-
摘要:
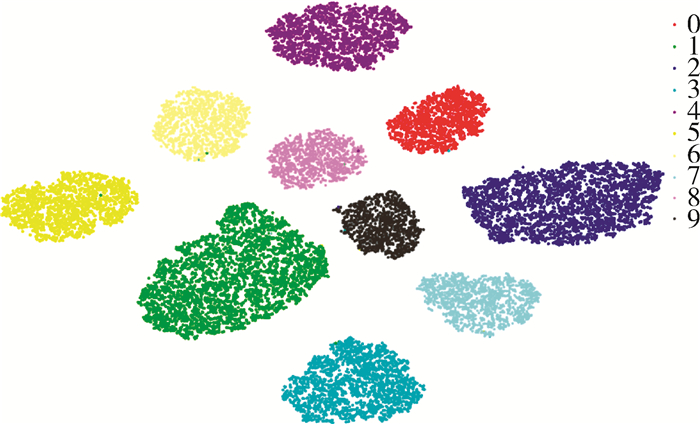
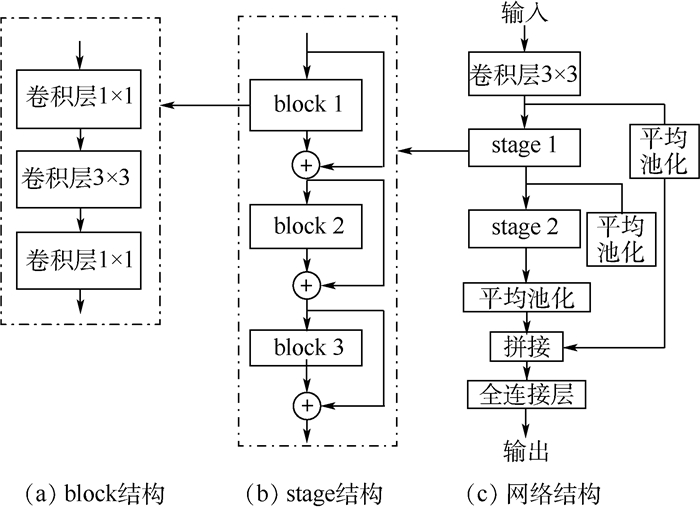
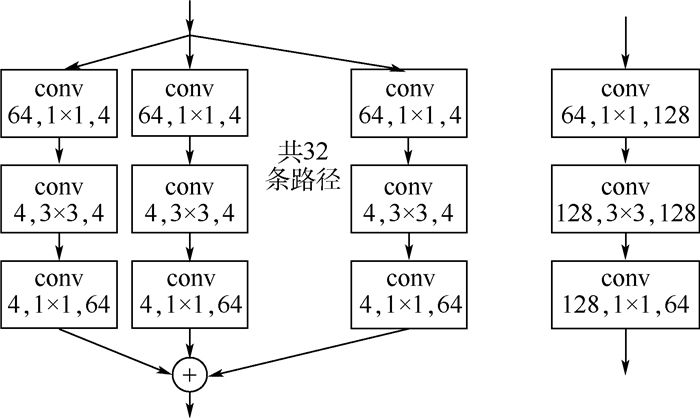
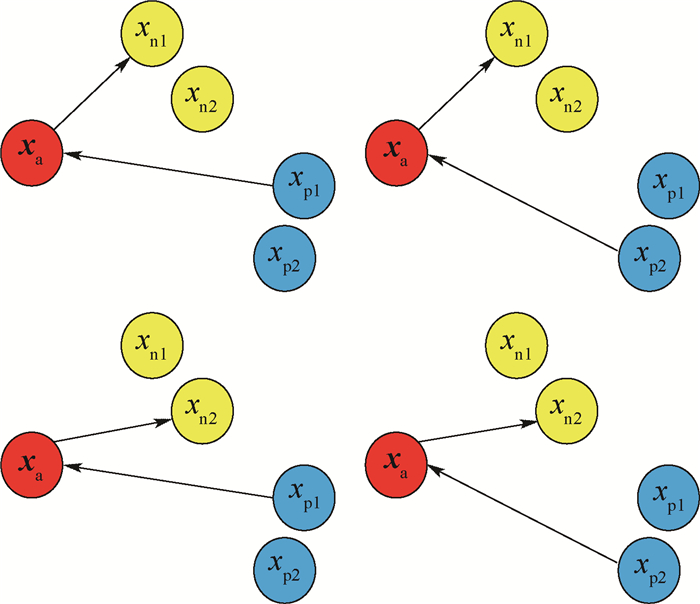
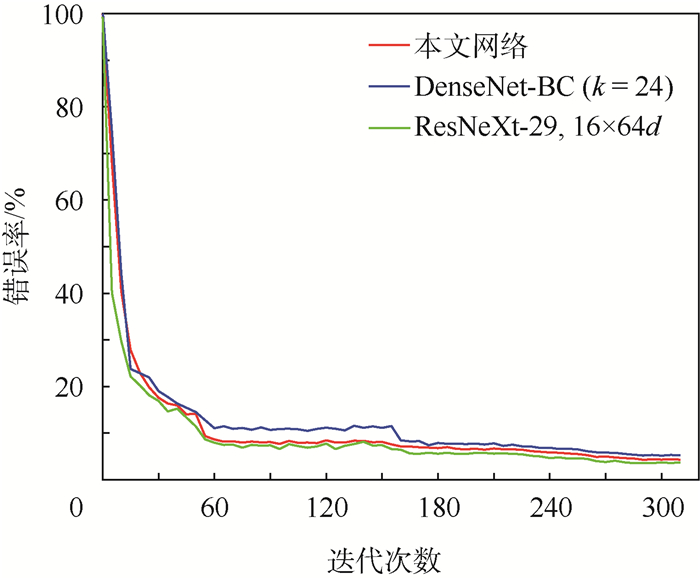
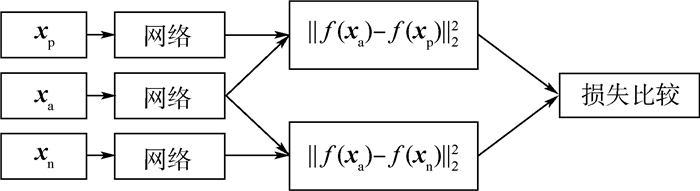
针对图像多分类任务,提出基于深度卷积的残差三生网络,旨在通过残差学习和距离比较来训练神经网络得到有效的特征表示。首先,设计了一个21层的深度卷积神经网络作为三生网络的嵌入网络,其中该卷积网络共连接6个块(block)。利用残差学习的方式,每个block的输出层由卷积层的输出和该block的输入共同组成,降低网络学习难度,避免网络出现退化问题。然后,每个block中采用相同拓扑结构分路的卷积层,拓宽网络的宽度。最后,在全连接层拼接了来自前面卷积层和block的输出,加强特征信息的传递。训练前,针对正负样本采用交叉组合的采样方法来增加有效训练样本量;训练期间,用样本中心点更换原点样本作为输入,能平均降低0.5%错误率。在与其他三生网络的对比实验中,在MNIST、CIFAR10和SVHN数据库上达到最好的效果,在所有分类网络中,本文网络在MNIST上达到最好的效果,在CIFAR10和SVHN上表现优异。
Abstract:For multi-classification image tasks, a residual triplet network based on deep convolution is proposed, which aims to train neural networks to obtain useful feature representations through residual learning and distance comparison. Firstly, a 21-layer deep convolution neural network is designed as the embedded network of the triplet network, where the convolutional network is connected with 6 blocks. By using residual learning, the output of each block is combined with the input of this block and the output of the convolutional layer which focus on reducing the difficulty of network learning and avoiding degradation. Then, each block employed the convolution layers with the same topological branch to broaden the width of the network.Finally, to enhance the transfer of feature information, the fully-connected layer concatenated the output of the previous convolutional layers and blocks. Before training, the cross-combined sampling method is used to increase effective samples for hard samples. During training, using the sample center point to replace the anchor sample as an input can reduce the error rate by 0.5% on average. Among the triplet network series, we achieved the best results on the MNIST, CIFAR10, and SVHN. In all classification networks, we achieved the best results on the MNIST and performed well on CIFAR10 and SVHN.
-
Key words:
- convolution neural network /
- triplet loss /
- residual learning /
- hard sample mining /
- sample center point
-
表 1 网络配置
Table 1. Network configuration
区 块 网络层 通道数变化 步长/填充量 池化层 stage1 block1 conv3 3-64 s=1, p=1 avgpool conv1 64-512 s=1, p=0 conv3 512-512 s=2, p=1 conv1 512-256 s=1, p=0 block2 conv1 256-512 s=1,p=0 conv3 512-512 s=1, p=1 conv1 512-256 s=1, p=0 block3 conv1 256-512 s=1, p=0 conv3 512-512 s=1, p=1 conv1 512-256 s=1, p=0 avgpool stage2 block1 conv1 256-1 024 s=1, p=0 conv3 1 024-1 024 s=2,p=1 conv1 1 024-512 s=1, p=0 block2 conv1 512-1 024 s=1, p=0 conv3 1 024-1 024 s=1, p=1 conv1 1 024-512 s=1, p=0 block3 conv1 512-1 024 s=1, p=0 conv3 1 024-1 024 s=1, p=1 conv1 1 024-512 s=1, p=0 avgpool fc-32 注:以32×32RGB图像为例。 表 2 CIFAR10上的错误率
Table 2. Error rates on CIFAR10
表 3 网络训练迭代次数(CIFAR10)
Table 3. Iteration times of network training (CIFAR10)
表 4 MNIST上的错误率
Table 4. Error rates on MNIST
表 5 SVHN上的错误率
Table 5. Error rates on SVHN
表 6 样本组合的实验对比(CIFAR10)
Table 6. Experimental comparison of sample combination (CIFAR10)
正负样本组合 训练时间/s 错误率/% 1正1负 230 4.74 1正2负 410 4.52 2正2负 750 4.28 2正3负 1190 4.29 -
[1] LECUN Y, BOTTOU L, BENGIO Y, et al.Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition[J].Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11):2278-2324. doi: 10.1109/5.726791 [2] RUSSAKOVSKY O, DENG J, SU H, et al.ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge[J].International Journal of Computer Vision, 2014, 115(3):211-252. [3] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, HINTON G.Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]//International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems.New York: Curran Associates Inc., 2012: 1097-1105. [4] SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A.Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]//International Conference on Learning Representations, 2015: 1-14. [5] SZEGEDY C, LIU W, JIA Y.Going deeper with convolutions[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2015: 1-9. [6] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al.Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2016: 770-778. [7] SZEGEDY C, VINCENT V, IOFFE S.Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2016: 2818-2826. [8] GIRSHICK R, DONAHUE J, DARRELL T, et al.Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2014: 580-587. [9] WANG N, YEUNG D Y.Learning a deep compact image representation for visual tracking[C]//International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems.New York: Curran Associates Inc., 2013: 809-817. [10] KARPATHY A, TODERICI G, SHETTY S, et al.Large-scale video classification with convolutional neural networks[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2014: 1725-1732. [11] KANG B N, KIM K Y, KIM D J.Deep convolutional neural network using triplets of faces, deep ensemble, and score-level fusion for face recognition[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2017: 611-618. [12] WANG C, LAN X P, ZHANG X.How to train triplet networks with 100K identities [C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2017: 1907-1915. [13] SCHROFF F, KALENICHENKO D, PHILBIN J.Facenet: A unified embedding for face recognition and clustering[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2015: 815-823. [14] LIU Y S, HUANG C.Scene classification via triplet networks[J].IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(1):220-237. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2761800 [15] HERMANS A, BEYER L, LEIBE B.In defense of the triplet loss for person re-identification[EB/OL].(2017-11-21)[2018-12-01]. [16] LIU H, TIAN Y, WANG Y, et al.Deep relative distance learning tell the difference between similar vehicles[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2016: 2167-2175. [17] CHENG D, GONG Y H, ZHOU S P, et al.Person re-identification by multi-channel parts-based CNN with improved triplet loss function[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2016: 1335-1344. [18] ZHANG S, GONG Y, WANG J.Deep metric learning with improved triplet loss for face clustering in video[C]//Pacific-rim Conference on Advances in Multimedia Information Processing.Berlin: Springer, 2016: 497-508. [19] CHEN W, CHEN X, ZHANG J, et al.Beyond triplet loss: A deep quadruplet network for person re-identification[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2017: 1320-1329. [20] HUANG G, LIU Z, MAATEN L, et al.Densely connected convolutional networks[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2017: 2261-2269. [21] SZEGEDY C, IOFFE S, VANHOUCKE V, et al.Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning[C]//AAAI Conference on Artifical Intelligence.Palo Atlo, CA: AAAI Press, 2017: 4278-4284. [22] XIE S, GIRSHICK R, DOLLAR P, et al.Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2017: 5987-5995. [23] IOFFE S, SZEGEDY C.Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift[C]//International Conference on Machine Learning.Boston: MIT Press, 2015: 448-456. [24] DING S, LIN L, WANG G, et al.Deep feature learning with relative distance comparison for person re-identification[J].Pattern Recognition, 2015, 48(10):2993-3003. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2015.04.005 [25] ZEILER M D, FERGUS R.Stochastic pooling for regularization of deep convolutional neural networks[EB/OL].(2013-01-16)[2018-11-25]. [26] GOODFELLOW I J, WARDE-FARLEY D, MIRZA M, et al.Maxout networks[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning.Boston: MIT Press, 2013: 1319-1327. [27] LIN M, CHEN Q, YAN S.Network in network[C]//International Conference on Learning Representations, 2014: 1-10. [28] LEE C Y, XIE S N, GALLAGHER P W, et al.Deeply-supervised nets[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics.San Diego, California: PMLR, 2015: 562-570. [29] LIAO Z B, CARNEIRO G.Competitive multi-scale convolution[EB/OL].(2015-11-18)[2018-11-10]. [30] XU C Y, LU C Y, LIANG X D, et al.Multi-loss regularized deep neural network[J].IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2016, 26(12):2273-2283. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2015.2477937 [31] HOFFER E, AILON N.Deep metric learning using triplet network[C]//International Workshop on Similarity-based Pattern Recognition.Berlin: Springer, 2015: 84-92. [32] KRIZHEVSKY A, HINTON G.Learning multiple layers of features from tiny images[D].Toronto: University of Toronto, 2009: 32-35. [33] NETZER Y, WANG T, COATES A, et al.Reading digits in natural images with unsupervised feature learning[C]//NIPS Workshop on Deep Learning and Unsupervised Feature Learning.New York: Curran Associates Inc., 2011: 1-9. -







 下载:
下载: