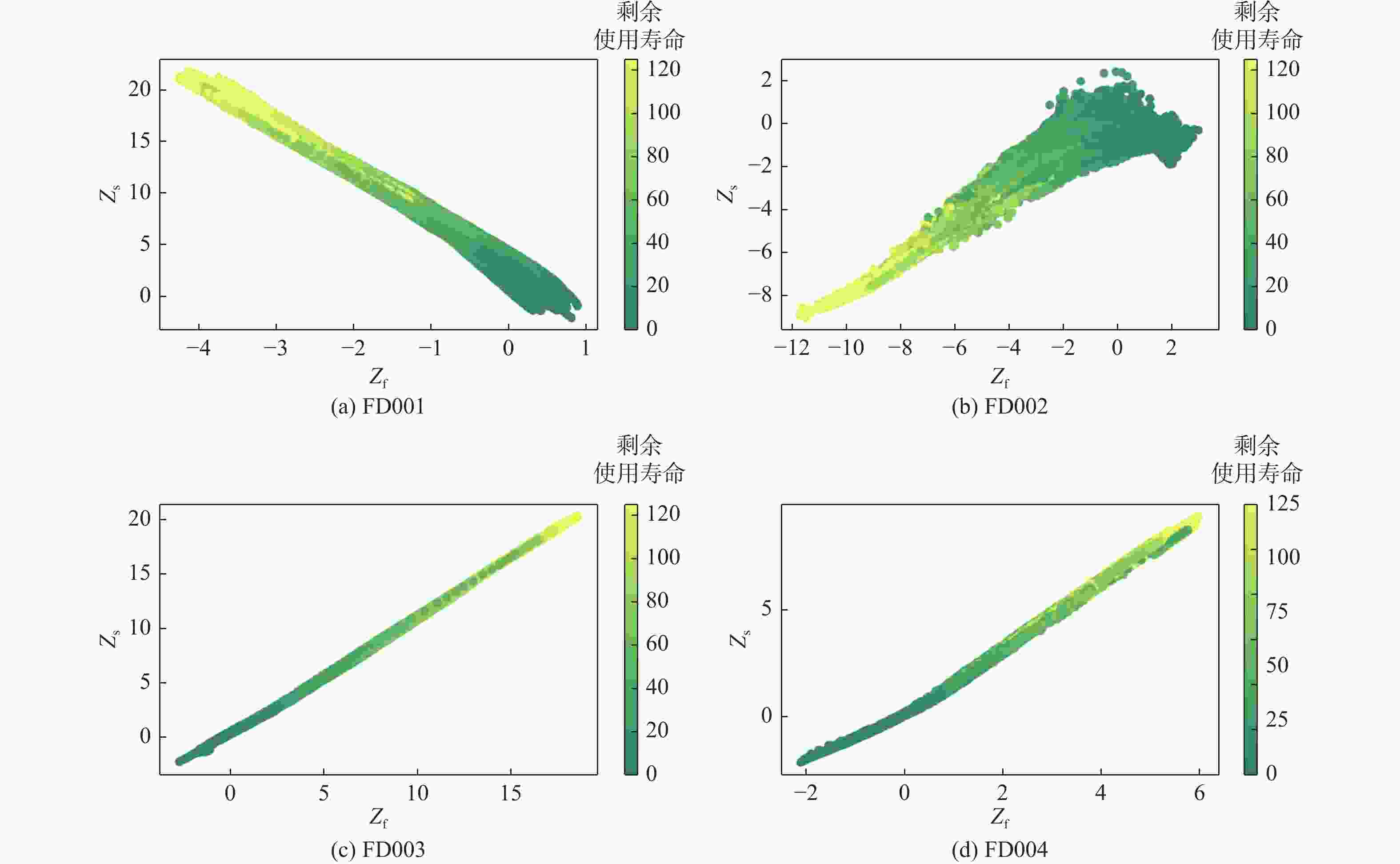
剩余使用寿命(RUL)的准确预测对航空发动机的稳定性、可靠性和安全性至关重要。针对现有RUL预测方法无法充分挖掘传感器数据退化特征的问题,提出一种基于深度学习模型BSVAR的航空发动机RUL预测方法。采用双向长短期记忆(Bi-LSTM)网络与基于自注意力机制的变分自编码器(SVAE)提取传感器数据的深层次退化信息;基于变分推理对传感器数据具有的退化特征进行聚类,生成潜在空间;将Bi-LSTM、SVAE和回归器相结合建立RUL预测模型,充分提取传感器数据的退化特征,提升RUL预测精度。在航空发动机C-MAPSS数据集上进行实验验证,实验结果表明:所提方法可以在潜在空间中标记发动机的退化进程;相比于现有的RUL预测方法具有更高的预测精度。
Abstract:Accurate prediction of remaining useful life (RUL) is critical to the stability, reliability, and safety of aircraft engines. A new deep learning model called BSVAR is suggested for RUL prediction in order to address the issue that current RUL prediction techniques are unable to properly utilize the deterioration information of sensor data. The deep degradation information of sensor data is extracted using a bidirectional long-short-term memory (Bi-LSTM) networks and self-attention based variational autoencoder (SVAE). With the utilization of variational inference, the sensor data is clustered according to the implied degradation information, meanwhile, the latent space can be generated. The combination of the Bi-LSTM, the SVAE, and the regressor is used to establish a RUL prediction model to sufficiently extract the degradation features of sensor data to improve the prediction accuracy. Results from experimental validation on the aero-engine C-MAPSS dataset demonstrate that the suggested approach outperforms the current RUL prediction approaches in terms of prediction performance and can identify the engines’ degree of degradation in the latent space.
-
表 1 C-MAPSS数据集
Table 1. C-MAPSS dataset
数据集 训练集发动机台数 测试集发动机台数 工作条件 故障模式 FD001 100 100 1 1 FD002 260 259 6 1 FD003 100 100 1 2 FD004 249 248 6 2 表 2 超参数设置
Table 2. Hyperparameter setup
参数 数值 时间窗(FD001/FD002/FD003/FD004) 25/20/30/15 潜在空间维数 2 学习率 0.001 迭代次数 10 Bi-LSTM单元个数 300 批大小 256 全连接层神经元个数 200 表 3 与最新方法比较
Table 3. Comparison with state-of-the-art approaches
方法 RMSE Score FD001 FD002 FD003 FD004 FD001 FD002 FD003 FD004 DCNN[5] 12.61 22.36 12.64 23.31 273.7 10412 284.1 12466 Bi-LSTM[8] 25.11 26.61 4793 4971 HDNN[9] 13.01 15.24 12.22 18.156 245 1282.42 287.72 1527.42 BGRU-TSAM[10] 12.56 18.92 12.45 20.47 213.35 2264.13 232.86 3610.34 Dual-Att[12] 12.25 17.08 13.39 19.68 198 1575 290 1741 BSVAR 12.39 14.88 13 15.52 246.58 854.11 317.51 1160.17 EN[14] 13.58 19.59 19.16 22.15 228 2650 1727 2901 RVE[20] 13.42 14.92 12.51 16.37 323.82 1379.17 256.36 1845.99 表 4 所选4台发动机的RUL值
Table 4. RUL values for the selected four engines
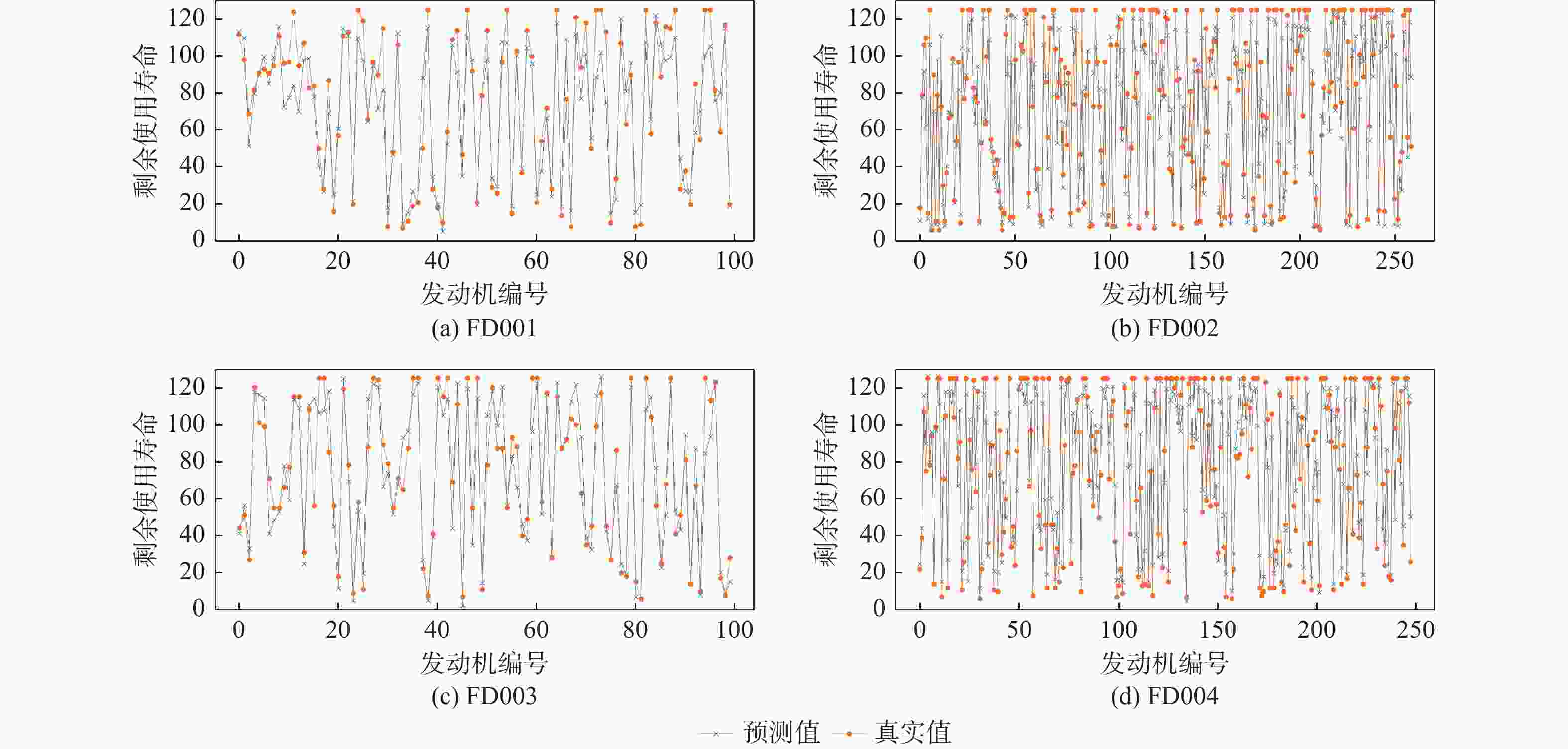
发动机编号 真实RUL值 预测RUL值 1# 112 118.34 11# 97 95.64 77# 34 23.55 100# 20 19.07 -
[1] CHEN X Z, YU J S, TANG D Y, et al. Remaining useful life prognostic estimation for aircraft subsystems or components: a review[C]//Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Electronic Measurement & Instruments. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011: 94-98. [2] NGUYEN K T P, MEDJAHER K, TRAN D T. A review of artificial intelligence methods for engineering prognostics and health management with implementation guidelines[J]. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2023, 56(4): 3659-3709. doi: 10.1007/s10462-022-10260-y [3] CHIACHÍO J, JALÓN M L, CHIACHÍO M, et al. A Markov chains prognostics framework for complex degradation processes[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2020, 195: 106621. [4] SHI Y, ZHU W H, XIANG Y S, et al. Condition-based maintenance optimization for multi-component systems subject to a system reliability requirement[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2020, 202: 107042. [5] LI X, DING Q, SUN J Q. Remaining useful life estimation in prognostics using deep convolution neural networks[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2018, 172: 1-11. [6] GUO L, LI N P, JIA F, et al. A recurrent neural network based health indicator for remaining useful life prediction of bearings[J]. Neurocomputing, 2017, 240: 98-109. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.02.045 [7] CHEN J L, JING H J, CHANG Y H, et al. Gated recurrent unit based recurrent neural network for remaining useful life prediction of nonlinear deterioration process[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2019, 185: 372-382. [8] HUANG C G, HUANG H Z, LI Y F. A bidirectional LSTM prognostics method under multiple operational conditions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2019, 66(11): 8792-8802. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2019.2891463 [9] AL-DULAIMI A, ZABIHI S, ASIF A, et al. A multimodal and hybrid deep neural network model for Remaining Useful Life estimation[J]. Computers in Industry, 2019, 108: 186-196. doi: 10.1016/j.compind.2019.02.004 [10] ZHANG J S, JIANG Y C, WU S M, et al. Prediction of remaining useful life based on bidirectional gated recurrent unit with temporal self-attention mechanism[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2022, 221: 108297. [11] 聂磊, 徐诗奕, 张吕凡, 等. 基于多头注意力机制的飞机发动机寿命预测研究[J]. 推进技术, 2023, 44(8): 197-205.NIE L, XU S Y, ZHANG L F, et al. Remaining useful life prediction of aeroengine based on multi-head attention[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 2023, 44(8): 197-205(in Chinese). [12] LIU L, SONG X, ZHOU Z T. Aircraft engine remaining useful life estimation by a double attention-based data-driven architecture[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2022, 221: 108330. [13] 王进花, 高媛, 曹洁, 等. 基于AE-BN的发电机滚动轴承故障诊断[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2023, 49(8): 1896-1903.WANG J H, GAO Y, CAO J, et al. Fault diagnosis of generator rolling bearing based on AE-BN[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2023, 49(8): 1896-1903(in Chinese). [14] YU W N, KIM I Y, MECHEFSKE C. An improved similarity-based prognostic algorithm for RUL estimation using an RNN autoencoder scheme[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2020, 199: 106926. [15] KINGMA D P, WELING M. Auto-encoding variational bayes[EB/OL]. (2022-12-10)[2023-02-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1312.6114. [16] WANG X X, PI D C, ZHANG X Y, et al. Variational transformer-based anomaly detection approach for multivariate time series[J]. Measurement, 2022, 191: 110791. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2022.110791 [17] LI L Y, YAN J C, WANG H Y, et al. Anomaly detection of time series with smoothness-inducing sequential variational auto-encoder[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021, 32(3): 1177-1191. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.2980749 [18] REMADNA I, TERRISSA L S, AL MASRY Z, et al. RUL prediction using a fusion of attention-based convolutional variational AutoEncoder and ensemble learning classifier[J]. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2023, 72(1): 106-124. doi: 10.1109/TR.2022.3190639 [19] LIU X B, TENG W, WU S M, et al. Sparse dictionary learning based adversarial variational auto-encoders for fault identification of wind turbines[J]. Measurement, 2021, 183: 109810. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2021.109810 [20] COSTA N, SÁNCHEZ L. Variational encoding approach for interpretable assessment of remaining useful life estimation[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2022, 222: 108353. [21] 周哲韬, 刘路, 宋晓, 等. 基于Transformer模型的滚动轴承剩余使用寿命预测方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2023, 49(2): 430-443.ZHOU Z T, LIU L, SONG X, et al. Remaining useful life prediction method of rolling bearing based on Transformer model[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2023, 49(2): 430-443(in Chinese). [22] SAXENA A, GEOBEL K. NASA prognostics repository [EB/OL]. (2008-10-01) [2023-02-01]. https://ti.arc.nasa.gov/tech/dash/groups/pcoe/prognostic-data-repository/. [23] ARIAS CHAO M, KULKARNI C, GOEBEL K, et al. Aircraft engine run-to-failure dataset under real flight conditions for prognostics and diagnostics[J]. Data, 2021, 6(1): 5. doi: 10.3390/data6010005 -






 下载:
下载: