Localized multi-kernel diagnosis model for avionics based on affinity propagation clustering
-
摘要:
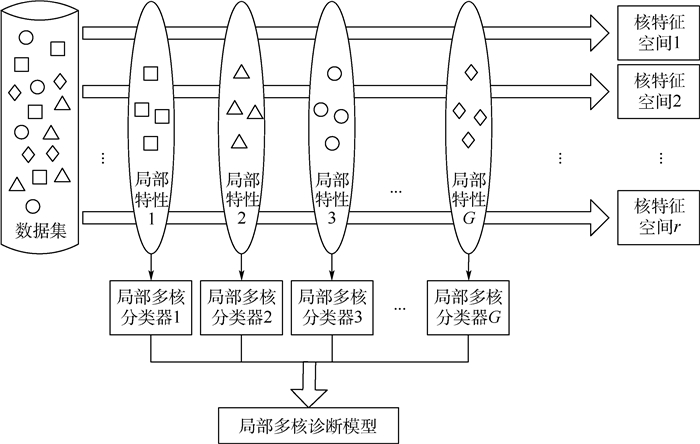
针对小样本条件下,航空电子部件功能模块故障诊断精度不高的问题,将局部多核学习(LMKL)算法的多分辨率解释与局部特征自适应表示能力和超限学习机(ELM)运算高效的特点相结合,提出一种新的局部聚类MK-ELM(LCMKELM)诊断模型。通过引入近邻传播(AP)聚类,在挖掘训练样本局部特征信息的同时,有效约减了局部算法的计算复杂性,避免了过学习问题的出现;通过分别分析输入空间与特征空间的聚类特征,构造了相应的2种选通函数
M 1、M 2,以优化选通函数的模型参数取代优化局部权重,有效解决了核超限学习机(KELM)的对偶优化形式关于局部权重二次非凸的问题。将本文模型应用于某型机旋转变压器激励发生电路功能模块故障诊断,结果表明:相比于4种常用的多核诊断算法,模型在实现低漏警、低虚警的同时,采用M 1选通函数的诊断算法将诊断精度平均提升了3.80%,采用M 2选通函数的诊断算法将诊断精度平均提升了5.98%。同时,模型在实现与流行的LMKL算法相近的训练时间的同时,测试时间更短。Abstract:In consideration of the low diagnosis accuracy for avionics functional module fault, a new offline localized clustering multi-kernel extreme learning machine (LCMKELM) diagnosis model is proposed in this paper by combining the capabilities of multi-resolution interpretation and local feature self-adaptive representation from localized multi-kernel learning (LMKL) with the characteristic of high-performance operation from extreme learning machine (ELM). In order to avoid overfitting issue, affinity propagation (AP) clustering is used to make full use of the underlying localities in the training data and effectively reduce the computational complexity. Considering that the updating of localized kernel weights in dual optimization form of kernel ELM (KELM)is a difficult quadratic nonconvex problem, gating function
M 1 andM 2 are respectively constructed to approximate localized weights by analyzing the clustering characteristics in input space and feature space. The proposed method is applied to actual fault diagnosis task of rotary transformer excitation generating circuit, and the experimental results show that the proposed method has the lower false alarm rate and missing alarm rate in comparison with four state-of-the-art multi-kernel learning algorithms, and meanwhile the diagnosis accuracy is averagely increased by 3.80% whenM 1 gating model is used, and increased by 5.98% whenM 2 gating model is used. Moreover, compared with canonical LMKL algorithms, the proposed method obtains similar training time cost, but it has less testing time cost. -
表 1 Gauss 4数据集分类结果比较
Table 1. Comparison of classification results on Gauss 4 dataset
评价指标 M1-LCMKELM M2-LCMKELM SimpleMKL 分类精度/% 90.500 0±0.684 7 90.850 0±0.602 1 89.350 0±1.206 8 F1值 0.904 9±0.006 8 0.908 5±0.006 1 0.895 8±0.012 4 G-mean 0.904 6±0.006 9 0.908 2±0.006 2 0.893 2±0.011 9 表 2 不同训练样本数量下分类精度比较
Table 2. Comparison of classification accuracy with different sizes of training sample
训练样本数量 分类精度/% M1-LCMKELM M2-LCMKELM 16 81.8±1.923 5 82.6±1.673 3 32 85.2±1.483 2 86.2±1.483 2 48 86.4±2.073 6 86.6±1.516 5 64 86.4±1.516 5 86.6±1.673 3 144 87.2±1.095 4 87.4±1.140 2 400 87.0±1.870 8 87.2±1.303 8 600 87.8±1.095 4 88.2±0.836 7 800 88.0±0.707 1 88.6±0.894 4 表 3 诊断数据聚类结果
Table 3. Clustering results of diagnosis data
聚类 聚类中心 类内元素 1 5 {2, 4, 5, 6, 9, 11, 15, 18, 34, 35} 2 12 {8, 10, 12, 13, 20, 25} 3 17 {1, 3, 7, 17} 4 23 {16, 23, 33} 5 26 {14, 19, 26, 29, 32} 6 30 {24, 30, 31, 41} 7 40 {21, 22, 28, 37, 38, 40, 42, 45} 8 43 {27, 36, 39, 43, 44, 46} 表 4 不同算法诊断结果比较
Table 4. Comparison of diagnosis results based on different algorithms
算法 漏警率/
%虚警率/
%训练诊断精度/% 测试诊断精度/% SimpleMKL 2.857 1 0 100 91.304 3 GMKL-SVM 0 0 100 93.478 3 LMKL-softmax 0 5.405 4 100 89.130 4 LMKL-sigmoid 2.857 1 0 100 93.478 3 M1-LCMKELM 0 0 100 95.652 2 M2-LCMKELM 0 0 100 97.826 1 表 5 不同算法F1值和G-mean比较
Table 5. Comparison of F1 score and G-mean based on different algorithms
算法 F1值 G-mean SimpleMKL 0.898 7 0.882 6 GMKL-SVM 0.920 8 0.910 3 LMKL-softamx 0.885 5 0.874 5 LMKL-sigmoid 0.924 3 0.910 3 M1-LCMKELM 0.944 4 0.934 9 M2-LCMKELM 0.972 9 0.969 6 表 6 不同算法诊断时间花费比较
Table 6. Comparison of diagnosis time cost based on different algorithms
算法 训练时间/s 测试时间/s SimpleMKL 0.991 7±0.082 9 0.201 8±0.045 1 GMKL-SVM 0.832 5±0.036 0 0.167 9±0.008 2 LMKL-softamx 1.493 4±0.062 5 0.173 5±0.011 1 LMKL-sigmoid 2.715 9±0.129 2 0.176 9±0.015 7 M1-LCMKELM 2.497 9±0.213 7 0.129 9±0.005 9 M2-LCMKELM 1.789 7±0.201 4 0.152 1±0.016 7 -
[1] LUO H, WANG Y R, LIN H, et al.Module level fault diagnosis for analog circuits based on system identification and genetic algorithm[J].Measurement, 2012, 45(4):769-777. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2011.12.010 [2] 孙伟超, 李文海, 李文峰.融合粗糙集与D-S证据理论的航空装备故障诊断[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2015, 41(10):1902-1909. http://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract13502.shtmlSUN W C, LI W H, LI W F.Avionic devices fault diagnosis based on fusion method of rough set and D-S theory[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2015, 41(10):1902-1909(in Chinese). http://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract13502.shtml [3] KNVPPEL T, BLANKE M, ØSTERGAARD J.Fault diagnosis for electrical distribution systems using structural analysis[J].International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2014, 24(8-9):1446-1465. doi: 10.1002/rnc.v24.8-9 [4] JAMIL T, MOHAMMED I.Simulation of VICTOR algorithm for fault diagnosis of digital circuits[J].International Journal of Computer Theory and Engineering, 2015, 7(2):103-107. doi: 10.7763/IJCTE.2015.V7.939 [5] DAI X W, GAO Z W.From model, signal to knowledge:A data-driven perspective of fault detection and diagnosis[J].IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2013, 9(4):2226-2238. doi: 10.1109/TII.2013.2243743 [6] 蒋栋年, 李炜.基于自适应阈值的粒子滤波非线性系统故障诊断[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2016, 42(10):2099-2106. http://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract13736.shtmlJIANG D N, LI W.Fault diagnosis of particle filter nonlinear systems based on adaptive threshold[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2016, 42(10):2099-2106(in Chinese). http://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract13736.shtml [7] GAO Z W, CECATI C, DING S X.A survey of fault diagnosis and fault tolerant techniques-Part Ⅰ:Fault diagnosis with model-based and signal-based approaches[J].IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2015, 62(6):3757-3767. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2015.2417501 [8] SAHRI Z B, YUSOF R B.Support vector machine-based fault diagnosis of power transformer using k nearest-neighbor imputed DGA dataset[J].Journal of Computer and Communications, 2014, 2(9):22-31. doi: 10.4236/jcc.2014.29004 [9] YIN G, ZHANG Y T, LI Z N, et al.Online fault diagnosis method based on incremental support vector data description and extreme learning machine with incremental output structure[J].Neurocomputing, 2014, 128:224-231. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2013.01.061 [10] GÖNEN M, ALPAYDIN E.Multiple kernel learning algorithms[J].Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2011, 12:2211-2268. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zdhxb201410022 [11] YE F M, ZHANG Z B, CHAKRABARTY K, et al.Board-level functional fault diagnosis using multikernel support vector machines and incremental learning[J].IEEE Transactions on Computer-aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2014, 33(2):279-290. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2013.2287184 [12] LI Y X, REN C Q, BO J Y, et al.The application of GMKL algorithm to fault diagnosis of local area network[J].Journal of Networks, 2014, 9(3):747-753. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=Doaj000003637841 [13] RAKOTOMAMONJY A, BACH F R, CANU S, et al.SimpleMKL[J].Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2008, 9:2491-2521. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gcsj201602012 [14] HAN Y N, YANG K, MA Y L, et al.Localized multiple kernel learning via sample-wise alternating optimization[J].IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2014, 44(1):137-147. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2013.2248710 [15] SONG Y, ZHENG Y T, TANG S, et al.Localized multiple kernel learning for realistic human action recognition in videos[J].IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2011, 21(9):1193-1202. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2011.2130230 [16] GÖNEN M, ALPAYDIN E.Localized algorithms for multiple kernel learning[J].Pattern Recognition, 2013, 46(3):795-807. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2012.09.002 [17] WANG X M, HUANG Z X, DU Y J.Improving localized multiple kernel learning via radius-margin bound[J].Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2017, 2017:4579214. doi: 10.1155/2017/4579214 [18] HAN Y N, LIU G Z.Probability-confidence-kernel-based localized multiple kernel learning with Lp norm[J].IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics-Part B:Cybernetics, 2012, 42(3):827-837. doi: 10.1109/TSMCB.2011.2179291 [19] HAN Y N, YANG K D, LIU G Z.Lp norm localized multiple kernel learning via semi-definite programming[J].IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2012, 19(10):688-691. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2012.2212431 [20] FREY B J, DUECK D.Clustering by passing messages between data points[J].Science, 2007, 315(5814):972-976. doi: 10.1126/science.1136800 [21] NAPOLEON D, BASKAR G, PAVALAKODI S.An efficient clustering technique for message passing between data points using affinity propagation[J].International Journal on Computer Science and Engineering, 2011, 3(1):8-13. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_8f6b58a2aefdd722217c806bcb9766ca [22] SOKOLOVA M, LAPALME G.A systematic analysis of performance measures for classification tasks[J].Information Processing and Management, 2009, 45(4):427-437. doi: 10.1016/j.ipm.2009.03.002 [23] PHOUNGPHOL P, ZHANG Y Q, ZHAO Y C.Robust multiclass classification for learning from imbalanced biomedical data[J].Tsinghua Science and Technology, 2012, 17(6):619-628. doi: 10.1109/TST.2012.6374363 -







 下载:
下载: