-
摘要:
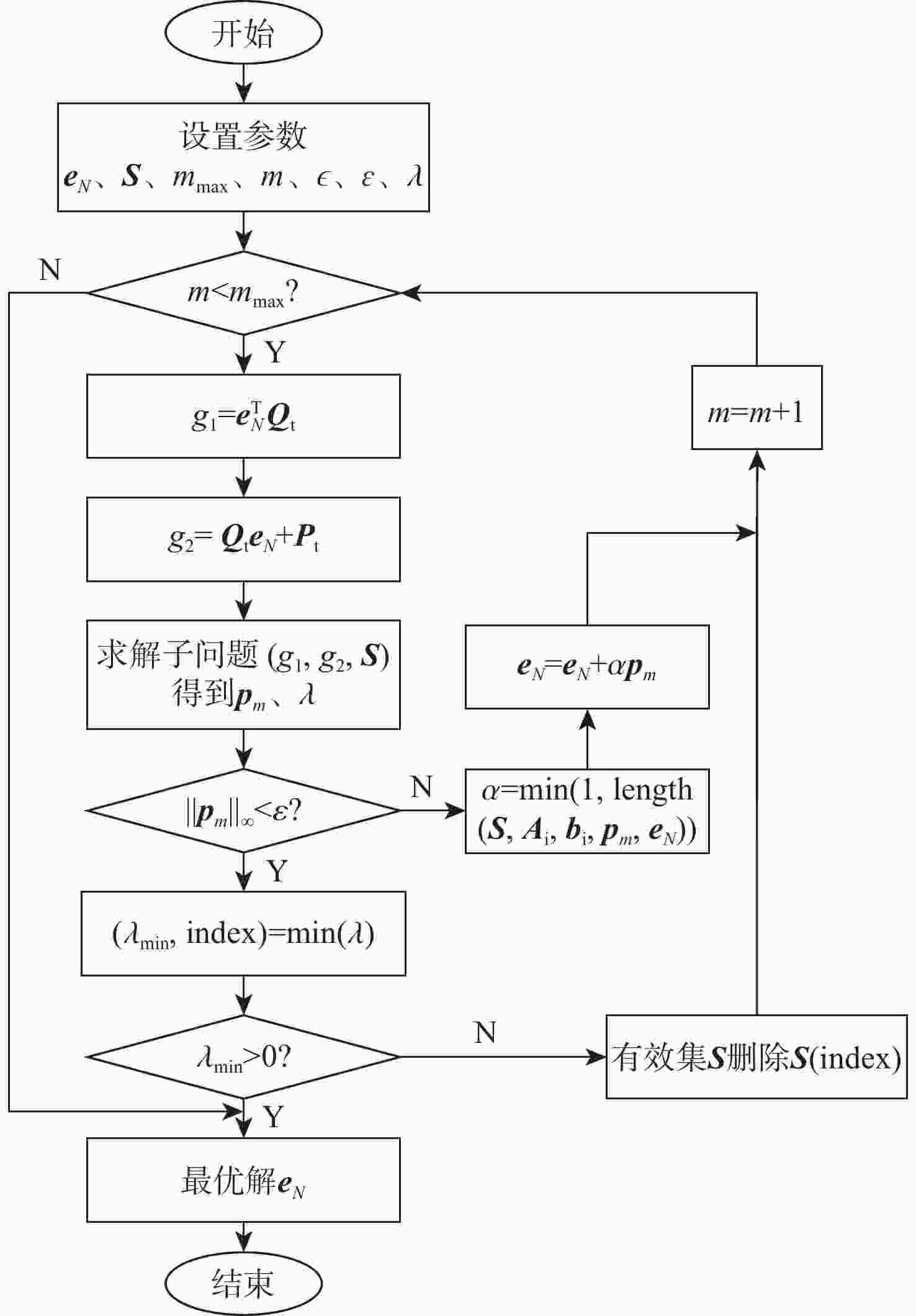
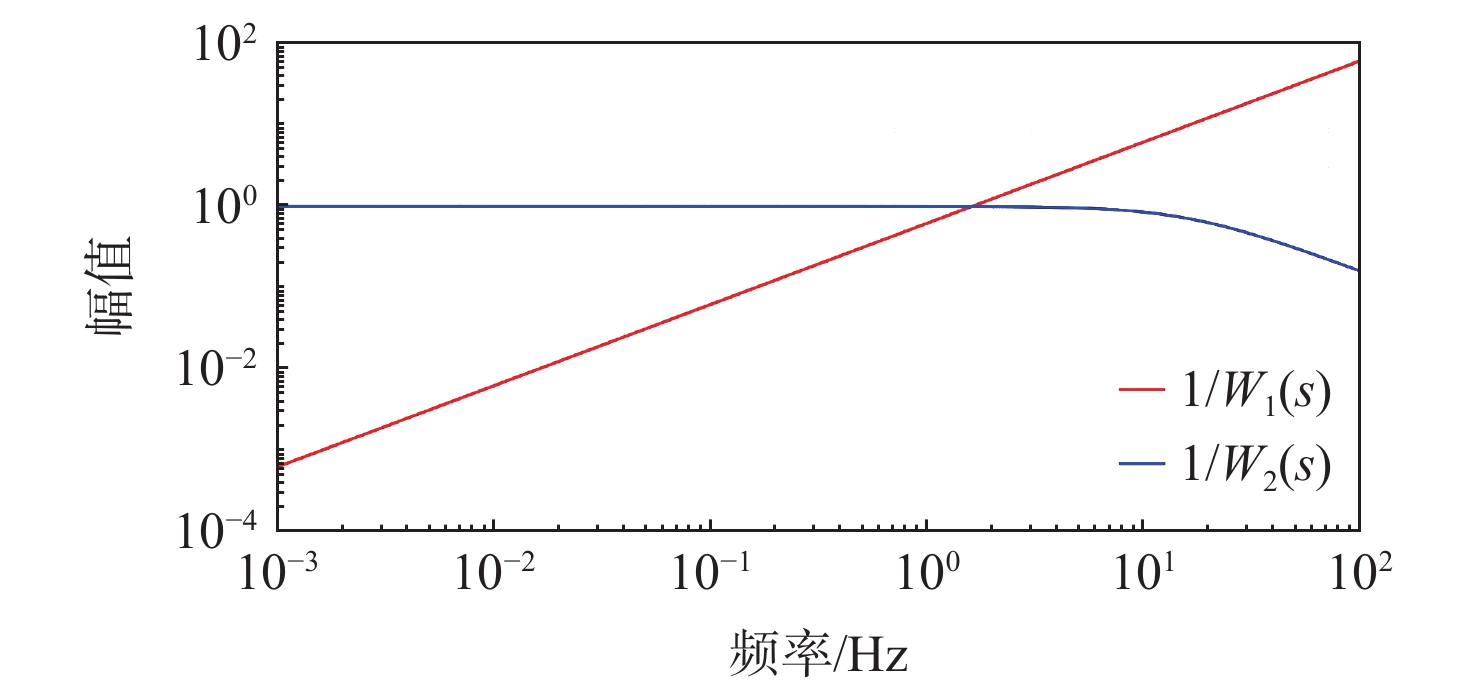
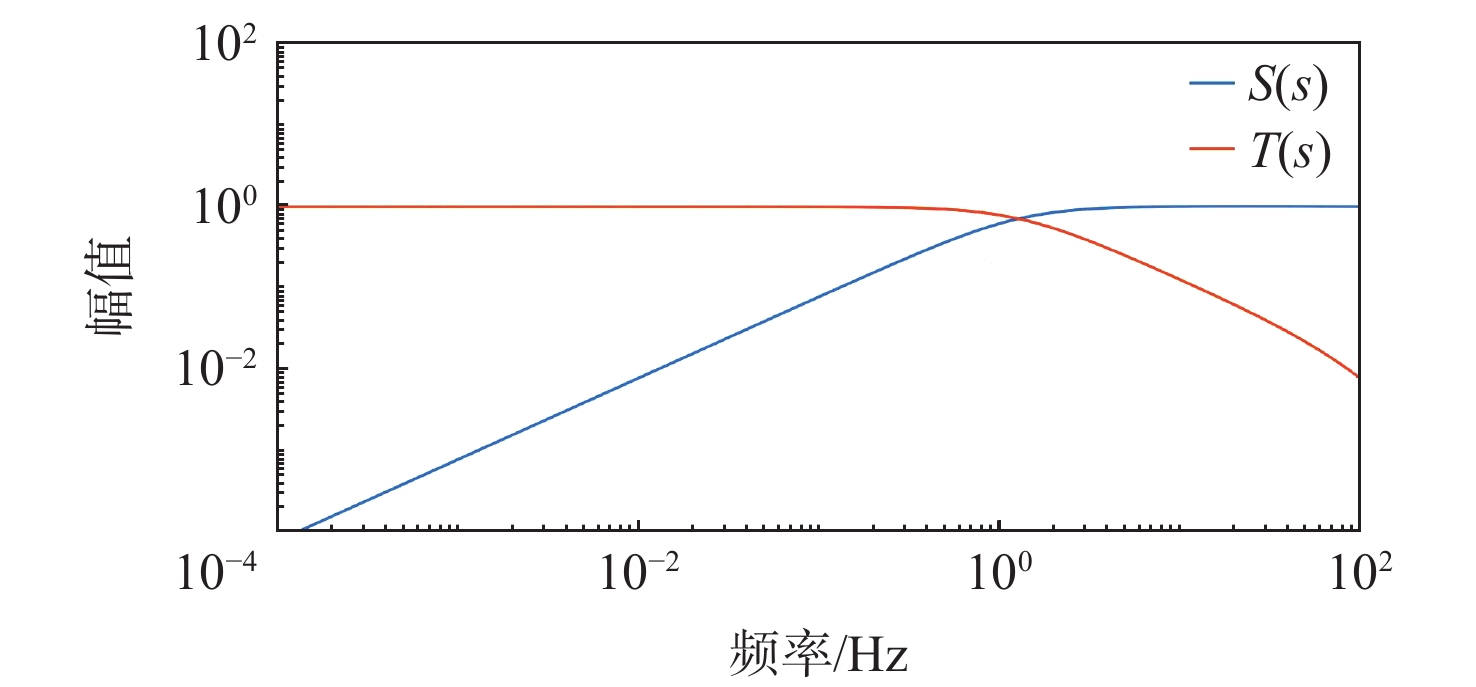
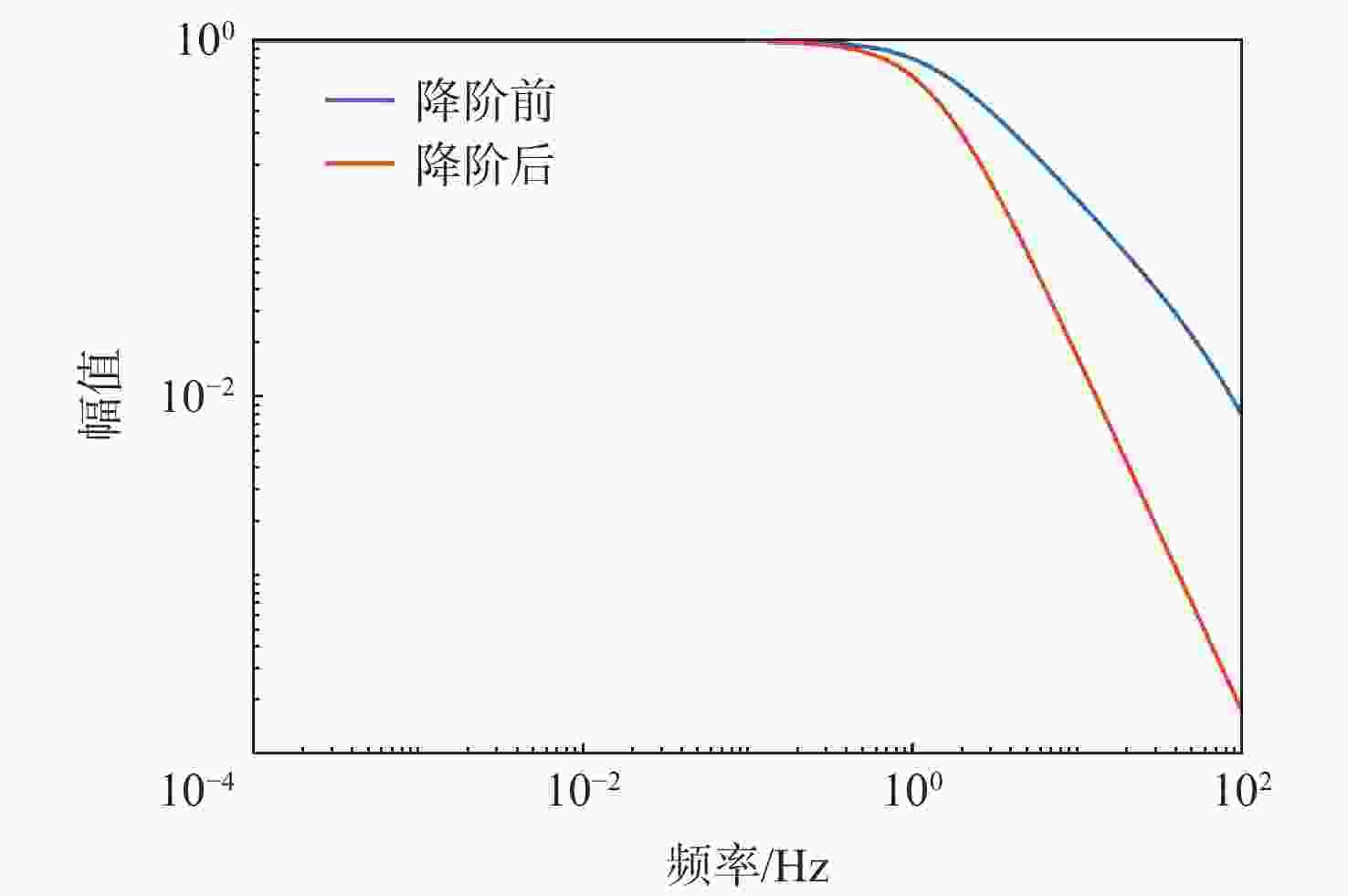
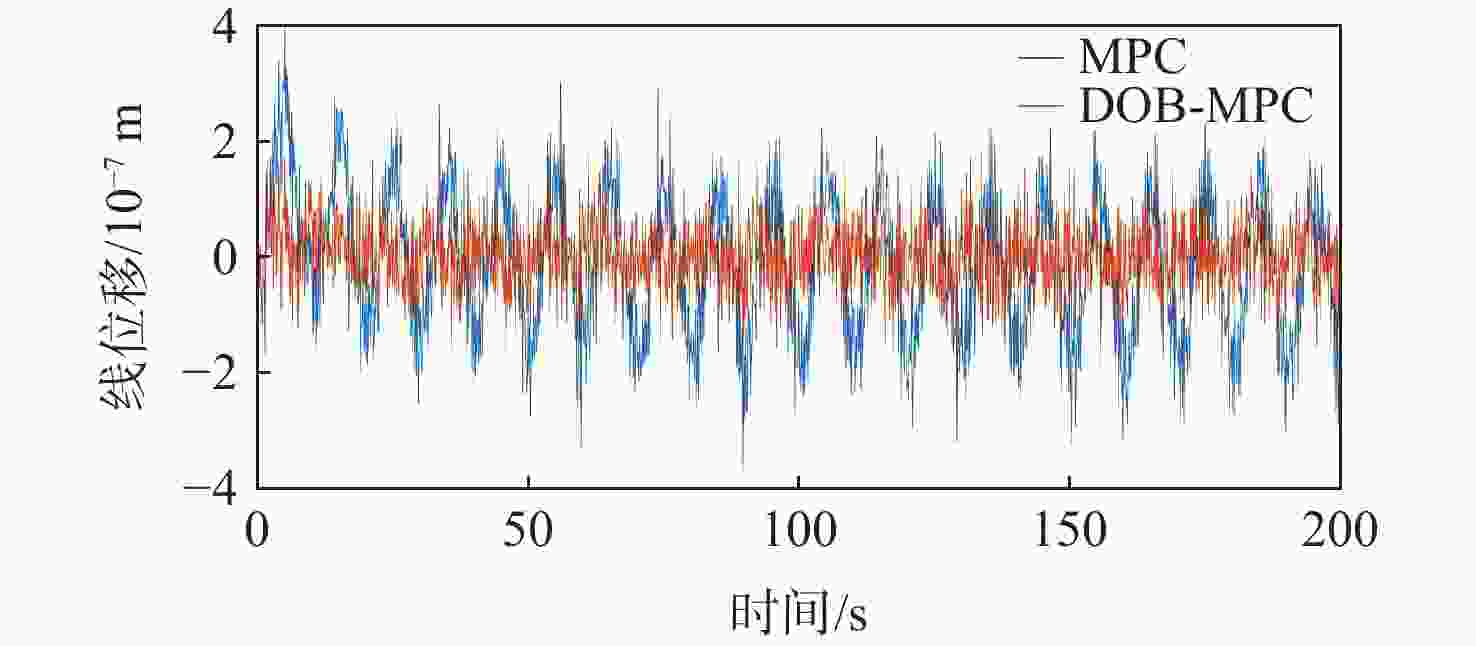
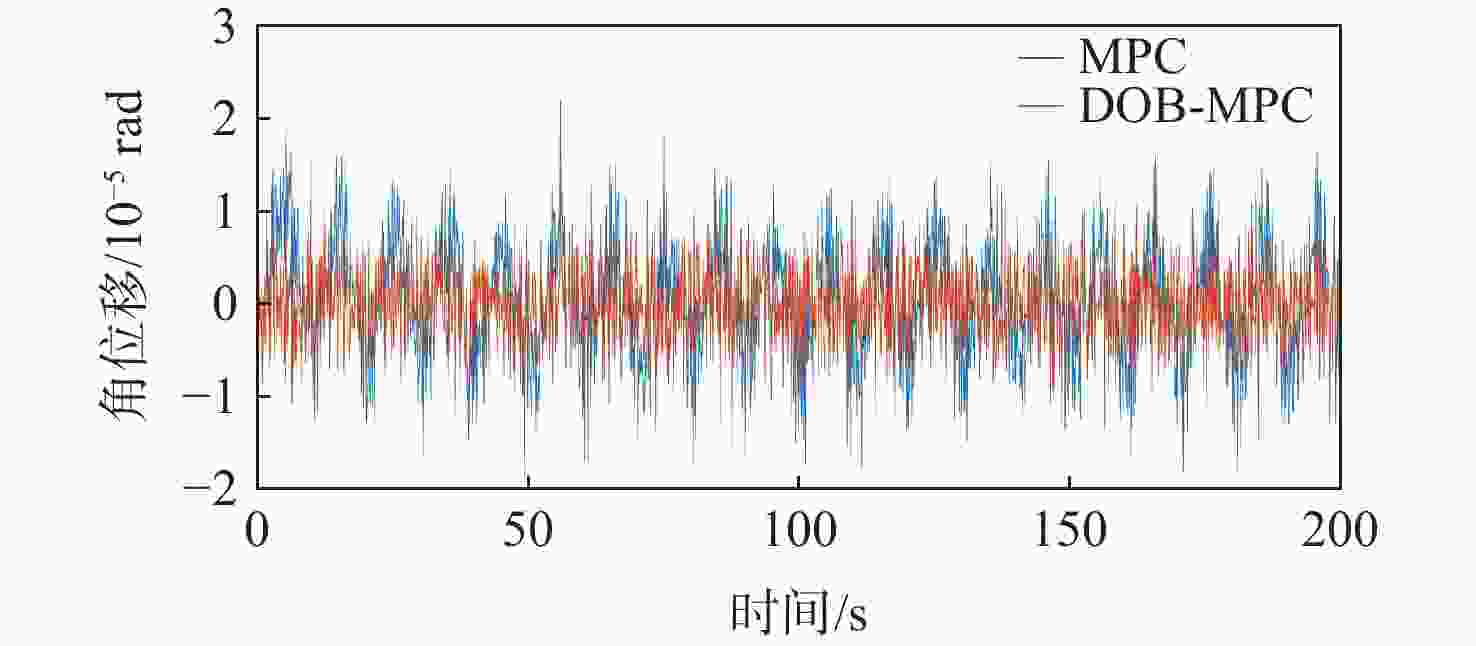
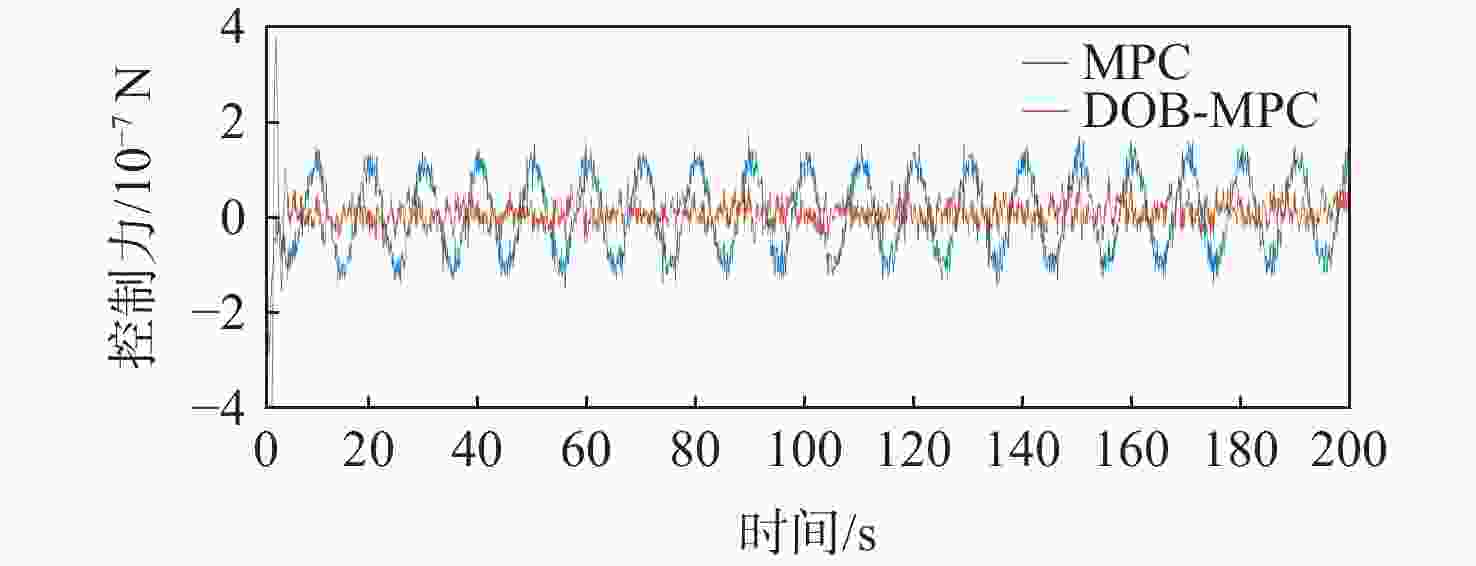
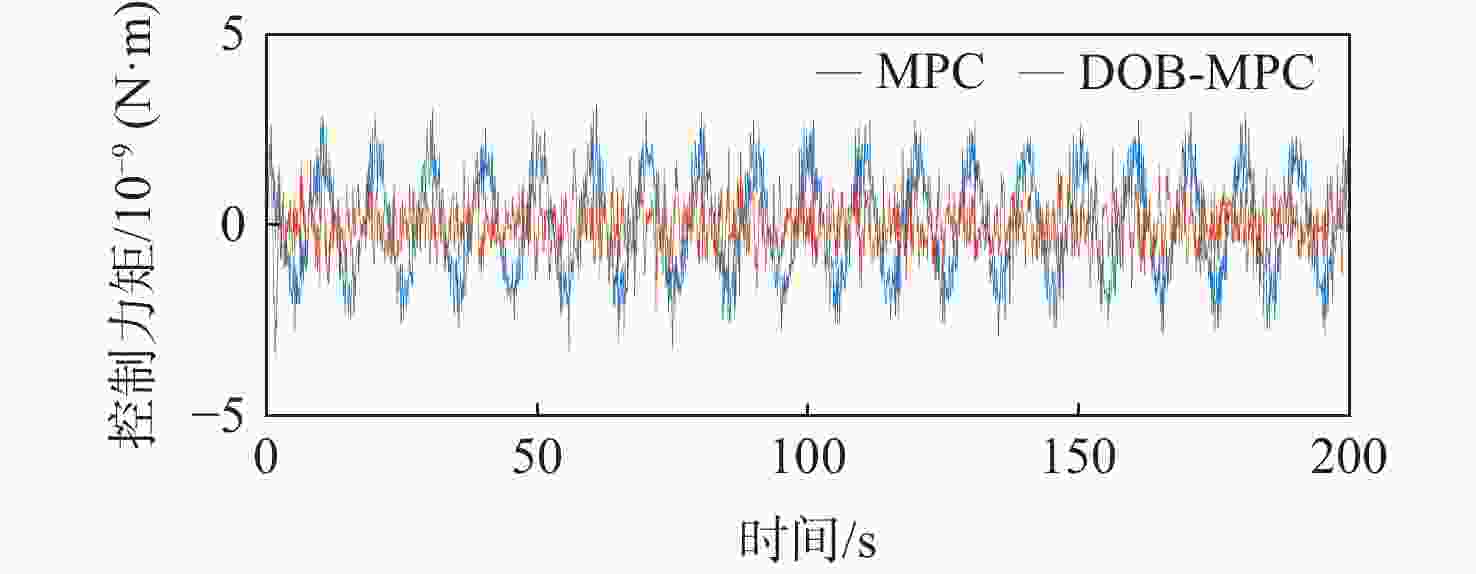
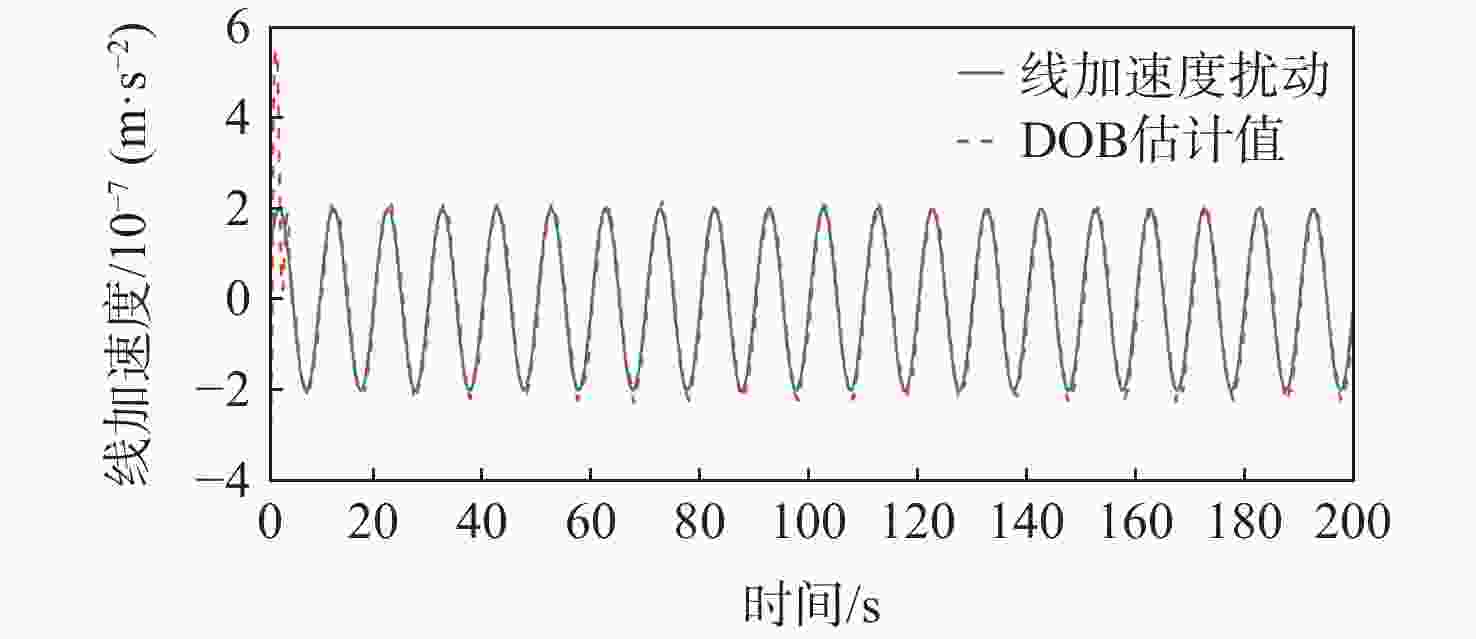
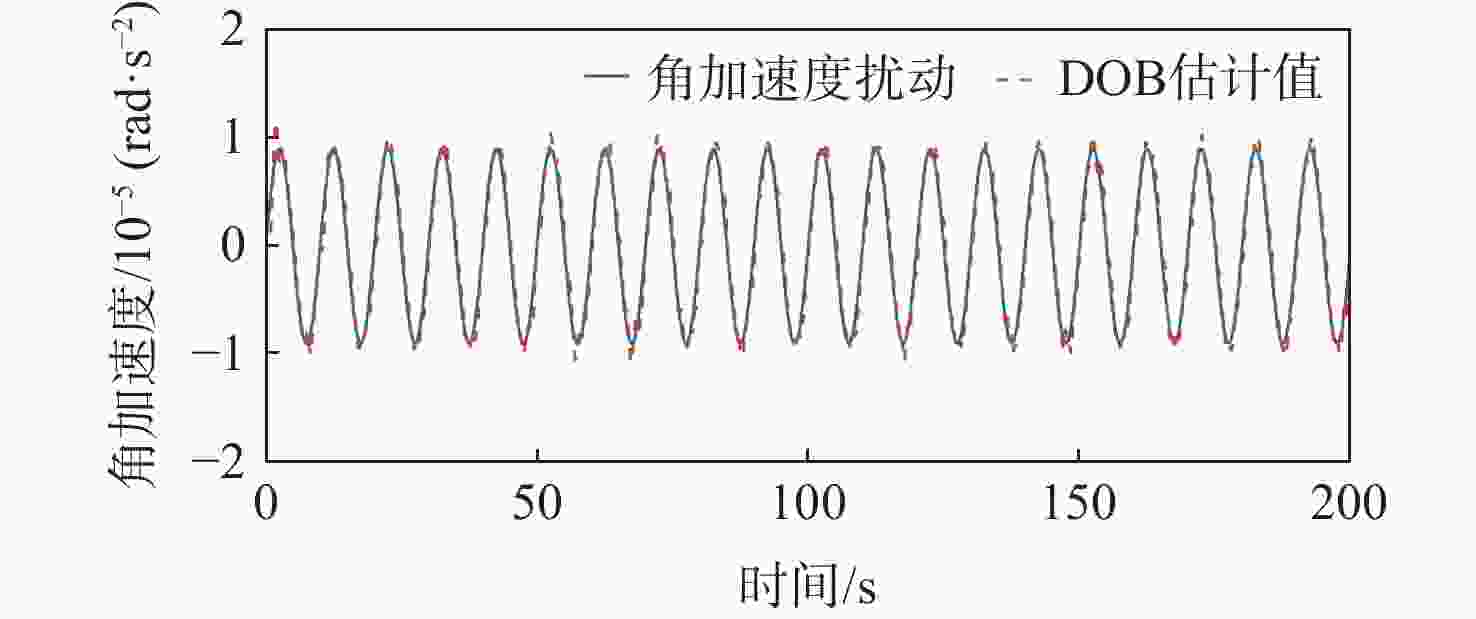
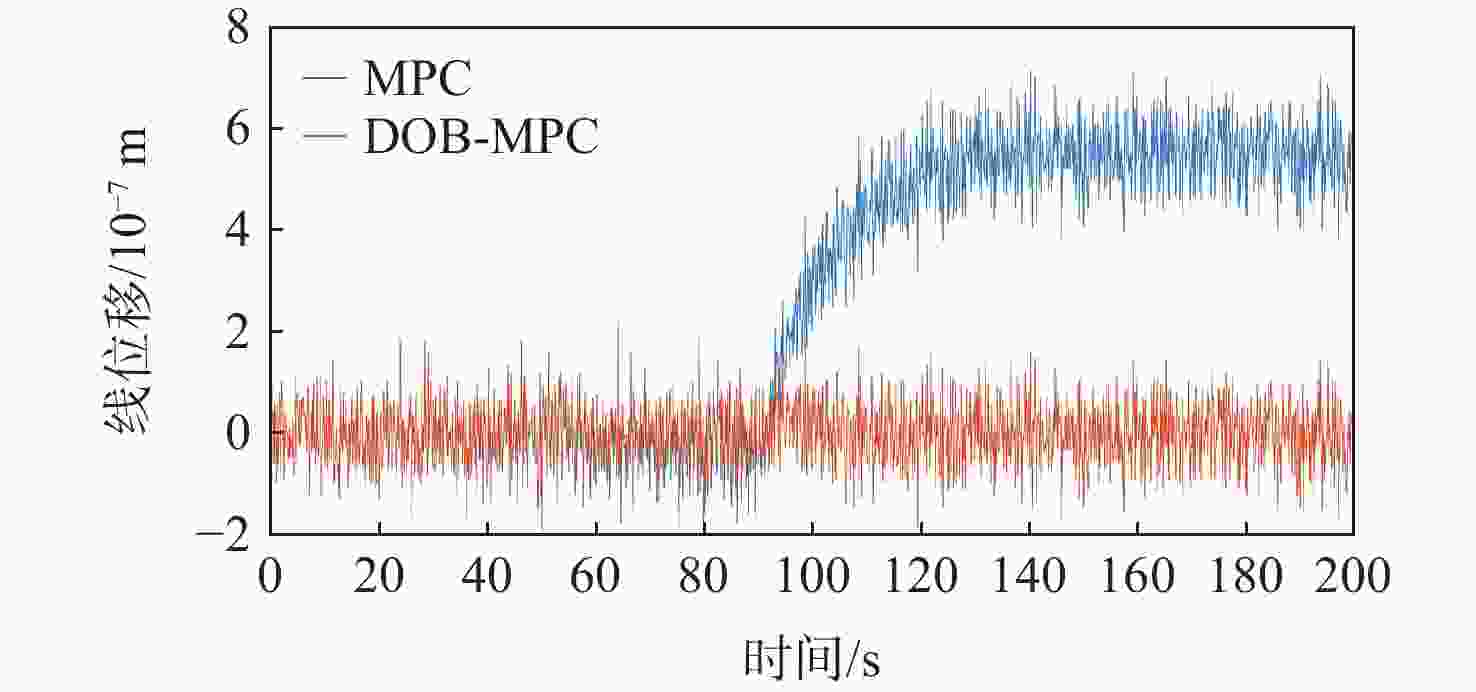
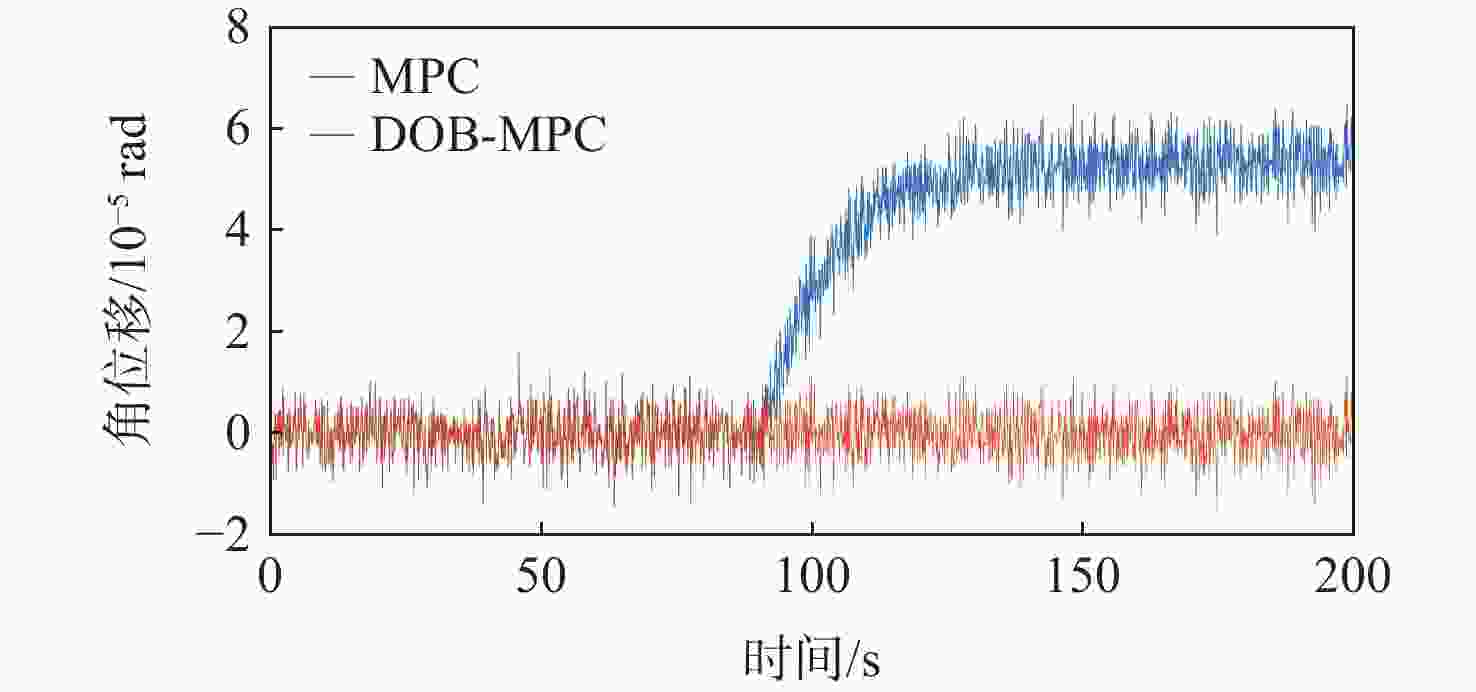
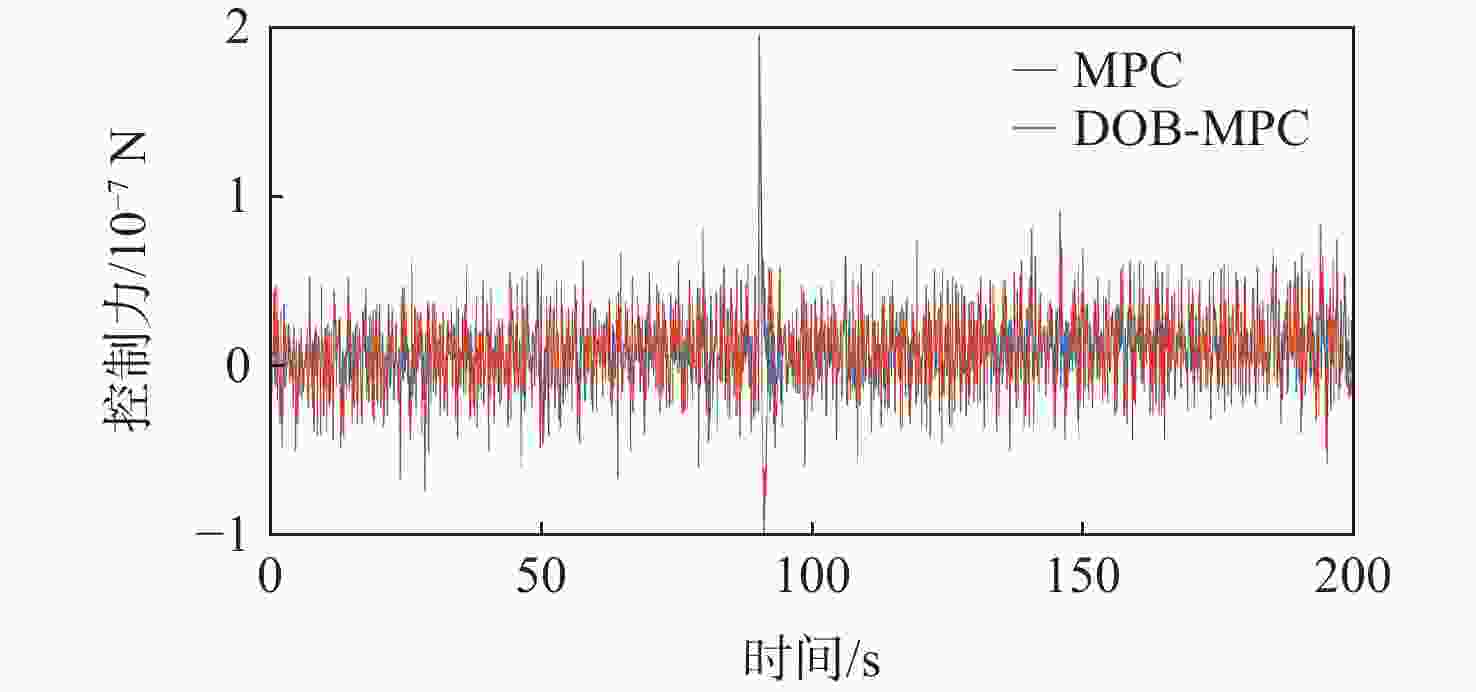
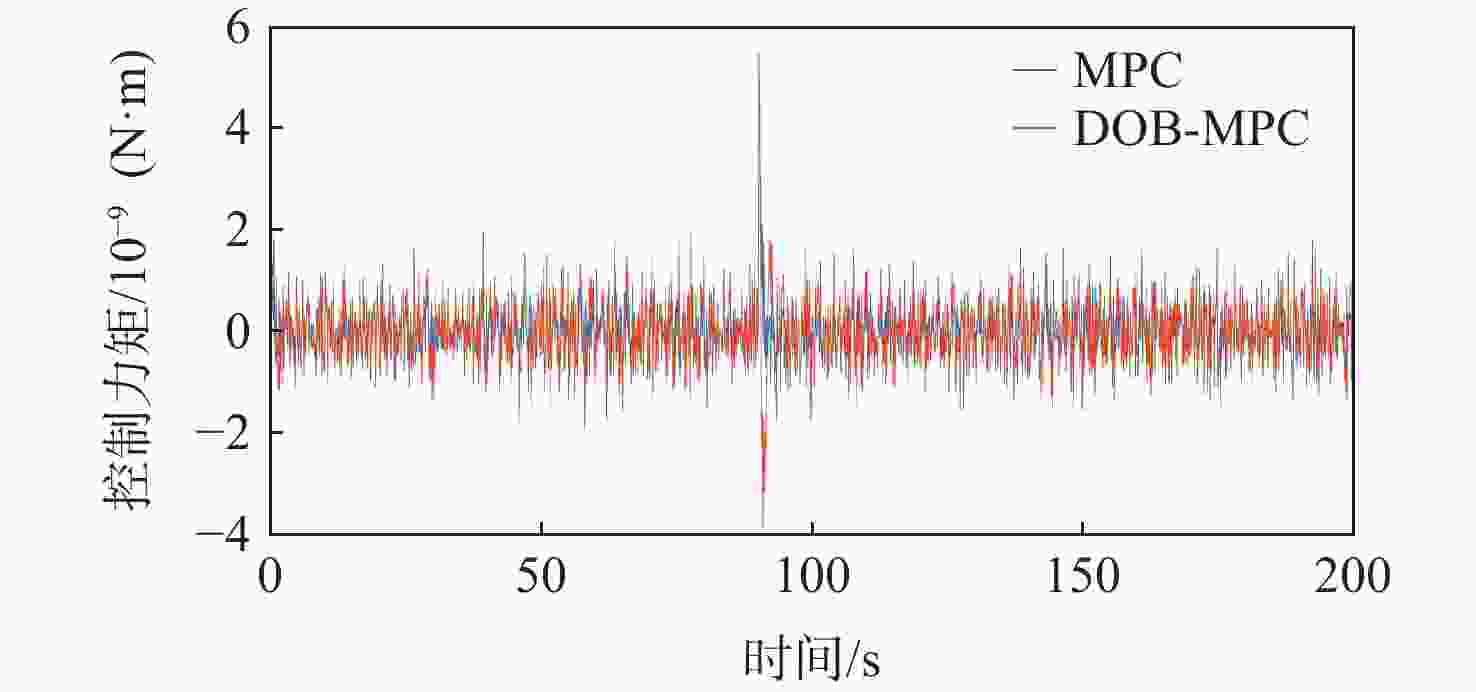
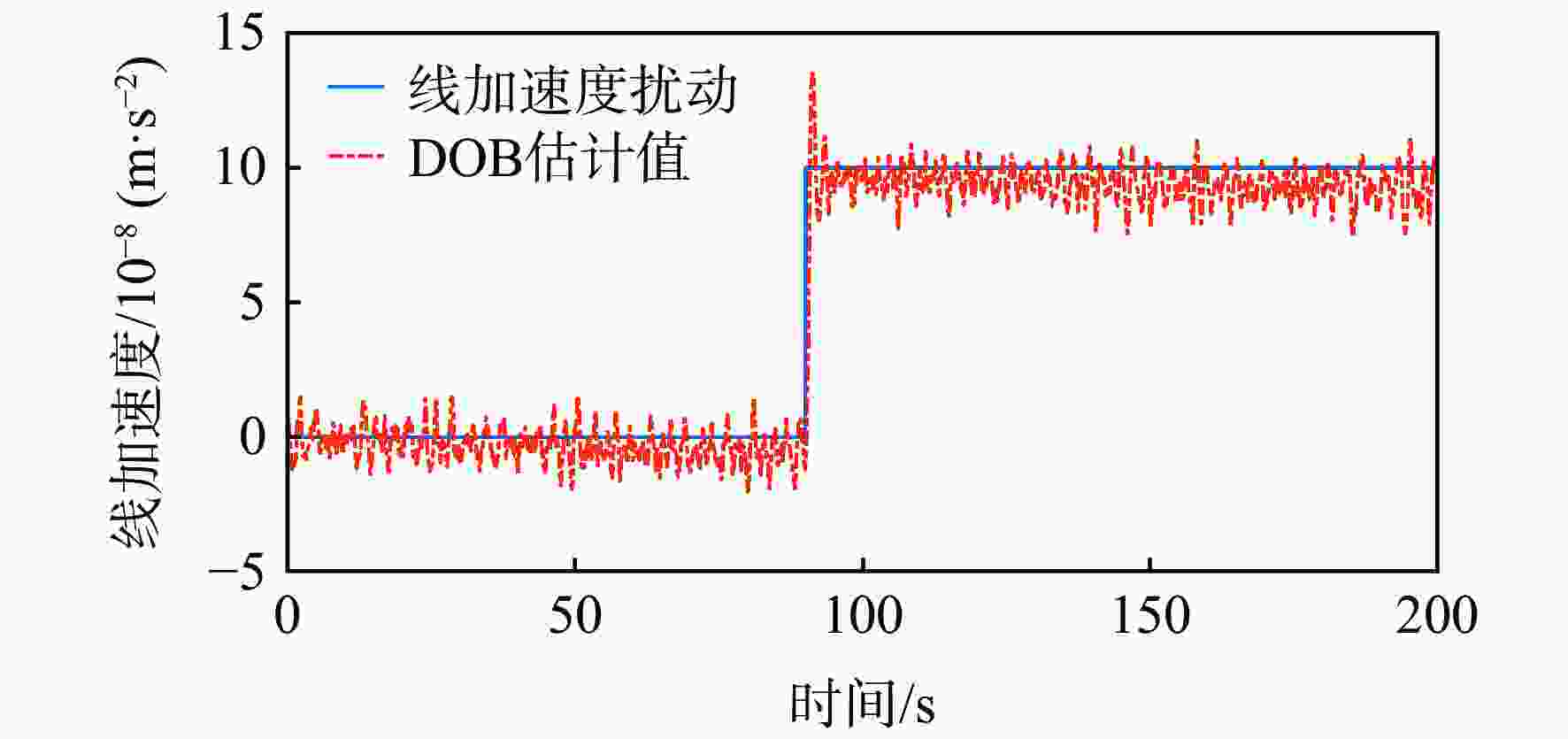
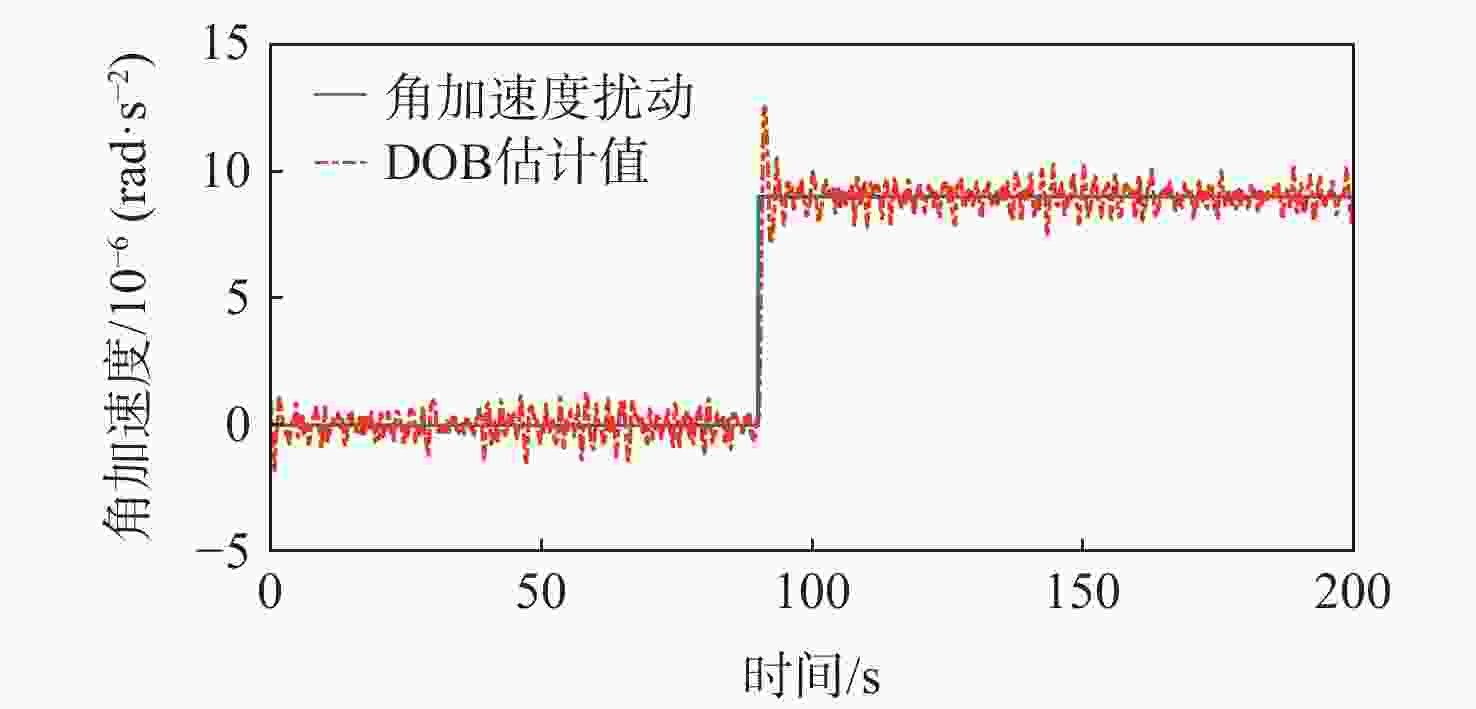
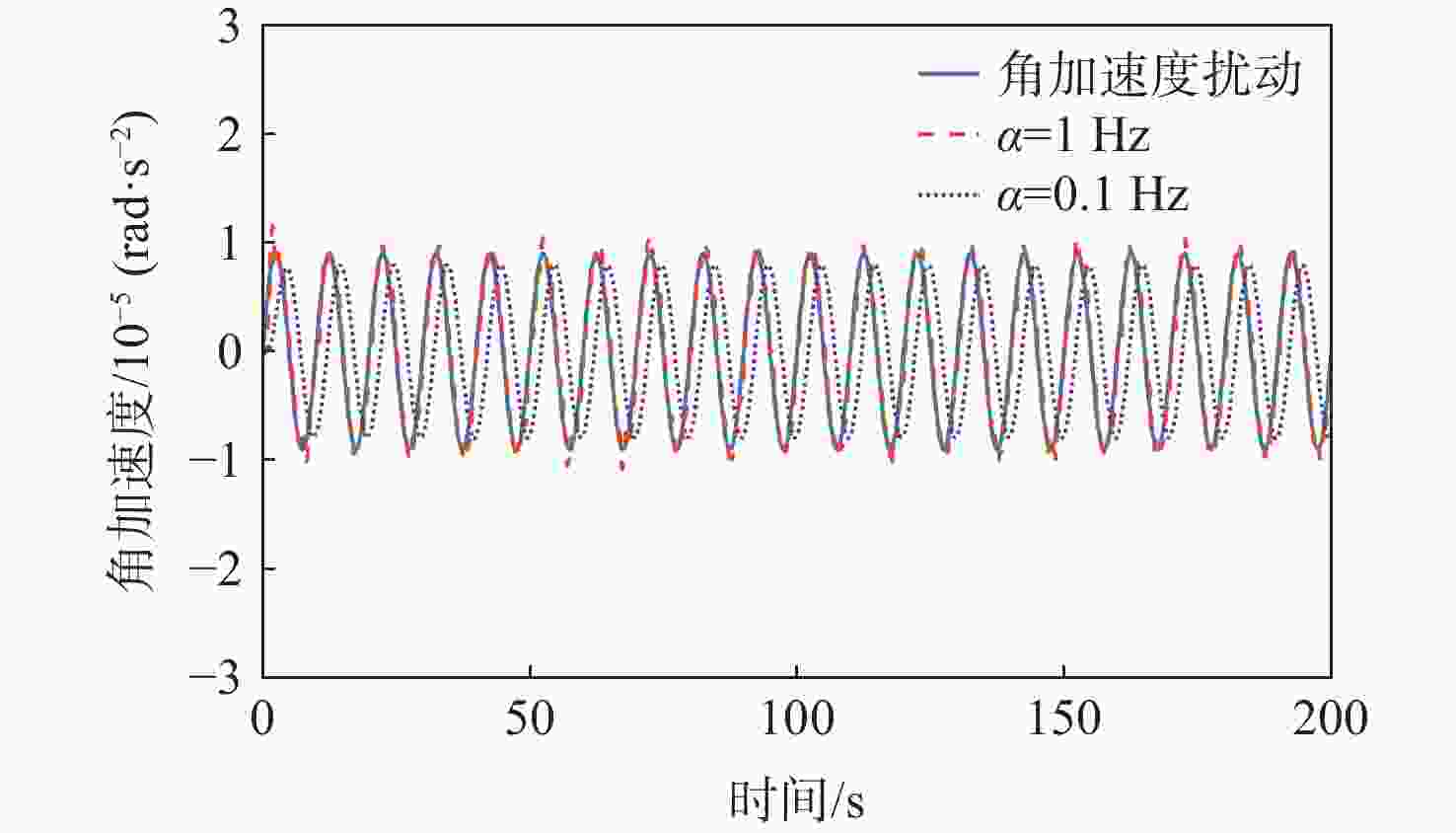
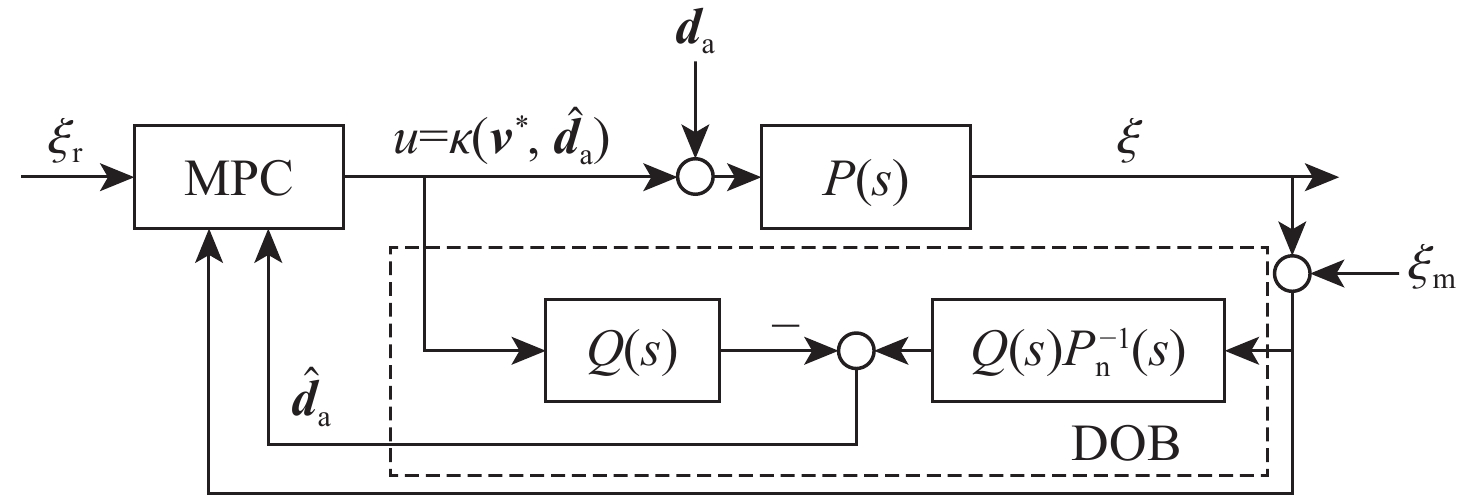
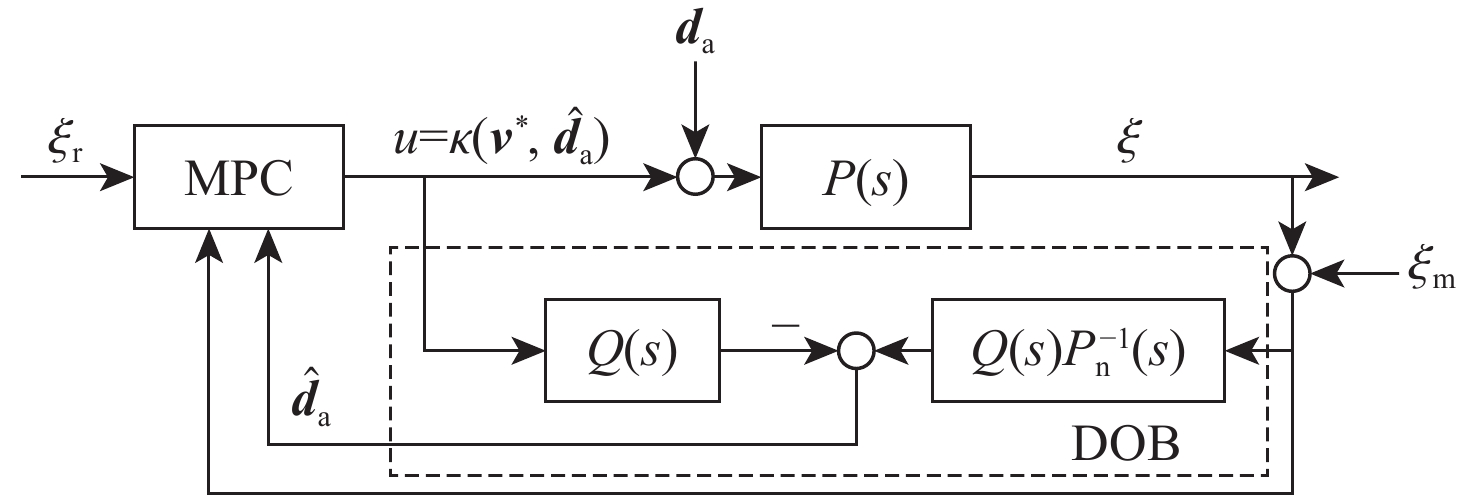
为提升深空引力波探测任务中检验质量释放阶段的控制器抗干扰性能,提出一种面向检验质量稳态建立的基于扰动观测器(DOB)的渐进管道模型预测控制(MPC)方法。采用DOB提高控制器抗干扰性能,利用虚拟回路技术将DOB的设计问题归结为标准$ {H}_{\mathrm{\infty }} $混合灵敏度优化问题,并实现高精度估计。同时,设计渐进管道MPC,利用有效集法求解优化问题,结合DOB的扰动估计值实现强干扰和强执行约束下的高精度检验质量抗扰控制。在航天器-双检验质量全自由度仿真平台上进行仿真验证,在基本噪声及干扰的基础上引入0.1 Hz的正弦干扰和阶跃干扰,结果表明:DOB对扰动实现了准确估计,所提方法能够在干扰下实现对检验质量的高精度控制,同时,对量测噪声起到抑制作用。
Abstract:To improve the anti-interference performance of the controller during the test mass release phase of the space-borne gravitational wave detection mission, disturbance-observer (DOB) based trumpet tube model predictive control (MPC) is proposed for the steady-state establishment of the test mass. On the one hand, the controller’s performance in terms of disturbance immunity is enhanced by the DOB, and high precision estimation is achieved by reducing the DOB design problem to the standard $ {H}_{\mathrm{\infty }} $ mixed sensitivity optimization problem using virtual loop technology. On the other hand, the trumpet tube MPC is designed, and the active set method is used to solve the optimization problem, and the high-precision test mass anti-disturbance control is realized under strong interference and strong execution constraints. Finally, the proposed method is verified by simulation on the full degree of freedom simulation platform of spacecraft-double test masses. Step matching interference and sine matching interference at 0.1 Hz are proposed based on the fundamentals of noise and interference. The results show that the DOB can accurately estimate the disturbance, and the method can realize high-precision control of the test mass under interference. The measurement noise is also inhibited.
-
表 1 MPC优化权重
Table 1. Optimization weights of MPC
自由度 位移 速度 控制 x 1 5 10 y 1 5 10 z 1 10 10 ϕ 1 10 10 θ 1 5 10 ψ 1 10 10 -
[1] SCHLEICHER A, ZIEGLER T, SCHUBERT R, et al. In-orbit performance of the LISA Pathfinder drag-free and attitude control system[J]. CEAS Space Journal, 2018, 10(4): 471-485. doi: 10.1007/s12567-018-0204-x [2] 罗子人, 张敏, 靳刚, 等. 中国空间引力波探测“太极计划”及“太极1号”在轨测试[J]. 深空探测学报, 2020, 7(1): 3-10.LUO Z R, ZHANG M, JIN G, et al. Introduction of Chinese space-borne gravitational wave detection program“Taiji” and “Taiji-1” satellite mission[J]. Journal of Deep Space Exploration, 2020, 7(1): 3-10(in Chinese). [3] 罗俊, 艾凌皓, 艾艳丽, 等. 天琴计划简介[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 60(1): 1-19.LUO J, AI L H, AI Y L, et al. A brief introduction to the TianQin project[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 2021, 60(1): 1-19(in Chinese). [4] 李洪银, 叶小容, 刘佳恒, 等. 天琴无拖曳控制研究的关键问题[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 60(增刊1): 213-224.LI H Y, YE X R, LIU J H, et al. Key issues in the research on drag-free control for TianQin[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 2021, 60(Sup 1): 213-224(in Chinese). [5] VIDANO S, NOVARA C, PAGONE M, et al. The LISA DFACS: model predictive control design for the test mass release phase[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2022, 193: 731-743. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2021.12.056 [6] SUN Z Q, XIA Y Q, DAI L, et al. Disturbance rejection MPC for tracking of wheeled mobile robot[J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2017, 22(6): 2576-2587. doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2017.2758603 [7] ZHANG S X, DAI L, XIA Y Q. Adaptive MPC for constrained systems with parameter uncertainty and additive disturbance[J]. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2019, 13(15): 2500-2506. [8] MA D L, XIA Y Q, LI T Y, et al. Active disturbance rejection and predictive control strategy for a quadrotor helicopter[J]. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2016, 10(17): 2213-2222. [9] ZHOU P, CHAI T Y, ZHAO J H. DOB design for nonminimum-phase delay systems and its application in multivariable MPC control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2012, 59(8): 525-529. [10] YANG J, ZHENG W X. Offset-free nonlinear MPC for mismatched disturbance attenuation with application to a static var compensator[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2014, 61(1): 49-53. [11] PANNOCCHIA G, BEMPORAD A. Combined design of disturbance model and observer for offset-free model predictive control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2007, 52(6): 1048-1053. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2007.899096 [12] MAEDER U, BORRELLI F, MORARI M. Linear offset-free model predictive control[J]. Automatica, 2009, 45(10): 2214-2222. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2009.06.005 [13] MAEDER U, MORARI M. Offset-free reference tracking with model predictive control[J]. Automatica, 2010, 46(9): 1469-1476. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2010.05.023 [14] MORARI M, MAEDER U. Nonlinear offset-free model predictive control[J]. Automatica, 2012, 48(9): 2059-2067. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2012.06.038 [15] KWON S, KYUN W. A discrete-time design and analysis of perturbation observer for motion control applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2003, 11(3): 399-407. doi: 10.1109/TCST.2003.810398 [16] 王璐. 基于观测器的抗干扰控制策略研究及性能评估[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2015.WANG L. Observer-based disturbance rejection control methodology and performance evaluation[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2015(in Chinese). -






 下载:
下载: