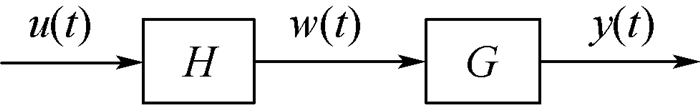Dynamic nonlinear system modeling of electronic throttle body based on Hammerstein structure
-
摘要:
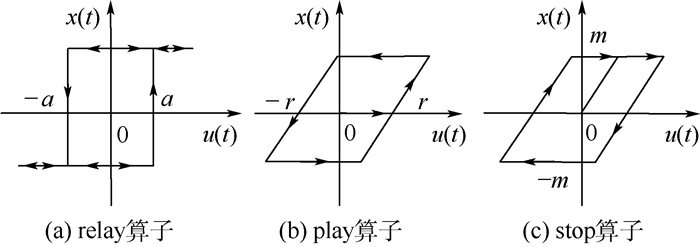
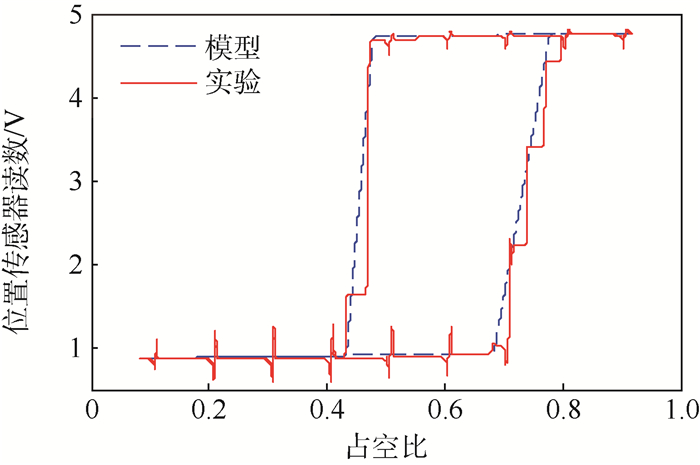
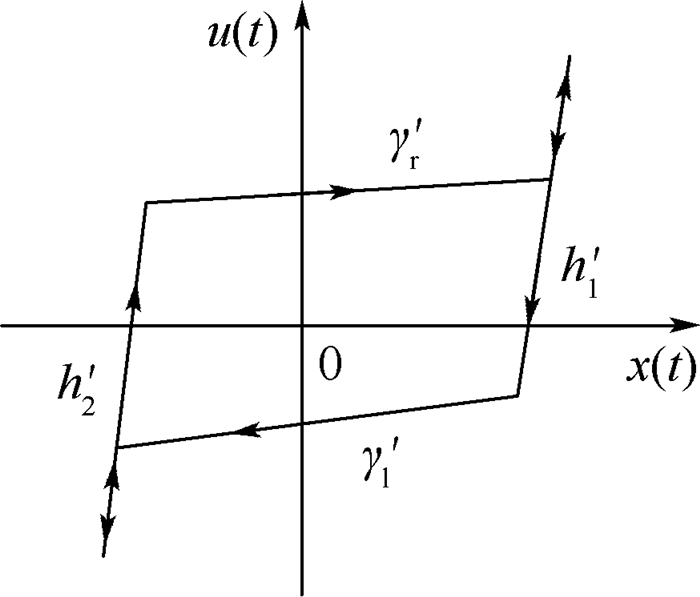
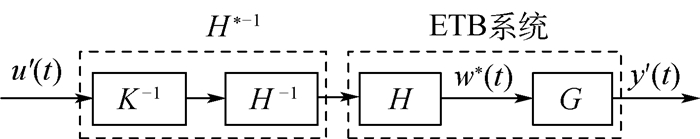
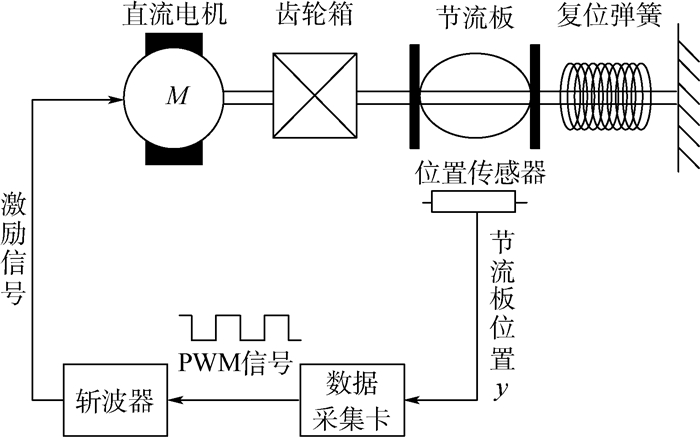
为实现对配装于5.7 L汽油发动机的某型汽车电子节气门(ETB)系统的鲁棒控制,需先建立ETB系统的非线性逆模型以抵消动态迟滞非线性对系统控制性能的影响,针对该ETB系统非线性特性进行了研究,基于Hammerstein模型结构对ETB的动态迟滞非线性进行了建模。首先为了描述ETB特殊的迟滞非线性特性,构造了一种新的静态迟滞算子作为Hammerstein系统中的非线性子系统并推导得到了静态迟滞算子的解析逆;然后基于迟滞逆补偿策略估计出Hammerstein系统中的中间不可测变量;最后基于最小二乘估计法辨识得到Hammerstein系统中的线性子系统。建模结果与实验结果对比表明本文模型能够很好地描述ETB的动态迟滞特性。
-
关键词:
- 电子节气门(ETB) /
- 迟滞非线性 /
- Hammerstein模型 /
- 迟滞逆补偿 /
- 最小二乘估计
Abstract:In order to realize the robust control of an electronic throttle body (ETB) system equipped with 5.7 L gasoline engine, the nonlinear inverse model of the ETB system must be established to counteract the effect of dynamic hysteresis nonlinearity on the control performance of the system. In this paper, the dynamic nonlinear characteristics of the ETB system are studied and a dynamic hysteresis model for the ETB system is proposed and identified based on the structure of Hammerstein system. It is challenging for the existing static hysteresis operators to cover the nonlinear characteristics of the ETB system. Thus, to describe the special hysteresis nonlinear characteristics of ETB system, a new static hysteresis nonlinear operator is constructed as the nonlinear subsystem for the Hammerstein model. The analytical inverse operator of the static hysteresis operator is also derived. The unmeasurable internal state in the Hammerstein system is then estimated based on the hysteresis inverse compensation strategy. Finally, the linear subsystem in the Hammerstein system is identified using the estimation method of least square. The comparison between the modeling results and experimental results shows that the proposed model can describe the dynamic hysteresis nonlinear characteristics of the ETB.
-
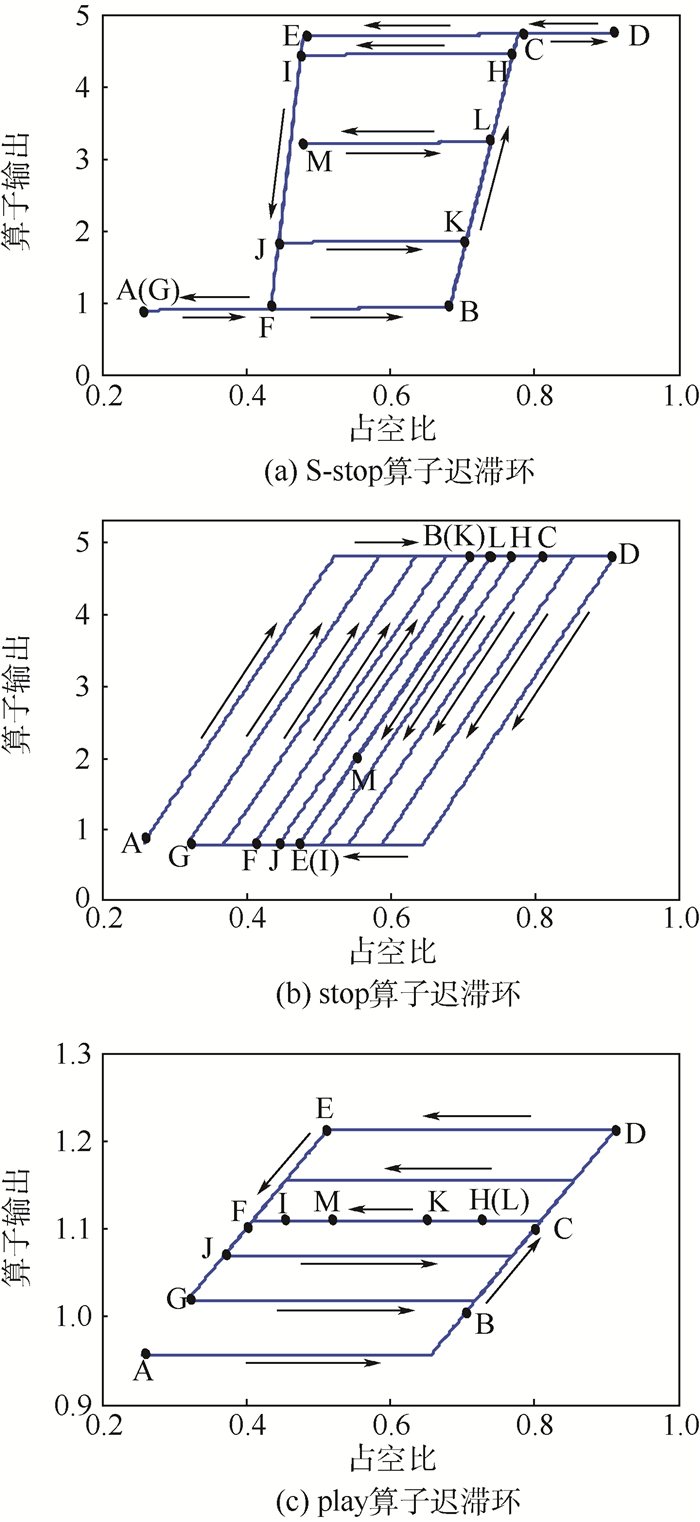
表 1 基于S-stop算子的Hammerstein模型建模效果
Table 1. Modeling effect of Hammerstein model based on S-stop operator
频率/Hz RMSE/V RE/% 0.05 0.101 7 3.20 0.08 0.144 2 4.67 0.1 0.162 8 5.14 0.3 0.458 9 14.80 表 2 开环系统的阶跃响应相对误差
Table 2. Step response relative error of open-loop system
占空比 0.8 0.75 0.7 RE/% 4.40 6.55 1.23 -
[1] 葛晓成, 彭忆强.电子节气门辨识建模方法研究[J].车用发动机, 2009(3):5-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2222.2009.03.002GE X C, PENG Y Q.Research on modeling method of electronic throttle identification[J].Vehicle Engine, 2009(3):5-9(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2222.2009.03.002 [2] GREPL R, LEE B.Modeling, parameter estimation and nonlinear control of automotive electronic throttle using a rapid-control prototyping technique[J].International Journal of Automotive Technology, 2010, 11(4):601-610. doi: 10.1007/s12239-010-0072-7 [3] DEUR J, PAVKOVIC D, PERIC N, et al.An electronic throttle control strategy including compensation of friction and limp-home effects[J].IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2004, 40(3):821-834. doi: 10.1109/TIA.2004.827441 [4] YUAN X F, WANG Y N, WU L H.SVM-based approximate model control for electronic throttle valve[J].IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2008, 57(5):2747-2756. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2008.917222 [5] RAJAEI N, CHEN X, ZHENG M.Estimation of spring torque in an electronic throttle valve[C]//Proceeding of IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2010: 1-6. [6] THOMASSON A, ERIKSSON L.Model-based throttle control using static compensators and pole placement[J].Oil & Gas Science and Technology, 2011, 66(4):717-727. [7] SALEM A, JENS B, MICHAEL T.Electronic throttle simulation using nonlinear Hammerstein model[C]//SAE 2006 World Congress & Exhibition.Warrendale: SAE International, 2007: 12-21. [8] ANSON L, WITT T, JAN S P, et al.Electronic throttle control system:Modeling, identification and model-based control designs[J].Engineering, 2013, 5(7):587-600. doi: 10.4236/eng.2013.57071 [9] SCATTOLINI R, SIVIERO C, MAZZUCCO M, et al.Modeling and identification of an electromechanical internal combustion engine throttle body[J].Control Engineering Practive, 1997, 5(9):1253-1259. doi: 10.1016/S0967-0661(97)84364-X [10] 肖寿高.电子节气门控制系统的研究与仿真[D].西安: 长安大学, 2011: 1-6.XIAO S G.The research and simulation of electronic throttle control system[D].Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2011: 1-6(in Chinese). [11] 陈凤祥, 刘玲, 章桐.基于自抗扰控制技术的电子节气门控制[J].中国科技论文, 2014, 9(10):1188-1191. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2783.2014.10.020CHEN F X, LIU L, ZHANG T.Control of electronic throttle based on active disturbance rejection control of technique[J].China Science Paper, 2014, 9(10):1188-1191(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2783.2014.10.020 [12] 宋同好.基于Backstepping的电子节气门控制[D].长春: 吉林大学, 2009: 2-5. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KZLY201104009.htmSONG T H.Electronic throttle control based on Backstepping[D].Changchun: Jilin University, 2009: 2-5(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KZLY201104009.htm [13] TAN Q Y, GAO H L, CHEN X, et al.Wiener structure based model identification for an electronic throttle body[C]//Proceeding of the 13th IEEE International Conference on Control and Automation.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2017: 18-22. [14] BAI E.Identification of linear systems with hard input nonlinearities of known structure[J].Automatica, 2002, 38(5):853-860. doi: 10.1016/S0005-1098(01)00281-3 [15] GIRI F, ROCHDI Y, BROURI A, et al.Identification of Hammerstein systems in presence of hysteresis-backlash and hysteresis-relay nonlinearities[J].Automatica, 2008, 44(3):767-775. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2007.07.005 [16] GIRI F, BAI E.Block oriented nonlinear system identification[M].Berlin:Springer Verlag, 2010:2-3. [17] GIRI F, ROCHDI Y, BROURI A, et al.Parameter identification of Hammerstein systems containing backlash operators with arbitrary-shape parametric borders[J].Automatica, 2011, 47(8):1827-1833. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2011.05.008 [18] TAN Q Y, CHEN X, ZHENG M.Control of electronic throttle body through extremum seeking approach[C]//Proceeding of 36th Chinese Control Conference.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2017: 1232-1238. [19] 郭咏新, 毛剑琴.超磁致伸缩作动器的率相关建模与跟踪控制[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2013, 39(10):1360-1365.GUO Y X, MAO J Q.Rate-dependent modeling and tracking control of giant magnetostrictive actuators[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2013, 39(10):1360-1365(in Chinese). [20] AI JANAIDEH M, RAKHEJA S, SU C Y.A generalized Prandtl-ishlinskii model for characterizing rate dependent hysteresis[C]//Proceeding of IEEE International Conference on Control Applications.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2007: 343-348. [21] KRASNOSEL'SKⅡ M A, PIKROVSKⅡ A V.Systems with hysteresis[M].Berlin:Springer Verlag, 1983:22-24. [22] BARONE P, LARI I.On a class of parameters estimators in linear models dominating the least squaresone[J].Digital Signal Processing, 2016, 54:27-34. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2016.04.001 [23] ZHANG Z, DU C L, GAO T T, et al.Hysteresis modeling and compensation of PZT milliactuator in hard disk drives[C]//Proceeding of 13th International Conference on Control Automation Robotics & Vision.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2014: 980-985. -







 下载:
下载: