-
摘要:
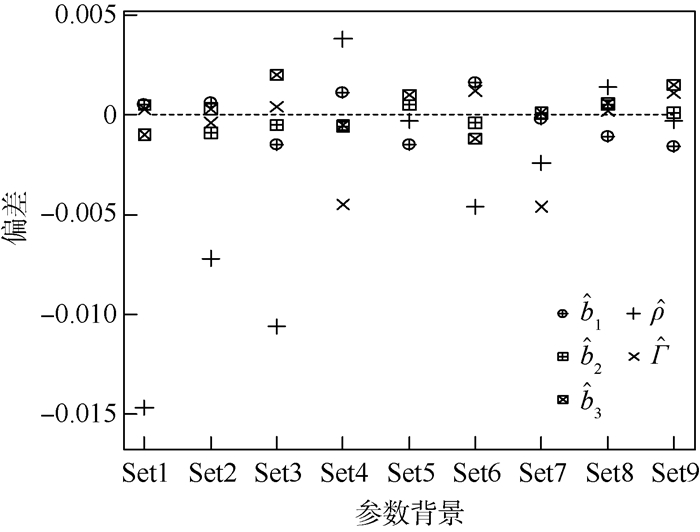
针对已有成分数据线性回归模型对研究对象相互独立的严格要求,提出了含有成分数据和普通数据的空间自回归模型,在此基础上提出了成分数据空间自回归模型的估计方法。新模型结合了空间自回归模型处理因变量之间相互依赖的优势,可同时处理成分数据和普通数据。通过利用等距对数比(ilr)变换将成分数据解约束,得到了新模型的参数估计量。蒙特卡罗模拟实验验证了所提估计方法的有效性。
-
关键词:
- 成分数据 /
- 等距对数比(ilr)变换 /
- 极大似然估计 /
- 空间依赖 /
- 空间自回归模型
Abstract:The existing compositional linear models assume that samples are independent, which is often violated in practice. To solve this problem, we put forward a spatial autoregressive model for compositional data, which contains both compositional covariates and scalar predictors. Furthermore, a new estimation method is proposed. The new model has advantages of coping with mixed compositional and numerical data and expressing dependence between the responses. And the parameter estimators are obtained through isometric logratio (ilr) transformation, which transforms dependent compositional data into independent real vector. A Monte-Carlo simulation experiment verifies the effectiveness of the proposed estimation method.
-
[1] RAMSAY J O, SILVERMAN B W.Functional data analysis[M].Berlin:Springer, 1997. [2] RAMSAY J O, SILVERMAN B W.Applied functional data analysis:Methods and case studies[M].Berlin:Springer, 2002. [3] VIEU P, FERRATY F.Nonparametric functional data analysis[M].Berlin:Springer, 2006. [4] PAWLOWSKY-GLAHN V, BUCCIANTI A.Compositional data analysis:Theory and applications[M].Chichester:Wiley-Blackwell, 2011. [5] BILLARD L, DIDAY E.Symbolic regression analysis[M]//JAJUGA K, SOKOLOWSKI A, BOCK H.Classification, clustering, and data analysis.Berlin: Springer, 2002: 281-288. [6] BILLARD L, DIDAY E.Regression analysis for interval-valued data[M].Berlin:Springer, 2000:369-374. [7] FRY J M, FRY T R L, MCLAREN K R.Compositional data analysis and zeros in micro data[J].Applied Economics, 2000, 32(8):953-959. doi: 10.1080/000368400322002 [8] PAWLOWSKY-GLAHN V, EGOZCUE J J.Exploring compositional data with the CoDa-dendrogram[J].Austrian Journal of Statistics, 2011, 40(1 & 2):103-113. [9] PAWLOWSKY-GLAHN V, EGOZCUE J J, TOLOSANA-DELGADO R.Modelling and analysis of compositional data[J].Hoboken:John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., 2015:152-154. [10] AITCHISON J.The statistical analysis of compositional data[M].Berlin:Springer, 1986. [11] AITCHISON J.The statistical analysis of compositional data[J].Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B, 1982, 44(2):139-177. [12] HRON K, FILZMOSER P, THOMPSON K.Linear regression with compositional explanatory variables[J].Journal of Applied Statistics, 2012, 39(5):1115-1128. doi: 10.1080/02664763.2011.644268 [13] ATCHISON J, SHEN S M.Logistic-normal distributions:Some properties and uses[J].Biometrika, 1980, 67(2):261-272. [14] WANG H, SHANGGUAN L, WU J, et al.Multiple linear regression modeling for compositional data[J].Neurocomputing, 2013, 122:490-500. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2013.05.025 [15] TOLOSANA-DELGADO R, EYNATTEN H V.Simplifying compositional multiple regression:Application to grain size controls on sediment geochemistry[J].Computers & Geosciences, 2010, 36(5):577-589. [16] ANSELIN L.Spatial econometrics:Methods and models[M].Berlin:Springer, 1988. [17] 林光平, 龙志和, 吴梅.中国地区经济σ-收敛的空间计量实证分析[J].数量经济技术经济研究, 2006, 23(4):14-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3894.2006.04.002LIN G P, LONG Z H, WU M.A spatial investigation of σ-convergence in China[J].The Journal of Quantitative & Technical Economics, 2006, 23(4):14-21(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3894.2006.04.002 [18] 郭金龙, 王宏伟.中国区域间资本流动与区域经济差距研究[J].管理世界, 2003(7):45-58.GUO J L, WANG H W.Study on the regional capital flows and regional economic differences in China[J].Management World, 2003(7):45-58(in Chinese). [19] TOPA G.Social interactions, local spillovers and unemployment[J].Review of Economic Studies, 2010, 68(2):261-295. [20] BAICKER K.The spillover effects of state spending[J].Journal of Public Economics, 2005, 89(2-3):529-544. doi: 10.1016/j.jpubeco.2003.11.003 [21] ORD H.Estimation methods for models of spatial interaction[J].Publications of the American Statistical Association, 1975, 70(349):120-126. doi: 10.1080/01621459.1975.10480272 [22] LEE L F.Asymptotic distributions of quasi-maximum likelihood estimators for spatial autoregressive models[J].Econometrica, 2004, 72(6):1899-1925. doi: 10.1111/ecta.2004.72.issue-6 [23] KELEJIAN H, PRUCHA I R.A generalized moments estimator for the autoregressive parameter in a spatial model[J].International Economic Review, 1999, 40(2):509-533. doi: 10.1111/iere.1999.40.issue-2 [24] LEE L F.GMM and 2SLS estimation of mixed regressive, spatial autoregressive models[J].Journal of Econometrics, 2007, 137(2):489-514. doi: 10.1016/j.jeconom.2005.10.004 [25] LESAGE J P, PACE R K.Introduction to spatial econometrics[M].New York:CRC Press, 2009:513-514. [26] EGOZCUE J J, PAWLOWSKYGLAHN V, MATEUFIGUERAS G, et al.Isometric logratio transformations for compositional data analysis[J].Mathematical Geology, 2003, 35(3):279-300. doi: 10.1023/A:1023818214614 [27] QU X, LEE L F.Estimating a spatial autoregressive model with an endogenous spatial weight matrix[J].Journal of Econometrics, 2015, 184(2):209-232. doi: 10.1016/j.jeconom.2014.08.008 -










 下载:
下载: