Multi-unmanned vehicle collaborative path planning method based on deep reinforcement learning
-
摘要:
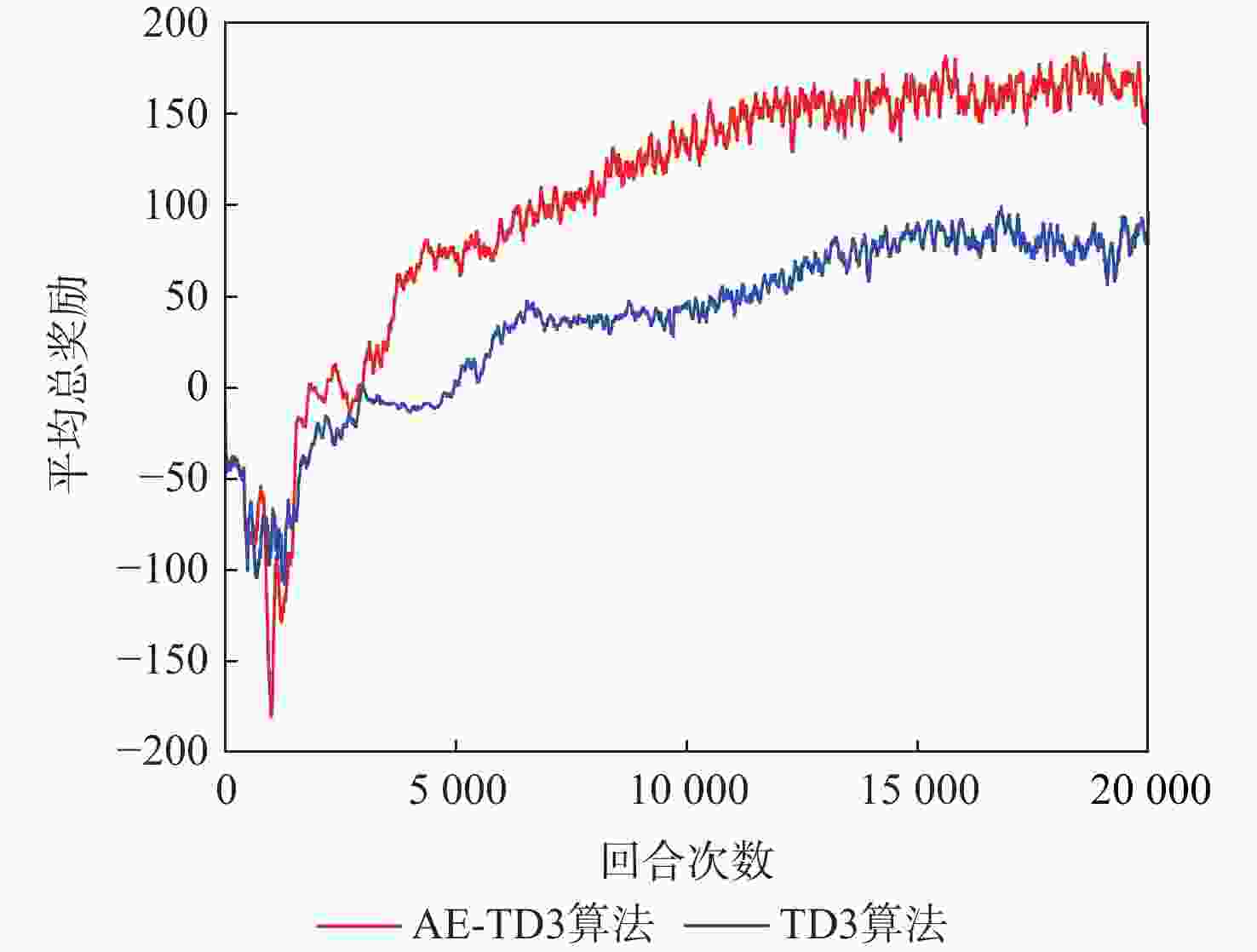
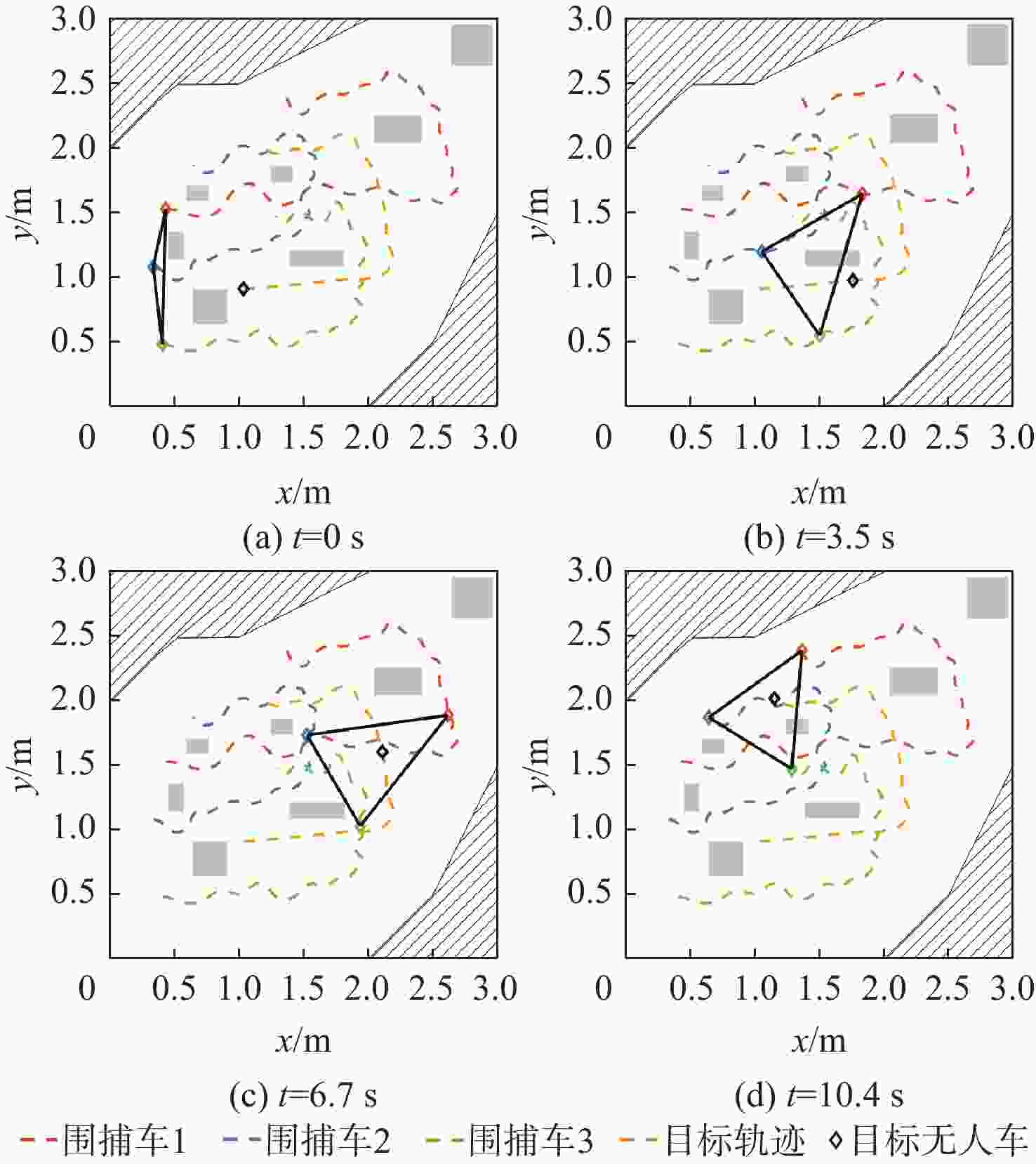
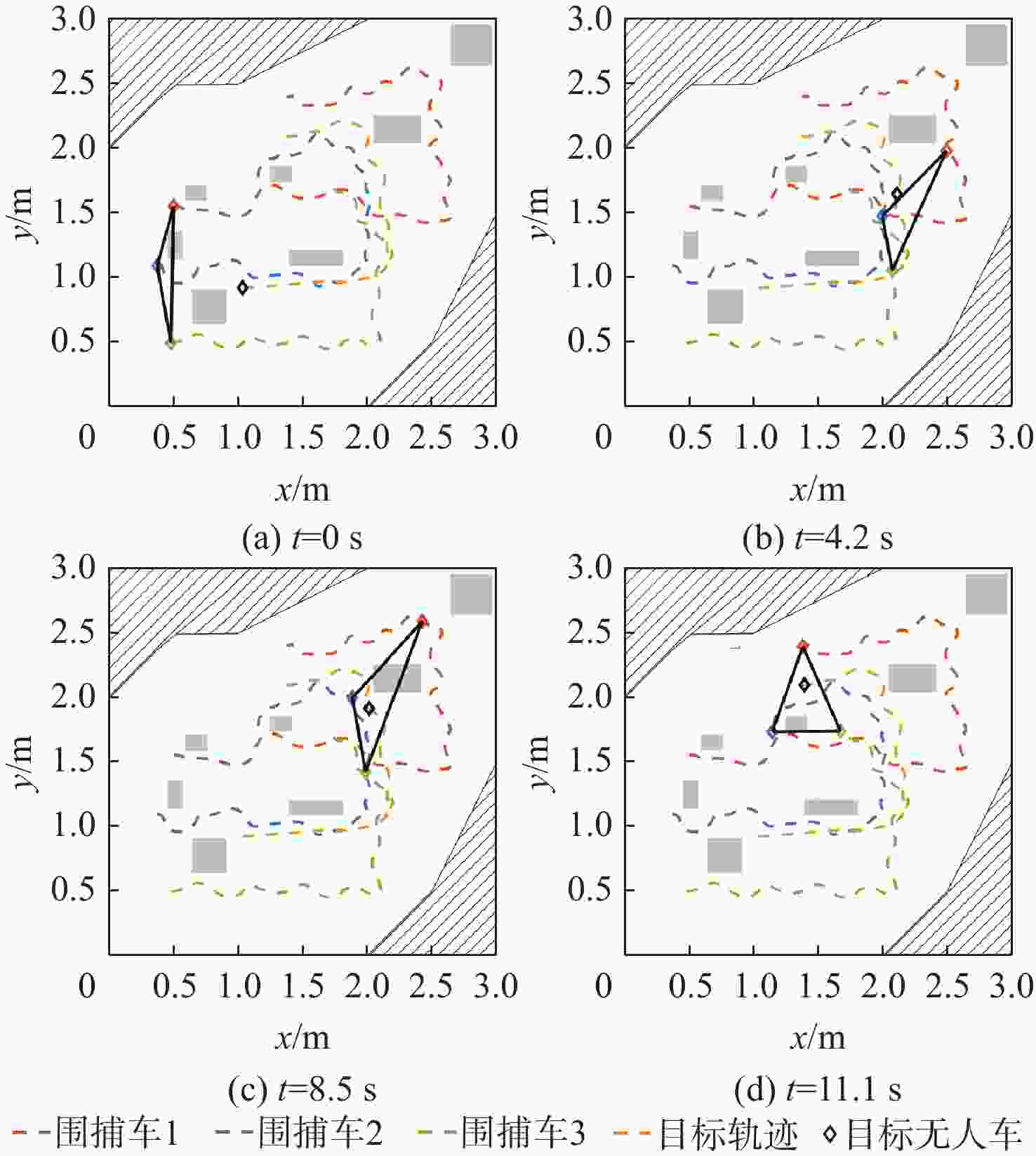
为解决多无人车系统中的协同路径规划问题,利用深度强化学习方法,设计了一种高效的路径规划框架。构建基于双轮差速无人车的运动学模型和协同避障场景的数学模型;在此基础上,进一步分析深度强化学习在处理高维度状态空间和连续动作空间等复杂动态场景时训练速度慢、采样效率低和适应能力差的机理,为多无人车协同路径规划研究提供理论基础。针对全部可观测条件下多无人车协同路径规划避障围捕的策略生成问题,提出改进双延迟深度确定性策略梯度(AE-TD3)算法,在围捕无人车输出的动作上添加来自高斯分布的随机噪声,并权衡探索或利用输出动作,使围捕无人车在未知环境中能更有效地探索,实现多无人车高效稳定的协同避障围捕。仿真实验表明,改进算法相较于双延迟深度确定性策略梯度(TD3)算法,平均奖励的收敛速度更快,围捕时间缩短16.7%,验证了改进算法的可行性。
-
关键词:
- 路径规划 /
- 协同避障和围捕 /
- 深度强化学习 /
- 双延迟深度确定性策略梯度算法 /
- 动作增强探索策略
Abstract:This study aims to tackle the collaborative path planning issue in multi-unmanned vehicle systems using deep reinforcement learning. We’ve devised an efficient path planning framework by first establishing kinematic and mathematical models for differential-drive unmanned vehicles and collaborative obstacle avoidance scenarios. Then, we addressed the challenges of slow training, low sampling efficiency, and poor adaptability of reinforcement learning in complex dynamic scenarios. For cooperative obstacle avoidance and pursuit, we suggested an improved twin delayed deep deterministic policy gradient (AE-TD3) algorithm. By introducing random noise to pursuing unmanned vehicle actions, exploration in unknown environments is improved, leading to efficient and stable collaborative obstacle avoidance and pursuit. Our method is validated by simulation results, which show faster convergence and a 16.7% reduction in pursuit time when compared to the twin delayed deep deterministic policy gradient (TD3) algorithm.
-
表 1 奖励函数机制
Table 1. Reward function mechanism
动作 奖励 结果 无人车与其他无人车/
边界/障碍物相撞惩罚矩阵为$ \boldsymbol{P}_{\text{c}} $ 终止 围捕无人车与目标无人车距离小于
围捕最大距离,大于碰撞距离奖励矩阵为$ \boldsymbol{R}_{\mathrm{p}m} $ 继续 目标无人车持续在围捕无人车
组成的三角形中奖励矩阵为$ \boldsymbol{R}_{\mathrm{b}} $ 终止 表 2 仿真环境无人车的相关参数
Table 2. Related parameters of unmanned vehicles in simulation environment
车轮
半径/m无人车
半径/m目标/围捕无人车
初始速度/(m·s−1)目标/围捕无人车
最大速度/(m·s−1)角速度范围/
(rad·s−1)0.0335 0.116 0.1/0.2 0.3/0.5 −1~1 表 3 强化学习训练超参数
Table 3. Reinforcement learning training hyperparameters
折扣
因子惯性
因子目标平滑
因子探索率 方差 神经网络
学习率经验池
大小0.99 0.01 0.005 0~1 0.2 0.001 100000 -
[1] 刘云平, 蒋长胜, 张婷婷, 等. 考虑内部避碰的多无人机有限时间环形编队控制[J]. 机械工程学报, 2022, 58(1): 61-68. doi: 10.3901/JME.2022.01.061LIU Y P, JIANG C S, ZHANG T T, et al. Multi-UAV finite-time ring formation control considering internal collision avoidance[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2022, 58(1): 61-68(in Chinese). doi: 10.3901/JME.2022.01.061 [2] XU C, ZHANG Y, WANG W G, et al. Pursuit and evasion strategy of a differential game based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2022, 10: 827408. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.827408 [3] SANG H Q, YOU Y S, SUN X J, et al. The hybrid path planning algorithm based on improved A* and artificial potential field for unmanned surface vehicle formations[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2021, 223: 108709. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2021.108709 [4] DING H W, CAO X G, WANG Z S, et al. Velocity clamping-assisted adaptive salp swarm algorithm: balance analysis and case studies[J]. Mathematical Biosciences and Engineering, 2022, 19(8): 7756-7804. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2022364 [5] WANG Z S, DING H W, YANG Z J, et al. Rank-driven salp swarm algorithm with orthogonal opposition-based learning for global optimization[J]. Applied Intelligence, 2022, 52(7): 7922-7964. doi: 10.1007/s10489-021-02776-7 [6] WANG Z S, DING H W, YANG J J, et al. Advanced orthogonal opposition-based learning-driven dynamic salp swarm algorithm: framework and case studies[J]. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2022, 16(10): 945-971. [7] WANG Z S, DING H W, WANG J, et al. Adaptive guided salp swarm algorithm with velocity clamping mechanism for solving optimization problems[J]. Journal of Computational Design and Engineering, 2022, 9(6): 2196-2234. doi: 10.1093/jcde/qwac094 [8] YUAN Z, WU T H, WANG Q W, et al. T3OMVP: a Transformer-based time and team reinforcement learning scheme for observation-constrained multi-vehicle pursuit in urban area[J]. Electronics, 2022, 11(9): 1339. doi: 10.3390/electronics11091339 [9] WANG W X, HAO J Y, WANG Y X, et al. Achieving cooperation through deep multiagent reinforcement learning in sequential prisoner’s dilemmas[C]//Proceedings of the First International Conference on Distributed Artificial Intelligence. New York: ACM, 2019: 1-7. [10] MAO W C, YANG L F, ZHANG K Q, et al. On improving model-free algorithms for decentralized multi-agent reinforcement learning[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning. San Diego: JMLR, 2022: 162. [11] HARTMANN G, SHILLER Z, AZARIA A. Competitive driving of autonomous vehicles[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 111772-111783. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3215984 [12] LOWE R, WU Y, TAMAR A, et al. Multi-agent actor-critic for mixed cooperative-competitive environments[C]//Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. La Jolla: NIPS, 2017: 30. [13] SUN Y, LAI J, CAO L, et al. A novel multi-agent parallel-critic network architecture for cooperative-competitive reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 135605-135616. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3011670 [14] ZHU P M, DAI W, YAO W J, et al. Multi-robot flocking control based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 150397-150406. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3016951 [15] 吴子沉, 胡斌. 基于态势认知的无人机集群围捕方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2021, 47(2): 424-430. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2020.0274WU Z C, HU B. Swarm rounding up method of UAV based on situation cognition[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2021, 47(2): 424-430(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2020.0274 [16] XU C, ZHU H, ZHU H T, et al. Improved RRT algorithm for automatic charging robot obstacle avoidance path planning in complex environments[J]. Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, 2023, 137(3): 2567-2591. [17] LI Q B, LIN W Z, LIU Z, et al. Message-aware graph attention networks for large-scale multi-robot path planning[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2021, 6(3): 5533-5540. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2021.3077863 [18] 符小卫, 王辉, 徐哲. 基于DE-MADDPG的多无人机协同追捕策略[J]. 航空学报, 2022, 43(5): 325311.FU X W, WANG H, XU Z. Cooperative pursuit strategy for multi-UAVs based on DE-MADDPG algorithm[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2022, 43(5): 325311(in Chinese). [19] 刘钊, 周壮壮, 张明阳, 等. 基于双延迟深度确定性策略梯度的船舶自主避碰方法[J]. 交通信息与安全, 2022, 40(3): 60-74. doi: 10.3963/j.jssn.1674-4861.2022.03.007LIU Z, ZHOU Z Z, ZHANG M Y, et al. A twin delayed deep deterministic policy gradient method for collision avoidance of autonomous ships[J]. Journal of Transport Information and Safety, 2022, 40(3): 60-74(in Chinese). doi: 10.3963/j.jssn.1674-4861.2022.03.007 -






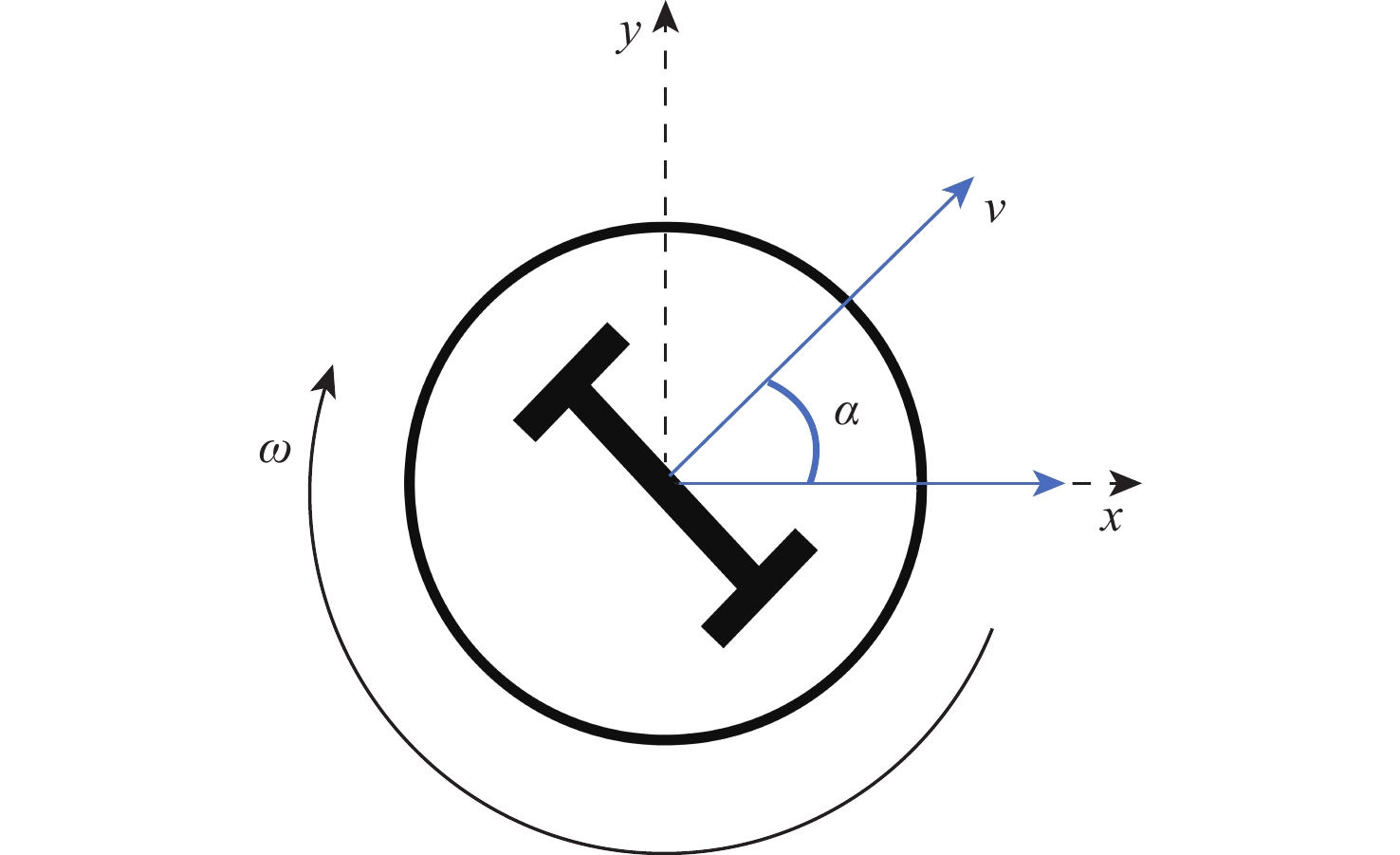
 下载:
下载: