-
摘要:
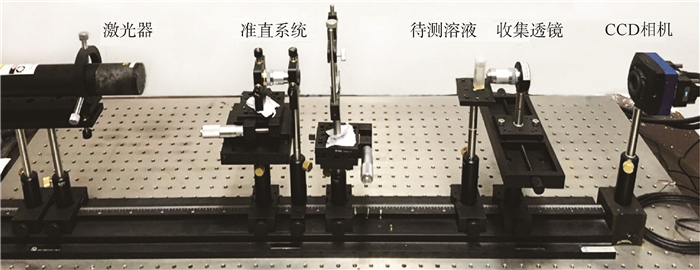
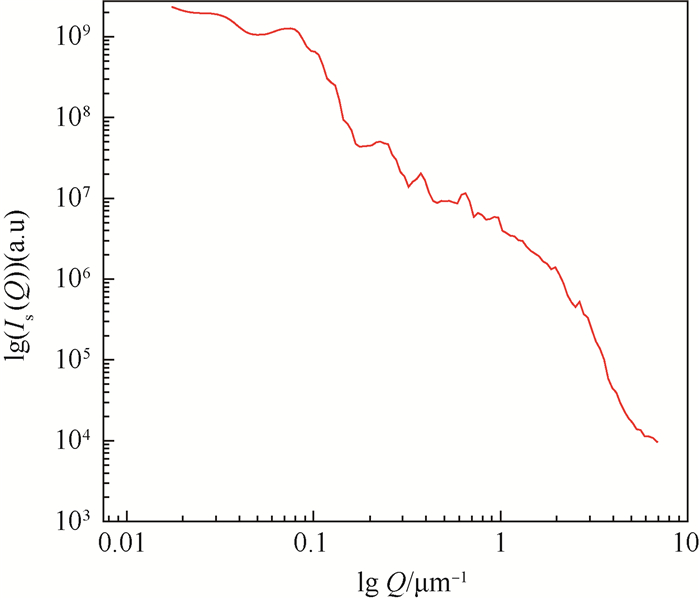
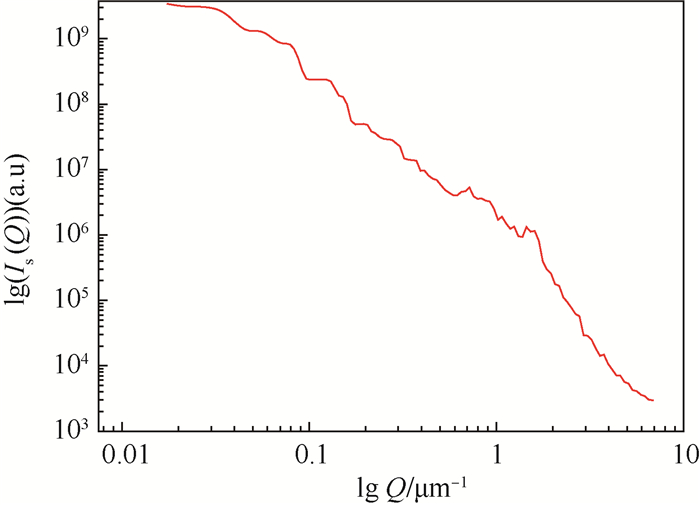
针对传统的前向小角散射粒径测量系统中心光过强、杂散光干扰、散射角过小等缺点,本文采用一种新型的近场散射(NFS)方法测量前向小角散射光,研究并搭建了基于近场散射的颗粒粒径测量系统,将最大散射角提高到40.5°;在无需空白测量的情况下采用差分方法对透射光和散射光干涉成的散斑图像进行处理,有效去除中心光和杂散光的影响;对差分散斑图像进行快速傅里叶变换(FFT)频谱处理得到散射光强分布,利用Chahine算法对颗粒粒径进行了反演。最后,利用已知粒径(39.2 μm和67.3 μm)的标准颗粒对测量系统的准确性进行了单峰分布的验证,测量误差在5%之内;对于粒径为39.2 μm和67.3 μm的混合颗粒进行了双峰分布验证,在43.3 μm和74.1 μm处出现峰值,测量误差在10%左右。
-
关键词:
- 粒径测量 /
- 近场散射(NFC) /
- 差分散斑 /
- 快速傅里叶变换(FFT) /
- Chahine算法
Abstract:To solve the problems such as high intensity of transmitted light, stray light interference and small scattering angle in the traditional low-angle light scattering techniques, a novel near field scattering (NFS) was adopted to derive the traditional low-angle scattering intensity. A particle size measurement system based on near filed scattering was proposed and built with the scattering angle up to 40.5°. Heterodyne method was applied to process the near field speckle images generated by interference between the transmitted and scattered fields, which is capable of completely removing the stray light. The angular intensity distribution was determined by fast Fourier transform (FFT) frequency spectral analysis of the heterodyne signal. The particle size distributions were inversed by Chahine algorithm. Experimental results on measurement of both monodisperse and bimodal samples with known diameters which are 39.2 μm and 67.3 μm, was presented. For monodisperse samples, the measurement error was less than 5%, for bimodal samples, there was two apparent peaks in 43.3 μm and 74.1 μm, the error was about 10%.
-
近20年来,无人机容错技术得到了长足的发展,特别针对大中型轮式起降无人机的机电系统容错理论也进行了深入的研究。刹车系统作为无人机的起飞着陆子系统的组成部分,对于保障无人机安全起飞、着陆及纠偏起到重要的作用。防滑刹车系统的可靠与否,直接关系到无人机载具的起降安全和任务完成程度。执行机构部分失效型故障普遍存在于各类非线性控制系统中,无人机刹车系统也不例外,对于无人机刹车系统的执行机构故障的自主解析冗余技术的研究有着重要的理论和应用价值。然而,此类研究文献却鲜有。
近些年来,反演算法被广泛应用于非线性系统的容错控制中[1-3]。Chen等[4]将反演迭代控制算法应用至飞机防滑刹车系统的滑移率跟踪控制,取得了较好的控制效果。文献[5]采用滑模迭代学习律进行故障估计,用以补偿执行机构故障和外部干扰的影响,但文献中的故障估计却依赖于现有故障估计误差的获取。文献[6-8]假设执行器的失效型故障量和卡死型故障量已知的前提下,针对纯反馈的非线性冗余执行器容错控制,提出自适应模糊反演控制策略,设置自适应模糊机构补偿系统非线性项,实际中真实故障值是无法取得的。
与此同时,随着自适应反演神经网络控制的发展,大量的先进控制方法被提出,例如Polycarpou[9]首次提出将自适应边界技术应用于估计神经网络逼近误差的未知上界。这种策略已经广泛应用于自适应神经网络的设计。Bechlioulis和Rovithakis[10]针对标准SISO不确定非线性系统提出了一种基于自适应神经网络的控制器,能够保证跟踪误差在一个时变的界内。然而只有当神经网络的估计性能受限在一定紧集内时,大多数自适应神经网络控制算法仅能够确保闭环控制系统的半全局一致稳定。Wang等[11]将水下无人机推进器故障量和外界扰动看作是系统的不确定项,构造径向基函数神经网络(Radial Basis Function Neural Network, RBFNN)用于估计不确定项,同时将滑模算法同反演控制相结合,对执行器故障进行容错控制。然而,其并未考虑系统跟踪状态量的受限与执行器饱和这一因素。
现有的文献研究[12-14]均是针对滑移率的调节使其对设定最优值进行跟踪,而对刹车系统稳定性问题却少有探讨。滑移率控制中刹车工作点常处于稳定或不稳定区域[15]。滑移率处于不稳定区域则会导致防滑效果不理想甚至使飞机主轮趋于抱死,导致不期望的侧向滑移,从而造成安全事故。为了保证跟踪误差在提前设定的界内,基于障碍Lyapunov函数的反演控制算法得到了广泛的研究[16-18],然而该方法的使用前提是系统所有可测状态量必须全程限定在已知的常数范围内,而且并未讨论故障状态下的系统稳定性能。
在不确定参数与各种外部扰动作用下执行机构受限将会对防滑性能产生很大的影响。特别地,当执行机构发生故障时,重构控制器与控制输入饱和之间的关系很难确定,因此控制输入受限这一问题亟待解决。文献[19-20]分别针对SISO、MIMO非线性系统的输出受限和输入控制饱和问题进行研究,利用了对称的障碍Lyapunov函数结合反演算法设计控制律,并分别利用神经网络和模糊项来逼近未知模型参数和干扰项。文献[21]应用RBFNN控制器补偿系统非线性和执行器缓变型故障,设定初始状态即为故障状态下进行的仿真分析,通过选择合适的控制器参数,使得全程RBFNN误差总保持在一定的紧集内,然而文献并未考虑系统工作过程中突发型未知故障对神经网络控制器稳定性的冲击影响。为了克服经典自适应神经网络控制器这一缺点,文献[22]引入鲁棒切换项,当神经网络的输入量超出逼近范围时,切换项起作用,将传统自适应神经网络控制项切除掉,随之而来的鲁棒项开始起作用,将用于补偿超出神经网络输入范围对系统的影响。基于预定义跟踪有限精度范围而设计一种自适应神经网络容错控制算法具有重大的理论和实际意义。但直至现在为止,并没有一种有效的自适应神经网络容错控制方法,用于解决非线性系统输入输出受限、机构故障的多重约束问题。
因此,本文在以上文献的研究基础上,探索了无人机防滑刹车系统在存在建模不确定性和执行机构未知失效故障,同时存在控制输入饱和情况下的滑移率受限问题。本文的主要工作如下:针对无人机防滑刹车系统故障模型中的非线性不确定项,使用自适应神经网络进行逼近,发生执行器失效故障时,若系统的约束量超出神经网络输入设定值,则通过切换鲁棒项,来补偿神经网络超出逼近设定值对系统稳定性的冲击影响,以达到快速容错的目的;针对控制输入饱和,设置了饱和补偿项,用于补偿超出饱和的部分;对于输出滑移率受限问题,使用了障碍Lyapunov函数设计容错控制器,确保了滑移率始终维持在受限条件之内。系统能够在故障未知,无需精确故障重构的情况下,以较少的可调参数,使整个系统实现快速稳定容错控制。
1. 问题描述与预备知识
考虑包含执行机构故障的刹车系统数学模型为不确定非线性系统。建立刹车系统模型时不考虑飞机的横侧向运动,假设所有主机轮的作动机构均具有一致性和同步性,因此刹车控制系统可以简化为仅对单个机轮的控制[4],而本文主要应用于基于滑移率设计的防滑刹车控制系统,则滑移率可以被定义为

(1) 对式(1) 两边求导可得

(2) 式中:

(3) 其中:

(4) 
(5) 式中:Vx为飞机速度;ωw为机轮转速;Tb为刹车力矩;δ为滑移率;Rvb为刹车半径;J为机轮转动惯量;其他飞机机轮建模相关参数的定义详见文献[23]。结合系数μ同δ之间具备非线性关系,即

(6) 表 1展示出μ-δ相关参数的数值。
表 1 μ-δ关系参数示意Table 1. Relationship of μ-δ parametric representation飞机跑道状态 D C B 干柏油跑道 0.8 1.534 4 14.032 6 湿柏油跑道 0.4 2.019 2 8.209 8 结冰跑道 0.2 2.087 5 7.201 8 由式(4)~式(6),可以看出滑移率同飞机速度和机轮转速,滑移率与结合系数都存在有非线性关系,从而使得无人机防滑刹车系统具有较强的非线性,将系统重新写成非线性状态方程:

(7) 式中:状态变量x=δ;控制输入u=Tb;f(x)=f(δ);g(x)=Rvb/(VxJ)。本文仅考虑执行机构发生部分失效故障,且将此故障建模为乘性因子形式,则执行机构故障下实际作用于刹车控制力矩为

(8) 式中:ρ(t)为执行器的故障程度,ρ(t)∈(0,1]。当ρ(t)=1时,则u=uc(uc为控制力矩),表示执行机构正常工作,指令控制刹车力矩与实际力矩一致;当ρ(t)∈(0,1) 时,表示执行机构产生部分失效故障。同时考虑刹车力矩作为控制输入的饱和受限问题,即0≤u≤umax(umax为最大刹车力矩),设计指令相应的uc以实现防滑刹车系统稳定容错控制。

(9) 式中:v为控制器的输入指令; umin为最小刹车力矩(本文为0)。至此,无人机防滑刹车系统方程在执行器部分失效故障发生时可以改写为

(10) 由式(6) 可知,滑移率与结合系数之间关系具有较强的非线性和不确定性,往往系统建模时不能够较为准确的获取,而且本文中的执行机构失效型故障程度未知,因此设置RBFNN直接用于逼近系统未知非线性项和故障项,从而将RBFNN引入容错控制器设计中具有重要的意义。
本文控制目标:针对式(10) 所描述的无人机防滑刹车系统,考虑执行机构部分失效故障与控制输入受限问题,设计容错控制器使得刹车过程中,实现对期望滑移率的跟踪,即使发生执行器故障也仍能满足刹车工作点快速调节并稳定在限定有界范围之内。
为了后续方便容错控制器设计及其稳定性分析,现将本文的数学符号做统一定义。令R表示实数域,R+表示全体实数构成的空间,Rn表示n维实数向量空间。
引理1 在一紧集域内ΩZ∈Rm,使用RBFNN,逼近未知连续非线性函数ϕ(Zin):Rm→R,形式如下:

(11) 式中:ε(Zin)为神经网络固有估计误差,且有界,满足|ε(Zin)|≤ε*,ε*∈R+为未知常数; 输入向量Zin∈ΩZ,H(Zin)=[h1(Zin), h2(Zin), …, hl(Zin)]Τ:ΩZ→Rl,且神经网络节点数l>1,H(Zin)为已知光滑向量值函数,选择RBFNN函数hi(Zin)(1≤i≤l)为高斯基函数,形式如下:

(12) 其中:ai∈ΩZ和bi∈R+分别为高斯基函数的中心和宽度。定义最优权值向量W*=[w1*, w2*, …, wl*]Τ为

(13) 式中:

引理2[24] 针对所有s∈Rp,同时给定常数0<r1<r2,且n阶光滑函数F(s)满足以下条件:
1) 当║s║≤r1,F(s)=0。
2) 当║s║≥r2>r1,F(s)=1。
3) F(s)≥n阶连续可导。
针对所有Zin∈Rp,本文选取切换函数为

(14) 式中:0<r1<r2,则M(Zin)为n阶光滑连续可导函数。
引理3[25] 对于所有满足|·|<kb,则不等式ln[kb2/(kb2-(·)2)]≤S2/(kb2-(·)2)恒成立。其中:S为跟踪误差;kb为跟踪误差的受限最大值。
假设1 存在已知光滑函数ψ(·),且存在未知常数λ∈R+保证不等式|f(·)|≤λψ(·)恒成立。
假设2 在执行机构容错控制器设计中,g(·)为已知函数,ġ(·)有界,在|·|<kb条件下,存在0<g0≤g(·)≤ḡ0恒成立,且g0,ḡ0∈R+,又故障程度ρ(t)满足ρ(t)∈(0, 1],且ρ(t)微分有界,


假设3 由于∀t∈[0, +∞)

(15) 式中:-ka为跟踪误差的受限最小值。
故而定存在一个正常数θ满足|(1-q)/(ka2-(·)2)+q/(kb2-(·)2)|≤θ。
2. 自适应鲁棒容错控制器设计
本文提出的容错控制器思想是将滑移率控制视为含有系统输出约束条件的控制问题,通过约束条件的限定,使得滑移率始终在受限区域之内,即使发生执行器故障也仍能满足刹车工作点快速调节并稳定在限定有界范围之内。针对执行器故障下的无人机防滑刹车非线性系统式(10),基于假设1和假设2,定义S=y-yr,y为测量信号,yr为参考信号,σ(t)=ρ(t)g(x),对S求导可得

(16) 选取障碍Lyapunov候选函数:

(17) 式中:

γΤ=γ为设定的正定对角阵,选取参数τ,ϑ∈R+,并且RBFNN权值的估计误差定义为





(18) 代入引理3,则式(18) 可以进一步放缩为

(19) 定义Z=[x, yr, ẏr]Τ∈R3,则未知非线性项为

(20) 从式(3) 和式(6) 可知,f(x)具有较强的非线性,往往系统建模时不能够较为准确的获取,由于本文中的故障程度未知,因此设置RBFNN用于逼近未知非线性项ϕ(Z),同时根据引理2,同时考虑执行器饱和,则设计容错控制律为

(21) 式中:设计控制器uc的输入为

(22) 其中:K1和K2为待设计的控制参数;αn为传统自适应神经网络控制项;αr为鲁棒切换控制项,两者定义分别为

(23) 
(24) 自适应律设计为

(25) 
(26) 
(27) 设计饱和辅助机构为

(28) 式中:K3为待设计的参数;Δu=uc-v;待设计参数ξ,ϖ,κ,ζ∈R+。当系统发生执行器故障时,RBFNN的输入将会出现较大的波动,甚至超出RBFNN逼近范围,从而使得控制系统暂态性能变差,容错时间变长。当系统发生故障时,鲁棒项αr会随M(Z)而变化,起到对于超出逼近范围的补偿作用。
定理1 针对式(10) 所示故障无人机防滑刹车系统,应用自适应律式(23)~式(27),辅助机构式(28),设计控制器式(21),其中控制器uc的输入量v设计为式(22),若满足假设1~假设3,选取合适的控制参数,则可以保证滑移率始终维持在给定界内,闭环控制系统半全局一致稳定,所有信号有界。
证明 根据引理1可令:

(29) 考虑将式(29) 代入不等式(19),可得

(30) 根据式(28),则有

(31) 将控制器输入,式(22) 和式(31) 代入不等式(30):

(32) 考虑假设1~假设3,并根据Young不等式,可得

(33) 
(34) 同时将自适应律式(23)~式(28),代入不等式(32),可得

(35) 式中:


(36) 式中:λmin(γ)为求取矩阵γ的最小特征值。
式(36) 根据引理3,可以得到

(37) 这里令Θ=min{(K1-θ2)[(1-q)(ka2-S2)+q(kb2-S2)], λmin(γ)ϖ, κ, ξ, K3-0.5K22-0.5},则式(37) 可以被改写为

(38) 为了确保整个闭环容错系统的稳定性,控制器的参数满足

(39) 求解式(38),可得V(t)的值域范围为

(40) 根据假设2,并对式(40) 两边求取反对数可得

(41) 式(41) 经变换,可得|S(t)|=|x(t)-yr(t)|≤[(1-q)ka+qkb]

综上所述,即使在执行机构故障下,也能够通过选择合适的控制参数,使得滑移率跟踪误差S以任意精度趋近于0,并且系统输出滑移率全程稳定在受限稳定范围内。
3. 仿真分析
为了验证所提出的控制方法用于无人机防滑刹车执行器故障容错控制的有效性, 在MATLAB环境下对所提的方法进行了仿真研究。为了验证所提容错算法的可靠性,无人机在干柏油跑道着陆时可分2种情况进行仿真:① 在正常工况,切换不同跑道作用下系统响应;② 执行器故障,本文设计的容错控制器起作用下的系统响应。
刹车系统模型部分参数分别为:飞机质量m=3 000 kg;前轮至重心距离a=3.883 m;主轮至重心距离b=1.076 m;刹车半径Rvb=0.165 m;飞机重心高度h=1.32 m;最大刹车力矩umax=250 N·m。防滑控制的目标是刹车滑移率实时跟踪最优滑移率,且滑移率受限始终在稳定范围内。本文选取跑道参数详见表 1,其中对应的最优滑移率分别为:干柏油跑道最优滑移率选取0.117;湿柏油跑道最优滑移率选取0.12;结冰跑道最优滑移率选取0.13。在这里选取最佳滑移率跟踪误差S(t)=δ(t)-δr(t)受限的上下界分别为kb=kc-δr(t),ka]=kc-δ(0)。其中,δ(t)和δr(t)分别为滑移率、给定最优滑移率,选取参数kc=0.25。无人机的着陆刹车初始速度为Vx(0)=45.8 m/s,ω(0)=277.5 rad/s。RBFNN参数选取为:神经元个数为680;RBFNN中心ai平均分布于[-0.000 15, 0.14]×[0, 0.13]×[0, 1.3];宽度bi=0.5 (i=1, 2, …, 80)。为了实现故障状态下稳定控制,控制器和自适应律参数分别选择为:K1=30;K2=0.57;ψ(Z)=240;r1=1.18;r2=1.25;K3=4.5;|γ|=τ=1;ϑ=0.25;ϖ=0.02;κ=0.001;ζ=0.12。为了较为真实的模拟目标滑移率的设定,针对目标最佳滑移率的输出,设定传递函数δd=δc/(0.1s+1),s为传递函数,当飞机速度低于5 m/s,可视为防滑系统不再工作,仿真结束。
情况1 无故障仿真

(42) 本次仿真,在2 s时发生跑道切换,故而给定最优滑移率也发生变化,如式(42) 所示,由于跑道状态发生变化,跑道模型式(6) 中的参数也随之发生变化,系统参数出现摄动。通过仿真,当系统参数发生变化时,可以验证容错控制算法对不同给定最优滑移率的追踪能力。仿真结果如图 1所示。图 1(a)表示执行机构无故障时,无人机速度与机轮转速对比图,机轮并未出现滑移现象。图 1(b)表示滑移率的跟踪响应曲线,2 s时跑道发生切换,从干柏油跑道切至湿柏油跑道,0.3 s就可以完成切换,并未出现较大的超调。图 1(c)表示刹车力矩的系统响应控制输入,在跑道发生切换时,为了快速跟踪上变化的期望滑移率,刹车力矩进行了迅速响应,导致刹车力矩出现饱和,这时控制律中的辅助机构开始起作用进行补偿,将刹车力矩迅速拉回受限区域,使得刹车得以稳定控制,并未使机轮出现明显的抱死。
情况2 时变型故障仿真
结冰跑道着陆是无人机的一种极限着陆状况,对执行机构性能和控制律设计提出了更为严格的要求[26],情况2以结冰跑道工况为例,同时在执行器发生时变故障的条件下,来验证容错算法的有效性,故障注入方式为

(43) 仿真结果如图 2所示,从图 2(a)可以看出,当发生故障时,机轮转速并未出现明显波动。从图 2(b)可以看出,滑移率发生波动,由于容错算法中的鲁棒项的作用,使得滑移率从临界稳定区域快速调节至期望最优化率值,从而确保系统输出在稳定区域内的前提下,仍能够实现快速容错,从图中可以看出容错时间为0.2 s。图 2(c)表示为了减少故障对于系统稳定性的影响,在5 s时,根据本文算法设置,刹车力矩针对时变型故障进行了补偿容错控制,随着故障的不断变化,实时调节控制律输出。
4. 结论
本文在构建无人机刹车数学模型基础上,考虑系统输出滑移率受限,控制输入饱和及未知故障信息的情况下,设计一种基于障碍Lyapunov函数方法的自适应鲁棒RBFNN容错控制器,通过稳定性分析和仿真实验得到:
1) 针对无人机防滑刹车系统具有较强非线性参数时变等特点,提出执行器未知故障状态下的容错控制器算法,无需故障诊断,构建神经网络逼近系统的非线性不确定项,神经网络的应用有效避免了控制器设计中的奇点问题,切换项的引入,即可对系统进行快速容错控制,简化了容错控制器设计流程。
2) 采用障碍Lyapunov函数方法来设计容错控制器,可实现系统输出滑移率的实时约束,确保滑移率始终保持在稳定区域内,防止刹车打滑现象出现,改善了防滑刹车系统性能。
3) 不同类型跑道所对应的结合系数变化较大,在给定不同目标滑移率设定下,无需改变原有系统已有控制器参数设计,即可对系统稳定控制,针对刹车力矩控制输入饱和,设定的辅助饱和机构对执行器的饱和现象的快速抑制起到一定作用。
-
表 1 2种标准聚苯乙烯乳胶球
Table 1. Two certified polystyrene latex spheres
编号 直径/μm GBW (E)120028 39.2±0.6 GBW (E)120047 67.3±3.8 表 2 标准聚苯乙烯乳胶球测量值对比
Table 2. Comparison between the measurements of certified polystyrene latex spheres
标定直径/μm 测量直径/μm 误差/% 39.2±0.6 40.3±1.9 3.8 67.3±3.8 68.7±2.4 4.0 -
[1] 邵鸿飞, 柴娟, 黄辉.粒度分析及粒度标准物质研究进展[J].化学分析计量, 2012, 21(2):99-101. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXFJ201202033.htmSHAO H F, CHAI J, HUANG H.Research progress of particle size analysis and particle size standard reference material[J].Chemical Analysis and Meterage, 2012, 21(2):99-101(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXFJ201202033.htm [2] 王乃宁.颗粒粒径的光学测量技术及应用[M].北京:原子能出版社, 2002:168-175.WANG N N.Optic Measurement technology of particle size and its application[M].Beijing:Atomic Energy Press, 2002:168-175(in Chinese). [3] FERRI F.Use of a charge coupled device camera for low-angle elastic light scattering[J].Review of Scientific Instruments, 1997, 68(6):2265-2274. doi: 10.1063/1.1148135 [4] 王式民, 陆勇, 叶茂.前向小角散射法测量颗粒平均尺寸[J].武汉大学学报(自然科学版), 1997, 43(5):691-696. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHDY705.026.htmWANG S M, LU Y, YE M.Measurement of the particle mean size by the ratio of the scattering light intensitied at small angles near-forward[J].Journal of Wuhan University (Natural Science Edition), 1997, 43(5):691-696(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHDY705.026.htm [5] BROGIOLI D, VAILATI A, GIGLIO M.Heterodyne near-field scattering[J].Applied Physics Lertters, 2002, 81(22):4109-4111. doi: 10.1063/1.1524702 [6] SCHEFFOLD F, CERBINO R.New trends in light scattering[J].Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science, 2007, 12(1):50-57. [7] MAGATTI D, ALAIMO M D, POTENZA M A C, et al.Dynamic heterodyne near field scattering[J].Applied Physics Lertters, 2008, 92(24):241101-1-241101-3. doi: 10.1063/1.2937841 [8] CERBINO R, VAILATI A.Near-field scattering techniques:Novel instrumentation and results from time and spatially resolved investigations of soft matter systems[J].Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science, 2009, 14(6):416-425. [9] DAINTY J C.Laser speckle and related phenomena[M].Berlin:Springer-Verlag, 1984:132-135. [10] BORN M, WOLF E, HECHT E.Principles of optics:Electromagnetic theory of propagation, interference and diffraction of light[J].Brain Research Molecular Brain Research, 2005, 141(1):30-38. doi: 10.1016/j.molbrainres.2005.07.012 [11] GIGLIO M, BROGIOL D, POTENZA M A C, et al.Near field scattering[J].Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2004, 6(7):1547-1550. doi: 10.1039/B314600F [12] DORIANO B.Near filed speckles[D].Milano:Universita di Milano and INFM, 2009:73. [13] POTENZA M A C, PESCINI D, MAGATTI D, et al.A new particle sizing technique based on near field scattering[J].Nuclear Physics B-Proceedings Supplements, 2006, 150(1):334-338. [14] FERRI F, MAGATTI D, PESCINI D, et al.Heterodyne near-field scattering:A technique for complex fluids[J].Physical Review E Statistical Nonlinear & Soft Matter Physics, 2004, 70(4 Pt 1):174-195. [15] KOUZELIS D, CANDEL S M, ESPOSITO E, et al.Particle sizing by laser light diffraction:Improvements in optics and algorithms[J].Particle & Particle Systems Characterization, 1987, 4(1-4):151-156. [16] 曹丽霞.基于静态光散射的颗粒粒度检测技术的研究[D].杭州:中国计量学院, 2015:27-30.CAO L X.Research on measurement technology of particle size based on static light scattering[D].Hanzhou:China Jiliang University, 2015:27-30(in Chinese). [17] 曹丽霞, 赵军, 孔明, 等.基于改进的Chahine迭代算法的粒径分布反演[J].红外与激光工程, 2015, 44(9):2837-2843. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HWYJ201509052.htmCAO L X, ZHAO J, KONG M, et al.Inversion of particle size distribution based on improved Chahine algorithm[J].Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2015, 44(9):2837-2843(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HWYJ201509052.htm -







 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载: