-
摘要:
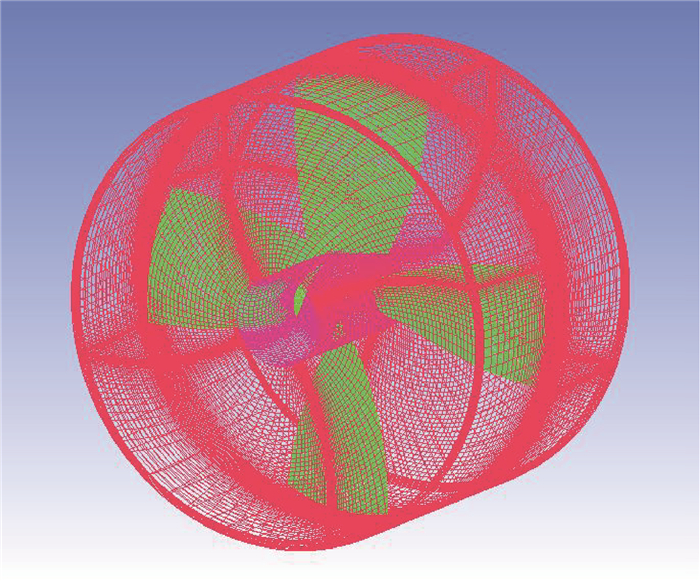
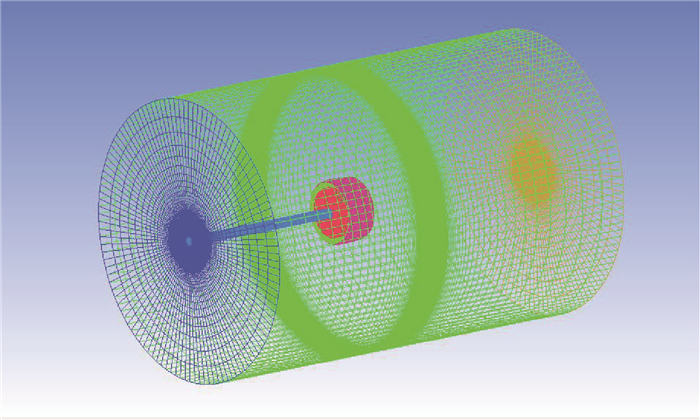
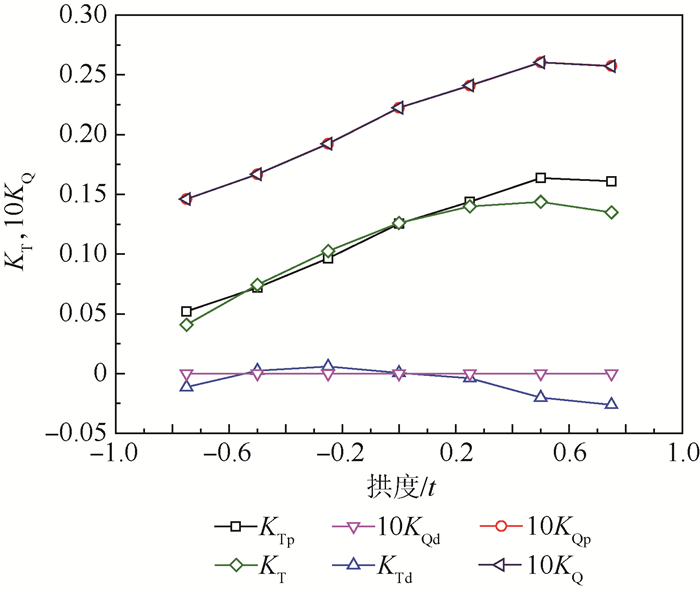
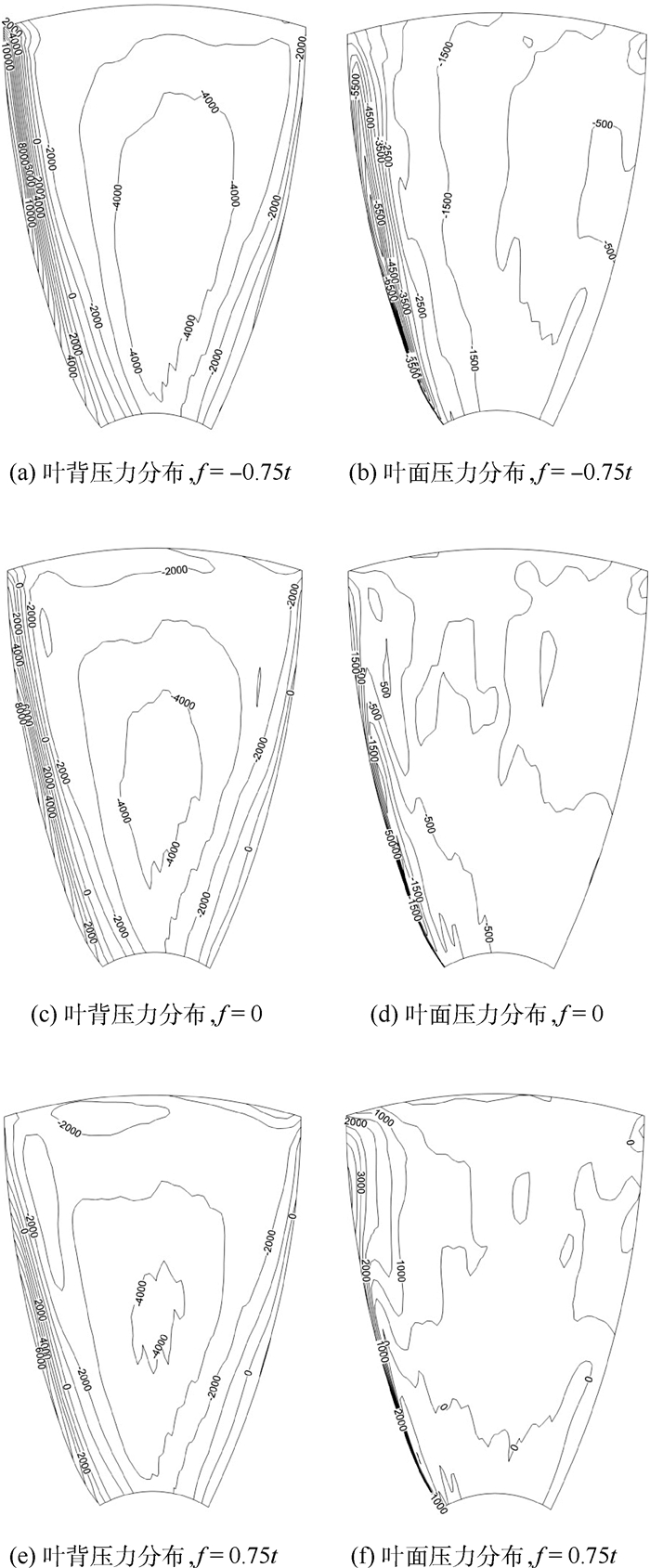
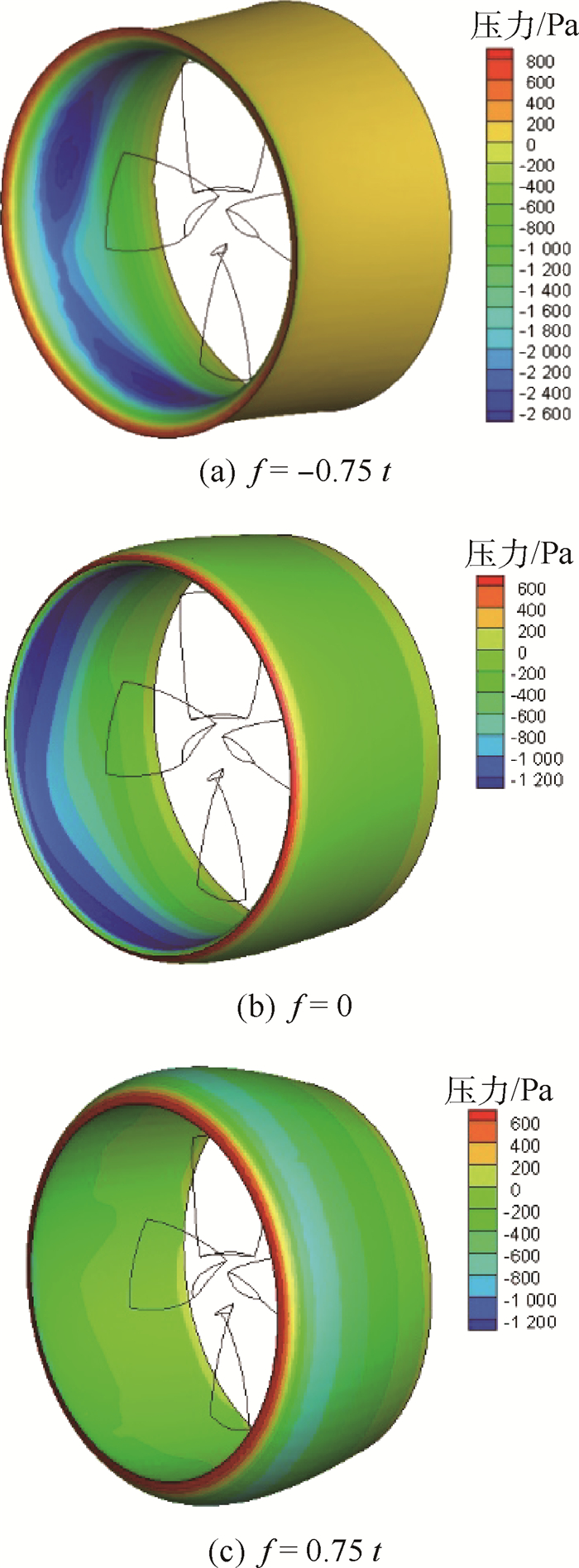
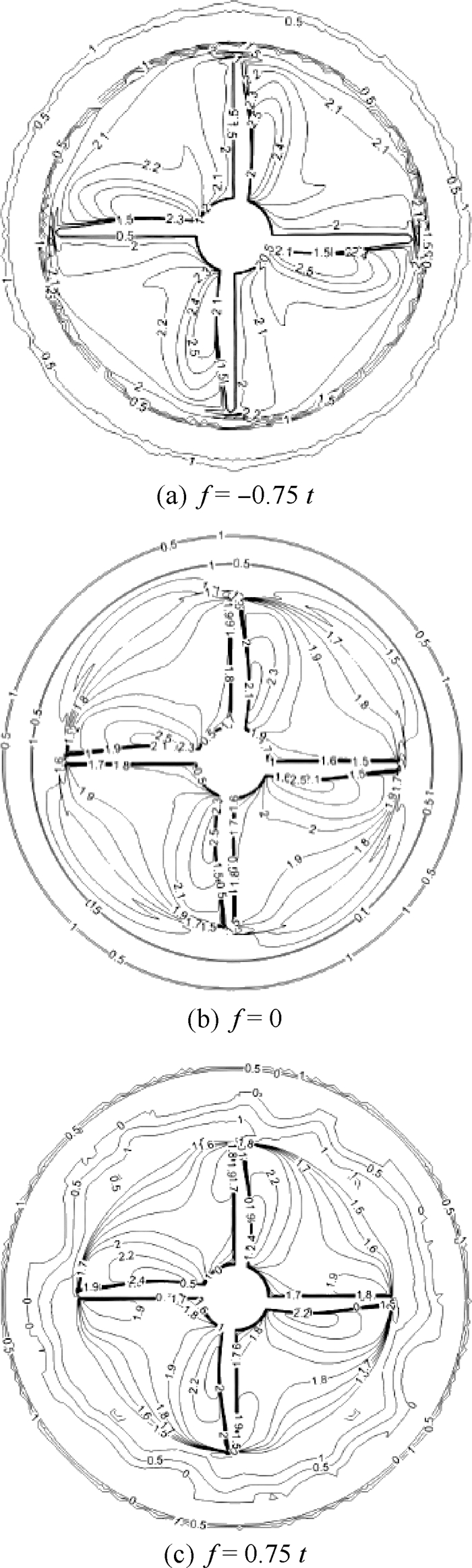
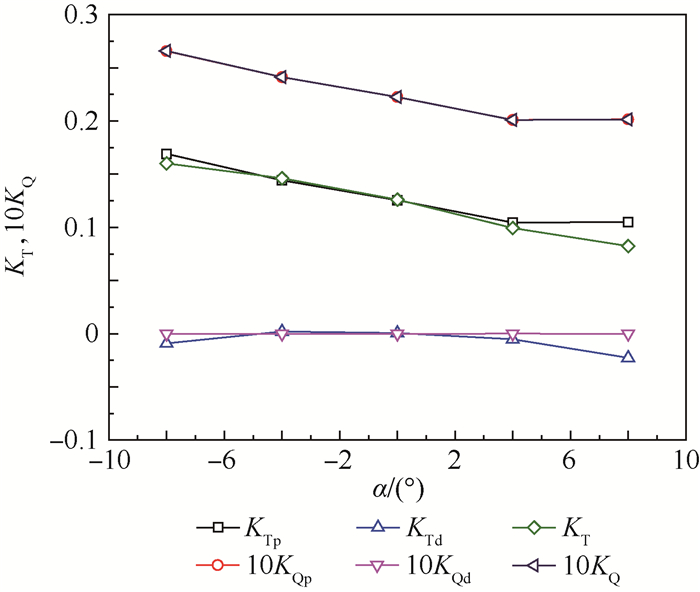
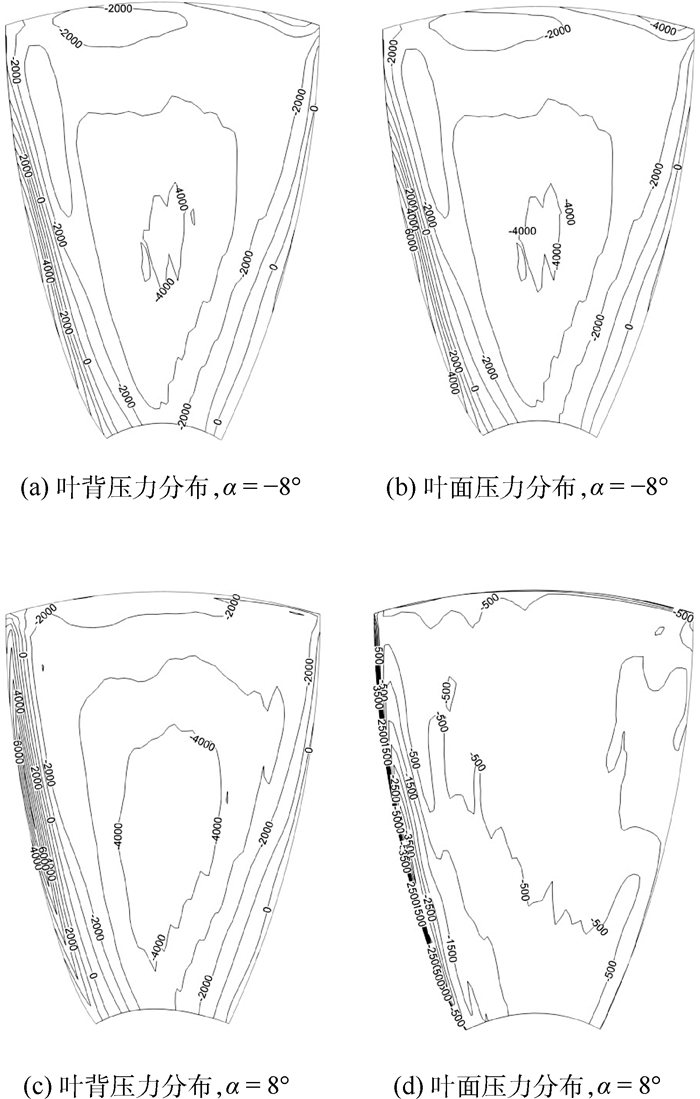
为了研究不同形式导管桨的载荷特点,采用计算流体力学(CFD)技术分析了加速、减速导管的水动力特性及其对螺旋桨水动力性能的影响。计算域被分为包含螺旋桨的柱形域、包含导管的大域2个部分,并采用全结构化网格技术对其进行离散,以便优化网格质量和提高计算精度。用交界面技术保证不同计算域之间流体速度和压力等物理量的连续性。首先分析了JD7704+Ka4-5508导管桨的水动力性能,然后将计算值与试验值进行对比,验证了本文模型和网格技术的合理性。在此基础上,分析了不同翼形剖面拱度和攻角的加速、减速导管的水动力特性,及其对螺旋桨载荷的影响。研究表明,通过改变拱度和攻角2种方式所得到的加速和减速导管具有不同的水动力特性,能极大地优化螺旋桨的工况和载荷特点。
-
关键词:
- 导管桨 /
- 加速导管 /
- 减速导管 /
- 计算流体力学(CFD) /
- 水动力性能
Abstract:In order to study the loading characteristics of different forms of ducted propellers, this paper analyzes the hydrodynamic performance of accelerating duct and decelerating duct and their influences on propellers by using computational fluid dynamics (CFD) method. The computation domain is divided into two parts:cylindrical domain containing the propeller and outer domain containing the duct. The computation domain is discretized by using fully structured gridding technique to optimize the quality of grids and improve the accuracy of calculation. The continuity of physical quantities such as fluid velocity and pressure between different domains is guaranteed by using the interface technique. This paper analyzes the hydrodynamic performance of JD7704+Ka4-5508 first, and the according results are compared with those by experiments to verify the rationality of the model and the grids technique. On this basis, this paper analyzes the hydrodynamic performance of accelerating duct and decelerating duct with varied cambers and angles of attack, and their influences on the loading state of propellers. The study shows that the accelerating duct and decelerating duct due to the variation of the cambers and angles of attack have different hydrodynamic performance, and they can optimize the propeller's operating conditions and loading characteristics greatly.
-
表 1 NACA0012翼形剖面导管主要参数
Table 1. Duct main parameters of NACA0012 airfoil section
参数 数值/m 长度 0.1665 导管外径 0.34 导管内径 0.30 叶梢间距 0.026 表 2 Ka4-5508螺旋桨主要参数
Table 2. Main parameters of Ka4-5508 propeller
参数 数值 直径/m 0.25 盘面比 0.55 毂径比 0.2 螺距比 0.8 桨叶数 4 表 3 数值模型及工况
Table 3. Numerical model and operating condition
数值方法 计算模型 求解器 三维单精度基于压力的定常隐式求解器 湍流模型 SST k-ω 运动模式 MRF 水的密度/(kg·m-3) 998.2 水的动力黏性系数/(kg·(m·s)-1) 0.001003 螺旋桨转速/(r·min-1) 600 入口速度/(m·s-1) 1.25 压力离散格式 Standard 耦合方式 SIMPLEC 差分方式 一阶迎风格式 表 4 改变拱度时不同截面轴向平均速度
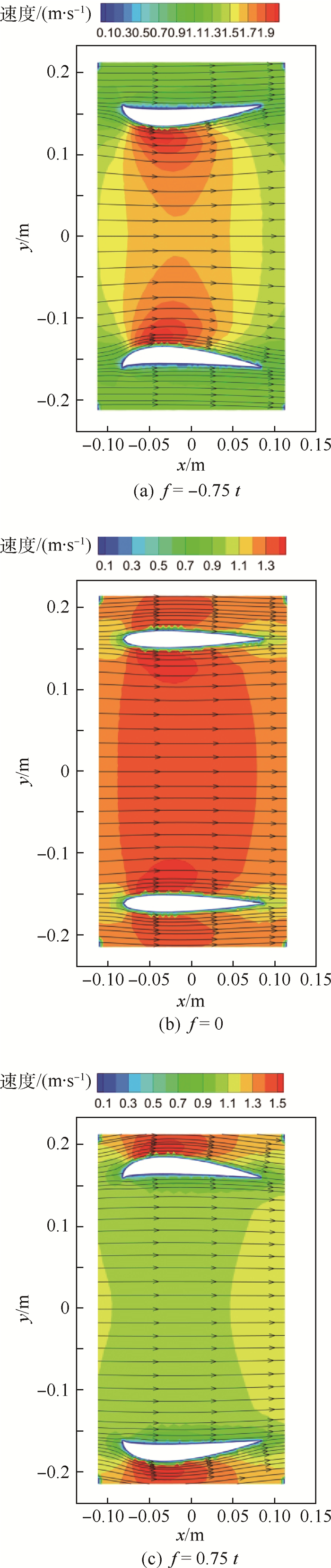
Table 4. Averaged axial velocity on different sections with varied camber
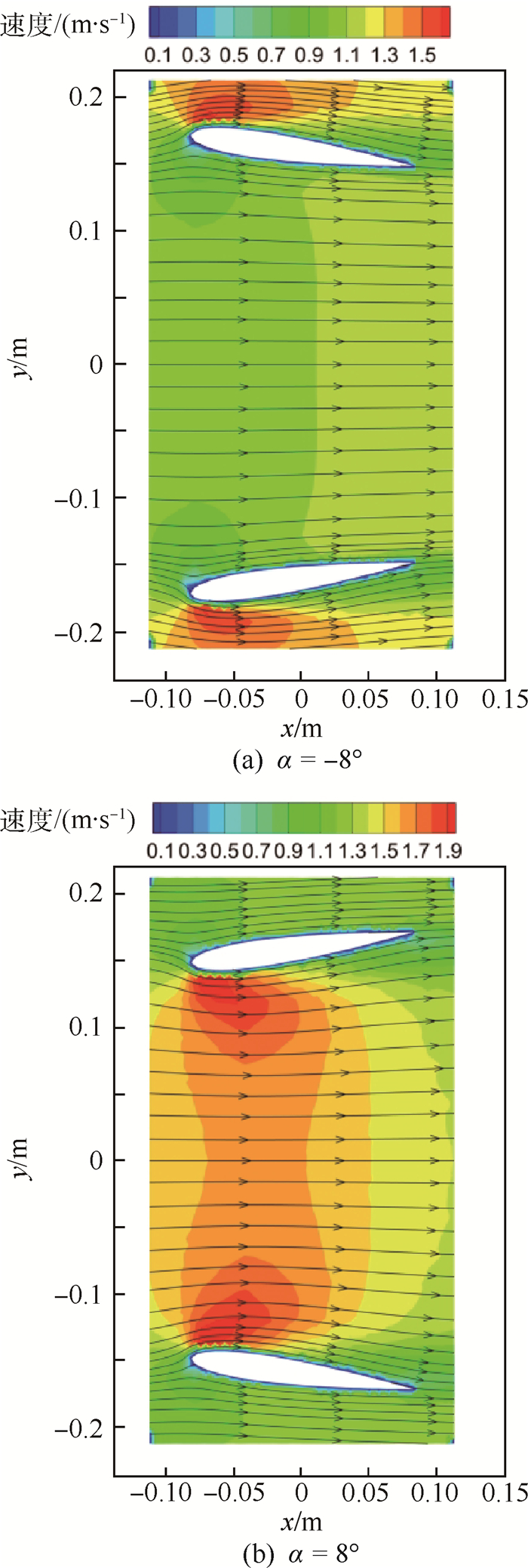
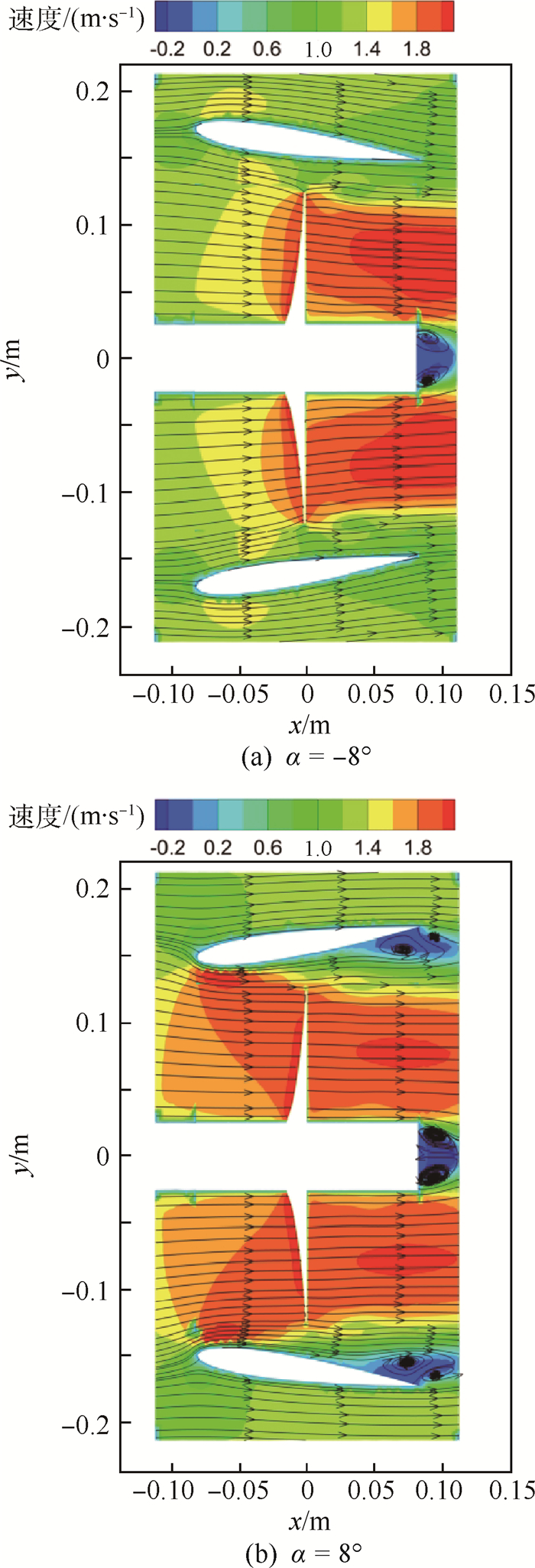
拱度 入口速度/(m·s-1) 中部速度/(m·s-1) 出口速度/(m·s-1) -0.75 t 1.314 474 1.808 438 1.267 485 0 1.193 269 1.366 831 1.190 093 0.75 t 1.047 939 0.909 793 1.023 590 表 5 改变攻角时不同截面轴向平均速度
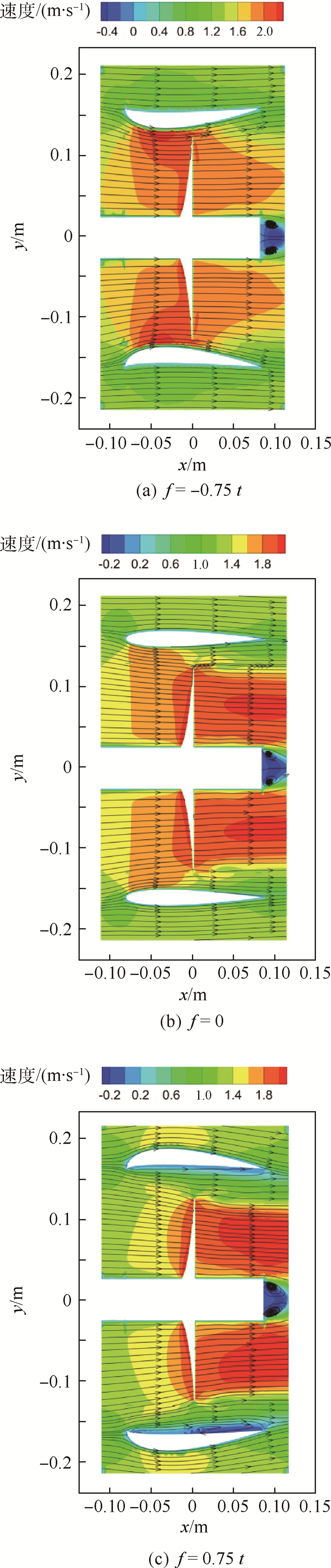
Table 5. Averaged axial velocity on different sections with varied attack angle
攻角/(°) 入口速度/(m·s-1) 中部速度/(m·s-1) 出口速度/(m·s-1) -8 0.750 235 1.086 298 1.117 297 0 1.193 269 1.366 831 1.190 093 8 1.682 453 1.472 395 1.130 847 -
[1] 马乾初, 汤忠谷, 张绍清.船舶附体节能的现状与前景[J].武汉造船, 1992(5):36-40. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHZC199205008.htmMA Q C, TANG Z G, ZHANG S Q.Present situation and prospect of energy-saving appendages[J].Wuhan Shipbuilding, 1992(5):36-40(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHZC199205008.htm [2] 王超, 黄胜, 常欣, 等.螺旋桨毂帽鳍水动力性能数值分析[J].船海工程, 2009, 38(6):20-24. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHZC200906007.htmWANG C, HUANG S, CHANG X, et al.The prediction of hydrodynamic performance of propeller boss cap fins[J].Ship & Ocean Engineering, 2009, 38(6):20-24(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHZC200906007.htm [3] 马骋, 蔡昊鹏, 钱正芳, 等.螺旋桨与毂帽鳍集成一体化优化设计方法研究[J].中国造船, 2014, 55(3):101-107. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZC201403011.htmMA C, CAI H P, QIAN Z F, et al.Research on integrated optimal design method of propeller and PBCF (propeller boss cap fins)[J].Shipbuilding of China, 2014, 55(3):101-107(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZC201403011.htm [4] 崔承根, 施能继.叶梢带端板螺旋桨的性能研究[J].华中科技大学学报(自然科学版), 1991(3):117-120. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HZLG199103026.htmCUI C G, SHI N J.An investigation on the performance of a screw with endplates at blade tips[J].Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 1991(3):117-120(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HZLG199103026.htm [5] 罗奕鑫, 崔承根.叶梢带端板螺旋桨的设计方法[J].造船技术, 1997(8):18-22. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZCJS199708007.htmLUO Y X, CUI C G.Design of a screw with endplates at blade tips[J].Journal of Marine Technology, 1997(8):18-22(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZCJS199708007.htm [6] 沈海龙.船体与节能附体及螺旋桨的非定常干扰研究[D].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工程大学, 2009.SHEN H L.Research on the unsteady interaction between ship hull and energy-saving appendage and propeller[D].Harbin:Harbin Engineering University, 2009(in Chinese). [7] 刘奕谦, 谢小龙.VLCC前置导管结构设计与强度分析[J].中国造船, 2013, 54(4):109-119.LIU Y Q, XIE X L.Structure design and stress assessment of wake equalizing duct for VLCC[J].Shipbuilding of China, 2013, 54(4):109-119(in Chinese). [8] 黄少锋, 黄国富, 杨奕.伴流补偿导管节能增效的CFD评估方法研究[J].中国造船, 2012, 53( http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZC2012S1003.htmA01):7-12.HUANG S F, HUANG G F, YANG Y.Numerical prediction for effectiveness of wake equalizing duct[J], Shipbuilding of China, 2012, 53(A01):7-12(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZC2012S1003.htm [9] FEITEN W, BAUER R, LAWITZKY G.Robust obstacle avoidance in unknown and cramped environments[C]//1994 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation.Piscataway, NJ:IEEE Press, 1994:2412-2417. [10] 叶元培, 周连第, 郑永敏.导管螺旋桨空泡性能系列试验研究[J].中国造船, 1980(4):27-41. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZC198004001.htmYE Y P, ZHOU L D, ZHENG Y M.Experimental investigations of the performance of ducted propeller series in cavitating conditions[J].Shipbuilding of China, 1980(4):27-41(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZC198004001.htm [11] 叶元培, 沈贻德.双体导管螺旋桨系列试验研究[J].中国造船, 1979(2):3-36. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZC197902000.htmYE Y P, SHEN Y D.A systematic study on the performance characteristics of propeller series with slotted nozzles[J].Shipbuilding of China, 1979(2):3-36(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZC197902000.htm [12] KHATIB M.Sensor-based motion control for mobile robots[D].Toulouse:LAAS-CNRS, 1996. [13] 韩宝玉, 熊鹰, 叶金铭.面元法预估导管螺旋桨定常性能的一种简便方法[J].船海工程, 2007, 36(3):42-45. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHZC200703014.htmHAN B Y, XIONG Y, YE J M.A simple method to predict the steady performance of ducted propeller with surface panel method[J].Ship & Ocean Engineering, 2007, 36(3):42-45(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHZC200703014.htm [14] 刘小龙, 王国强.导管螺旋桨定常性能预估的基于速度势的面元法[J].船舶力学, 2006, 10(3):26-35. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CBLX200603003.htmLIU X L, WANG G Q.A potential based panel method for prediction of steady performance of ducted propeller[J].Journal of Ship Mechanics, 2006, 10(3):26-35(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CBLX200603003.htm [15] 杨晨俊, 王国强.导管螺旋桨定常性能理论计算[J].上海交通大学学报, 1997, 31(11):36-39. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHJT711.006.htmYANG C J, WANG G Q.Theoretical prediction of the steady performance of ducted propellers[J].Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, 1997, 31(11):36-39(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHJT711.006.htm [16] KAWAKITA C.A surface panel method for ducted propellers with new wake model based on velocity measurements[J].Journal of the Society of Naval Architects of Japan, 1992(172):187-202. [17] KINNAS S, HSIN C Y, KEENAN D.A potential based panel method for the unsteady flow around open and ducted propellers[C]//18th ONR, 1990:21-38. [18] 解学参, 黄胜, 胡健, 等.导管桨内部流场的数值计算[J].哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2009, 30(1):7-12. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HEBG200901003.htmXIE X C, HUANG S, HU J, et al.Inner flow field calculations for ducted propellers[J].Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2009, 30(1):7-12(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HEBG200901003.htm [19] 胡健, 黄胜, 马骋, 等.影响导管桨内部流场的几个因素[J].天津大学学报, 2009, 42(4):340-344. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJDX200904012.htmHU J, HUANG S, MA C, et al.Several influence factors for the inner flow field of ducted propeller[J].Journal of Tianjin University, 2009, 42(4):340-344(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJDX200904012.htm [20] SANCHEZ-CAJA A, RAUTAHEIMO P, SIIKONEN T.Simulation of incompressible viscous flow around a ducted propeller using a RANS equation solver[C]//Proceedings of the 23rd Symposium on Naval Hydrodynamics.Washington, D.C.:National Academy Press, 2000:527-539. [21] PARK W G, JUNG Y R, KIM C K.Numerical flow analysis of single-stage ducted marine propulsor[J].Ocean Engineering, 2005, 32(10):1260-1277. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2004.10.022 [22] 崔立新.导管螺旋桨的水动力性能及噪声性能预报[D].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工程大学, 2013.CUI L X.Prediction of hydrodynamic performances and noise of ducted propeller[D].Harbin:Harbin Engineering University, 2013(in Chinese). -








 下载:
下载: