-
摘要:
航天、核电等复杂系统源发故障概率通常难于获取,由此导致基于最大后验概率准则的诊断方法失效。针对上述问题,从测试可靠性先验概率入手,提出了一种基于相关矩阵和灰色系统理论的故障诊断方法,通过对系统建立故障-测试相关矩阵,生成有排序的测试报警概率矩阵,并利用灰色关联度衡量测试结果向量与故障特征向量的接近度,实现了对多发故障的模糊诊断。实验结果表明,该方法在诊断指标权重调整、诊断精细度、重点关注故障检出等方面优势明显,诊断结论正确率满足实用需求。
Abstract:The failure probability is usually hard to collect for complicated systems in aerospace or nuclear power, which makes fault diagnosis based on Bayesian model inapplicable. By surveying this problem in test space, a novel multi-fault fuzzy diagnosis method based on dependency matrix and grey theory was proposed. A fault-testing dependency matrix was described first, and the fault alarm probability matrix with interest priority was developed. By calculating grey correlation degrees between test vectors and fault feature vectors, suspect faults can be located. Experimental results show that the proposed method can support diagnosis parameters' adjustment and report interested faults first, and the diagnosis conclusion has suitable accuracy, which can meet the practical demand.
-
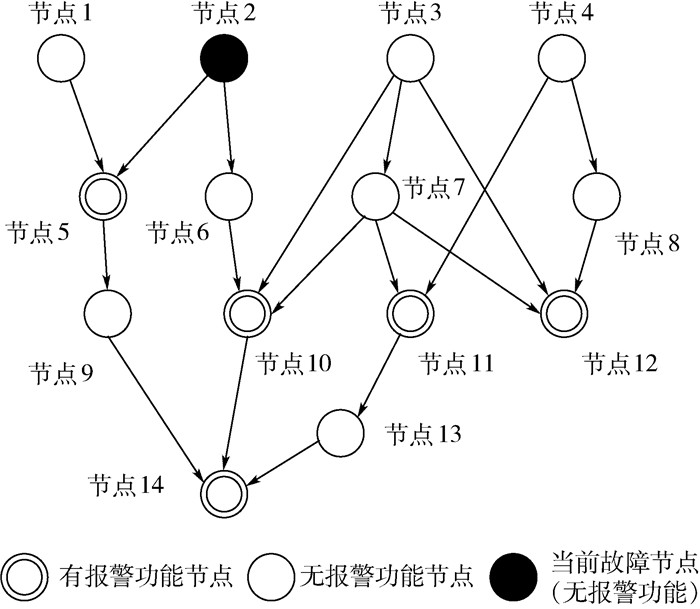
表 1 示例系统的DFT矩阵
Table 1. DFT matrix for sample system
故障节点 测试/报警节点号 1/5 2/10 3/11 4/12 5/14 1 1 0 0 0 1 2 1 1 0 0 1 3 0 1 1 1 1 4 0 0 1 1 1 5 1 0 0 0 1 6 0 1 0 0 1 7 0 1 1 1 1 8 0 0 0 1 0 9 0 0 0 0 1 10 0 1 0 0 1 11 0 0 1 0 1 12 0 0 0 1 0 13 0 0 0 0 1 14 0 0 0 0 1 表 2 示例系统的PAL矩阵
Table 2. PAL matrix of sample system
故障节点 测试/报警节点号 1/5 2/10 3/11 4/12 5/14 1 FDR11 FAR32 FAR33 FAR34 FDR15 2 FDR21 FDR22 FAR33 FAR34 FDR25 3 FAR31 FDR32 FDR33 FDR34 FDR35 4 FAR31 FAR32 FDR43 FDR44 FDR45 5 FDR51 FAR32 FAR33 FAR34 FDR55 6 FAR31 FDR62 FAR33 FAR34 FDR65 7 FAR31 FDR72 FDR73 FDR74 FDR75 8 FAR31 FAR32 FAR33 FDR84 FAR35 9 FAR31 FAR32 FAR33 FAR34 FDR95 10 FAR31 FDR10, 2 FAR33 FAR34 FDR10, 5 11 FAR31 FAR32 FDR11, 3 FAR34 FDR11, 5 12 FAR31 FAR32 FAR33 FDR12, 4 FAR35 13 FAR31 FAR32 FAR33 FAR34 FDR13, 5 14 FAR31 FAR32 FAR33 FAR34 FDR14, 5 表 3 示例系统的PEX矩阵
Table 3. PEX matrix of sample system
故障节点 测试/报警节点号 1/5 2/10 3/11 4/12 5/14 1 FDR11 FAR32 FAR33 FAR34 FDR15 1, 2 FDR11 FDR22 FAR33 FAR34 FDR15 1, 3 FDR11 FDR32 FDR33 FDR34 FDR15 1, 14 FDR11 FAR32 FAR33 FAR34 FDR15 2 FDR21 FDR22 FAR33 FAR34 FDR25 2, 3 FDR21 FDR22 FDR33 FDR34 FDR25 2, 14 FDR21 FDR22 FAR33 FAR34 FDR25 13 FAR31 FAR32 FAR33 FAR34 FDR13, 5 13, 14 FAR31 FAR32 FAR33 FAR34 FDR13, 5 14 FAR31 FAR32 FAR33 FAR34 FDR14, 5 表 4 阿波罗飞船发射前系统状态DFT矩阵
Table 4. System state matrix DFT before launch of Apollo spacecraft
故障节点 测试节点 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 2 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 3 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 4 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 5 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 6 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 7 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 8 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 9 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 10 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 表 5 理想输入条件下的诊断结果
Table 5. Diagnosis results under ideal input condition
故障状态 报警传感器 文献[8]方法诊断结论 本文方法诊断结论 输出排序 故障序号 诊断判据 判据结果 输出排序 故障序号 诊断判据 判据结果 1 4, 8, 10, 11, 12, 13 最可能 1 相似度 0.996 3 最可能 1 接近度 0.933 3 次可能 1, 2 相似度 0.906 9 次可能 1, 2 接近度 0.805 3 第三可能 1, 7 相似度 0.906 9 第三可能 1, 6 接近度 0.762 6 3 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12, 15 最可能 3 相似度 0.997 8 最可能 3 接近度 0.911 1 次可能 2, 3 相似度 0.946 1 次可能 2, 3 接近度 0.825 7 第三可能 3, 4 相似度 0.946 1 第三可能 3, 4 接近度 0.825 7 5 2, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 13, 14 最可能 5 相似度 0.998 3 最可能 5 接近度 0.900 0 次可能 4, 5 相似度 0.973 2 次可能 4, 5 接近度 0.857 3 第三可能 1, 5 相似度 0.951 4 第三可能 1, 5 接近度 0.814 6 7 1, 4, 5, 8, 11, 13, 15 最可能 7 相似度 0.997 2 最可能 7 接近度 1.000 0 次可能 1, 7 相似度 0.939 5 次可能 1, 7 接近度 0.997 1 第三可能 7, 9 相似度 0.939 5 第三可能 7, 9 接近度 0.997 1 9 1, 4, 5, 12, 14, 15 最可能 9 相似度 0.996 3 最可能 9 接近度 1.000 0 次可能 2, 9 相似度 0.931 1 次可能 2, 9 接近度 0.997 1 第三可能 4, 9 相似度 0.906 9 第三可能 4, 9 接近度 0.995 7 2, 4 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 11, 12, 14, 15 最可能 2, 4 相似度 0.998 3 最可能 2, 4 接近度 0.900 0 次可能 3, 8 相似度 0.932 5 次可能 2, 3 接近度 0.781 4 第三可能 2, 3 相似度 0.925 8 第三可能 3, 4 接近度 0.781 4 4, 6 2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 12, 13, 14, 15 最可能 4, 6 相似度 0.999 4 最可能 4, 6 接近度 0.866 7 次可能 5, 6 相似度 0.999 4 次可能 5, 6 接近度 0.866 7 第三可能 3, 5 相似度 0.980 0 第三可能 3, 5 接近度 0.824 0 6, 8 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15 最可能 6, 8 相似度 1.000 0 最可能 6, 8 接近度 1.000 0 次可能 3, 10 相似度 0.986 3 次可能 3, 10 接近度 0.998 6 第三可能 6, 10 相似度 0.986 3 第三可能 6, 10 接近度 0.998 6 8, 10 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 13, 14 最可能 8, 10 相似度 0.999 1 最可能 8, 10 接近度 1.000 0 次可能 5, 8 相似度 0.978 1 次可能 5, 8 接近度 0.998 6 第三可能 5, 10 相似度 0.978 1 第三可能 5, 10 接近度 0.998 6 1, 10 1, 2, 3, 4, 7, 8, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14 最可能 1, 10 相似度 0.999 1 最可能 1, 10 接近度 1.000 0 次可能 1, 8 相似度 0.959 6 次可能 1, 8 接近度 0.997 1 第三可能 6, 10 相似度 0.943 0 第三可能 2, 10 接近度 0.995 7 表 6 故障组合(1, 10) 的接近度量值与候选诊断结论示例
Table 6. Example of approximate measurement value and candidate diagnosis result of fault combination (1, 10)
接近度量值 候选诊断结论(疑似故障/故障组合) 0.995 7 2, 10 5, 8 5, 10 6, 10 10 -
[1] HASHTRUDIZAD S, KWONG R H, WONHAM W M.Fault diagnosis in discrete-event systems:Framework and model reduction[J].IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2003, 48(7):1199-1212. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2003.814099 [2] 田仲, 石君友.系统测试性设计分析和验证[M].北京:北京航空航天大学出版社, 2003:4-8.TIAN Z, SHI Z Y.System testability design analysis and verification[M].Beijing:Beihang University Press, 2003:4-8(in Chinese). [3] DE PAUL R.A logic modeling as a tool for testability[C]//Proceedings of IEEE International Automatic Testing Conference.Piscataway, NJ:IEEE Press, 1985:203-207. [4] DEB S, PATTIPATI K R, RAGHAVAN V.Multi-signal flow graphs:A novel approach for system testability analysis and fault diagnosis[J].IEEE Aerospace & Electronic Systems Magazine, 1995, 10(5):14-25. [5] RAO N S V.On parallel algorithms for single-fault diagnosis in fault propagate on graph systems[J].IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 1996, 7(12):1217-1223. doi: 10.1109/71.553268 [6] KOKAWA M, MIYAZAKI S, SHINGAI S.Fault location using digraph and inverse direction search with application[J].Automatic, 1983, 19(6):729-735. doi: 10.1016/0005-1098(83)90039-0 [7] 尹园威, 尚朝轩, 马彦恒, 等.层次测试性模型的评估方法[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2015, 41(1):90-95. http://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract13130.shtmlYIN Y W, SHANG C X, MA Y H, et al.Method of testability evaluation using hierarchical testability model[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2015, 41(1):90-95(in Chinese). http://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract13130.shtml [8] 连可, 黄建国, 龙兵.一种基于有向图模型的模糊多故障诊断算法[J].系统工程与电子技术, 2008, 30(3):568-571. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTYD200803047.htmLIAN K, HUANG J G, LONG B.Fuzzy multiple fault diagnosis algorithm based on digraph models[J].Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2008, 30(3):568-571(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTYD200803047.htm [9] 杨鹏, 邱静, 刘冠军.基于扩展的关联模型的测试性分析技术研究[J].系统工程与电子技术, 2008, 30(2):371-374. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTYD200802045.htmYANG P, QIU J, LIU G J.Research on extended dependency model-based testability analysis[J].Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2008, 30(2):371-374(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTYD200802045.htm [10] 梁爽, 于劲松, 唐荻音, 等.基于多信号流图与分支定界算法的故障诊断[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2016, 42(1):180-186. http://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract13689.shtmlLIANG S, YU J S, TANG D Y, et al.Research on fault diagnosis based on multi-signal flow graph and branch and bound algorithm[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2016, 42(1):180-186(in Chinese). http://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract13689.shtml [11] 方甲永, 肖明清, 王学奇, 等.测试不可靠条件下多故障诊断方法[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2011, 37(4):433-438. http://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract11938.shtmlFANG J Y, XIAO M Q, WANG X Q, et al.Multiple fault diagnosis method with unreliable test[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2011, 37(4):433-438(in Chinese). http://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract11938.shtml [12] 沈琳, 于劲松, 唐荻音, 等.图模型与学习算法结合的贝叶斯网络自动建模[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2016, 42(7):1486-1493. http://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract13478.shtmlSHEN L, YU J S, TANG D Y, et al.Automatic learning of Bayesian network structure using graph model and learning algorithm[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2016, 42(7):1486-1493(in Chinese). http://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract13478.shtml [13] SHAKERI M, RAGHAVAN V, PATTIPATI K R, et al.Sequential testing algorithms for multiple fault diagnosis[J].IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, 2000, 30(1):1-14. http://www.academia.edu/25189253/Sequential_testing_algorithms_for_multiple_fault_diagnosis [14] U.S.Department of Defense.Basic dependency modeling terminology[EB/OL].Washington, D.C.:Office of the Secretary of Defense, DoD, 2008(2008-06-16)[2016-09-02].http://www.testability.com/Reference/Glossaries.aspx?Glossary=DependencyModeling. [15] CHESSA S, SANTI P.Operative diagnosis of graph-based systems in multiple faults[J].IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, 2001, 31(2):112-119. doi: 10.1109/3468.911368 [16] DENG J L.Introduction to grey system theory[J].Journal of Grey System, 1989, 1(1):1-24. [17] 刘思峰, 杨英杰, 吴利丰, 等.灰色系统理论及其应用[M].北京:科学出版社, 2014:63-75.LIU S F, YANG Y J, WU L F, et al.The grey system theory and its application[M].Beijing:Science Press, 2014:63-75(in Chinese). [18] WOHL J G.Information automation and the Apollo program:A retrospective[J].IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, 1982, 12(4):469-478. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.1982.4308851 -







 下载:
下载: