-
摘要:
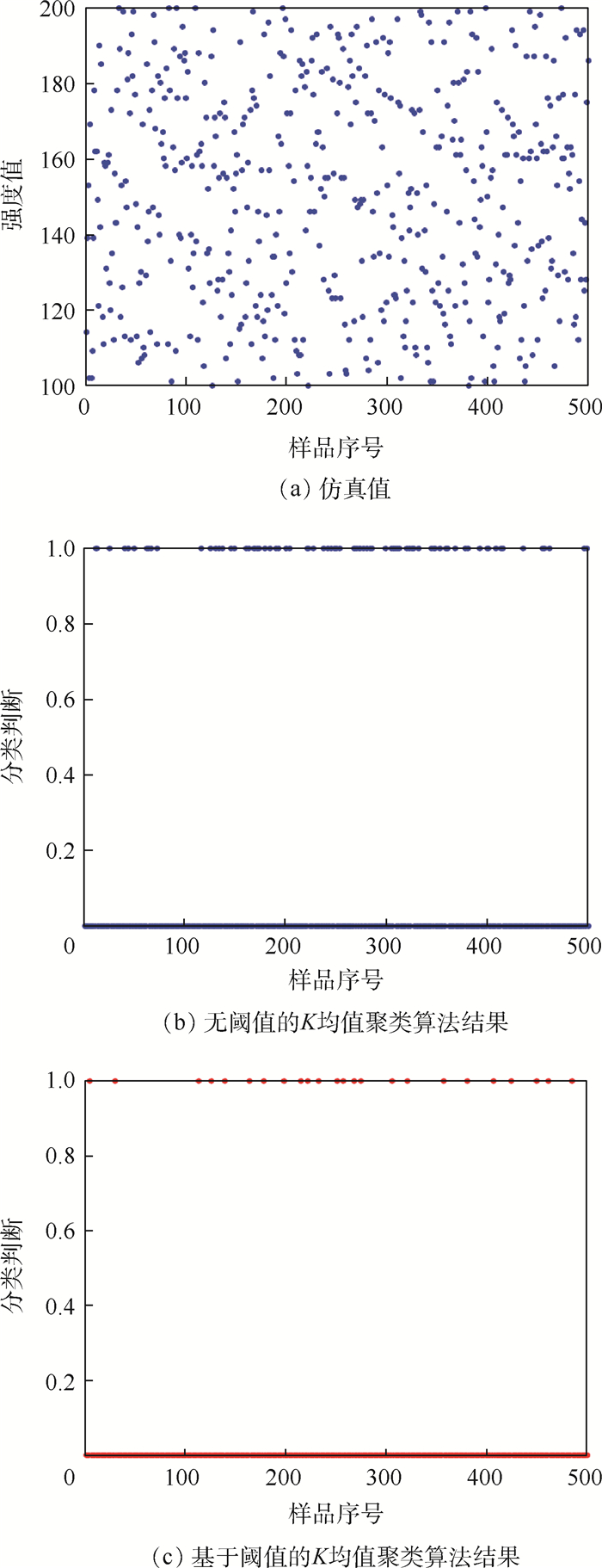
针对同一距离不同目标的激光雷达全波形回波数据聚类准确率低的问题,在分析
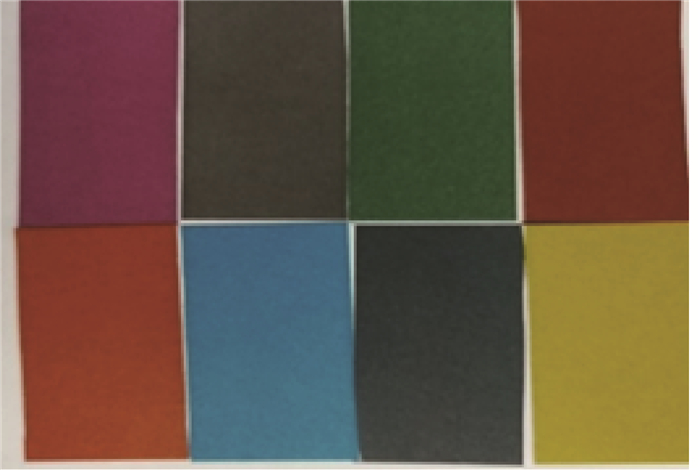
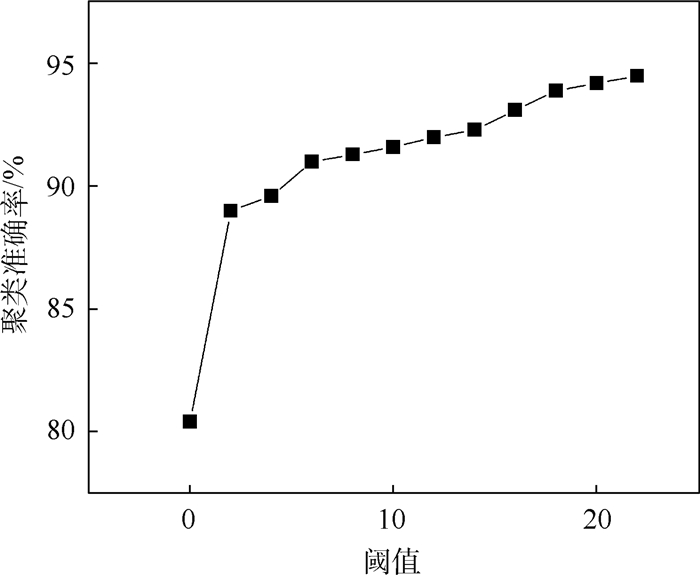
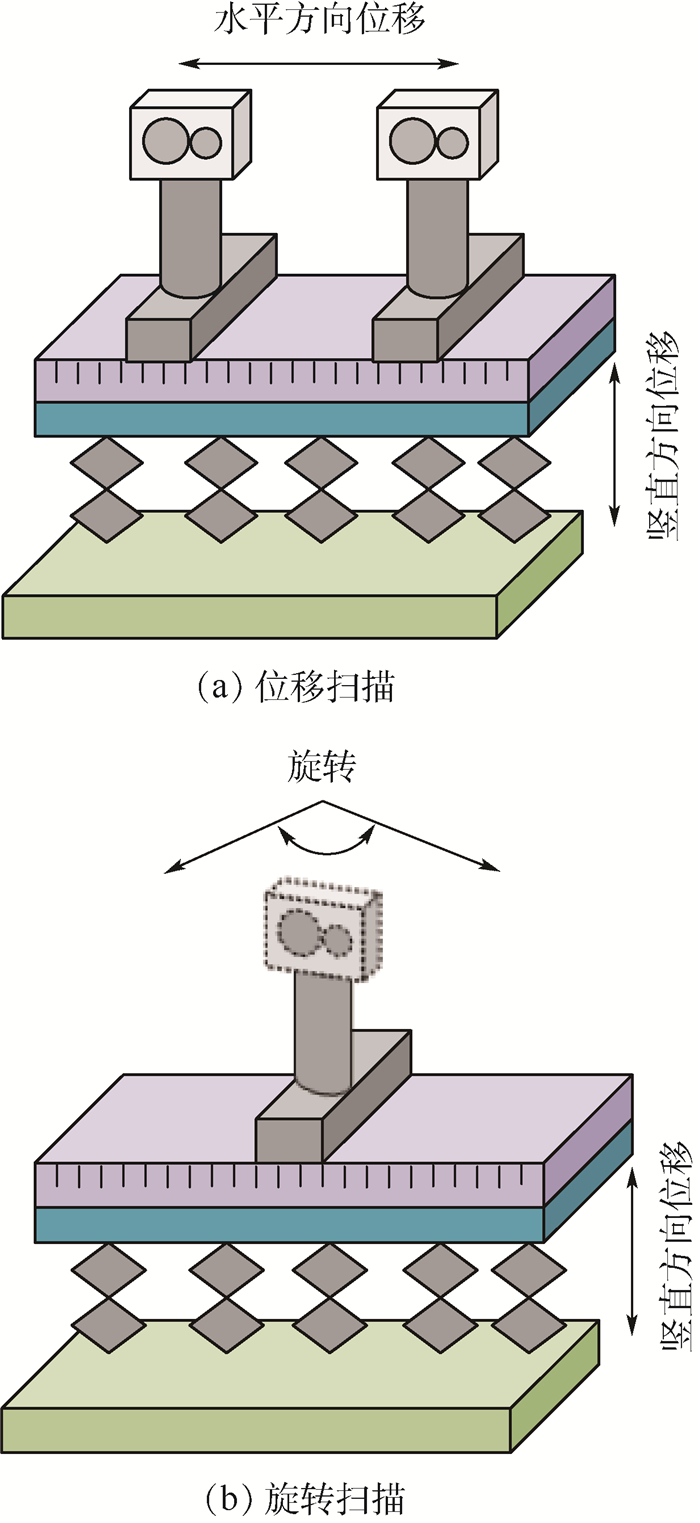
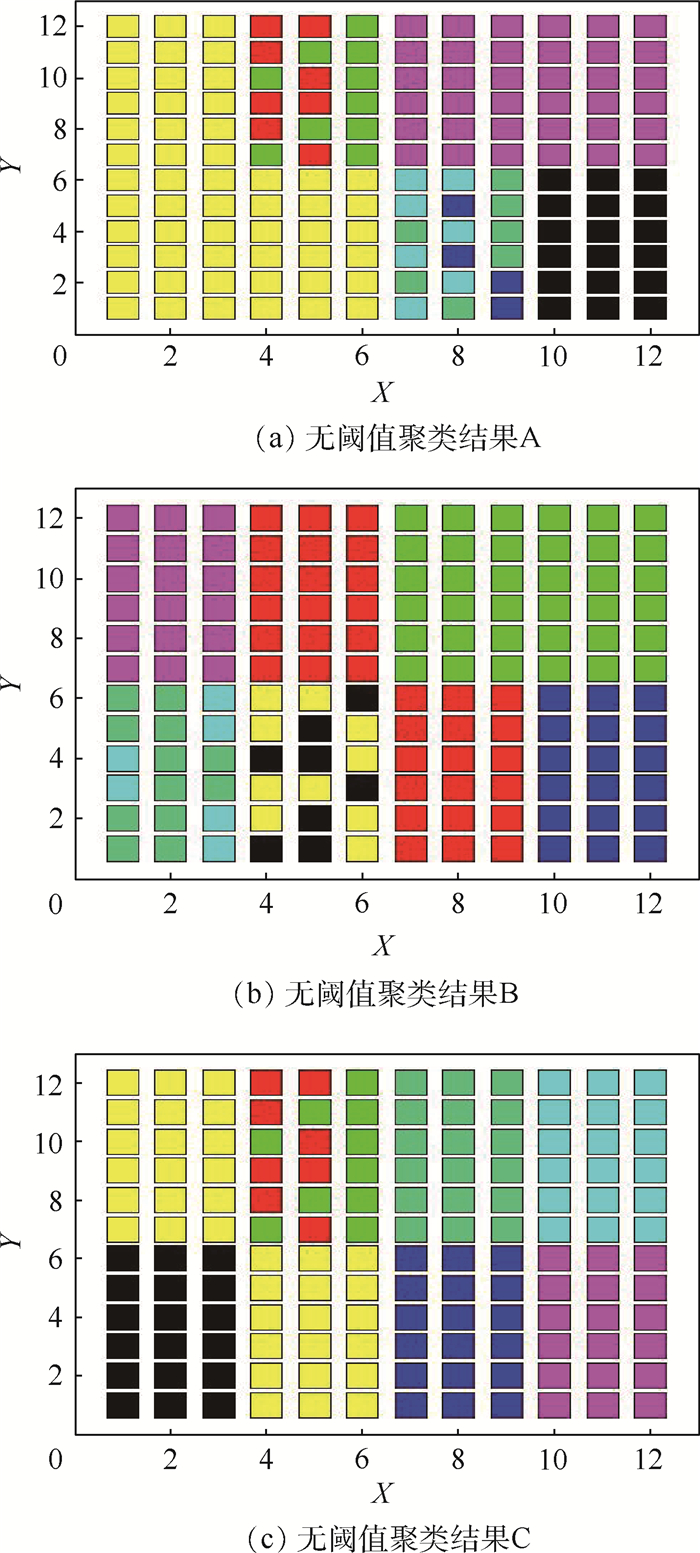
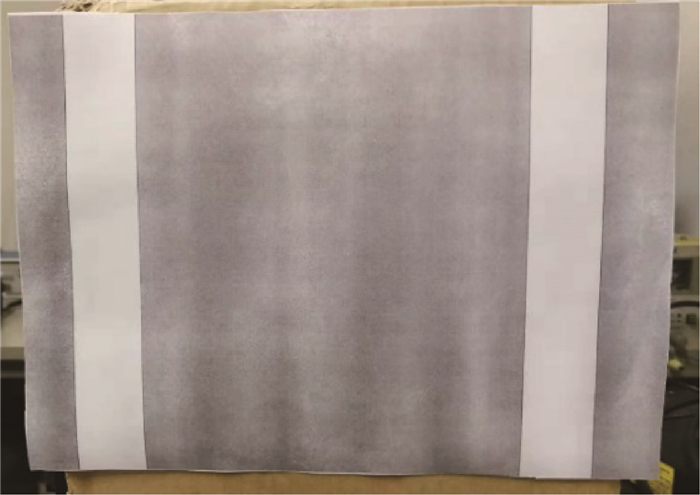
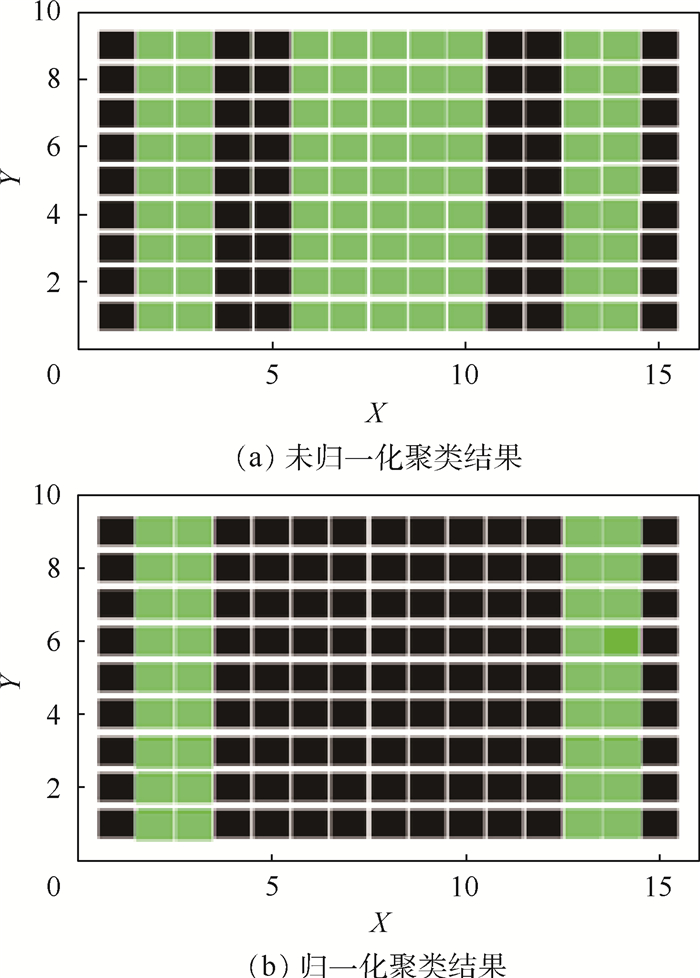
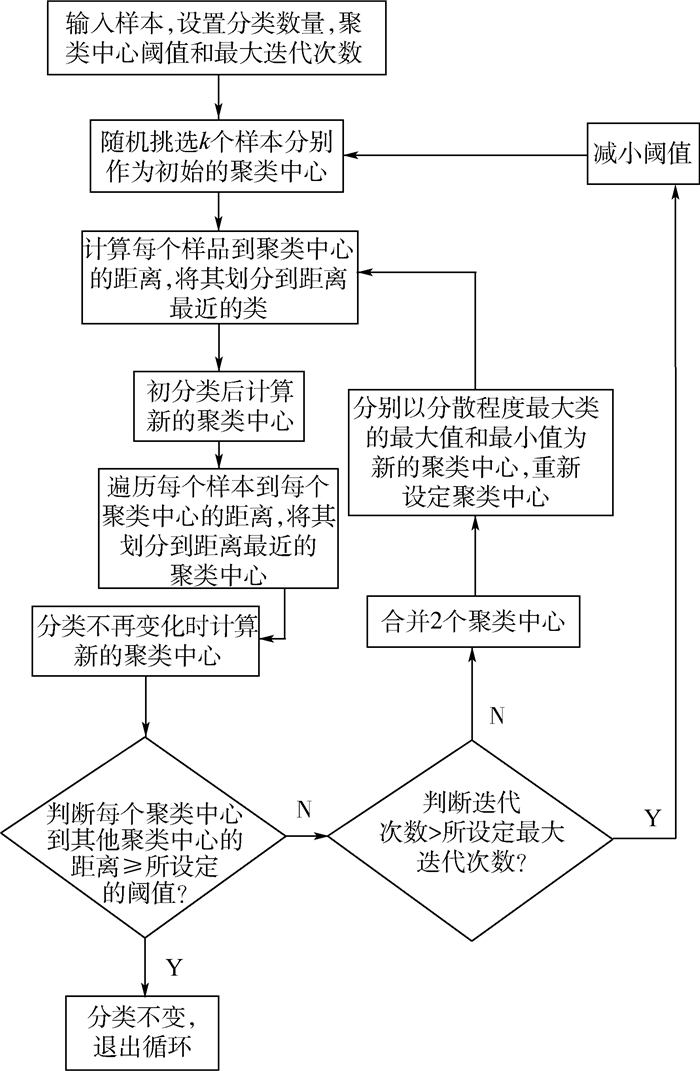
K 均值聚类算法原理的基础上,提出了一种基于阈值的K 均值聚类算法。首先,利用强度信息对距离信息进行标定,使用强度信息作为特征进行聚类以区分同距离的不同目标。然后,利用阈值限定聚类中心间的最小距离,提高聚类准确率。最后,搭建了扫描验证平台进行平移和旋转成像,对算法有效性进行验证。通过不同颜色目标和模拟道路回波数据聚类实验表明,在不同阈值的情况下,提出的基于阈值的K 均值聚类算法的聚类准确率均在90%以上,相比于无阈值的K 均值聚类算法准确率提升10%以上,能够有效进行目标聚类和模拟道路提取。Abstract:For this question of low clustering accuracy problem in LiDAR full-waveform echo data with different targets at the same distance, a threshold-based
K -means clustering algorithm was proposed based on the analysis ofK -means clustering algorithm. Firstly, The distance information was calibrated using the intensity information, and the intensity information was used as a feature to distinguish different targets at the same distance by clustering. Secondly, the threshold was used to define the minimum distance between clustering centers to improve the clustering accuracy. Finally, the scanning verification platform was built for translation and rotation imaging to verify the effectiveness of the algorithm. The clustering experiments of different color targets and simulated road echo data show that the clustering accuracy rate of threshold-basedK -means clustering algorithm is above 90% under different thresholds, and increases more than 10% compared with the threshold-freeK -means clustering algorithm, which can effectively perform target clustering and simulation road extraction.-
Key words:
- LiDAR /
- full waveform /
- threshold /
- K-means algorithm /
- classification accuracy
-
[1] XU W, CHEN Q, GU G H.Research on laser ranging system based on time delay estimation[C]//Symposium on Photonics & Optoelectronics.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2011: 1-3. [2] 王金虎, 李传荣, 周梅.机载全波形激光雷达数据处理及其应用[J].国外电子测量技术, 2012, 31(6):71-75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8978.2012.06.020WANG J H, LI C R, ZHOU M.Data processing and application of airborne full waveform LiDAR[J].Journal of Foreign Electronic Measurement Technology, 2012, 31(6):71-75(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8978.2012.06.020 [3] WARDG J.Measuring and modeling anisotropic reflection[J].ACM SIGGRAPH Computer Graphics, 1992, 26(2):265-272. doi: 10.1145/142920.134078 [4] MILIARESIS G, KOKKAS N.Segmentation and object-based classification for the extraction of the building class from LIDAR DEMs[J].Computers & Geosciences, 2007, 33:1076-1087. [5] SANDEEP G, HOLGER W, BARBARA K.Comparative analysis of clustering-based approaches for 3-D single tree detection using airborne fullwave LiDAR data[J].Remote Sensing, 2010, 2(4):968-989. doi: 10.3390/rs2040968 [6] SAMPATH A, SHAN J.Segmentation and reconstruction of polyhedral building roofs from aerial LiDAR point clouds[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(3):1554-1567. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2030180 [7] 龚亮, 张永生, 李正国, 等.基于强度信息聚类的机载LiDAR点云道路提取[J].测绘通报, 2011(9):15-17.GONG L, ZHANG Y S, LI Z G, et al.Airborne LiDAR point cloud road extraction based on intensity information clustering[J].Journal of Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2011(9):15-17(in Chinese). [8] KONG D, XU L J, LI X L, et al.K-plane-based classification of airborne LiDAR data for accurate building roof measurement[J].IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation & Measurement, 2014, 63(5):1200-1214. [9] DÍAZ-VILARIÑO L, GONZÁLEZ-JORGE H, BUENO M, et al.Automatic classification of urban pavements using mobile LiDAR data and roughness descriptors[J].Construction and Building Materials, 2015, 102(1):208-215. [10] KASHANI A G, GRAETTINGER A J.Cluster-based roof covering damage detection in ground-based LiDAR data[J].Automation in Construction, 2015, 58:19-27. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2015.07.007 [11] CHEN J, ZHU H, LI X.Automatic extraction of discontinuity orientation from rock mass surface 3D point cloud[J].Computers & Geosciences, 2016, 95:18-31. [12] CHUYEN N, MICHAEL S, PHILIPPE T, et al. Unsupervised clustering method for complexity reduction of terrestrial LiDAR data in marshes[J].Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(1):133-154. doi: 10.3390/rs10010133 [13] RENATO C D S, MAURICIO G, VILMA M T.Classification of LiDAR data over building roofs using k means and principal component analysis[J].Boletim de Ciênccas Geodésicas, 2018, 24(1):69-84. doi: 10.1590/s1982-21702018000100006 [14] NIMA E, CRAIG G, CARLOS F D J.Classification of airborne multispectral LiDAR point clouds for land cover mapping[J].IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(6):2068-2078. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2018.2835483 [15] LI X, LIANG Y, XU L.Bidirectional reflectance distribution function based surface modeling of non-Lambertian using intensity data of light detection and ranging[J].Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 2014, 31(9):2055. doi: 10.1364/JOSAA.31.002055 -







 下载:
下载: