-
摘要:
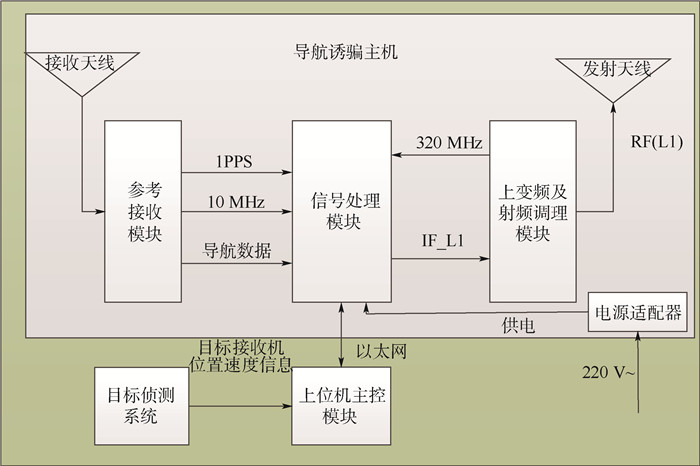
出于对"低、慢、小"无人机进行导航定位诱骗的实际需求,在实验室原有的异步生成式GPS欺骗干扰源的基础上,研制了一种小型化的同步生成式GPS欺骗干扰源。首先,在异步生成式GPS欺骗干扰源射频信号模型的基础上,考虑到干扰源信号处理延时、欺骗信号的传播延时、无人机上目标接收机所接收真实卫星信号状态以及无人机运动模型,建立了对同步欺骗信号仿真时间和状态参数进行精确计算的数学模型。其次,通过本地授时型接收机提供驯服后的基准时钟和秒脉冲(1PPS)信号,实现欺骗干扰信号与真实卫星信号系统时的同步,并通过高阶直接数字频率合成(DDS)技术精确控制信号参数、保证欺骗信号到达目标接收机接收天线相位中心时与真实信号的相位状态在成功诱骗所允许的误差范围之内。最后,通过商用接收机和无人机进行了实验验证,在无人机上目标接收机正常跟踪真实卫星信号的前提下,开启同步生成式GPS欺骗干扰源发射欺骗信号,能够使目标接收机逐渐偏离正常定位测速结果而产生受控的定位测速结果。结果验证了同步信号模型和所设计同步信号生成电路的正确性,且表明同步生成式GPS欺骗干扰源能够实现对商用接收机和无人机导航定位的诱骗。
-
关键词:
- GPS欺骗干扰源 /
- 同步生成式 /
- 时基同步 /
- 同步信号模型 /
- 无人机(UAV)诱骗
Abstract:In order to meet the actual requirements of navigation spoofing of "low, slow, small" UAV, a miniaturized synchronous GPS spoofer has been developed based on our asynchronous GPS generator spoofer. Firstly, based on asynchronous GPS generator spoofer RF signal model, considering the spoofer signal processing delay, the spoofing signal propagation delay, the status of the authentic satellite signal received by the UAV receiver, and the dynamic model of the UAV, established the mathematical model to accurately calculate the simulation time and state parameters of the synchronous spoofing signal. Secondly, a local timing receiver is employed to provide the disciplined reference clock and 1 pulse per second (1PPS) signal to synchronize the spoofing signal with the authentic system time, and high-order direct digital synthesis(DDS) technology is applied to accurately control the signal parameters and ensure that the difference between the spoofing signal and the authentic signal is within the tolerances allowed for successful spoofing when the spoofing signal reaches the phase center of the receiving antenna of the target receiver. Finally, the test results using a popular commercial UAV and a commercial receiver are presented. When the UAV receiver tracks the authentic satellite signal, the synchronous GPS spoofer begins to transmit the spoofing signal, which gradually deviates the target receiver from its normal measurements and makes it output the position and velocity results under control. The results verify the established synchronous signal model, the designed synchronous signal generation circuit, and indicate the synchronous GPS spoofer can achieve navigation spoofing of commercial UAV and commercial receiver.
-
-
[1] LOH R, BIAN Y, ROE T.UAVs in civil airspace: Safety requirements[C]//IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2009: 5-17. [2] KERNS A J, SHEPARD D P, BHATTI J A, et al.Unmanned aircraft capture and control via GPS spoofing[J].Journal of Field Robotics, 2014, 31(4):617-636. doi: 10.1002/rob.21513 [3] AKOS D M.Who's afraid of the spoofer GPS/GNSS spoofing detection via automatic gain control (AGC)[J].Journal of the Institute of Navigation, 2012, 59(4):281-290. doi: 10.1002/navi.19 [4] 高志刚, 孟繁智.GPS转发式欺骗干扰原理与仿真研究[J].遥控遥测, 2011, 32(6):44-47.GAO Z G, MENG F Z.Principle and simulation research of GPS repeater deception jammng[J].Journal of Telemetry, Tracking and Command, 2011, 32(6):44-47(in Chinese). [5] 庞晶, 倪少杰, 聂俊伟, 等.GNSS欺骗干扰技术研究[J].火力与指挥控制, 2016, 41(7):1-4.PANG J, NI S J, NIE J W, et al.An overview to GNSS spoofing technologies[J].Fire Control & Command Control, 2016, 41(7):1-4(in Chinese). [6] CAVALERI A, MOTELLA B, PINI M, et al.Detection of spoofed GPS signals at code and carrier tracking level[C]//Satellite Navigation Technologies and European Workshop on GNSS Signals and Signal Processing (NAVITEC).Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2011: 1-6. [7] JOVANOVIC A, BOTTERON C, FARINE P A.Multi-test detection and protection algorithm against spoofing attacks on GNSS receivers[J].Position, Location & Navigation Symposium-plans, 2014, 7(4):1258-1271. [8] HUMPHREYS T E, LEDVINA B M, PSIAKI M L, et al.Assessing the spoofing threat: Development of a portable GPS civilian spoofer[C]//21st International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation.Manassas, VA: The Institute of Navigation, 2008: 2314-2325. [9] 黄龙, 吕志成, 王飞雪.针对卫星导航接收机的欺骗干扰研究[J].宇航学报, 2012, 33(7):884-890.HUANG L, LV Z C, WANG F X.Spoofing pattern research on GNSS receivers[J].Journal of Astronautics, 2012, 33(7):884-890(in Chinese). [10] 陈碧, 郭承军.GPS欺骗干扰过程研究[J].科技通报, 2016, 32(10):164-169.CHEN B, GUO C J.Study on GPS spoofing pattern process[J].Bulletin of Science and Technology, 2016, 32(10):164-169(in Chinese). [11] 马克, 孙迅, 聂裕平.GPS生成式欺骗干扰关键技术[J].航天电子对抗, 2014, 30(6):24-26.MA K, SUN X, NIE Y P.Research on key technologies of GPS generated spoofing[J].Aerospace Electronic Warfare, 2014, 30(6):24-26(in Chinese). [12] 何亮, 李炜, 郭承军.生成式欺骗干扰研究[J].计算机应用研究, 2016, 33(8):2405-2408.HE L, LI W, GUO C J.Study on GPS generated spoofing attacks[J].Application Research of Computers, 2016, 33(8):2405-2408(in Chinese). [13] 寇艳红.GNSS软件接收机与信号模拟器系统研究[D].北京: 北京航空航天大学, 2006: 55.KOU Y H.Research on GNSS software receiver and signal simulator[D].Beijing: Beihang University, 2006: 55(in Chinese). [14] 李铭涵.生成式GPS欺骗无人机干扰源设计与实现[D].北京: 北京航空航天大学, 2018: 14.LI M H.Research and implementation of a GPS signal generator spoofing UAVs[D].Beijing: Beihang University, 2018: 14(in Chinese). [15] 谢刚.GPS原理与接收机设计[M].北京:电子工业出版社, 2009:79.XIE G.Principles of GPS and receiver design[M].Beijing:Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2009:79(in Chinese). [16] 樊鼎.GPS同步生成式欺骗干扰及检测方法研究[D].北京.北京航空航天大学, 2018: 9-12.FAN D.Design of GNSS multiplexing signal quality monitoring receiver[D].Beijing: Beihang University, 2018: 9-12(in Chinese). [17] ZHOU M, LIU Y, XIE L, et al.Performance analysis of spoofing signal ratio for receiver-spoofer[C]//Proceedings of the 2017 International Technical Meeting of the Institute of Navigation.Washington, D.C.: INST Navigation, 2017: 898-911. [18] 潘虹臣.GNSS信号质量监测接收机设计[D].北京.北京航空航天大学, 2016: 8.PAN H C.Design of GNSS signal quality monitoring receiver[D].Beijing: Beihang University, 2016: 8(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: