Effect of swirl number of pilot stage on TeLESS Ⅱ combustor's lean blow-out performance
-
摘要:
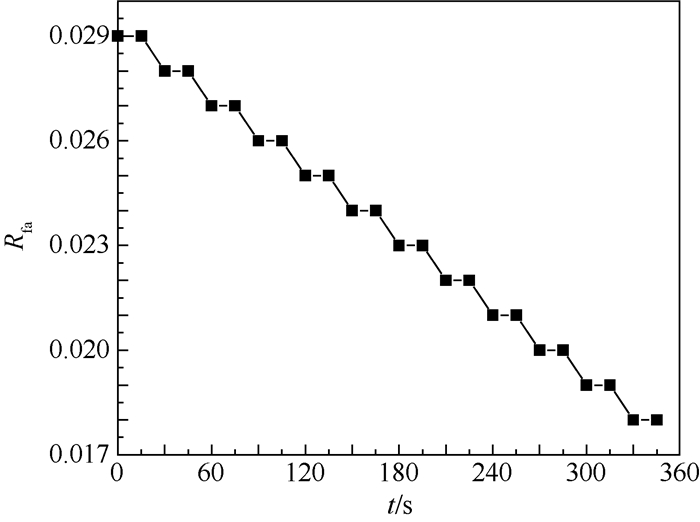
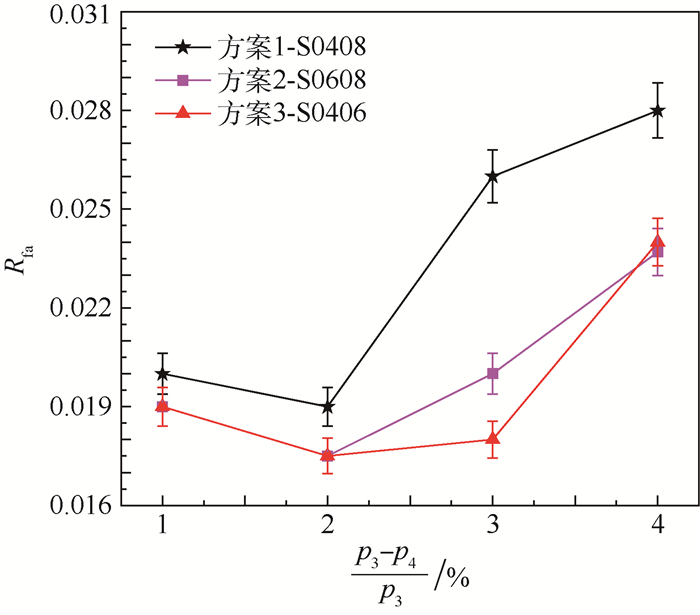
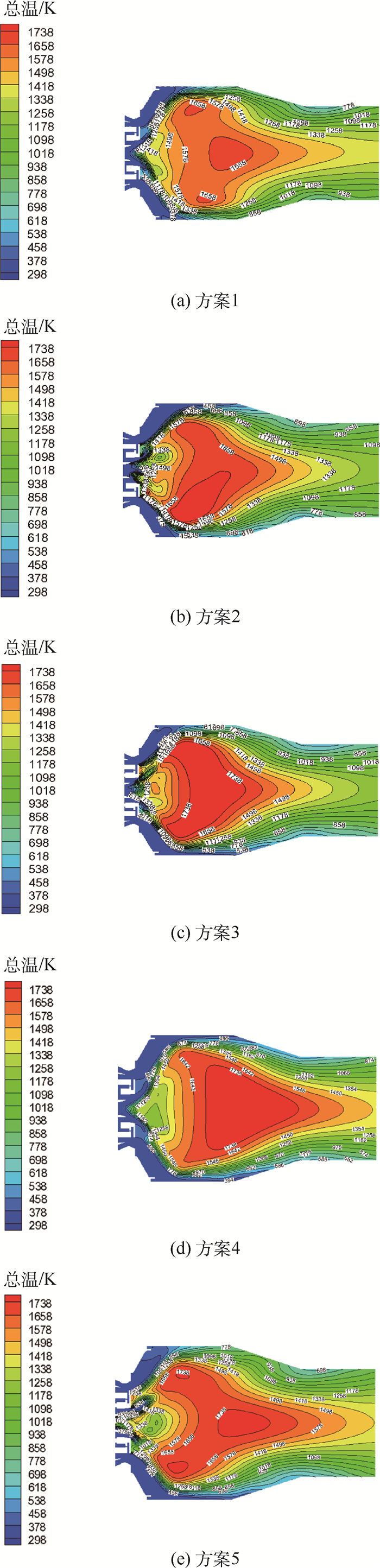
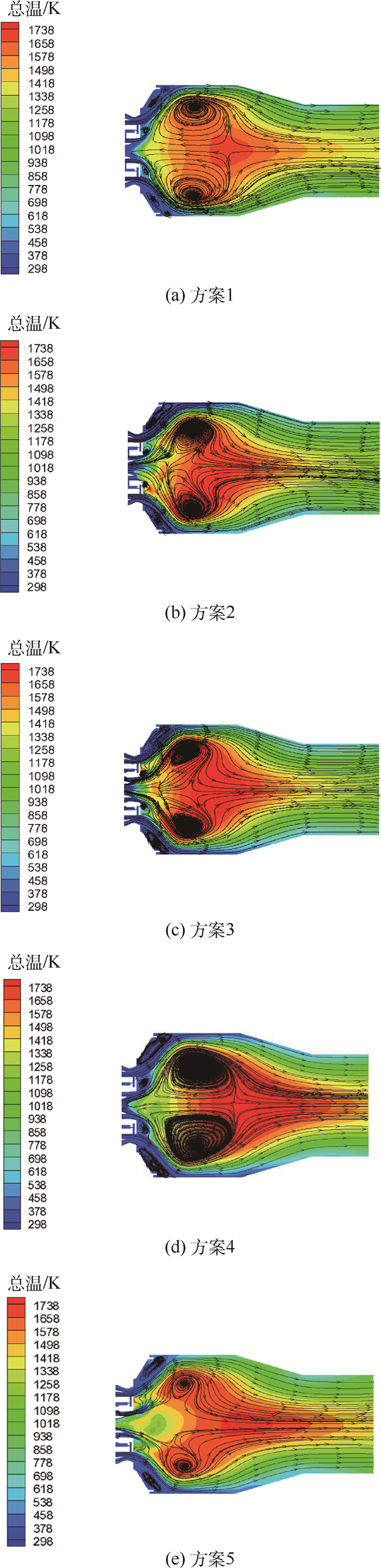
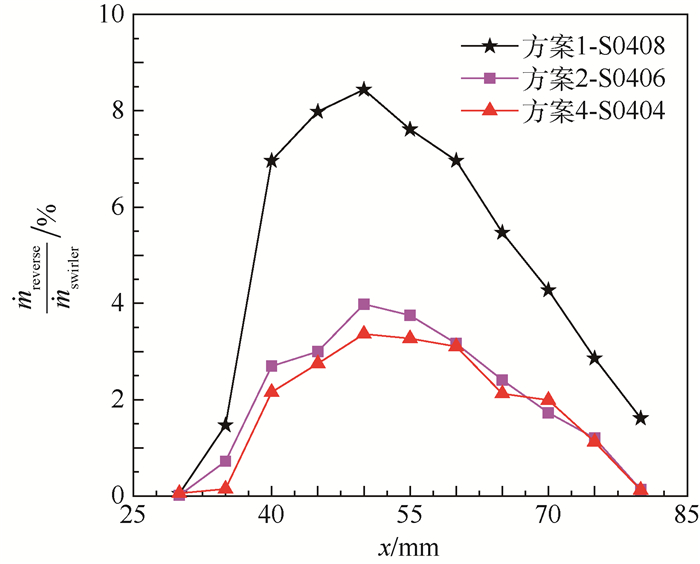
北京航空航天大学发展的TeLESSⅡ低排放燃烧室采用中心分级的布局方式,其中心为经典的旋流杯结构预燃级,为燃烧室提供稳定的点火源,预燃级外圈采用预混设计的单级轴向旋流器的主燃级以降低排放。研究了预燃级一级旋流器和二级旋流器的旋流数组合对燃烧室熄火性能的影响,研究表明预燃级的设计在中心分级低排放燃烧室火焰稳定中扮演重要角色。在常温常压条件下的单头部燃烧室上测量贫油熄火油气比,并通过数值计算对比分析不同方案在熄火时的气动热力特征。研究表明:回流区总温越高燃烧室贫油熄火油气比越低,二级旋流数减少有利于火焰和流场的耦合,从而提高回流区火焰稳定,拓宽贫油熄火边界。一级旋流数增加贫油熄火油气比不是随之降低。
Abstract:The next generation of technology of low emission of stirred swirl (TeLESSⅡ)low-emission combustor developed by Beihang University adopted a central staged arrangement. The center of the dome was classic swirl cup pilot structure which could provide a stable ignition source for the combustor. The main stage arranged outer of the pilot stage which adopted a pre-mixed single axial cyclone design was used to reduce emission. The influence of the combination of the swirl number of the pilot first stage and the secondary stage on the blow-out performance of the combustor was studied. The pilot stage is found playing an important role in the stabilization of flame in low-emission combustor. The gas-oil ratio was measured in the single dome combustor under normal temperature and pressure conditions. The aerodynamic characteristics of different cases were analyzed by numerical calculation. The results show that the higher the total temperature in the recirculation zone is, the lower the gas-oil ratio for lean blow-out is, and the decrease of pilot secondary stage's swirl number isfavorable to the coupling between the flame and flow field. Therefore, the flame in the recirculation zone is more stable and the lean blow-out boundary becomes broader. With the increase of the pilot first stage's swirl number, the gas-oil ratio for lean blow-out is not reduced.
-
Key words:
- central staged combustor /
- pilot stage /
- swirl number /
- swirl cup /
- lean blow-out
-
表 1 各方案设计参数
Table 1. Design parameters of each case
方案 预燃级一级旋流数 预燃级二级旋流数 方案1 0.4 0.8 方案2 0.4 0.6 方案3 0.6 0.8 方案4 0.4 0.4 方案5 0.8 0.8 表 2 回流区体积和总温
Table 2. Recirculation zone volume and total temperature
方案 压降/
%回流区体积/m3 流体域体积/m3 回流区占流体域比例/% 回流区平均总温/K 方案1 2 0.473 0 2.996 3 15.79 1 656.608 方案2 2 0.261 7 2.996 3 8.73 1 769.055 方案3 2 0.253 1 2.996 3 8.45 1 774.167 方案4 2 0.243 1 2.996 3 8.11 1 781.759 方案5 2 0.291 1 2.996 3 9.71 1 726.936 方案1 3 0.436 2 2.996 3 14.56 1 594.235 方案2 3 0.241 3 2.996 3 8.05 1 720.237 方案3 3 0.224 2 2.996 3 7.48 1 758.021 方案4 3 0.220 7 2.996 3 7.37 1 752.239 方案5 3 0.271 0 2.996 3 9.04 1 680.236 方案1 4 0.339 3 2.996 3 11.32 1 566.672 方案2 4 0.212 9 2.996 3 7.11 1 684.975 方案3 4 0.196 1 2.996 3 6.54 1 702.293 方案4 4 0.193 6 2.996 3 6.46 1 714.822 方案5 4 0.255 9 2.996 3 8.54 1 635.813 -
[1] LEFEBVRE A H.Fuel effects on gas turbine combustion ignition, stability and combustion efficiebcy[J].ASME Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power, 1985, 107(1):24-37. doi: 10.1115/1.3239693 [2] PERTERS J E, MELLOR A M.A spark ignition model for liquid fuel sprays applied to gas turbine combustor[J].Journal of Energy, 1982, 6(4):272-274. doi: 10.2514/3.48048 [3] PERTERS J E, MELLOR A M.Characteristic time ignition model extended to an annular gas turbine combustor[J].Journal of Energy, 1982, 6(6):439-441. doi: 10.2514/3.48061 [4] SEN S, CHAUDHARI R R, MUKHOPADHYAY A. Lean blowout detection techniques for partially premixed flames in a dump combustor[M]//AGARWAL A, PANDEY A, AGGARWAL S, et al. Novel combustion concepts for sustainable energy development. Berlin: Springer, 2014: 199-232. [5] YI T, GUTMARK E J.Real-time prediction of incipient lean blowout in gas turbine combustors[J].AIAA Journal, 2015, 45(7):1734-1739. doi: 10.2514/1.25847 [6] SARKAR S, RAY A, MUKHOPADHYAY A, et al.Dynamic data-driven prediction of lean blowout in a swirl-stabilized combustor[J].Spray & Combustion Dynamics, 2015, 7(3):209-242. [7] FOUST M J, THOMSEN D, STICKLES R, et al. Development of the GE aviation low emissions TAPS combustor for next generation aircraft engines: AIAA-2012-0936[R]Reston: AIAA, 2012. [8] MONGIA H C. Engineering aspects of complex gas turbine combustion mixers: PartⅠhigh ΔT: AIAA-2011-106[R]. Reston: AIAA, 2011. [9] 邹博文, 许全宏, 曹文宇, 等.中心分级燃烧室耦合回流区贫油熄火机理[J].航空动力学报, 2013, 28(8):1759-1763. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HKDI201405002.htmZOU B W, XU Q H, CAO W Y, et al.Lean blowout mechanism of coupled recirculation zone in concentric staged combustor[J].Journal of Aerospace Power, 2013, 28(8):1759-1763(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HKDI201405002.htm [10] SULABH K D, JACOB E T, DRISCOOL J F, et al.Unsteady aspects of lean premixed-prevaporized (LPP) gas turbine combustors:Flame-flame interactions[J].Journal of Propulsion and Power, 2011, 27(3):631-641. doi: 10.2514/1.B34001 [11] SULABH K D, JAMES F D. Instantaneous flow structures in a reacting gas turbine combustor: AIAA-2008-4683[R]. Reston: AIAA, 2008. [12] MOHAMMAD B S, JEMGS S M.Gas turbine combustor sector flow structure[J].Journal of Propulsion and Power, 2011, 27(3):710-717. doi: 10.2514/1.B34114 [13] BAKE S, LAZIK W, DOERR T, et al. Development of lean-burn low-NOx combustion technology at rolls-royce deutschland[C]//Proceedings of ASME Turbo Expo 2008: Power for Land, Sea and Air. New York: ASME, 2008: 797-807. [14] MEIER U, HEINZE J, LANGE L, et al.Characterisation of the combustion performance of low emission fuel injectors with laser measurements[J].CEAS Aeronautical Journal, 2012, 3(1):45-53. doi: 10.1007/s13272-012-0042-z [15] YAMAMOTO T, SHIMODAIRA K, KUROSAWA Y, et al. Investigations of a staged fuel nozzle for aeroengines by multi-sector combustor test[C]//Proceedings of ASME Turbo Expo 2010: Power for Land, Sea and Air. New York: ASME, 2010: 961-973. [16] YAMAMOTO T, SHIMODAIRA K, KUROSAWA Y, et al. Research and development of staging fuel nozzle for aeroengine[C]//Proceedings of ASME Turbo Expo 2009: Power for Land, Sea and Air. New York: ASME, 2009: 639-646. [17] 王铮钧, 索建秦, 黎明, 等.基于贫油预混预蒸发(LPP)的多点喷射低污染燃烧室头部方案研究[J].科学技术与工程, 2013, 13(34):10409-10420. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2013.34.059WANG Z J, SUO J Q, LI M, et al.Study on the effects of simulation method of condition boundary on modal analysis[J].Science Technology and Engineering, 2013, 13(34):10409-10420(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2013.34.059 [18] 刘富强, 穆勇, 刘存喜, 等.燃油分级对中心分级燃烧室NOx排放的影响[J].燃烧科学与技术, 2013, 19(3):254-260.LIU F Q, MU Y, LIU C X, et al.Influence of fuel stage proportion on NOx emission from central stage combustor[J].Journal of Combustion Science and Technology, 2013, 19(3):254-260(in Chinese). [19] 邓远灏, 马存祥, 郭凯, 等.贫油预混预蒸发燃烧室排放试验研究[J].推进技术, 2016, 37(4):691-697.DENG Y H, MA C X, GUO K, et al.Experimental investigation on emission of lean premixed preevaporation combustor[J].Journal of Propulsion Technology, 2016, 37(4):691-697(in Chinese). [20] 刘殿春, 董玉玺, 尚守堂, 等.单环腔中心分级燃烧室流场数值模拟[J].航空动力学报, 2010, 25(6):1251-1257.LIU D C, DONG Y X, SHANG S T, et al.Numerical simulation of the flow field in a single annular concentric staged combustor[J].Journal of Aerospace Power, 2010, 25(6):1251-1257(in Chinese). [21] 高贤智, 李锋, 郭大鹏.超高温升中心分级燃烧室设计及计算分析[J].航空发动机, 2015, 41(1):9-15.GAO X Z, LI F, GUO D P.Design and computational analysis of ultra-High temperature rise concentric staged combustor[J].Aeroengine, 2015, 41(1):9-15(in Chinese). [22] 郭凯, 马鑫, 马存祥, 等.一种贫油燃烧室进口温度和压力对污染物排放影响的试验研究[J].燃气涡轮试验与研究, 2014, 27(1):28-31.GUO K, MA X, MA C X, et al.Experimental research of the influence of inlet pressure and temperature on pollutant emissions for an inter-staged lean combustor[J].Gas Turbine Experiment and Research, 2014, 27(1):28-31(in Chinese). [23] 付镇柏, 林宇震, 张弛, 等.中心分级燃烧室预燃级燃烧性能实验[J].航空动力学报, 2015, 30(1):46-52.FU Z B, LIN Y Z, ZHANG C, et al.Experiment of combustion performance of internally-staged combustor pilot stage[J].Journal of Aerospace Power, 2015, 30(1):46-52(in Chinese). [24] 付镇柏, 林宇震, 傅奇慧, 等.不同台阶高度对中心分级燃烧室点火熄火性能的影响[J].航空动力学报2014, 29(5):1062-1070.FU Z B, LIN Y Z, FU Q H, et al.Effect of different step heights on ignition blowout performance of internally-staged combustor[J].Journal of Aerospace Power, 2014, 29(5):1062-1070(in Chinese). [25] 李海涛, 许全宏, 付镇柏, 等.中心分级燃烧室预燃级贫油熄火性能试验[J].航空动力学报, 2014, 29(9):2188-2194.LI H T, XU Q H, FU Z B, et al.Experiment on lean biow-out performance of pilot stage in internally-staged combustor[J].Journal of Aerospace Power, 2014, 29(9):2188-2194(in Chinese). [26] 代威, 林宇震, 张弛.第2级径向旋流器旋流数对燃烧室点火和贫油熄火性能的影响[J].航空动力学报, 2015, 30(5):1092-1098. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HKDI201505011.htmDAI W, LIN Y Z, ZHANG C.Effects of swirl number of second stage radial swirler on combustor ignition and lean blow-out performances[J].Journal of Aerospace Power, 2015, 30(5):1092-1098(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HKDI201505011.htm [27] WANG B, ZHANG C, LIN Y, et al.Influence of main swirler vane angle on the ignition performance of TeLESS-Ⅱ combustor[J].Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines & Power, 2016, 139(1):011501-011508. [28] WANG B, ZHANG C, HUI X, et al. Influence of sleeve angle on the LBO performance of TeLESS-Ⅱ combustor: AIAA-2016-4693[R]. Reston: AIAA, 2016. [29] BEER J M, CHIGIER N A.Combustion aerodynamics[M].London:Applied Science Publishers Ltd., 1972. [30] BALLAL D R, LEFEBVRE A H.Weak extinction limits of turbulent flowing mixtures[J].Journal of Engineering for Power, 101(3):343-348. doi: 10.1115/1.3446582 -








 下载:
下载: