-
摘要:
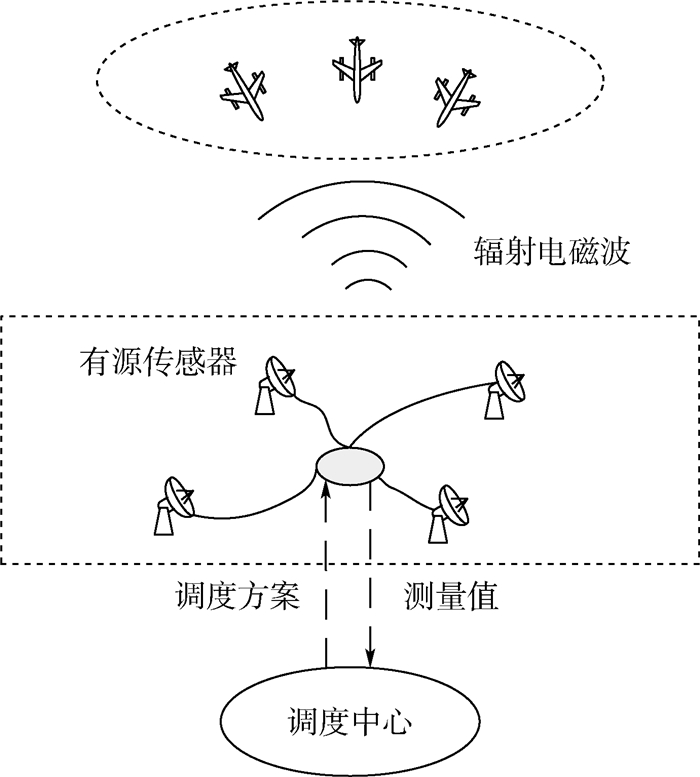
为了降低有源传感器在获得目标持续量测时被敌方截获的风险,提出一种多传感器协同跟踪与辐射控制的调度算法。该算法首先采用辐射度影响(ELI)衡量传感器辐射,将目标跟踪与辐射控制过程建立为部分可观马尔可夫决策(POMDP)过程。然后以隐马尔可夫模型(HMM)滤波器更新传感器辐射状态、推导长时辐射风险,以无迹卡尔曼滤波(UKF)更新目标状态、估计跟踪精度。最后考虑跟踪任务需求,构建精度约束下辐射控制的长时调度模型,并将该长时调度问题转化为决策树寻优问题,给出决策树节点次优下界值,采用改进分支定界技术(IB & B)快速求解最优调度序列。仿真结果验证了本文算法的有效性。
Abstract:Active sensors obtain the target continuous measurements that can be intercepted by enemy system. To reduce the interception risk, a scheduling algorithm for multi-sensor collaboration tracking and radiation control is proposed. Firstly, the sensor radiation is represented by the emission level impact (ELI) and the processes of target tracking and radiation control are formulated as a partially observable Markov decision process (POMDP). Secondly, the hidden Markov model (HMM) filter is utilized to update the sensor radiation state and derive the non-myopic radiation risk. Meanwhile, the target state is updated by the unscented Kalman filter (UKF) which is also used to evaluate the target tracking accuracy. Finally, considering the tracking task requirement, the non-myopic scheduling model of radiation control is set up with tracking accuracy constraint and the scheduling problem is translated to a decision tree optimization problem. Then, the suboptimal lower bound of each decision tree node is given and the optimal scheduling sequence is obtained by improved branch and bound (IB & B) technique. Simulation results prove the validity of the proposed algorithm.
-
表 1 算法搜索性能对比
Table 1. Comparison of search performance among algorithms
算法 H=2 H=3 H=4 H=5 节点打开数(占比) 最大存储节点 节点打开数(占比) 最大存储节点 节点打开数(占比) 最大存储节点 节点打开数(占比) 最大存储节点 ES 20 16 84 64 340 256 1 364 1 024 UCS 17(85%) 4 69(82%) 16 240(70%) 64 856(63%) 251 ε-UCS 17(85%) 4 62(74%) 16 177(52%) 64 533(39%) 251 IB & B 9(45%) 4 19(23%) 12 36(11%) 28 73(5%) 66 -
[1] LI Y, KRAKOW L W, CHONG E K P, et al.Approximate stochastic dynamic programming for sensor scheduling to track multiple targets[J].Digital Signal Processing, 2009, 19(6):978-989. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2007.05.004 [2] 刘钦, 刘铮.一种基于Rényi信息增量的机动目标协同跟踪算法[J].控制与决策, 2012, 27(9):1437-1440. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kzyjc201209030LIU Q, LIU Z.A method of maneuvering target collaboration tracking based on Rényi information gain[J].Control and Decision, 2012, 27(9):1437-1440(in Chinese). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kzyjc201209030 [3] 程洪玮, 王博, 安玮.一种基于信息决策树的低轨星座传感器调度算法[J].电子学报, 2010, 38(11):2630-2634. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dianzixb201011030CHENG H W, WANG B, AN W.A sensor scheduling method of LEO constellation based on information decision tree[J].Acta Electronica Sinica, 2010, 38(11):2630-2634(in Chinese). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dianzixb201011030 [4] CHHETRI A S, MORRELL D, PAPANDREOU S A.Nonmyopic sensor scheduling and its efficient implementation for target tracking applications[J].EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2006(1):1-18. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1ebee867e0057291d07b4f18a7c7dc1a&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [5] SUNBERG Z, CHAKRAVORTY S, ERWIN R S.Information space receding horizon control for multisensor tasking problem[J].IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2016, 46(6):1325-1336. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2015.2445744 [6] LIU B, JI C L, ZHANG Y Y, et al.Blending sensor scheduling strategy with particle filter to track a smart target[J].Wireless Sensor Network, 2009, 1:300-305. doi: 10.4236/wsn.2009.14037 [7] 吴巍, 王国宏, 双炜, 等.多机载平台多目标跟踪与辐射控制[J].系统工程与电子技术, 2012, 34(3):495-501. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95985X/201203/41194934.htmlWU W, WANG G H, SHUANG W, et al.Multi-airborne-platform multi-target tracking and radiation control technology[J].Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2012, 34(3):495-501(in Chinese). http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95985X/201203/41194934.html [8] 吴卫华, 江晶, 高岚.机载雷达辅助无源传感器对杂波环境下机动目标跟踪[J].控制与决策, 2015, 30(2):277-282. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kzyjc201502014WU W H, JIANG J, GAO L.Tracking maneuvering target in clutter with passive sensor aided by airborne radar[J].Control and Decision, 2015, 30(2):277-282(in Chinese). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kzyjc201502014 [9] ZHANG Z, SHAN G.UTS-based foresight optimization of sensor scheduling for low interception risk tracking[J].International Journal of Adaptive Control and Signal Processing, 2014, 28(10):921-931. doi: 10.1002/acs.v28.10 [10] ZHANG Z, SHAN G.Non-myopic sensor scheduling to track multiple reactive targets[J].IET Signal Processing, 2015, 9(1):37-47. doi: 10.1049/iet-spr.2013.0187 [11] SHE J, WANG F, ZHOU J.A novel sensor selection and power allocation algorithm for multiple-target tracking in an LPI radar network[J].Sensors, 2016, 16(12):2193-2206. doi: 10.3390/s16122193 [12] KRISHNAMURTHY V.Emission management for low probability intercept sensors in network centric warfare[J].IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2005, 41(1):133-151. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2005.1413752 [13] 单甘霖, 张子宁.面向目标跟踪的单平台主被动传感器长期调度[J].系统工程与电子技术, 2014, 36(3):458-463. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xtgcydzjs201403009SHAN G L, ZHANG Z N.Non-myopic sensor scheduling in a single platform for target tracking[J].Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2014, 36(3):458-463(in Chinese). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xtgcydzjs201403009 [14] SHAN G, ZHANG Z.Non-myopic sensor scheduling for low radiation risk tracking using mixed POMDP[J].Transactions of the Institute of Measurement and Control, 2017, 39(2):230-243. doi: 10.1177/0142331215604211 [15] KALANDROS M.Covariance control for multisensor systems[J].IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2002, 38(4):1138-1157. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2002.1145739 [16] SONG H, XIAO M, XIAO J, et al.A POMDP approach for scheduling the usage of airborne electronic countermeasures in air operations[J].Aerospace Science and Technology, 2016, 48:86-93. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2015.11.001 [17] ROY A, MITRA D.Unscented-Kalman-filter-based multitarget tracking algorithms for airborne surveillance application[J].Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2016, 39(9):1949-1966. doi: 10.2514/1.G001587 [18] HUBER M F.Optimal pruning for multi-step sensor scheduling[J].IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2012, 57(5):1338-1343. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2011.2175070 [19] 宋海方, 肖明清, 陈游, 等.基于MDP的战机对抗导弹措施优化算法[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2017, 43(5):942-950. http://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract14298.shtmlSONG H F, XIAO M Q, CHEN Y, et al.MDP method for optimization of fighter aircraft's countermeasures against missile[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2017, 43(5):942-950(in Chinese). http://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract14298.shtml -







 下载:
下载: