Optimal maneuver penetration strategy based on power series solution of miss distance
-
摘要:
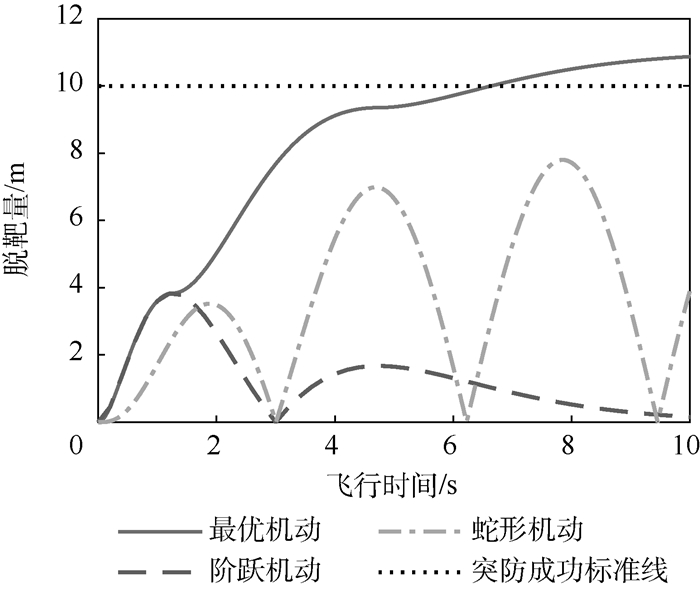
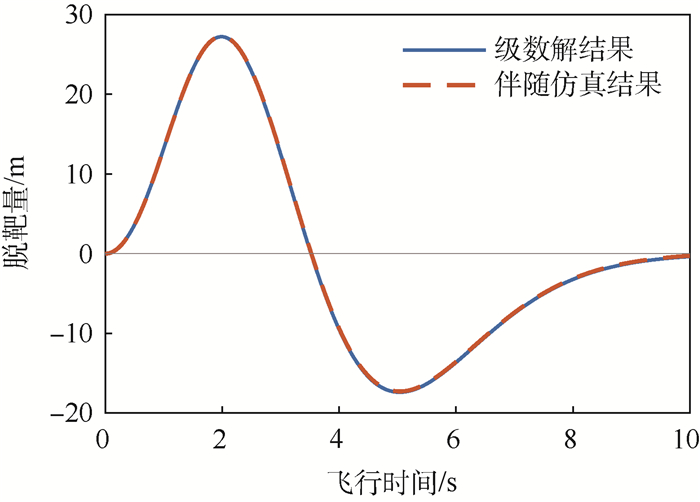
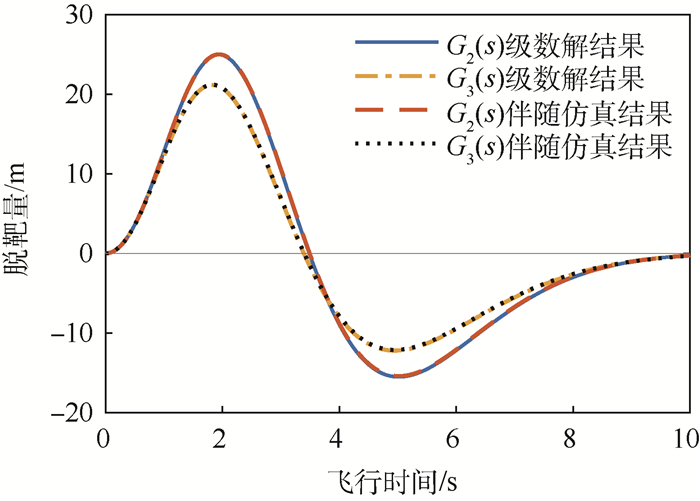
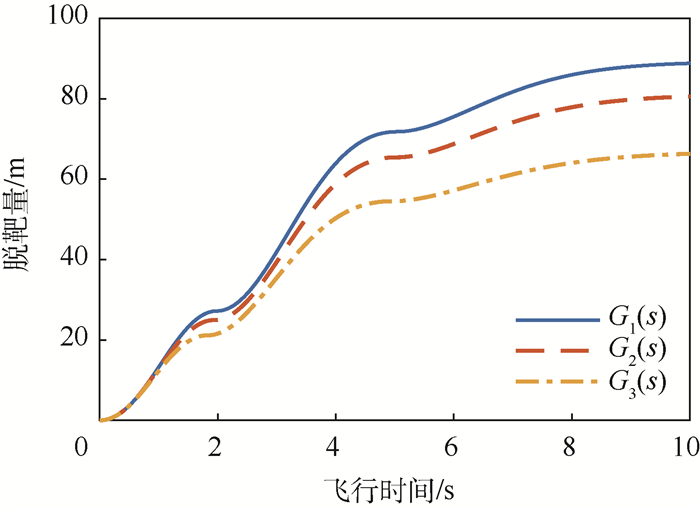
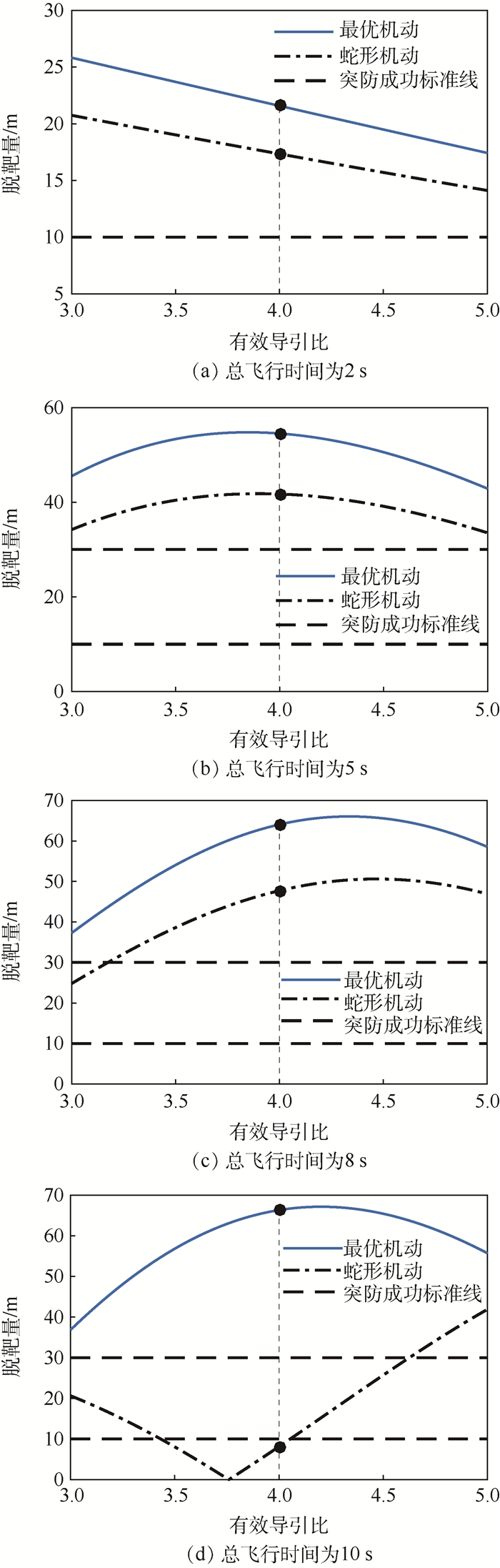
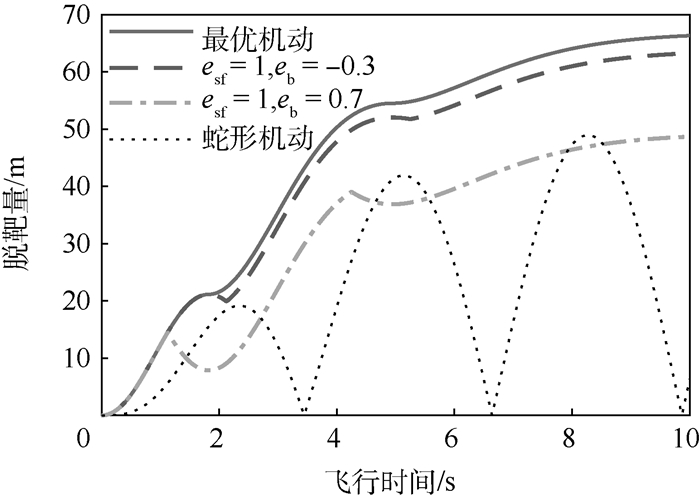
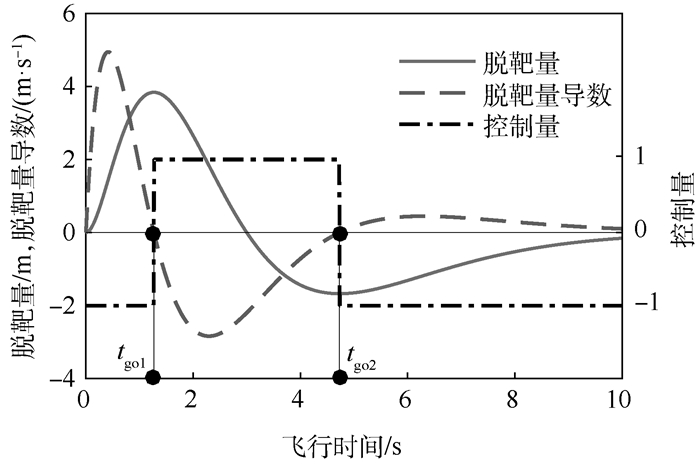
针对比例导引控制的拦截弹,建立高阶制导系统状态空间模型,基于脱靶量级数解公式,对目标最优机动突防策略及其影响因素进行了研究。首先,针对拦截弹的制导系统为线性一阶、线性高阶时,目标最优机动突防效果进行了仿真分析,结果表明拦截弹弹体模型的准确性对突防效果存在影响,高阶系统对应脱靶量更大且效果更真实;将结果与一次阶跃机动和蛇形机动对比,发现最优机动突防效果最佳。然后,建立弹目运动的二维非线性模型,仿真得出目标最优机动产生的脱靶量曲线与线性系统吻合度较高,线性模型选取合适。最后,研究了有效导引比和剩余飞行时间估计误差对最优机动突防效果产生的影响,结果表明有效导引比估计误差对最优机动突防效果影响不大,剩余飞行时间估计误差则会使目标最优机动突防性能大幅下降,甚至部分情况比蛇形机动突防效果差。
Abstract:Aimed at the proportional guidance missile, the state space model of high-order guidance system was established, and the optimal maneuver penetration strategy and influencing factors were studied based on power series solution of miss distance. First, when the missile guidance system was linear first-order and high-order, the simulations of optimal target maneuver penetration were carried out. The results show that the accuracy of the missile guidance model has an impact on the penetration effect, and the high order has larger miss distance and is more realistic. Then, the results were compared with step maneuver and weaving maneuver, the optimal maneuver penetration effect is the best. Furthermore, a two-dimensional nonlinear missile-target engagement model was established, and the simulation shows that the miss distance curve of optimal maneuver is highly identical with the linear system, and the linear system is selected appropriately. Finally, the impacts of effective navigation ratio and time-to-go estimation error on the optimal maneuver penetration effect were studied. The effective navigation ratio estimation error has little effect on the optimal maneuver penetration effect, the time-to-go estimation error makes the target optimal maneuver penetration performance decline greatly, and in some cases it is even worse than the weaving maneuver penetration effect.
-
表 1 一阶系统最优控制切换时刻及最大脱靶量
Table 1. Optimal control switching time and maximum miss distance of first-order system
N tgo/s w(tgo)/m Mmax/m 3 2.00 7.96 15.85 4 1.27 3.84 10.87 4.73 -1.67 5 0.94 2.27 8.45 3.31 -1.73 7.76 0.32 表 2 传递函数系数
Table 2. Transfer function coefficient
传递函数 系数取值 G2(s) α1=0.066 7, α2=0.133, α3=0.2, α4=0.267, α5=0.333 G3(s) α1=0.1, α2=0.2, α3=0.56, β=0.1, ξ=0.7 表 3 弹目仿真参数
Table 3. Simulation parameter of missile and target
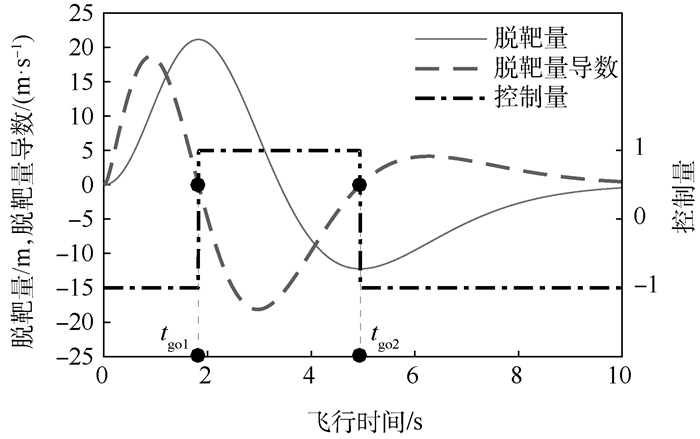
弹目 初始速度/(m·s-1) 初始高度/m 初始水平位置/m 控制切换时刻 导弹 915 3 050 0 目标 305 3 050 (0, 122 00] tgo1=1.82 s, tgo2=4.94 s 注:总飞行时间为[0, 10]s。 表 4 标度系数误差变化时目标最优机动产生脱靶量(tf=10 s)
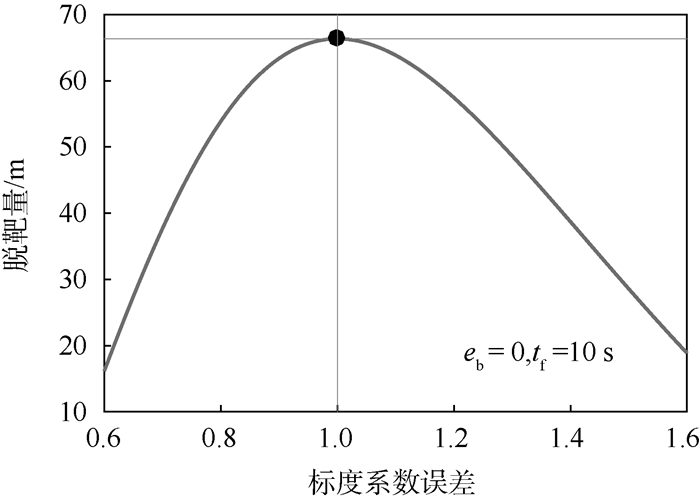
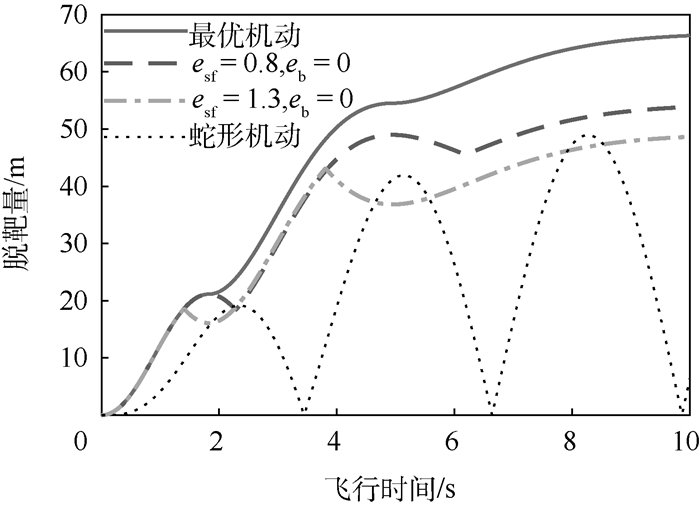
Table 4. Target optimal maneuver miss distance when scale factor error changes (tf=10 s)
esf tgo/s Mmax/m 0.8 tgo1=2.28,tgo2=6.19 53.87 1.0 tgo1=1.82, tgo2=4.94 66.33 1.3 tgo1=1.40, tgo2=3.81 48.64 表 5 零偏误差变化时目标最优机动产生脱靶量(tf=10 s)
Table 5. Target optimal maneuver miss distance when bias error changes (tf=10 s)
eb tgo/s Mmax/m -0.3 tgo1=2.12,tgo2=5.24 63.26 0 tgo1=1.82,tgo2=4.94 66.33 0.7 tgo1=1.12, tgo2=4.24 48.70 -
[1] WEISS M.Adjoint method for missile performance analysison state-space models[J].Journal of Guidance, Control and Dynamics, 2005, 28(2):236-248. doi: 10.2514/1.7342 [2] ZARCHAN P.Tactical and strategic missile guidance[M].6th ed.Reston:AIAA, 2012:35-105. [3] LANING J H, BATTIN R H.Random processes in autmatic control[M].New York:McGraw-Hill Book Company, Inc., 1956:225-253. [4] BENASHER J Z.Application to missile guidance:Proportional navigation[M].Reston:AIAA, 2010:231-239. [5] NESLINE F W, ZARCHAN P.A new look at classical vs modern homing missile guidance[J].Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2012, 4(1):78-85. [6] 高雁翎, 张保庆.2017年世界弹道导弹防御发展分析[J].战术导弹技术, 2018(1):42-46.GAO Y L, ZHANG B Q.2017 world ballistic missile defense development analysis[J].Tactical Missile Technology, 2018(1):42-46(in Chinese). [7] 郑玉航, 于海燕, 孙鹏.导弹突防策略与措施研究[J].国防技术基础, 2002(5):46-48.ZHENG Y H, YU H Y, SUN P.Study on missile penetration strategies and measures[J].Technology Foundation of National Defence, 2002(5):46-48(in Chinese). [8] ZARCHAN P.Proportional navigation and weaving targets[J].Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 1995, 18(5):969-974. doi: 10.2514/3.21492 [9] 雍恩米, 唐国金, 罗亚中.弹道导弹中段机动突防制导问题的仿真研究[J].导弹与航天运载技术, 2005(4):13-18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7182.2005.04.003YONG E M, TANG G J, LUO Y Z.Research on maneuvering penetration guidance law of ballistic missile in middle-course flight by simulation method[J].Missiles and Space Vehicles, 2005(4):13-18(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7182.2005.04.003 [10] SAILARANTA T, SILTAVUORI A, PANKKONEN A. Simple missile models against high-g barrel roll maneuver: AIAA-2011-6570[R].Reston: AIAA, 2011. [11] SHINAR J, STEINBERG D.Analysis of optimal evasive maneuvers based on a linearized two-dimensional kinematic model[J].Journal of Aircraft, 1977, 14(8):795-802. doi: 10.2514/3.58855 [12] 迟泽晨, 李长文, 王健.临近空间导弹最优机动突防控制策略研究[C]//中国空天安全会议, 2017.CHI Z C, LI C W, WANG J.Analysis of optimal evasive maneuvers control in near-space[C]//China Space Security Conference, 2017(in Chinese). [13] DHANANJAY N, GHOSE D.Accurate time-to-go estimation for proportional navigation guidance[J].Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2014, 37(4):1378-1383. doi: 10.2514/1.G000082 [14] 庄志洪, 涂建平, 王宏波.导弹目标遭遇过程中的剩余飞行时间估计[J].宇航学报, 2002, 23(5):32-38. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1328.2002.05.007ZHUANG Z H, TU J P, WANG H B.Prediction of time to go during missile-target encounter[J].Journal of Astronautics, 2002, 23(5):32-38(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1328.2002.05.007 [15] HE T L, CHEN W C.A new interpretation of adjoint method in linear time-varying system analysis[C]//IEEE International Conference on CIS & RAM.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2017: 58-63. [16] 赫泰龙, 陈万春, 周浩.高阶线性比例制导系统脱靶量幂级数解[J].航空学报, 2018, 39(11):322241.HE T L, CHEN W C, ZHOU H.Power series solution for miss distance of higher-order linear proportional navigation guidance systems.[J].Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2018, 39(11):322241(in Chinese). [17] SPEYER J L, JACOBSON D H.Primer on optimal control theory[M].Philadelphia:Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, 2010:79-83. [18] MURTAUGH S A, CRIEL H E. Fundamentals of proportional navigation[J]. Spectrum IEEE, 1966, 3(12):75-85. doi: 10.1109/MSPEC.1966.5217080 -







 下载:
下载: