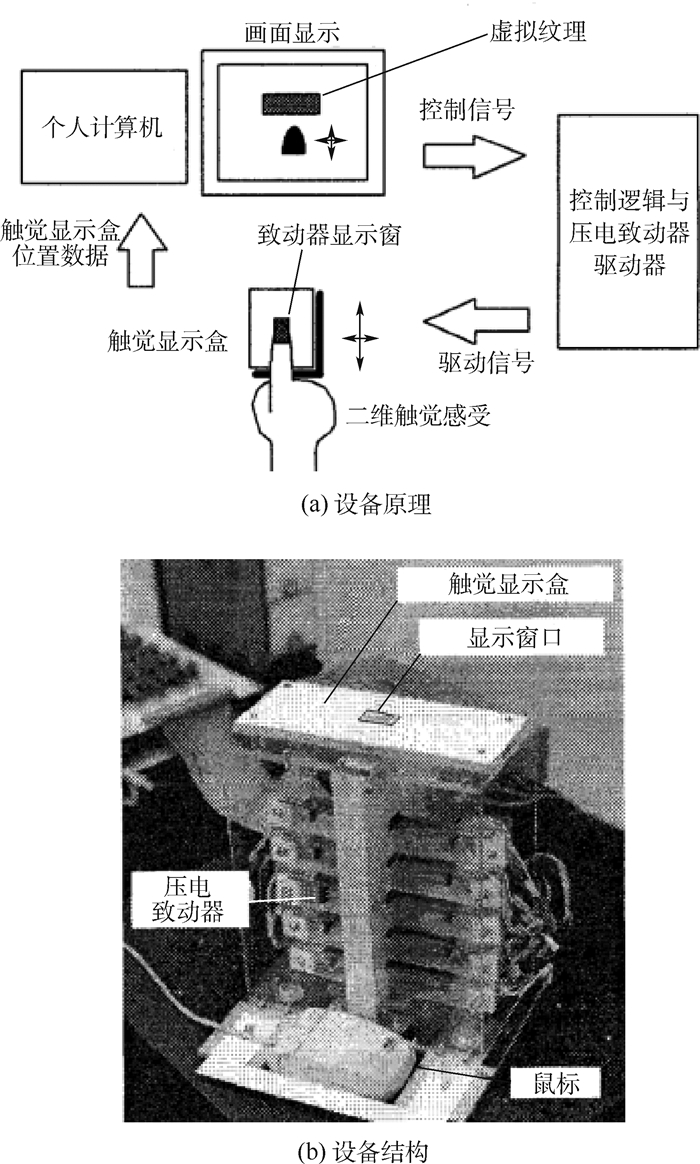
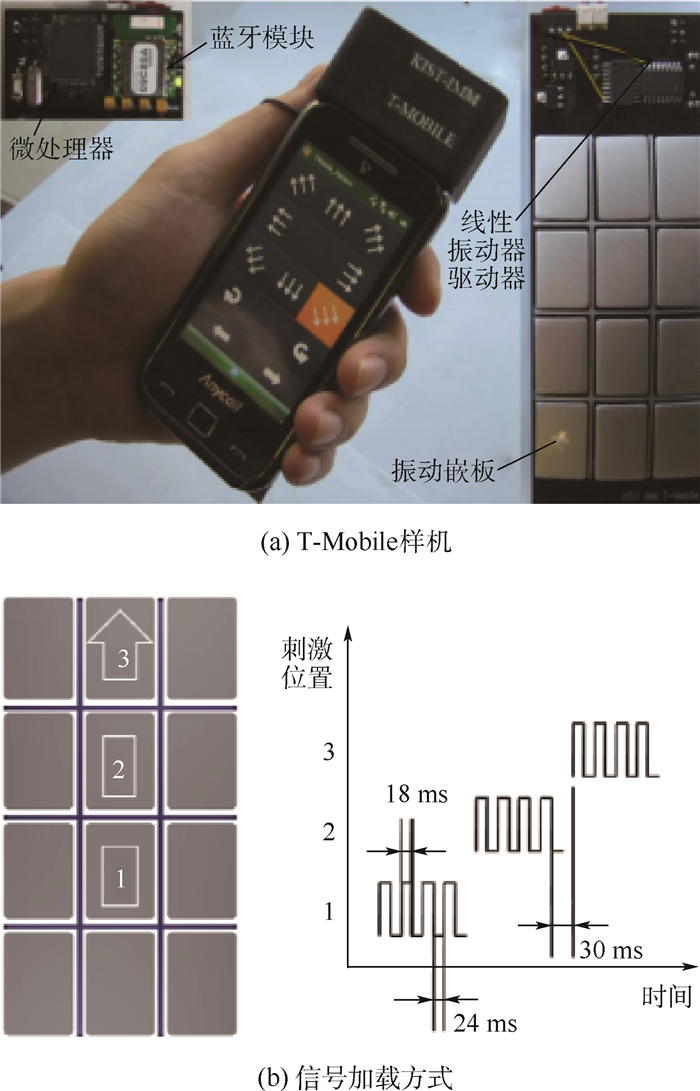
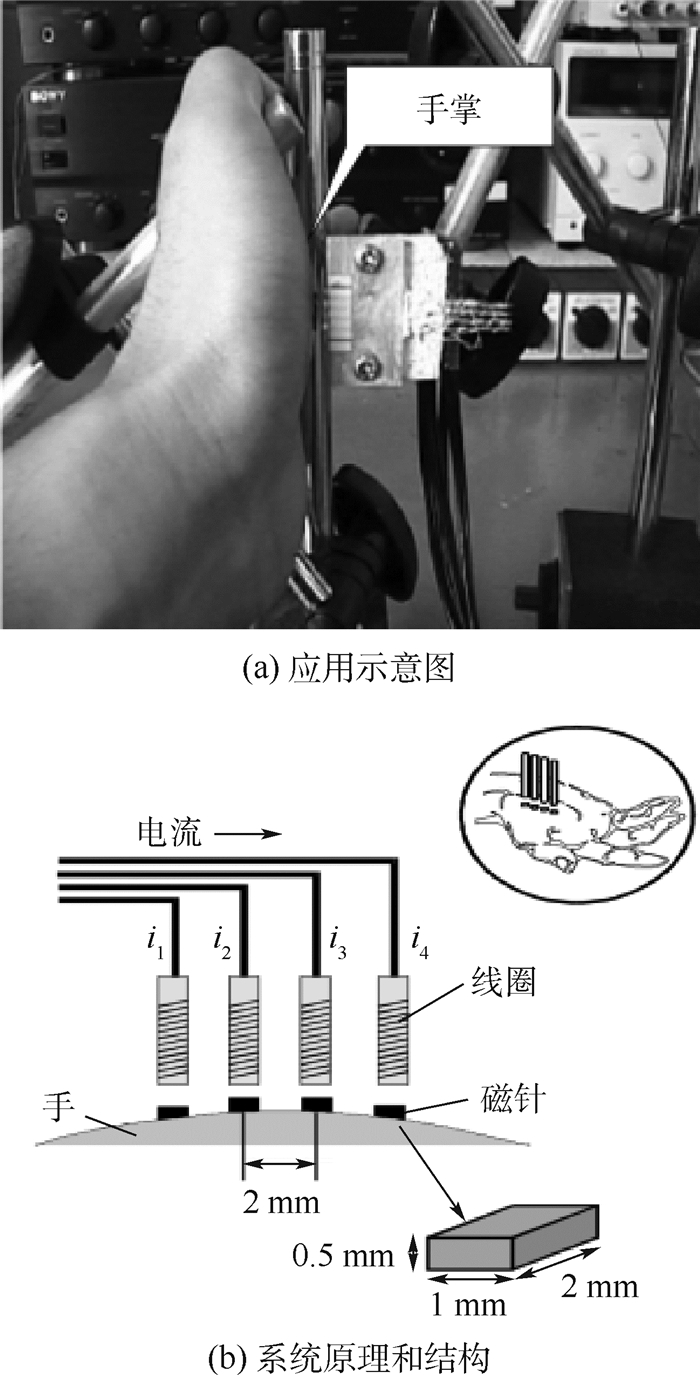
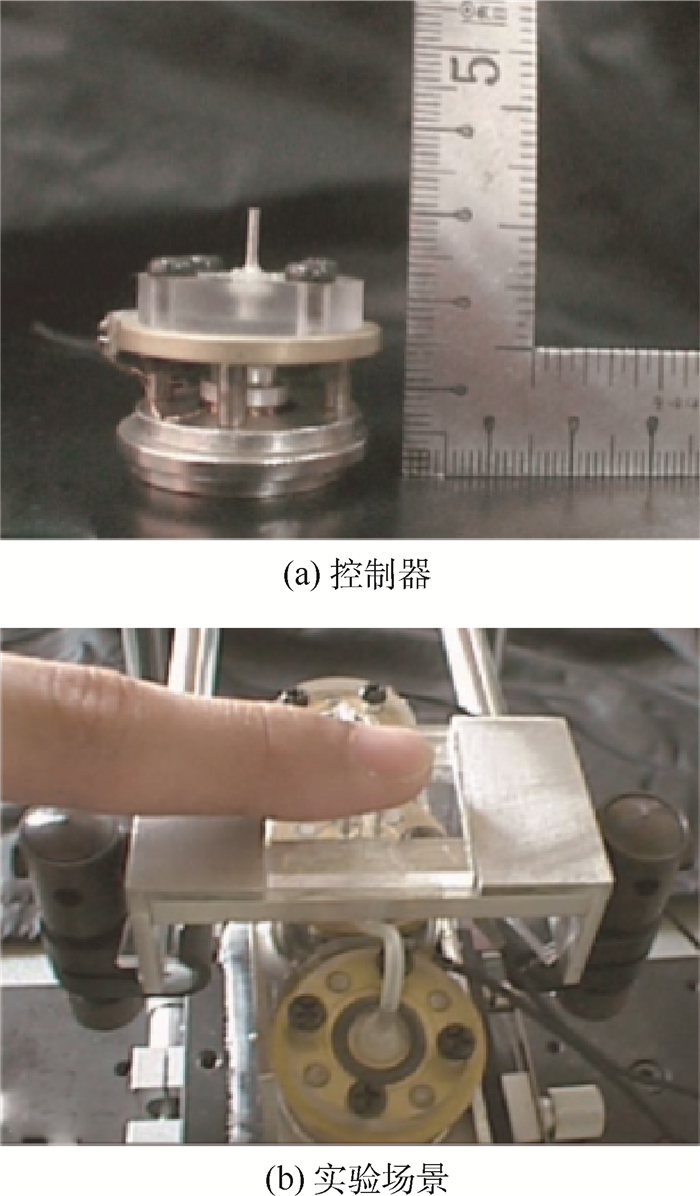
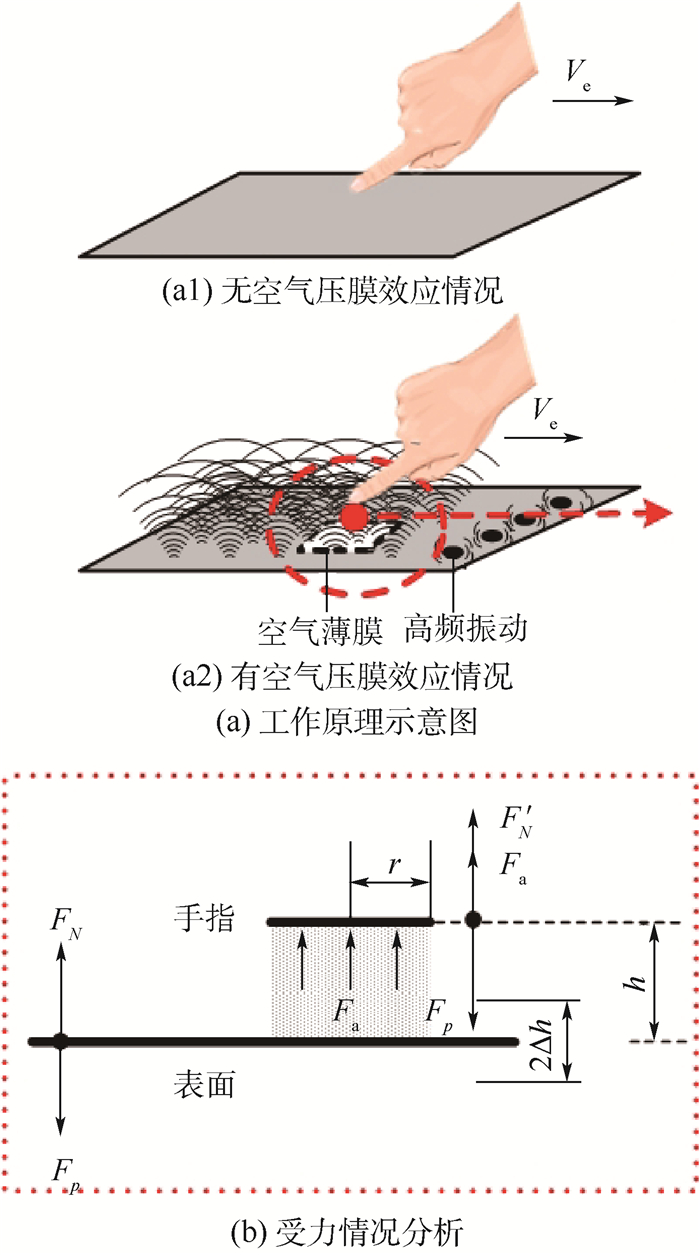
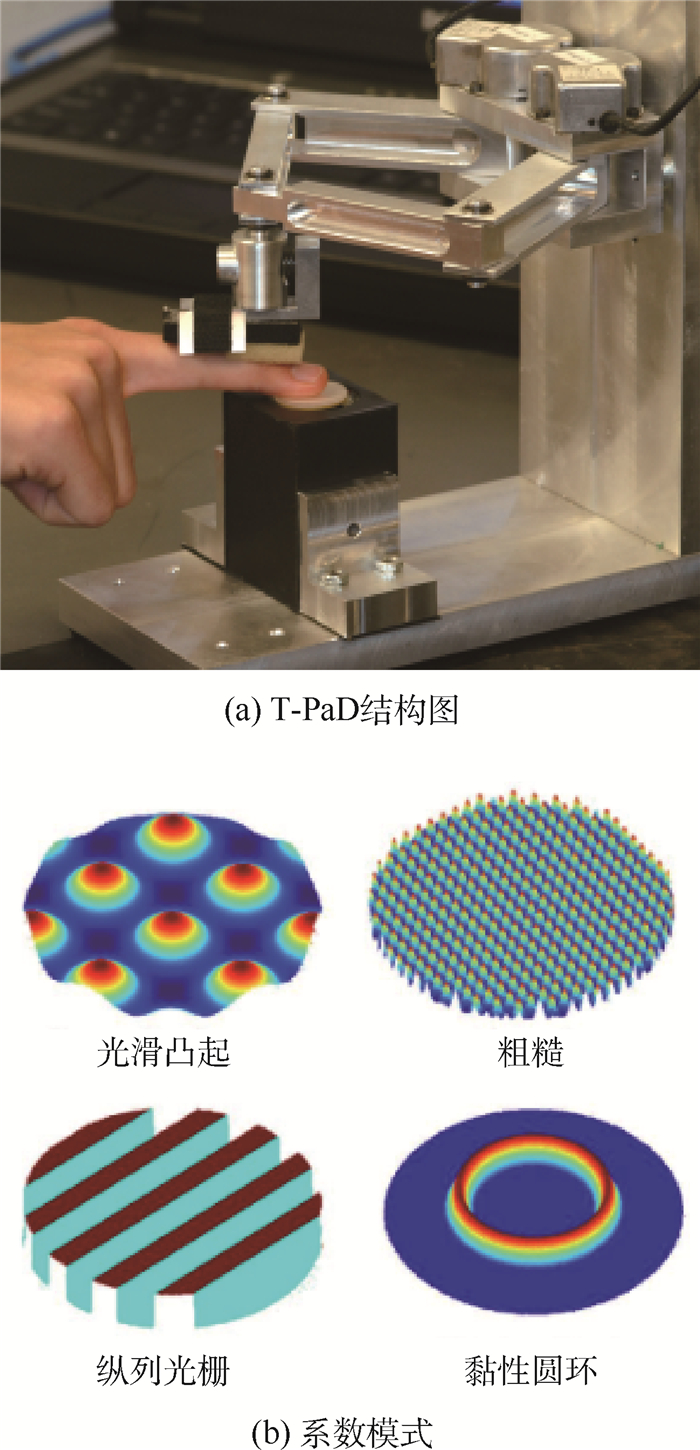
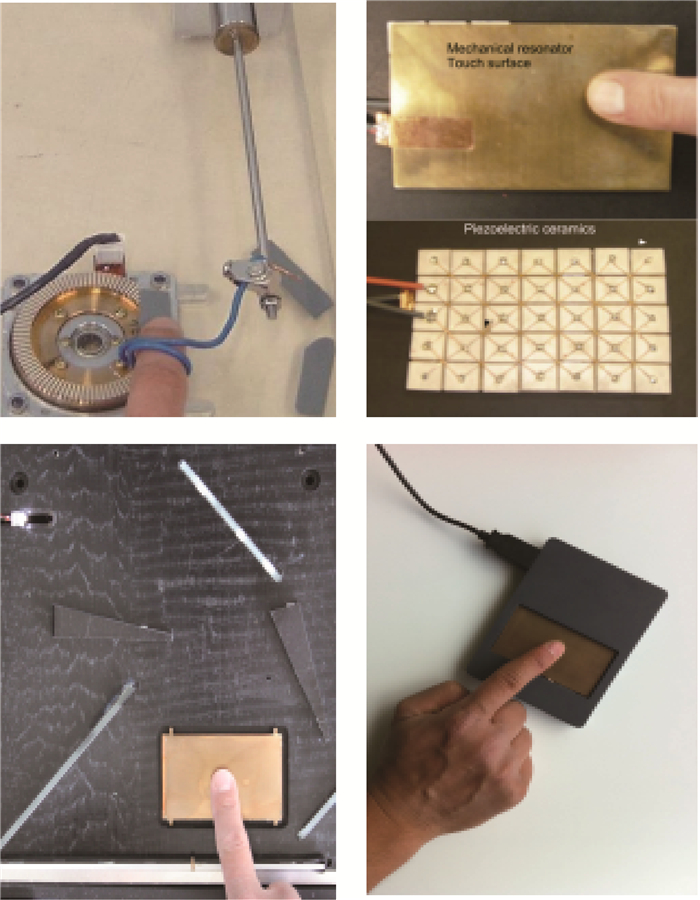
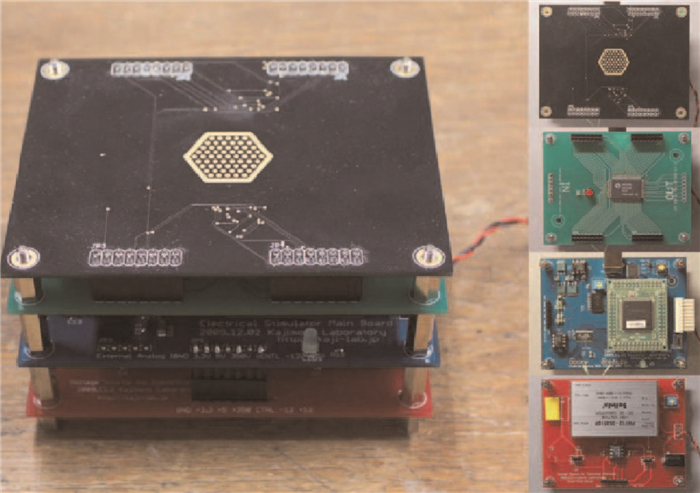
-
摘要:
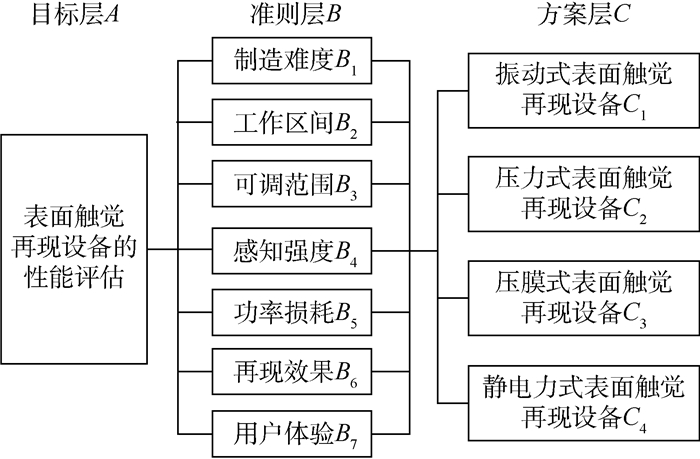
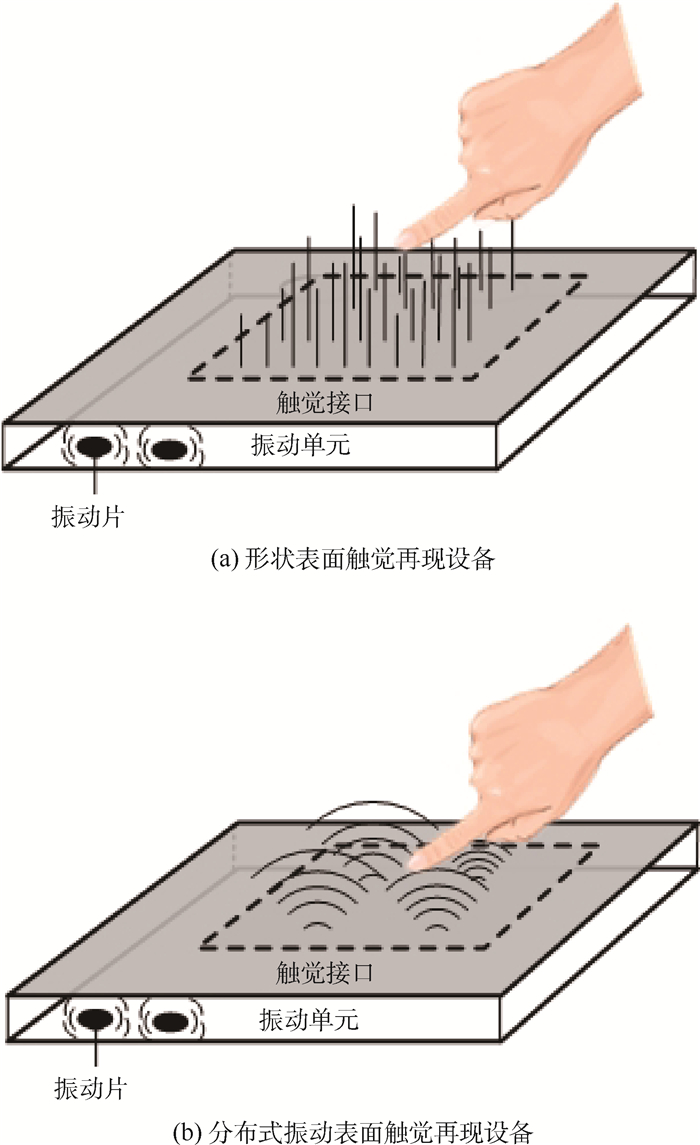
表面触觉再现技术可通过裸指触摸屏幕来感知物体特性,在多媒体终端实现高效自然的交互,具有巨大的研究价值,因而得到国内外研究学者的广泛关注。然而,现有研究多集中于力觉交互设备,未对表面触觉再现设备进行系统分析,且对设备的各项性能评价过于主观,未给出客观可信的表面触觉再现技术评估标准。首先,在充分研究现有表面触觉再现技术的基础上,重点对近十年表面触觉再现技术进行补充和完善。将表面触觉再现设备分为振动式、压力式、压膜式、静电力式和电刺激式,重点从工作原理、装置构成和性能指标等方面对典型设备进行详细分析和介绍,总结设备在触觉表达方面存在的优缺点。然后,针对现有评价方式过于粗糙和主观的问题,提出一种表面触觉再现技术的评估方法。通过制造难度、工作区间等7种评价指标全面评价设备的性能,采用专家打分法和层次分析法获得振动式、压力式、压膜式、静电力式4种设备在每种评价指标下的权重,并对4种设备在多媒体终端应用中的性能优劣进行排序,为不同领域下选择和评价表面触觉再现设备提供参考。最后,总结现有设备的不足,讨论其未来的研究和改进方向。
Abstract:Surface tactile representation technology can display characteristics of the displayed contents through our bare fingers, realizing efficient and natural interaction on multimedia terminal screens. However, most studies in this field focus on the force tactile interaction device, and do not systematically analyze the surface tactile representation device. Moreover, their performance evaluation methods for the devices are too subjective to provide an objective and reliable evaluation standard. Based on the sufficient studies of the existing tactile representation technology, this paper focuses on supplementing and improving the surface tactile representation technology in the last decade. We divide surface tactile representation devices into five types:Vibration, stress, air squeeze-film, electrostatic and electrotactile devices. Then, we introduce and analyze the typical devices from working principles, device structures and performance indexes in detail. Finally, advantages and disadvantages of these devices are summarized. In addition, to solve the problem that the existing evaluation method is too rough and subjective, this paper presents an evaluation method to the surface tactile representation technology and seven evaluation indexes such as manufacturing difficulty and work area are used to comprehensively evaluate the performance of the surface tactile representation devices. Expert evaluation method and analytic hierarchy process are used to obtain the weights of four devices under each evaluation index. We also obtain the performance sorting of four kinds of devices in multimedia terminal application, providing reference for selection and evaluation of the surface tactile representation devices in other fields. Finally, we summarize the shortages of the existing devices and discuss the future research and improvement directions.
-
Bij (或Cij) 含义 1 i与j同等重要 3 i比j稍微重要一些 5 i明显比j重要 7 i比j重要很多 9 与j相比,i极其重要 2,4,6,8 判断标准的中间值 倒数 如果i与j的重要程度是Bij,则j与i的重要程度Bji=1/Bij n RI 1 0 2 0 3 0.52 4 0.89 5 1.12 6 1.24 7 1.36 8 1.41 9 1.46 表 3 表面触觉再现设备的制造难度权重
Table 3. Manufacture difficulty weight of surface tactile representation devices
设备 权重 振动式 0.434 1 压力式 0.111 3 压膜式 0.187 8 静电力式 0.266 9 CR 0.042 4 表 4 表面触觉再现设备的工作区间权重
Table 4. Operating range weight of surface tactile representation devices
设备 权重 振动式 0.345 4 压力式 0.135 8 压膜式 0.198 6 静电力式 0.320 1 CR 0.014 2 表 5 表面触觉再现设备的可调范围权重
Table 5. Adjustable range weight of surface tactile representation devices
设备 权重 压力式 0.244 2 压膜式 0.315 9 静电力式 0.327 3 CR 0.053 2 表 6 表面触觉再现设备的感知强度权重
Table 6. Perceptual intensity weight of surface tactile representation devices
设备 权重 振动式 0.422 0 压力式 0.263 6 压膜式 0.185 4 静电力式 0.129 0 CR 0.051 3 表 7 表面触觉再现设备的功率损耗权重
Table 7. Power loss weight of surface tactile representation devices
设备 权重 振动式 0.306 4 压力式 0.129 5 压膜式 0.102 3 静电力式 0.461 8 CR 0.042 9 表 8 表面触觉再现设备的再现效果权重
Table 8. Represented effect weight of surface tactile representation devices
设备 权重 振动式 0.069 7 压力式 0.133 5 压膜式 0.251 1 静电力式 0.545 7 CR 0.074 1 表 9 表面触觉再现设备的用户体验权重
Table 9. User experience weight of surface tactile representation devices
设备 权重 振动式 0.144 1 压力式 0.105 0 压膜式 0.177 3 静电力式 0.573 6 CR 0.048 9 表 10 准则层和方案层对目标层的合成权重
Table 10. Synthetical weight of criterion layer and scheme layer for target layer
性能评价指标(权值) 振动式设备 压力式设备 压膜式设备 静电力式设备 制造难度(0.075 1) 0.236 6 0.099 1 0.132 4 0.101 7 工作区间(0.039 3) 0.188 3 0.120 9 0.140 0 0.122 0 可调范围(0.064 3) 0.061 4 0.217 5 0.222 7 0.124 7 感知强度(0.094 6) 0.230 0 0.234 8 0.130 7 0.049 1 功率损耗(0.111 3) 0.167 0 0.115 3 0.072 1 0.176 0 再现效果(0.207 4) 0.038 0 0.118 9 0.177 0 0.207 9 用户体验(0.407 9) 0.078 5 0.093 5 0.125 0 0.218 6 合成权重 0.109 4 0.124 0 0.137 9 0.177 0 -
[1] 蒋树强, 闵巍庆, 王树徽.面向智能交互的图像识别技术综述与展望[J].计算机研究与发展, 2016, 53(1):113-122.JIANG S Q, MIN W Q, WANG S H.Survey and prospect of intelligent interaction-oriented image recognition techniques[J].Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2016, 53(1):113-122(in Chinese). [2] 张全贵, 闫健卓, 王普.基于语义虚拟接口的三维用户界面组态[J].北京工业大学学报, 2012(7):1062-1067.ZHANG Q G, YAN J Z, WANG P.3D user interface configuration based on semantic virtual connector[J].Journal of Bejing University of Technology, 2012(7):1062-1067(in Chinese). [3] 季白桦, 袁修干, 温文彪.三维人体运动数据提取的人机交互方法及实验[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2000, 26(1):91-94. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5965.2000.01.025JI B H, YUAN X G, WEN W B.Interactive method and experiment in 3D human motion data abstraction[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2000, 26(1):91-94(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5965.2000.01.025 [4] CAMPBELL P.Editorial on special issue on big data:Community cleverness required[J].Nature, 2008, 455(7209):1. doi: 10.1038/455001a [5] ROBLES-DE-LA-TORRE G, HAYWARD V.Force can overcome object geometry in the perception of shape through active touch[J].Nature, 2001, 412(6845):445-448. doi: 10.1038/35086588 [6] ROSENBERG L, BRAVE S.Using force feedback to enhance human performance in graphical user interfaces[C]//Proceedings of ACM International Conference Companion on Human Factors in Computing Systems.New York: ACM, 1996: 291-292. [7] CAMPBELL C S, ZHAI S, MAY K W, et al.What you feel must be what you see: Adding tactile feedback to the trackpoint[C]//Proceedings of Interact '99: IFIP Conference on Human Computer Interaction.Amsterdam: IOS Press, 1999: 383-390. [8] 陈彦钊, 周以齐, 程祥利, 等.面向脊髓损伤早期康复的虚拟现实训练环境[J].北京工业大学学报, 2014, 40(2):272-277.CHEN Y Z, ZHOU Y Q, CHENG X L, et al.VR training environment for early spinal cord injury rehabilitation[J].Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 2014, 40(2):272-277(in Chinese). [9] 王飞, 杨湘龙, 冯允成.虚拟现实仿真技术及在飞机装配中的应用[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2001, 27(2):213-216. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5965.2001.02.024WANG F, YANG X L, FENG Y C.Virtual reality simulation and its application on aircraft assembling[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2001, 27(2):213-216(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5965.2001.02.024 [10] 张运超, 陈靖, 王涌天, 等.基于移动增强现实的智慧城市导览[J].计算机研究与发展, 2014, 51(2):302-310.ZHANG Y C, CHEN J, WANG Y T, et al.Smart city guide using mobile augmented reality[J].Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2014, 51(2):302-310(in Chinese). [11] 陈旭, 宋爱国.纹理触觉再现技术的研究现状及发展[J].工业仪表与自动化装置, 2006(3):72-74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0682.2006.03.023CHEN X, SONG A G.An overview on the development of texture haptic display[J].Industrial Instrumentation & Automation, 2006(3):72-74(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0682.2006.03.023 [12] 王爱民, 戴金桥.人机交互中的力/触觉设备进展综述[J].工业仪表与自动化装置, 2007(2):14-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0682.2007.02.004WANG A M, DAI J Q.The advancement of haptic devices in man-machine interaction[J].Industrial Instrumentation & Automation, 2007(2):14-18(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0682.2007.02.004 [13] 陆熊, 宋爱国.力/触觉再现设备的研究现状与应用[J].测控技术, 2008, 27(8):6-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8829.2008.08.002LU X, SONG A G.Recent developments of haptic device and its applications[J].Measurement & Control Technology, 2008, 27(8):6-10(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8829.2008.08.002 [14] CHOUVARDAS V G, MILIOU A N, HATALIS M K.Tactile displays:Overview and recent advances[J].Displays, 2008, 29(3):185-194. doi: 10.1016/j.displa.2007.07.003 [15] 郝飞, 卢伟, 宋爱国, 等.信息触觉表达技术的研究现状与应用[J].测控技术, 2011, 30(1):6-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8829.2011.01.002HAO F, LU W, SONG A G, et al.Recent developments and applications of tactile information display technology[J].Measurement & Control Technology, 2011, 30(1):6-9(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8829.2011.01.002 [16] HAYWARD V, CRUZ-HERNANDEZ M.Tactile display device using distributed lateral skin stretch[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Symposium on Haptic Interfaces for Virtual Environment and Teleoperator Systems.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2000: 1309-1314. [17] IKEI Y, WAKAMATSU K, FUKUDA S.Texture presentation by vibratory tactile display[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Annual Virtual Reality International Symposium.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 1997: 199-205. [18] WAGNER C R, LEDERMAN S J, HOWE R D.A tactile shape display using RC servomotors[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Symposium on Haptic Interfaces for Virtual Environment and Tele-operator Systems.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2002: 354-355. [19] YATANI K, TRUONG K N.SemFeel: A user interface with semantic tactile feedback for mobile touch-screen devices[C]//Proceedings of the 22nd Annual ACM Symposium Uist'09.New York: ACM, 2009: 111-120. [20] YANG G H, JIN M, JIN Y, et al.T-mobile: Vibrotactile display pad with spatial and directional information for hand-held device[C]//2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS).Piscataway.NJ: IEEE Press, 2010: 5245-5250. [21] 寇良朋.基于气动载荷的手指力学响应研究[D].南京: 南京理工大学, 2013.KOU L P.Mechanical response research of fingers under pneumatic dynamic load[D].Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2013(in Chinese). [22] ASAMURA N, TOMORI N, SHINODA H.A tactile feeling display based on selective stimulation to skin receptors[C]//Proceedings of IEEE on Virtual Reality International Symposium.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 1998: 36-42. [23] ASAMURA N, YOKOYAMA N, SHINODA H.Selectively sti-mulating skin receptors for tactile display[J].IEEE Computer Graphics & Applications, 1998, 18(6):32-37. [24] MAKINO Y, SHINODA H.Selective stimulation to skin receptors by suction pressure control[C]//SICE 2004 Annual Conference.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2004: 2103-2108. [25] KOO I M, JUNG K, KOO J C, et al.Development of soft-actuator-based wearable tactile display[J].IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2008, 24(3):549-558. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2008.921561 [26] SALBU E O J.Compressible squeeze films and squeeze bearings[J].Journal of Basic Engineering, 1964, 86(2):355-364. doi: 10.1115/1.3653080 [27] WIESENDANGER M.Squeeze film air bearings using piezo-electric bending elements[D].Lausanne: Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, 2001: 20-21. [28] WINFIELD L, GLASSMIRE J, COLGATE J E, et al.T-PaD: Tactile pattern display through variable friction reduction[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Symposium on Haptic Interfaces for Virtual Environment and Teleoperator Systems.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2007: 421-426. [29] MARCHUK N D, COLGATE J E, PESHKIN M A.Friction measurements on a large area TPaD[C]//Proceedings of Haptics Symposium.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2010: 317-320. [30] LÉVESQUE V, ORAM L, MACLEAN K, et al.Enhancing phy-sicality in touch interaction with programmable friction[C]//Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems.New York: ACM, 2011: 2481-2490. [31] LÉVESQUE V, ORAM L, MACLEAN K.Exploring the design space of programmable friction for scrolling interactions[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Haptics Symposium.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2012: 23-30. [32] AMBERG M, GIRAUD F, SEMAIL B, et al.STIMTAC: A tactile input device with programmable friction[C]//Proceedings of the 24th Annual ACM Symposium Adjunct on User Interface Software and Technology.New York: ACM, 2011: 7-8. [33] DAI X, GU J, CAO X, et al.SlickFeel: Sliding and clicking haptic feedback on a touchscreen[C]//Adjunct Proceedings of the 25th Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology.New York: ACM, 2012: 21-22. [34] 马露.基于摩擦力控制的触觉再现系统的研究[D].南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2014: 25-32.MA L.Research on tactile rendering system based on friction control[D].Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2014: 25-32(in Chinese). [35] SEDNAOUI T, VEZZOLI E, DZIDEK B, et al.Experimental evaluation of friction reduction in ultrasonic devices[C]//Proceedings of World Haptics Conference.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2015: 37-42. [36] WIERTLEWSKI M, FENTON F R, COLGATE J E.Partial squeeze film levitation modulates fingertip friction[J].Procee-dings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(33):9210-9215. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1603908113 [37] GUEORGUIEV D, VEZZOLI E, SEDNAOUI T, et al.Feeling multiple edges: The tactile perception of short ultrasonic square reductions of the finger-surface friction[C]//Proceedings of IEEE World Haptics.Piscataway.NJ: IEEE Press, 2017: 125-129. [38] MALLINCKRODT E, HUGHES A L, JR S W.Perception by the skin of electrically induced vibrations[J].Science, 1953, 118(3062):277-278. doi: 10.1126/science.118.3062.277 [39] STRONG R M, TROXEL D E.An electrotactile display[J].IEEE Transactions on Man Machine Systems, 1970, 11(1):72-79. doi: 10.1109/TMMS.1970.299965 [40] KACZMAREK K A, NAMMI K, AGARWAL A K, et al.Polarity effect in electrovibration for tactile display[J].IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2006, 53(10):2047-2054. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2006.881804 [41] YAMAMOTO A, NAGASAWA S, YAMAMOTO H, et al.Electrostatic tactile display with thin film slider and its application to the tactile telepresentation systems[J].IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2006, 12(2):168-177. doi: 10.1109/TVCG.2006.28 [42] BAU O, POUPYREV I, ISRAR A, et al.TeslaTouch: Electrovibration for touch surfaces[C]//Proceedings of the 23rd Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology.New York: ACM, 2010: 283-292. [43] 董杨瑞.静电力触觉再现驱动信号合成技术研究[D].长春: 吉林大学, 2016.DONG Y R.Research on driviong signal synthesis technology of electrostatic force tactile representation[D].Changchun: Jilin University, 2016(in Chinese). [44] WU S W, SUN X Y, WANG Q L, et al.Tactile modeling and rendering image-textures based on electrovibration[J].The Visual Computer, 2017, 33(5):637-646. doi: 10.1007/s00371-016-1214-3 [45] WANG T T, SUN X Y.Electrostatic tactile rendering of image based on shape from shading[C]//International Conference on Audio, Language and Image Processing.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2015: 775-779. [46] 吴赛文, 陈建, 孙晓颖.面向视频感知的静电力触觉渲染方法[J].计算机应用, 2016, 36(4):1137-1140. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2016.04.039WU S W, CHEN J, SUN X Y.Electrostatic force tactile rendering method for video perception[J].Journal of Computer Application, 2016, 36(4):1137-1140(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2016.04.039 [47] TANG H, BEEBE D J.A microfabricated electrostatic haptic display for persons with visual impairments[J].IEEE Transactions on Rehabilitation Engineering, 1998, 6(3):241-248. doi: 10.1109/86.712216 [48] SAUNDERS F A.Information transmission across the skin:High-resolution tactile sensory aids for the deaf and the blind[J].International Journal of Neuroscience, 1983, 19(1-4):21-28. doi: 10.3109/00207458309148642 [49] 刘捷, 张竹茂, 任秋实, 等.基于电触觉替代视觉系统的汉字识别[J].中国医疗器械杂志, 2010, 34(5):313-316. doi: 10.3969/j.isnn.1671-7104.2010.05.001LIU J, ZHANG Z M, REN Q S, et al.Recognition of Chinese character on electrotactile vision substitution system[J].Chinese Journal of Medical Instrumentation, 2010, 34(5):313-316(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.isnn.1671-7104.2010.05.001 [50] KAJIMOTO H.Electrotactile display with real-time impedance feedback using pulse width modulation[J].IEEE Transactions on Haptics, 2012, 5(2):184-188. doi: 10.1109/TOH.2011.39 [51] KITAMURA N, CHIM J, MIKI N.Electrotactile display using microfabricated micro-needle array[J].Journal of Micromechanics & Microengineering, 2015, 25(2):025016. [52] TEZUKA M, KITAMURA N, TANAKA K, et al.Presentation of various tactile sensations using micro-needle electrotactile display[J].PLOS One, 2016, 11(2):e0148410. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148410 [53] FRANCESCHI M, SEMINARA L, DOSEN S, et al.A system for electrotactile feedback using electronic skin and flexible matrix electrodes:Experimental evaluation[J].IEEE Transactions on Haptics, 2017, 10(2):162-172. doi: 10.1109/TOH.2016.2618377 [54] KACZMAREK K A, TYLER M E, OKPARA U O, et al.Interaction of perceived frequency and intensity in fingertip electrotactile stimulation:Dissimilarity ratings and multidimensional scaling[J].IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2017, 25(11):2067-2074. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2017.2702628 [55] GIRAUD F, AMBERG M, LEMAIRE S B.Merging two tactile stimulation principles: Electrovibration and squeeze film effect[C]//Proceedings of World Haptics Conference.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2013: 199-203. [56] VEZZOLI E, MESSAOUD W B, AMBERG M, et al.Physical and perceptual independence of ultrasonic vibration and electrovibration for friction modulation[J].IEEE Transactions on Haptics, 2015, 8(2):235-239. doi: 10.1109/TOH.2015.2430353 [57] YANG Y.Design and control of an integrated haptic interface for touch screen applications[D].Lille: Lille University, 2013. [58] 李应南, 陈向科.基于层次分析法和专家打分法的交叉口交通安全评价研究[J].中华民居, 2014(15):245-248. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3954.2014.15.209LI Y N, CHEN X K.Traffic safety evaluation research at intersection based on the analytic hierarchy process and expert scoring method[J].China Homes, 2014(15):245-248(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3954.2014.15.209 [59] 任玉辉, 肖羽堂.层次分析法在校园火灾危险性分析中的应用[J].安全与环境工程, 2008, 15(1):85-88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1556.2008.01.023REN Y H, XIAO Y T.Application of analytic hierarchy process to the campus fire hazard analysis[J].Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2008, 15(1):85-88(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1556.2008.01.023 [60] SAATY T L.A scaling method for priorities in hierarchical structures[J].Journal of Mathematical Psychology, 2000, 15(3):234-281. doi: 10.1016-0022-2496(77)90033-5/ [61] 侯遵泽, 杨瑞.基于层次分析方法的城市火灾风险评估研究[J].火灾科学, 2004, 13(4):203-208. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5309.2004.04.001HOU Z Z, YANG R.City fire-safety evaluation with the method of analytic hierarchy process[J].Fire Safety Science, 2004, 13(4):203-208(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5309.2004.04.001 [62] 汪应洛.系统工程[M].2版.北京:机械工业出版社, 2003:130-140.WANG Y L.Systems engineering[M].2nd ed.Beijing:Mechanical Industry Press, 2003:130-140(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: