Influence of forward acceleration on hemodynamic characteristics of carotid arteries:A numerical simulation
-
摘要:
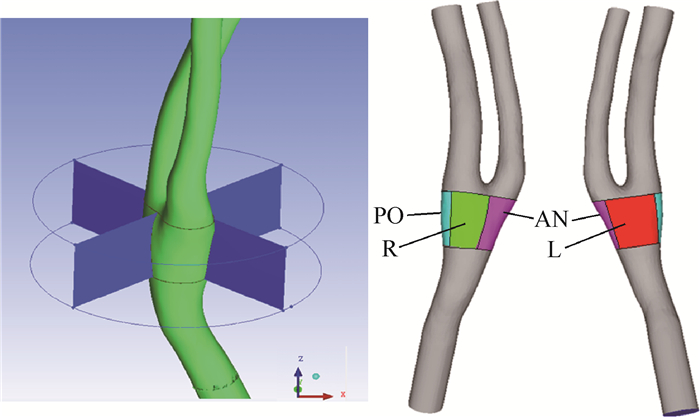
人们在日常或某些特殊条件下常会面临方向和大小发生迅速变化的加速度环境,已有研究发现加速度环境会影响心血管系统生理、病理特征。利用计算机模拟方法详细研究了向前加速度环境下人体颈动脉内的血流动力学参数变化规律。结果表明:加速度会对颈动脉内压力、压力梯度、壁面剪切应力等与血管生理、病理现象密切相关的血流动力学参数产生显著影响。研究结果为加速度环境下颈动脉生理、病理研究提供了一定的理论依据,也为航空航天领域加速度环境下人员防护提供参考。
Abstract:Humans are usually subjected to acceleration with fast changing directions and magnitude in ordinary or some special situations. Previous studies have found that acceleration had physiological and path-ological influence on cardiovascular system. However, more in-depth investigations need to be done at present. In this study, the computer simulation method was used to study the hemodynamic parameter variation features laws of carotid artery under forward acceleration condition. The results reveal that acceleration has significant influence on the hemodynamic parameters including pressure, pressure gradient, wall shear stress, etc. in carotid artery, which have close relationship with physiological and pathological behavior of artery. This study provides theoretical basis for the research of carotid artery physiology and pathology under acceleration conditions, and also gives reference for human protection under acceleration conditions in aeronautic and astronautic fields.
-
Key words:
- acceleration /
- carotid artery /
- hemodynamic characteristics /
- blood flow rate /
- pressure gradient
-
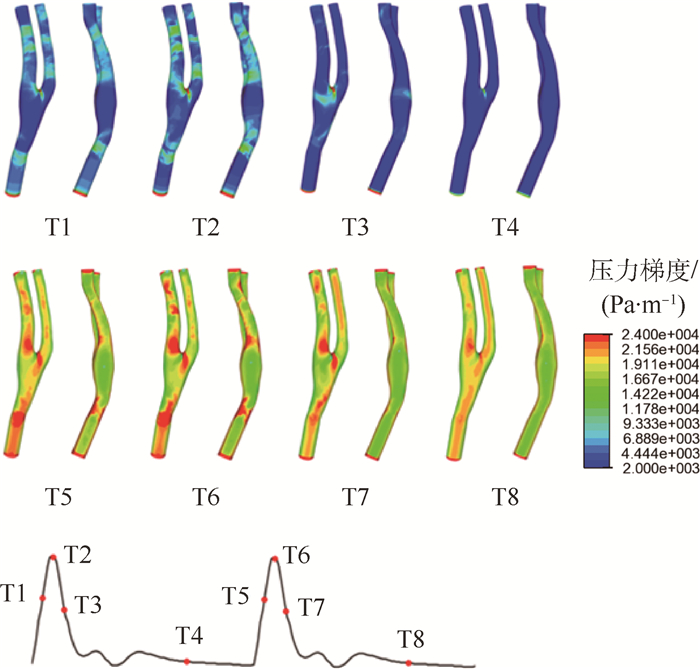
表 1 T1~T8代表的具体时刻(记录周期初始时刻为T = 0)
Table 1. Specific time represented by T1-T8 (beginning of cycle is defined as T = 0)
时间点 T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 T6 T7 T8 时间/s 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.7 1.05 1.1 1.15 1.7 -
[1] SUD V K, SEKHON G S.Analysis of blood flow through a model of the human arterial system under periodic body acceleration[J].Journal of Biomechanics, 1986, 19(11):929-941. doi: 10.1016/0021-9290(86)90188-0 [2] CHATURANI P, PALANISAMY V.Casson fluid model for pulsatile flow of blood under periodic body acceleration[J].Biorheology, 1990, 27(5):619-630. doi: 10.3233/BIR-1990-27501 [3] CHATURANI P, PALANISAMY V.Pulsatile flow of blood with periodic body acceleration[J].International Journal of Engineering Science, 1991, 29(1):113-121. doi: 10.1016/0020-7225(91)90081-D [4] MAJHI S N, NAIR V R.Pulsatile flow of third grade fluids under body acceleration-Modelling blood flow[J].International Journal of Engineering Science, 1994, 32(5):839-846. doi: 10.1016/0020-7225(94)90064-7 [5] CHAKRAVARTY S, DATTA A, MANDAL P K.Effect of body acceleration on unsteady flow of blood past a time-dependent arterial stenosis[J].Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 1996, 24(2):57-74. doi: 10.1016/0895-7177(96)00090-8 [6] MANDAL P K, CHAKRAVARTY S, MANDAL A, et al.Effect of body acceleration on unsteady pulsatile flow of non-Newtonian fluid through a stenosed artery[J].Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2007,189(1):766-779. doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2006.11.139 [7] JOU L D, BERGER S A.Numerical simulation of the flow in the carotid bifurcation[J].Theoretical and Computational Fluid Dynamics, 1998, 10(1-4):239-248. doi: 10.1007/s001620050061 [8] HOLDSWORTH D W, NORLEY C J, FRAYNE R, et al.Characterization of common carotid artery blood-flow waveforms in normal human subjects[J].Physiological Measurement, 1999, 20(3):219-240. doi: 10.1088/0967-3334/20/3/301 [9] DE SANTIS G, CONTI M, TRACHET B, et al.Haemodynamic impact of stent-vessel(mal)apposition following carotid artery stenting:Mind the gaps![J].Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering, 2013, 16(6):648-659. doi: 10.1080/10255842.2011.629997 [10] PATEL D J, VAISHNAV R N.Basic hemodynamics and its role in disease processes[M].Baltimore:University Park Press, 1980. [11] WANG Z, SUN A, FAN Y, et al.Comparative study of Newtonian and non-Newtonian simulations of drug transport in a model drug-eluting stent[J].Biorheology, 2012, 49(4):249-259. [12] SHAHED A R, BARBER J A, WERCHAN P M.Multiple +Gz exposures cause brain edema in rats[J].Aviation, Space, and Environmental Medicine, 1994, 65(6):522-526. [13] OYAMA J, PLATT W T.Metabolic alterations in rats exposed to acute acceleration stress[J].Endocrinology, 1965, 76:203-209. doi: 10.1210/endo-76-2-203 [14] ERICKSON H H, SANDLETR H, STONE H L.Cardiovascular function during sustained +Gz stress[J].Aviation, Space, and Environmental Medicine, 1976, 47(7):750-758. [15] KRISTOFFERSEN S, VETTI N, MORILD I.Traumatic dissection of the vertebral artery in a toddler following a short fall[J].Forensic Science International, 2012,221(1-3):E34-E38. doi: 10.1016/j.forsciint.2012.04.023 [16] KAISER C, SCHNABEL A, BERKEFELD J, et al.Traumatic rupture of the intracranial vertebral artery due to rotational acceleration[J].Forensic Science International, 2008,182(1-3):E15-E17. doi: 10.1016/j.forsciint.2008.10.001 [17] SALVATORI M, KODIKARA S, POLLANEN M.Fatal subarachnoid hemorrhage following traumatic rupture of the internal carotid artery[J].Legal Medicine, 2012, 14(6):328-330. doi: 10.1016/j.legalmed.2012.06.004 [18] LI Z, TAVIANI V, TANG T, et al.The mechanical triggers of plaque rupture:Shear stress vs pressure gradient[J].British Journal of Radiology, 2009, 82(1):S39-S45. doi: 10.1259/bjr/15036781 [19] MENDELL J T, OLSON E N.MicroRNAs in stress signaling and human disease[J].Cell, 2012,148(6):1172-1187. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.02.005 [20] KOUGIAS P, BISMUTH J, HUYNH T T, et al.Symptomatic aneurysm rupture without bleeding secondary to endotension 4 years after endovascular repair of an abdominal aortic aneurysm[J].Journal of Endovascular Therapy, 2008, 15(6):702-705. doi: 10.1583/08-2391.1 [21] SAMESHIMA N, YAMASHITA A, SATO S, et al.The values of wall shear stress, turbulence kinetic energy and blood pressure gradient are associated with atherosclerotic plaque erosion in rabbits[J].Journal of Atherosclerosis and THombosis, 2014, 21(8):831-838. doi: 10.5551/jat.23093 [22] FOLTS J. Arterial blood pressure gradient across vulnerable plaque might increase rupture[J].Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 2007, 50(25):2440. [23] SALIOU G, LEBLANC P E, CAUQUIL C, et al.Sudden loss of consciousness during a flight[J].Cerebrovascular Diseases, 2014, 37(6):470-471. doi: 10.1159/000363370 [24] WHINNERY J E, WHINNERY A M.Acceleration-induced loss of consciousness:A review of 500 episodes[J].Archives of Neurology, 1990, 47(7):764-776. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1990.00530070058012 -








 下载:
下载: