Lightweight identity authentication protocol based on dynamic ID in multi-server environment
-
摘要:
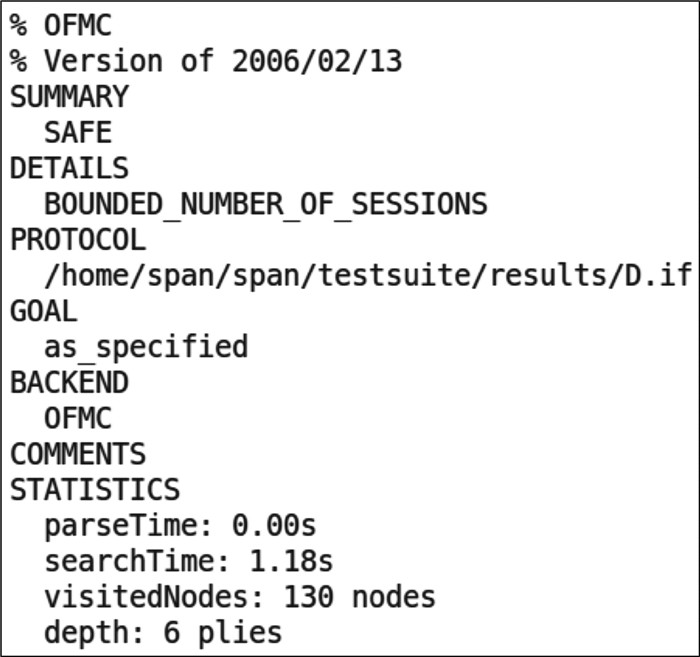
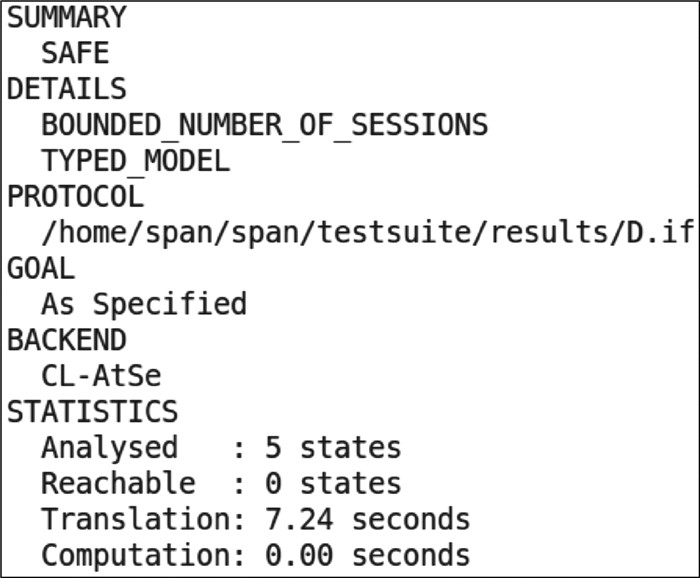
为了实现用户和服务器之间的通信安全及高效的身份认证,设计有效的身份认证协议成为研究热点。分析了已有协议的安全性,发现仍存在不能抵抗拒绝服务攻击(DOS)和离线口令猜测攻击的缺陷。因此,提出了新的基于动态ID的轻量级单向哈希函数身份认证协议,并通过非形式化安全性分析、随机预言机模型(ROM)分析和AVISPA实验仿真3种安全性分析,以及计算开销和通信开销的分析,比较证明了所提协议能够实现安全高效的身份认证。
-
关键词:
- 多服务器 /
- 身份认证 /
- 密钥协商 /
- 随机预言机模型(ROM) /
- AVISPA
Abstract:To realize the communication security and efficient identity authentication between users and servers, how to design effective identity authentication protocols has gradually become an important research hotspot, more and more identity authentication protocols are proposed. First, this paper analyses the security of the exiting protocols, and finds that it cannot resist Denial of Service (DOS) and offline password guessing attacks. Then, a new lightweight one-way hash function authentication protocol based on dynamic ID is proposed to remedy the security vulnerability mentioned above. For the security analysis, it is proved by non-formal security analysis and two formal analysis methods: Random Oracle Model (ROM) and AVISPA. Finally, the analysis and comparison of computation overheads and communication overheads prove that our protocol can achieve secure and efficient identity authentication.
-
Key words:
- multi-server /
- identity authentication /
- key agreement /
- Random Oracle Model (ROM) /
- AVISPA
-
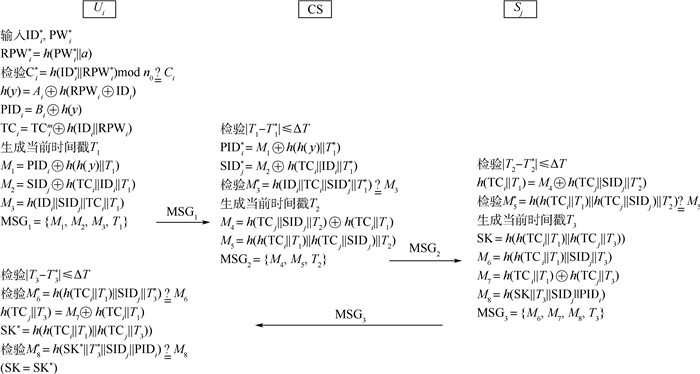
表 1 本文符号及说明
Table 1. Notation and description
符号 说明 Ui 用户 CS 控制服务器 Sj 接入服务器 IDi 用户Ui的身份标识 PWi 用户Ui的口令 SIDj 服务器Sj的身份标识 y 控制服务器CS的主密钥 TSi, TSj 用户Ui,服务器Sj注册时间戳 TCi, TCj 用户Ui,服务器Sj注册凭证 T1, T2, T3 系统时间戳 ΔT 最大通信时延 h(·) 单向哈希函数 ‖ 连接 ⊕ 异或运算 表 2 安全属性对比
Table 2. Comparison of security properties
-
[1] KHAN S U, LAVAGNO L, PASTRONE C, et al. Online authentication and key establishment scheme for heterogeneous sensor networks[J]. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2014, 2014: 718286. [2] LAMPORT L. Password authentication with insecure communication[J]. Communications of the ACM, 1981, 24(11): 770-772. doi: 10.1145/358790.358797 [3] AWASTHI A K, LAI S. An enhanced remote user authentication scheme using smart cards[J]. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 2004, 50(2): 583-586. doi: 10.1109/TCE.2004.1309430 [4] XU J, ZHU W T, FENG D G. An improved smart card based password authentication scheme with provable security[J]. Computer Standards & Interfaces, 2009, 31(4): 723-728. [5] LI X, QIU W, ZHENG D, et al. Anonymity enhancement on robust and efficient password-authenticated key agreement using smart cards[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2010, 57(2): 793-800. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2009.2028351 [6] ZHAO D W, PENG H P, LI L X, et al. A secure and effective anonymous authentication scheme for roaming service in global mobility networks[J]. Wireless Personal Communications, 2014, 78(1): 247-269. doi: 10.1007/s11277-014-1750-y [7] KHAN M K, KUMARI S. An improved user authentication protocol for healthcare services via wireless medical sensor networks[J]. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2014, 2014: 347169. [8] 沈忠华, 于秀源. 一个新的智能卡远程用户认证方案[J]. 浙江大学学报(理学版), 2008, 35(2): 145-149. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9497.2008.02.006SHEN Z H, YU X Y. A new remote user authentication scheme of using smart card[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University(Science Edition), 2008, 35(2): 145-149(in Chinese). doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9497.2008.02.006 [9] FAN C I, CHAN Y C, ZHANG Z K. Robust remote authentication scheme with smart cards[J]. Computers & Security, 2005, 24(8): 619-628. [10] HWANG M S, CHONG S K, CHEN T Y. DoS-resistant ID-based password authentication scheme using smart cards[J]. Journal of Systems and Software, 2010, 83(1): 163-172. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2009.07.050 [11] LEE S W, KIM H S, YOO K Y. Efficient nonce-based remote user authentication scheme using smart cards[J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2005, 167(1): 355-361. doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2004.06.111 [12] LIU J Y, ZHOU A M, GAO M X. A new mutual authentication scheme based on nonce and smart cards[J]. Computer Communications, 2008, 31(10): 2205-2209. doi: 10.1016/j.comcom.2008.02.002 [13] LI C T, HWANG M S. An efficient biometrics-based remote user authentication scheme using smart cards[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2010, 33(1): 1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2009.08.001 [14] SONG R. Advanced smart card based password authentication protocol[J]. Computer Standards & Interfaces, 2010, 32(5-6): 321-325. [15] SOOD S K, SARJE A K, SINGH K. A secure dynamic identity based authentication protocol for multi-server architecture[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2011, 34(2): 609-618. doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2010.11.011 [16] LI X, XIONG Y, MA J, et al. An efficient and security dynamic identity based authentication protocol for multi-server architecture using smart cards[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2012, 35(2): 763-769. doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2011.11.009 [17] XUE K, HONG P, MA C. A lightweight dynamic pseudonym identity based authentication and key agreement protocol without verification tables for multi-server architecture[J]. Journal of Computer and System Sciences, 2014, 80(1): 195-206. doi: 10.1016/j.jcss.2013.07.004 [18] LU Y R, LI L X, PENG H P, et al. A lightweight ID based authentication and key agreement protocol for multiserver architecture[J]. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2015, 2015: 16. [19] MISHRA D, DAS A K, MUKHOPADHYAY S. A secure user anonymity-preserving biometric-based multi-server authenticated key agreement scheme using smart cards[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2014, 41(18): 8129-8143. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2014.07.004 [20] WANG D, WANG P. Two birds with one stone: Two-factor authentication with security beyond conventional bound[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2018, 15(4): 708-722. [21] GU Y, LI S Q. Cryptanalysis and improvement of a biometrics-based multi-server authentication protocol [C]//2018 International Conference on Computing, Networking and Communications. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 1994: 16-20. [22] 唐郑熠, 李祥. Dolev-Yao攻击者模型的形式化描述[J]. 计算机工程与科学, 2010, 32(8): 36-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-130X.2010.08.010TANG Z Y, LI X. Formal description of Dolev-Yao attacker model[J]. Computer Engineering and Science, 2010, 32(8): 36-38(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-130X.2010.08.010 [23] WANG D, LI W, WANG P. Measuring two-factor authentication schemes for real-time data access in industrial wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2018, 14(9): 4081-4092. doi: 10.1109/TII.2018.2834351 [24] WANG C, XU G, SUN J. An enhanced three-factor user authentication scheme using elliptic curve cryptosystem for wireless sensor networks[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(12): 2946. doi: 10.3390/s17122946 [25] WANG D, ZHANG Z, WANG P, et al. Targeted online password guessing: An underestimated threat[C]//Proceedings of the 2016 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security. New York: ACM, 2016: 1242-1254. [26] CHRISTOPH G G. An identity-based key-exchange protocol[C]//Workshop on the Theory and Application of Crypto-graphic Techniques. Berlin: Springer, 1989: 235-258. [27] WEI F, VIJAYAKUMAR P, JIAN S, et al. A provably secure password-based anonymous authentication scheme for wireless body area networks[J]. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 2018, 65: 322-331. [28] FENG Q, HE D, ZEADALLY S, et al. Anonymous biometrics-based authentication scheme with key distribution for mobile multi-server environment[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2018, 84: 239-251. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2017.07.040 [29] AVISPA. Automated validation of internet security protocols and applications[EB/OL]. [2020-08-01]. -








 下载:
下载: