Reconstruction method of three-dimensional particle field based on focused light field imaging
-
摘要:
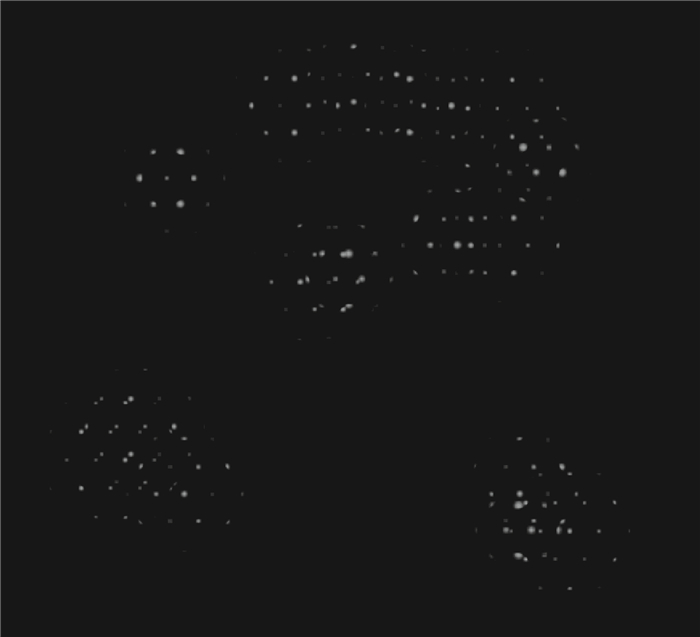
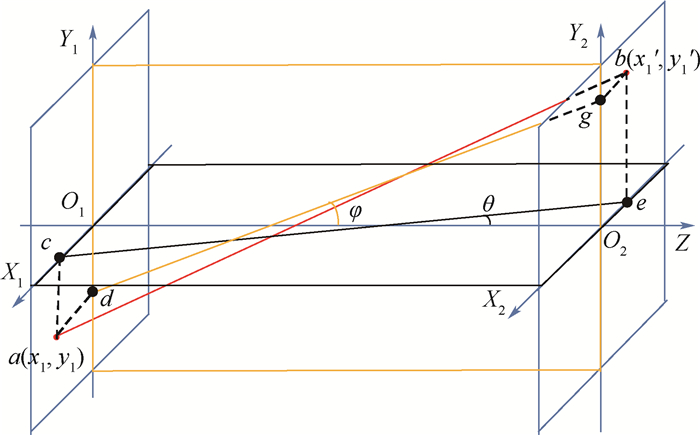
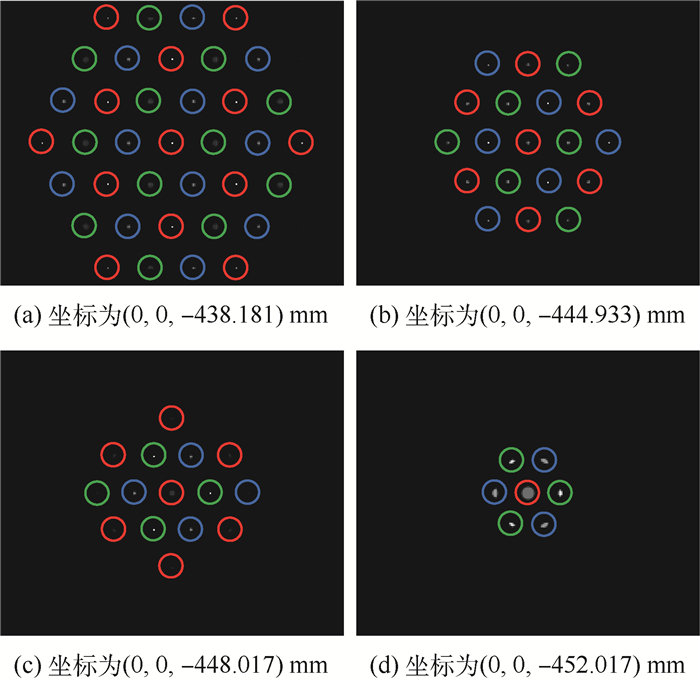
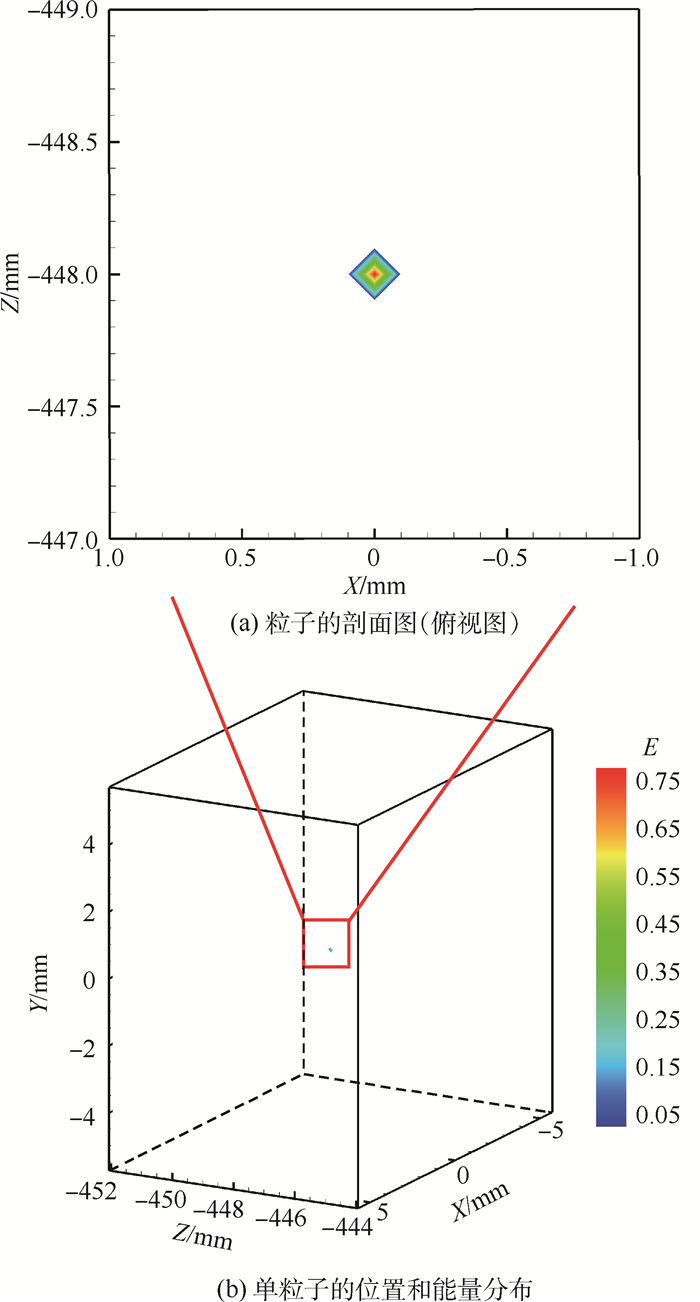
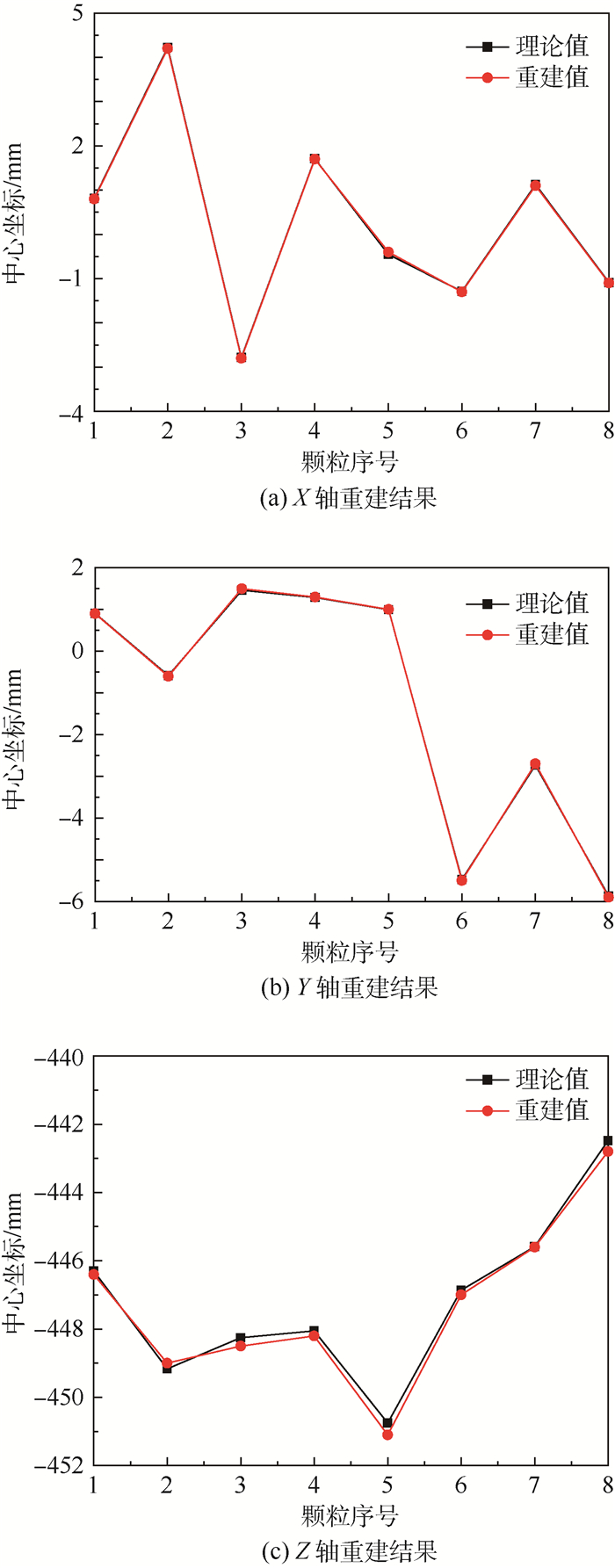
层析重建是层析粒子图像测速(Tomo-PIV)技术实现三维粒子位置和强度信息(三维粒子场)重构的核心步骤。相比于多相机的Tomo-PIV技术,单聚焦光场相机通过一次成像能够同时采集示踪粒子的散射光的方向和位置信息。因此,提出一种单聚焦光场相机的层析重建技术用于重构流场中的三维粒子场信息。为了验证本文方法的可行性及准确性,利用几何光学建立了示踪粒子的光场成像模型,利用光线追迹技术计算了粒子在聚焦光场相机中的成像,对比了被测流场中位于不同深度位置的粒子在聚焦光场相机中的成像差异;建立了基于单聚焦光场相机的层析重建数学模型,利用乘法代数重构技术(MART)对模拟所得的光场图像进行反演计算,实现了三维粒子场的重构,并利用归一化互相关系数来表征粒子的重建质量。结果表明,单个粒子在
Z 轴方向上的位置精度为±0.35 mm,初步证明了基于聚焦光场成像理论的三维粒子场重建方法的可行性。Abstract:Tomographic reconstruction is the core step of tomographic particle image velocimetry (Tomo-PIV) technology to realize the reconstruction of three-dimensional position and intensity information of particles (3D particle field). Compared to the Tomo-PIV based on the multiple conventional cameras, a single focused light field camera can simultaneously record the direction and position information of the scattered light produced by tracer particles. In this paper, a tomographic reconstruction technique based on a single focused light field camera is proposed to reconstruct the three-dimensional position and intensity information of the particles. To verify the feasibility and accuracy of the proposed method, the light field imaging model of the tracer particles is established by the geometrical optics. The imaging of the particle in the focused light field camera is simulated by ray tracing technique. The light field imaging differences of the tracer particles in different depth positions are compared. The tomographic reconstruction based on single focused light field camera is mathematically modeled. A multiplicative algebraic reconstruction technique (MART) is used to reconstruct the 3D particle field by retrieving the simulated light field image. Reconstruction quality of multiple particles is characterized by the normalized correlation coefficient. The reconstruction results show that the position accuracy of a single particle in the
Z axis direction is ±0.35 mm, which validates the feasibility of the 3D particle field reconstruction method based on focused light field imaging theory. -
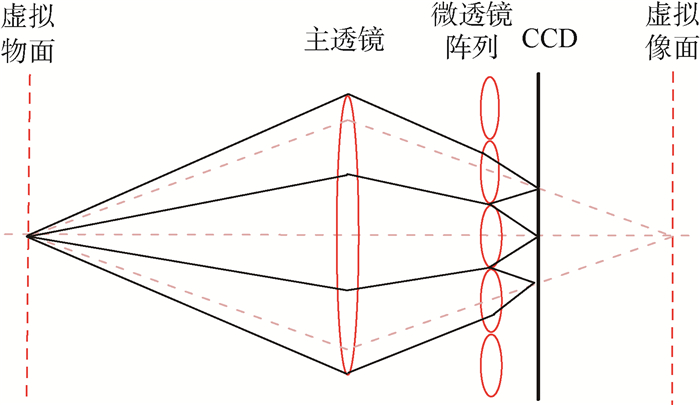
表 1 聚焦光场相机参数
Table 1. Parameters of focused light field camera
参数 数值/mm 主透镜焦距f 100 主透镜与微透镜的距离l1 147.425 虚拟物面B1与主透镜的距离l2 300 虚拟物面B2与主透镜的距离l3 296.916 虚拟物面B3与主透镜的距离l4 290.164 微透镜与CCD的距离d1 0.592 微透镜与虚拟像面I1的距离d2 2.575 微透镜与虚拟像面I2的距离d3 3.358 1 微透镜与虚拟像面I3的距离d4 5.161 3 主透镜的入瞳直径Pl 32.7 微透镜直径Pm 0.170 5 微透镜焦距f1, f2, f3 0.768 7, 0.718 7, 0.668 7 像元尺寸Pp 5.5×10-3 -
[1] COGOTTI A.Evolution of performance of an automotive wind tunnel[J].Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 2008, 96(6):667-700. [2] TOKAREV M P, SHARABORIN D K, LOBASOV A S, et al.3D velocity measurements in a premixed flame by tomographic PIV[J].Measurement Science & Technology, 2015, 26(6):1-13. doi: 10.1088/0957-0233/26/6/064001/meta [3] PARK H, YEOM E, LEE S J.X-ray PIV measurement of blood flow in deep vessels of a rat:An in vivo feasibility study[J].Scientific Reports, 2016, 6:1-8. doi: 10.1038/s41598-016-0001-8 [4] FILATOV N A, BELOUSOV K I, BUKATIN A S, et al.The study of mixing of reagents within a droplet in various designs of microfluidic chip[J].Journal of Physics:Conference Series, 2016, 741(1):1-6. [5] GAO Q, WANG H P, SHEN G X.Review on development of volumetric particle image velocimetry[J].Science Bulletin, 2013, 58(36):4541-4556. doi: 10.1007/s11434-013-6081-y [6] ELSINGA G E, SCARANO F, WIENEKE B, et al.Tomographic particle image velocimetry[J].Experiments in Fluids, 2006, 41(6):933-947. doi: 10.1007/s00348-006-0212-z [7] ATKINSON C H, SORIA J.Algebraic reconstruction techniques for tomographic particle image velocimetry[C]//16th Australasian Fluid Mechanics Conference, 2007:191-198. [8] ATKINSON C H, BUCHMANN N, STANISLAS M, et al.Adaptive MLOS-SMART improved accuracy tomographic PIV[C]//15th Sympoium on Applications of Laser Techniques to Fluid Mechanics, 2010:1-12. [9] GAO Q, WANG H P, WANG J J.A single camera volumetric particle image velocimetry and its application[J].Science China Technological Sciences, 2012, 55(9):2501-2510. doi: 10.1007/s11431-012-4921-7 [10] NG R, LEVOY M, BREDIF M, et al.Light field photography with a hand-held plenoptic camera[J].Computer Science Technical Report, 2005, 2(11):1-11. [11] FAHRINGER T, THUROW B S.Tomographic reconstruction of a 3-D flow field using a plenoptic camera[C]//42nd AIAA Fluid Dynamics Conference and Exhibit.Reston:AIAA, 2012:1-13. doi: 10.2514/6.2012-2826 [12] SHI S X, WANG J H, DING J F, et al.Parametric study on light field volumetric particle image velocimetry[J].Flow Measurement and Instrumentation, 2016, 49:70-88. doi: 10.1016/j.flowmeasinst.2016.05.006 [13] THUROW B S, FAHRINGER T.Recent development of volumetric PIV with a plenoptic camera[C]//10th International Symposium on Particle Image Velocimetry, 2013:1-7. [14] GERSHUN A.The light field[J].Studies in Applied Mathematics, 1939, 18(1-4):51-151. doi: 10.1002/sapm193918151/abstract [15] ADELSON E H, WANG J Y A.Single lens stereo with a plenoptic camera[J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 1992, 14(2):99-106. [16] LUMSDAINE A, GEORGIEV T.Full resolution lightfield rendering[R].San Jose:Adobe Systems, Inc., Technical Report, 2008:1-12. [17] GEORGIEV T, INTWALA C.Light field camera design for integral view photography[R].San Jose:Adobe System, Inc., Technical Report, 2006:1-13. [18] FAHRINGER T W, THUROW B S.3D particle position reconstruction accuracy in plenoptic PIV[C]//52nd Aerospace Sciences Meeting.Reston:AIAA, 2014:1-10. doi: 10.2514/6.2014-0398 [19] BAO Q, JIANG N.A simplified 3D reconstruction technique for tomographic particle image velocimetry[J].Advanced Materials Research, 2013, 718:2184-2190. [20] LYNCH K, FAHRINGER T, THUROW B.Three-dimensional particle image velocimetry using a plenoptic camera[C]//50th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting including the New Horizons Forum and Aerospace Exposition.Reston:AIAA, 2012:1-14. doi: 10.2514/6.2012-1056 -







 下载:
下载: