Influence of airfoil uncertainty on aerodynamic characteristics and shape inspection method
-
摘要:
评估翼型外形不确定性对气动特性产生的影响,对于提出飞行器全生命周期的外形监测指标有重要意义。传统外形参数化方法变量众多,加之气动特性计算复杂,外形与气动特性间的不确定性传递难以直接分析。采用类-形函数变换(CST)方法参数化描述翼型,通过随机分布的参数描述外形不确定性。通过计算流体力学(CFD)方法生成气动力样本库,使用最小角回归(LAR)算法建立稀疏混沌多项式代理模型。通过混沌多项式的系数直接计算外形参数的全局敏感度,并根据敏感度大小选取外形监测关键点。算例表明:仅控制2个关键点的偏差区间即可以将升力系数的方差降低25%,均值提升3.8%,为实际加工与维护提供了高效合理的监测方法。
Abstract:It is crucial to assess how airfoil form uncertainty affects aerodynamic properties in order to suggest shape inspection indicators throughout the aircraft's whole life cycle. The traditional shape parameterization method has many variables and the calculation of aerodynamic characteristics is complex, making it difficult to directly analyze the uncertainty propagation between shape and aerodynamic characteristics. Class shape transform (CST) is applied to reduce the necessary variables for airfoils parameterization. Uncertain shape is described with random shape parameters. Aerodynamic coefficients are calculated through computational fluid dynamics (CFD) to generate samples. To create surrogate models for aerodynamics calculations, the sparse polynomial chaos expansion approach with least angle regression (LAR) is utilized. The coefficients of the polynomial chaos are used to directly determine the global sensitivity of the shape parameters, and the sensitivity results are used to pick crucial points for shape inspection. Examples show that controlling the deviation intervals of only two key points can reduce the variance of the lift coefficient by 25% and increase the average value by 3.8%, providing a reasonable inspection method for actual processing and maintenance.
-
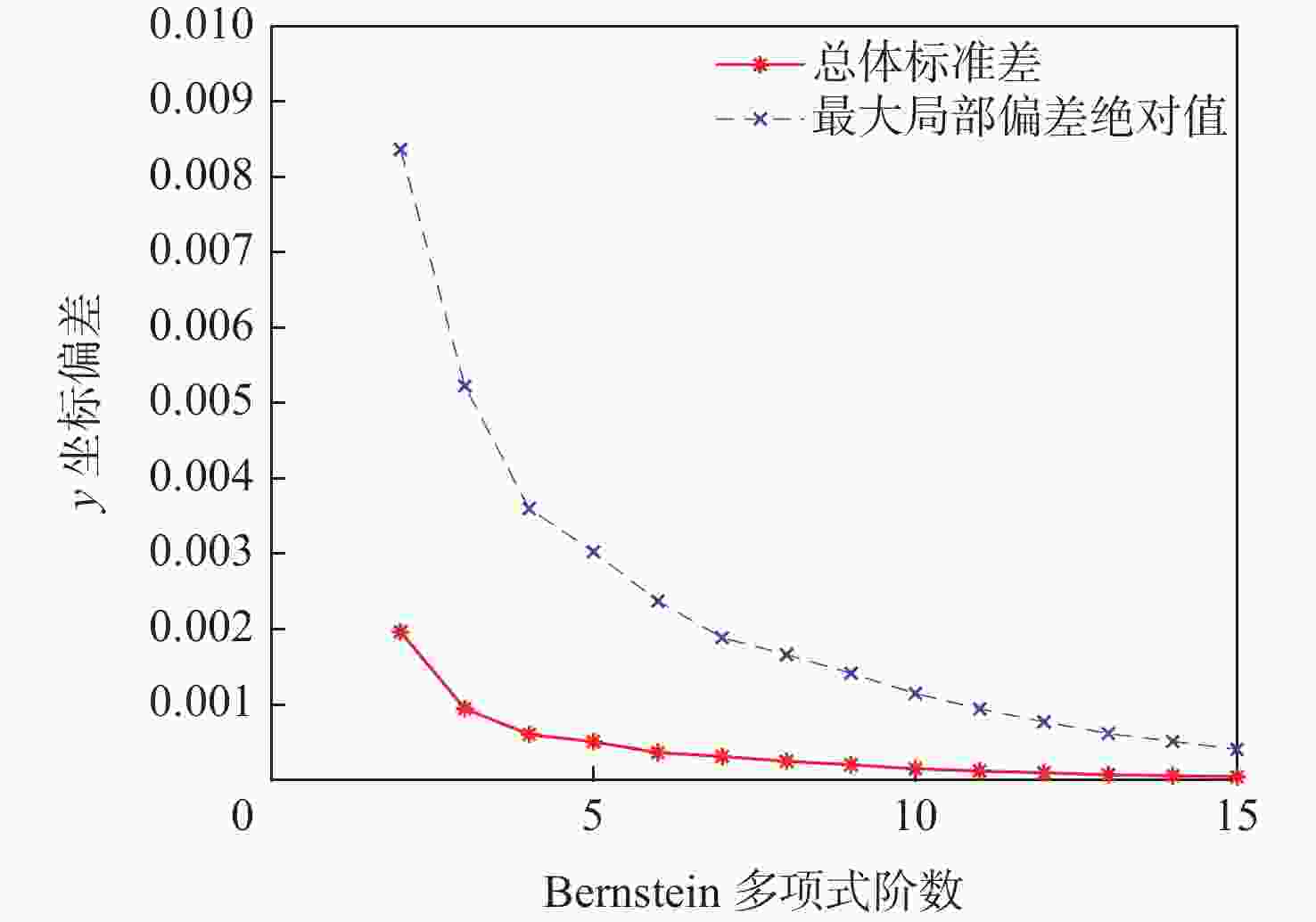
表 1 典型低速翼型CST拟合参数
Table 1. CST parameters for airfoil applied on typical low-speed aircraft
表面 w0 w1 w2 w3 w4 w5 w6 w7 w8 $ {\zeta}_{\text{TE}} $ 上表面 0.260 0.484 0.101 0.747 −0.119 0.738 0.017 0.439 0.228 −0.050 下表面 −0.194 0.129 −0.483 0.498 −0.775 0.477 −0.405 0.181 0.033 −0.054 表 2 计算条件设置
Table 2. Calculation condition settings
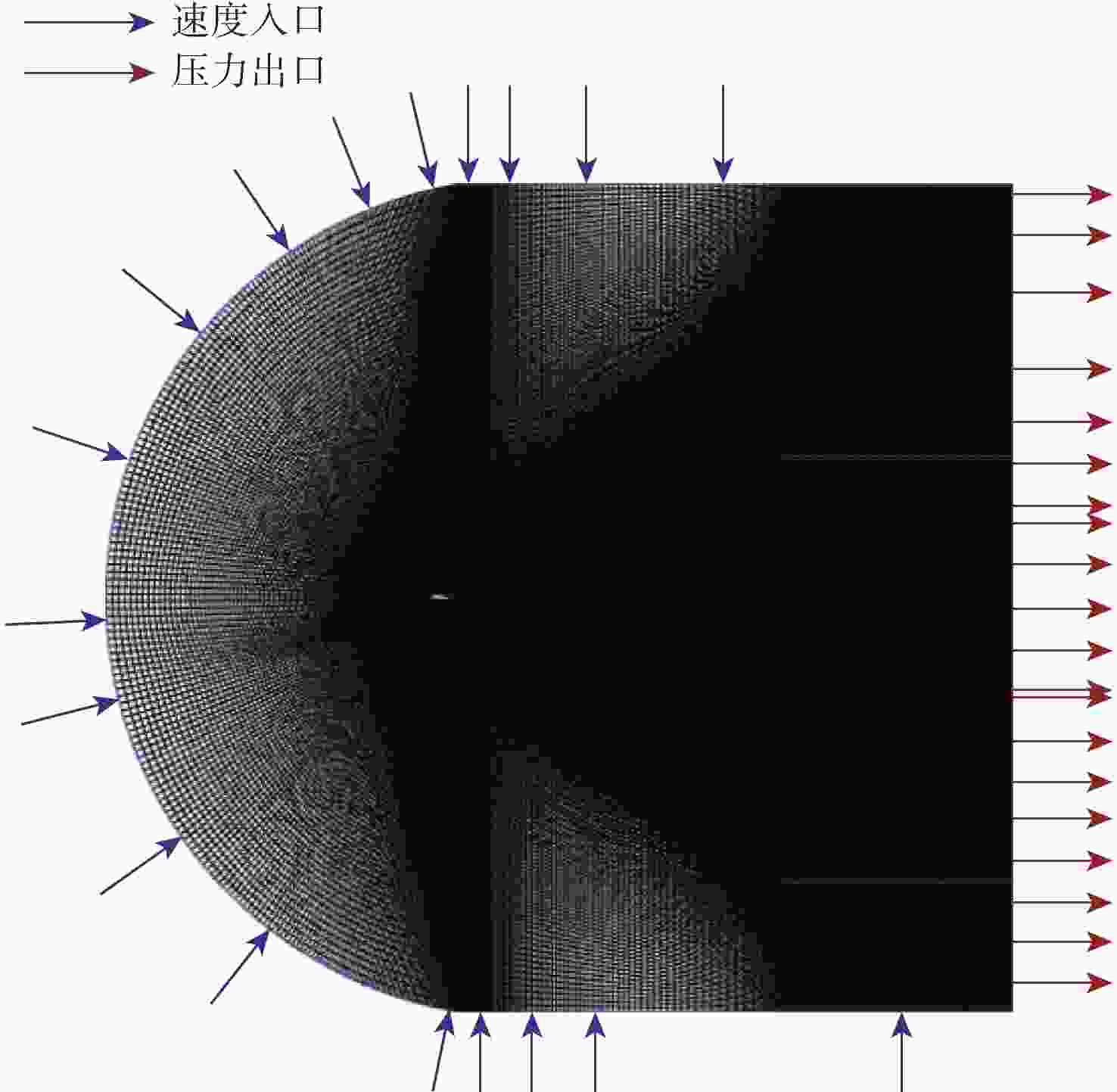
雷诺数 来流速度/(m·s−1) 攻角/(°) $ \text{2×}{\text{10}}^{\text{6}} $ 34 0 表 3 网格独立性检验
Table 3. Mesh independence check
网格数 升力系数CL 阻力系数CD 77170 0.90196 0.01488 90400 0.90262 0.01495 143650 0.90257 0.01497 表 4 外形参数的概率分布
Table 4. Probability distribution of shape parameters
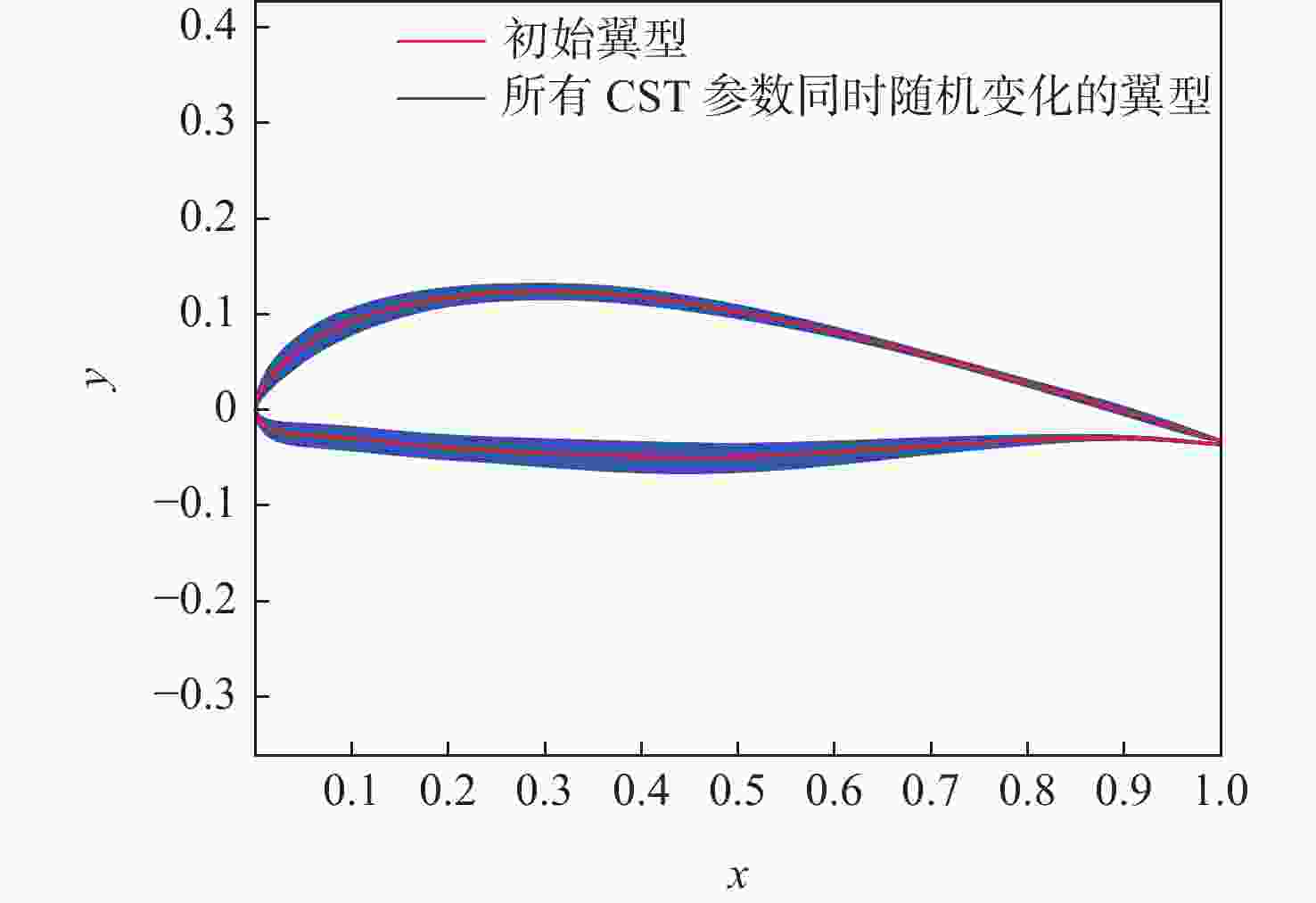
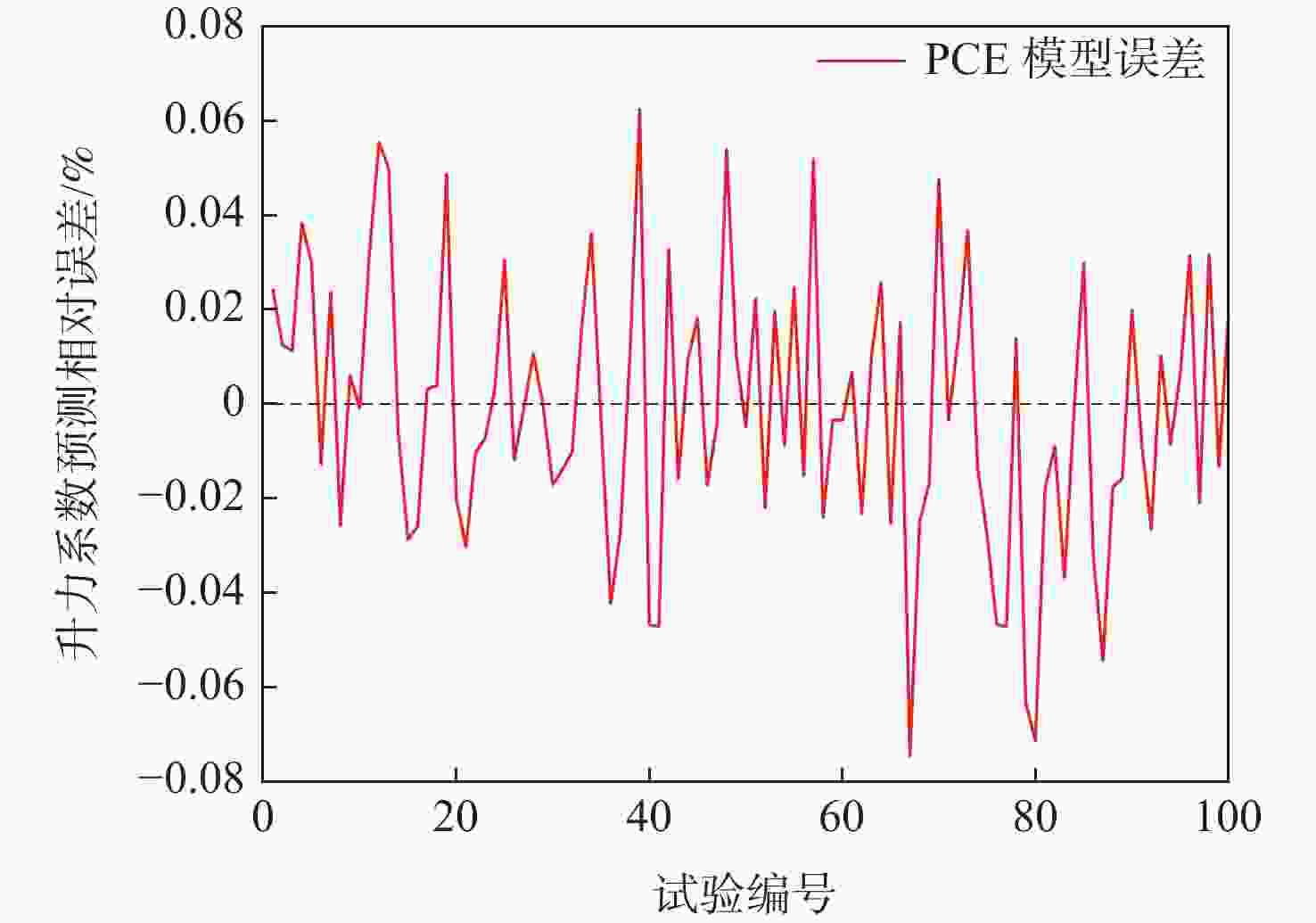
分布 wU wL 分布类型 均匀分布 均匀分布 偏差区间 $ \text{±0.05} $ $ \text{±0.05} $ 注:上表面外形参数wU,下表面外形参数wL的准确值参见表1。 表 5 PCE代理模型的LOO误差与统计矩
Table 5. LOO error and statistical moments of the PCE proxy model
变量 升力系数 阻力系数 $ {\varepsilon }_{\text{LOO}} $ $ \text{6.21×}{\text{10}}^{{-}\text{1}\text{3}} $ $ \text{1.05×}{\text{10}}^{{-11}} $ 均值 0.8936 0.0149 方差 $ \text{8.24×}{\text{10}}^{{-4}} $ $ \text{1.11×}{\text{10}}^{{-7}} $ 表 6 升力系数对外形参数敏感度的计算结果
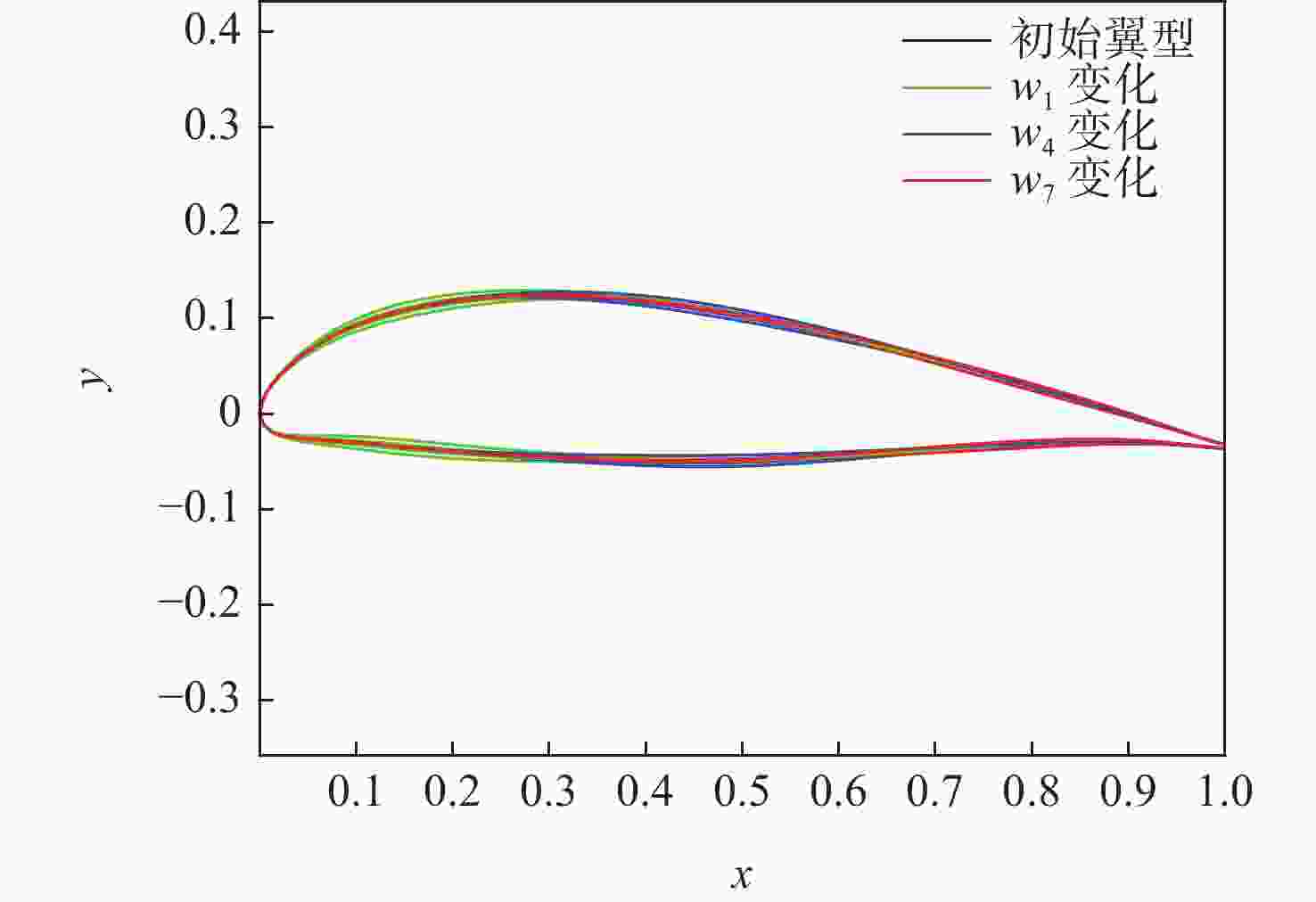
Table 6. Sensitivity results of lift coefficient with respect to shape parameters
CST参数 上表面CL敏感度 下表面CL敏感度 w0 0.021 0.012 w1 0.036 0.017 w2 0.041 0.023 w3 0.039 0.032 w4 0.034 0.042 w5 0.031 0.055 w6 0.031 0.074 w7 0.032 0.115 w8 0.029 0.337 表 7 阻力系数对外形参数敏感度的计算结果
Table 7. Sensitivity results of drag coefficient with respect to shape parameters
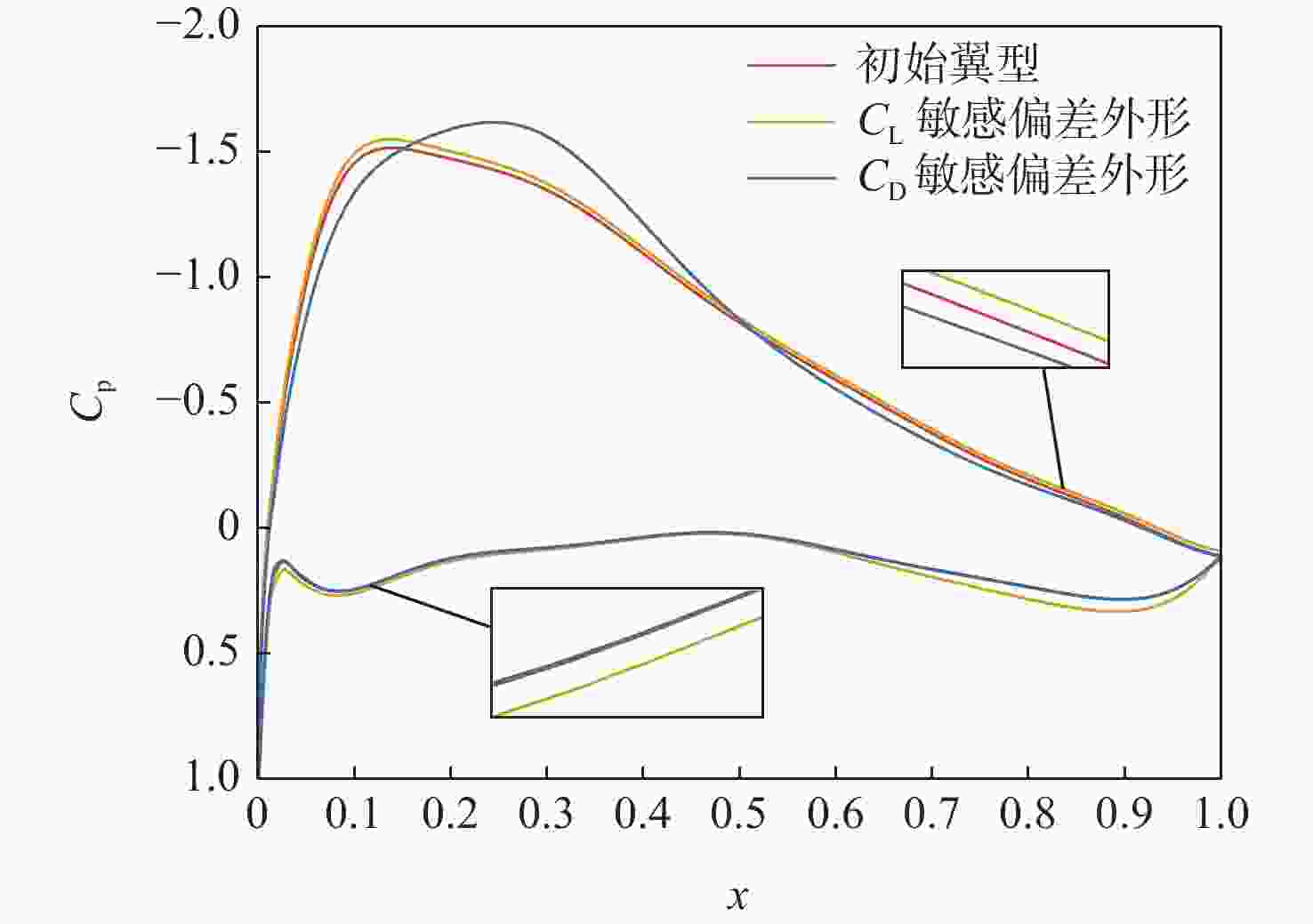
敏感度 w0 w1 w2 w3 w4 w5 w6 w7 w8 上表面CD敏感度 0.073 0.133 0.153 0.156 0.134 0.094 0.054 0.025 0.006 下表面CD敏感度 0.002 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.001 0.004 0.011 0.028 0.130 表 8 原始外形与CD敏感外形阻力系数对比
Table 8. Drag coefficient comparison between original airfoil and CD-sensitive deviated airfoil
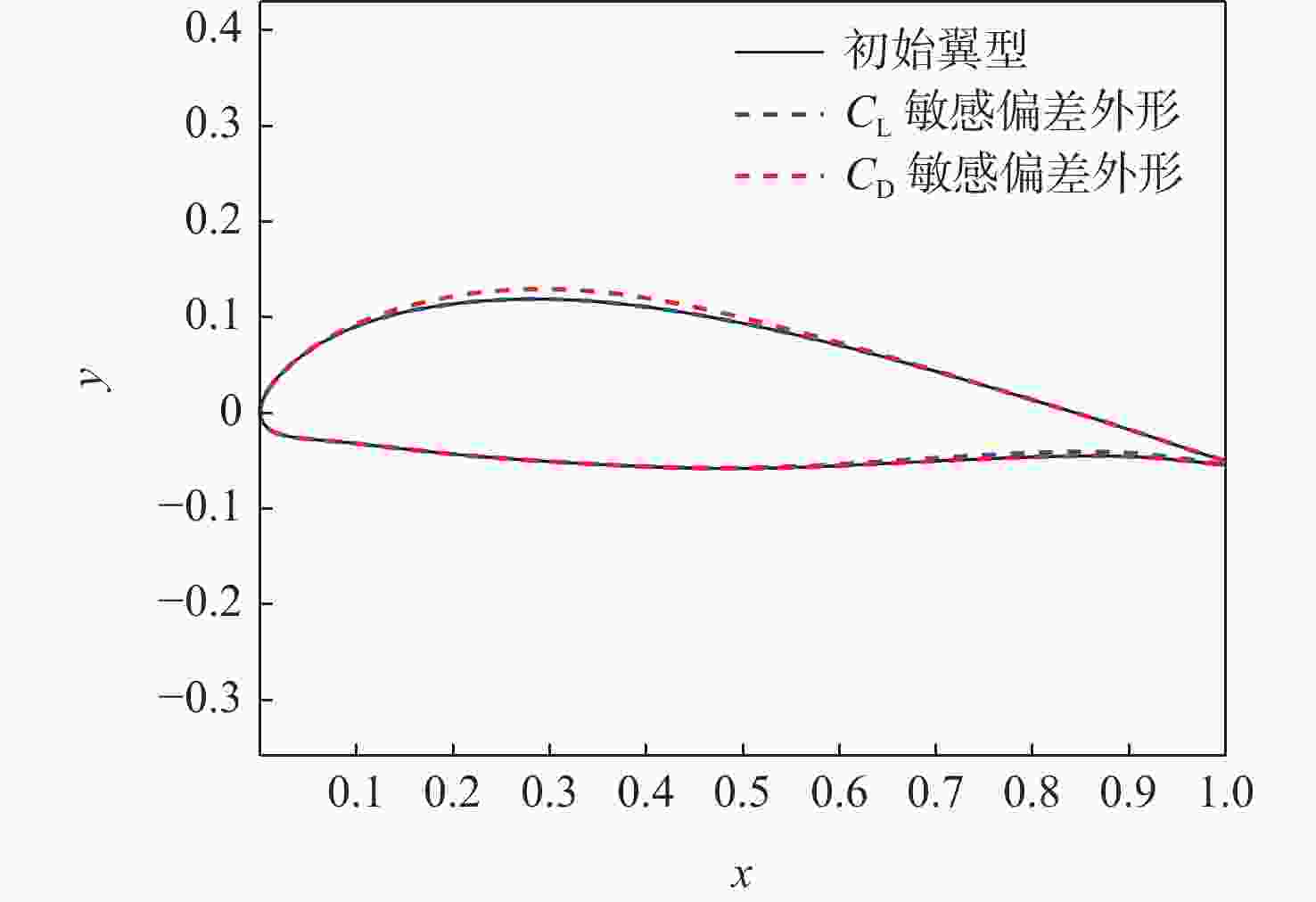
外形 压差阻力系数 摩擦阻力系数 原始外形 0.00665 0.00825 CD敏感偏差外形 0.00714 0.00826 表 9 上表面CST参数对应的外形关键点
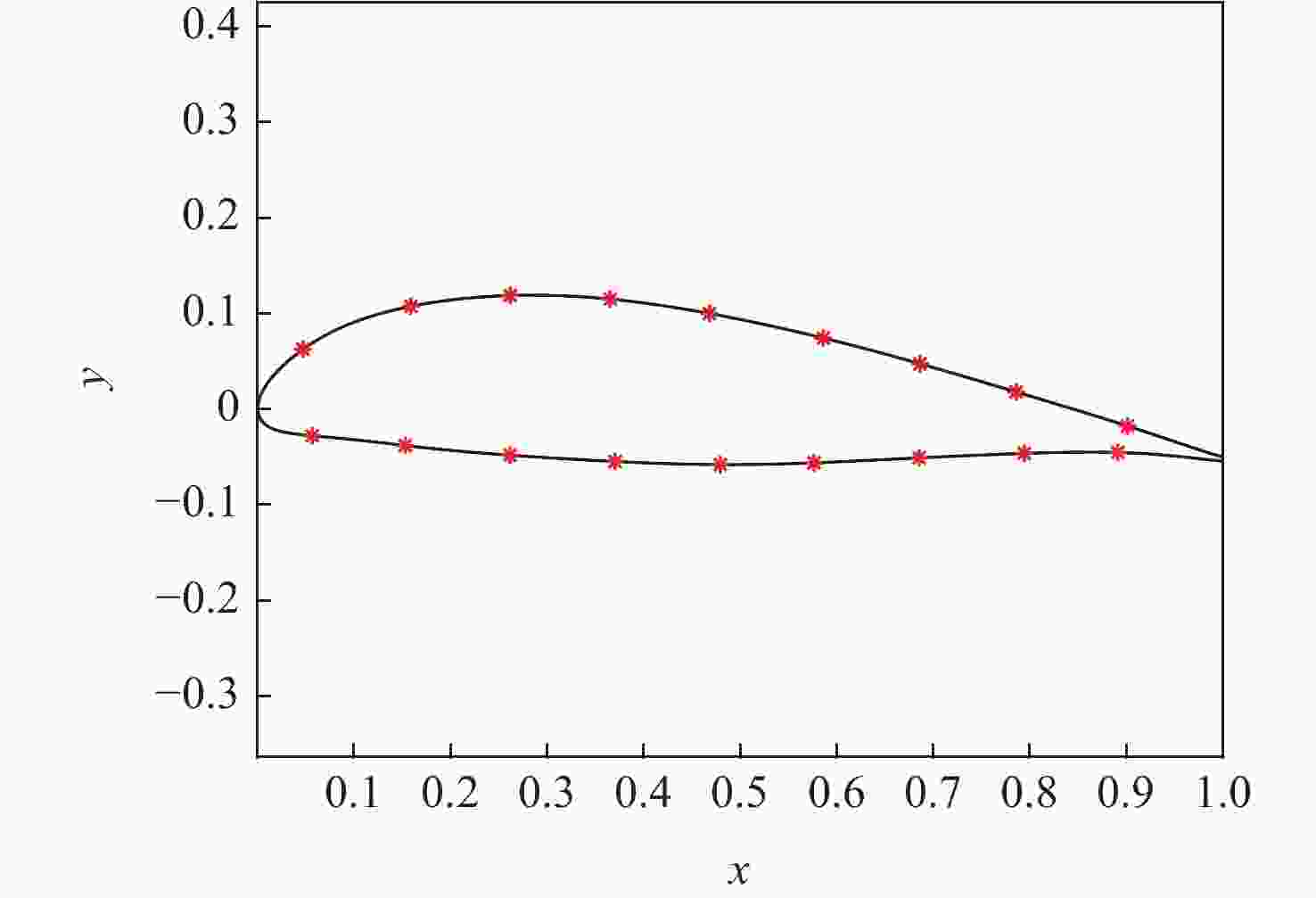
Table 9. CST parameters with corresponding shape key points on the upper surface
点编号 坐标 1 (0.047,0.063) 2 (0.159,0.108) 3 (0.262,0.119) 4 (0.365,0.115) 5 (0.468,0.100) 6 (0.586,0.074) 7 (0.686,0.047) 8 (0.786,0.018) 9 (0.901,−0.018) 表 10 下表面CST参数对应的外形关键点
Table 10. CST parameters with corresponding shape key points on the lower surface
点编号 坐标 10 (0.057,−0.028) 11 (0.153,−0.038) 12 (0.262,−0.048) 13 (0.370,−0.055) 14 (0.479,−0.058) 15 (0.576,−0.056) 16 (0.685,−0.051) 17 (0.794,−0.046) 18 (0.891,−0.045) 表 11 CST参数变化对应的关键点纵坐标变化区间
Table 11. Intervals of change in the vertical coordinates of keypoints corresponding to changes in CST parameters
点编号 纵坐标区间 点编号 纵坐标区间 1 [0.052,0.073] 10 [−0.039,−0.017] 2 [0.091,0.124] 11 [−0.055,−0.021] 3 [0.100,0.138] 12 [−0.067,−0.029] 4 [0.096,0.134] 13 [−0.074,−0.035] 5 [0.082,0.118] 14 [−0.076,−0.040] 6 [0.058,0.090] 15 [−0.072,−0.040] 7 [0.034,0.060] 16 [−0.064,−0.038] 8 [0.009,0.028] 17 [−0.055,−0.037] 9 [−0.022,−0.013] 18 [−0.050,−0.040] 表 12 减小关键点y坐标偏差对CL计算结果的影响
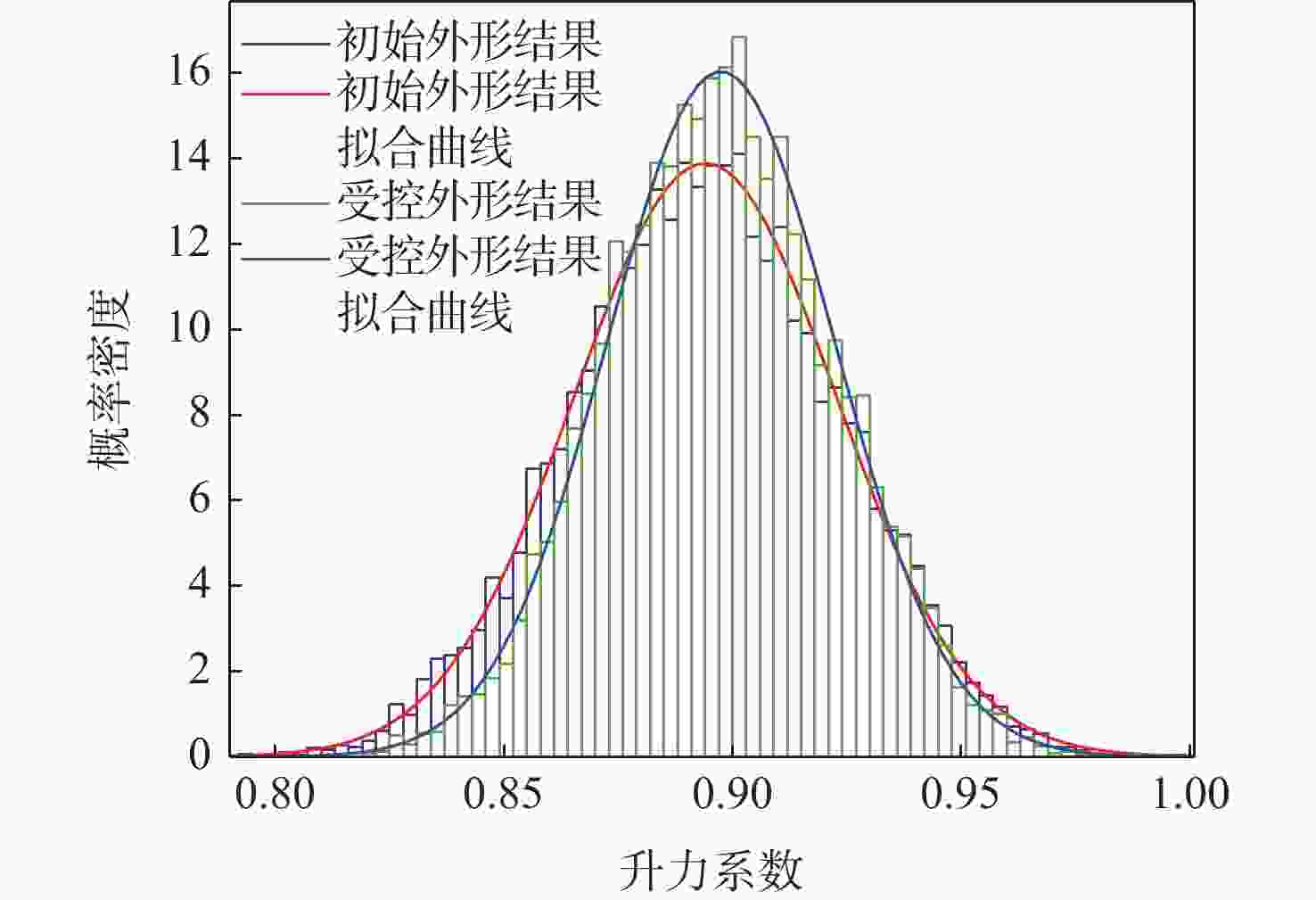
Table 12. Effects of reducing y-coordinate deviation of key points on CL results
外形 点17 y坐标 点18 y坐标 样本量 CL均值 CL方差 良品率 不控制
外形[−0.055,−0.037] [−0.050,−0.040] 10000 0.8940 8.25×10−4 0.896 控制
外形[−0.050,−0.041] [−0.047,−0.042] 8039 0.8974 6.18×10−4 0.948 -
[1] 陈登海. 基于室内GPS的飞机数字化水平测量技术研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2010.CHEN D. H. Research on digital level measurement of airplane based on indoor GPS[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2010(in Chinese). [2] 张开富. 飞机部件装配误差累积分析与容差优化方法研究[D]. 西安: 西北工业大学, 2006: 1-16.ZHANG K. F. Assembly error stack-up analysis and optimum tolerancing for aircraft assembly[D]. Xi’an: Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2006: 1-16(in Chinese). [3] HICKS P M, HENNE P A. Wing design by numerical optimization[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 1978, 15(7): 407-412. doi: 10.2514/3.58379 [4] SOBIECZKY H. Parametric airfoils and wings[M]//FUJII K, DULIKRAVICH G. Recent development of aerodynamic design methodologies. Berlin: Springer, 1999: 71-87. [5] BOEHM W. Bézier presentation of airfoils[J]. Computer Aided Geometric Design, 1987, 4(1-2): 17-22. doi: 10.1016/0167-8396(87)90021-5 [6] ROBINSON G M, KEANE A J. Concise orthogonal representation of supercritical airfoils[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2001, 38(3): 580-583. doi: 10.2514/2.2803 [7] KULFAN B M. Universal parametric geometry representation method[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2008, 45(1): 142-158. doi: 10.2514/1.29958 [8] KULFAN B M. A Universal parametric geometry representation method–“CST”[C]//Proceedings of the 45th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit. Reston: AIAA, 2007. [9] WIENER N. The homogeneous chaos[J]. American Journal of Mathematics, 1938, 60(4): 897-936. doi: 10.2307/2371268 [10] XIU D B, KARNIADAKIS G E. Modeling uncertainty in flow simulations via generalized polynomial chaos[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2003, 187(1): 137-167. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9991(03)00092-5 [11] GHANEM R. Ingredients for a general purpose stochastic finite elements implementation[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 1999, 168(1-4): 19-34. doi: 10.1016/S0045-7825(98)00106-6 [12] LÜTHEN N, MARELLI S, SUDRET B. Sparse polynomial chaos expansions: literature survey and benchmark[J]. SIAM/ASA Journal on Uncertainty Quantification, 2021, 9(2): 593-649. doi: 10.1137/20M1315774 [13] SOBOL I M. Global sensitivity indices for nonlinear mathematical models and their Monte Carlo estimates[J]. Mathematics and Computers in Simulation, 2001, 55(1-3): 271-280. doi: 10.1016/S0378-4754(00)00270-6 [14] SUDRET B. Global sensitivity analysis using polynomial chaos expansions[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2008, 93(7): 964-979. [15] MASTERS D A, TAYLOR N J, RENDALL T C S, et al. Geometric comparison of aerofoil shape parameterization methods[J]. AIAA Journal, 2017, 55(5): 1575-1589. doi: 10.2514/1.J054943 [16] KULFAN B, BUSSOLETTI J. "Fundamental" parameteric geometry representations for aircraft component shapes[C]//Proceedings of the 11th AIAA/ISSMO Multidisciplinary Analysis and Optimization Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2006. [17] XIU D B, KARNIADAKIS G E. Wiener-Askey polynomial chaos for stochastic differential equations[J]. SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing, 2002, 24(2): 619-644. doi: 10.1137/S1064827501387826 [18] BLATMAN G, SUDRET B. Adaptive sparse polynomial chaos expansion based on least angle regression[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 2011, 230(6): 2345-2367. doi: 10.1016/j.jcp.2010.12.021 -






 下载:
下载: