Knowledge discovery of telemetry data cross-correlation structure based on ensemble learning
-
摘要:
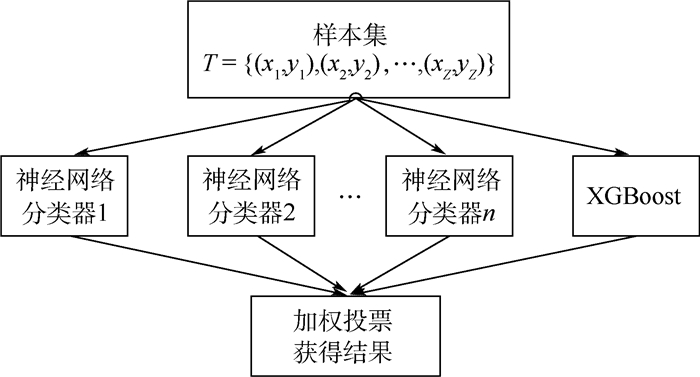
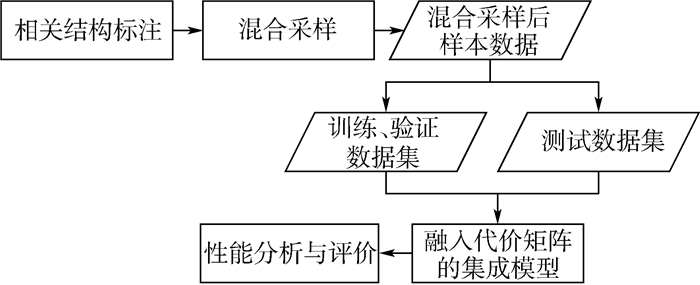
针对传统遥测数据相关性分析方法仅能发现相关程度知识,无法提供相关结构丰富信息的问题,提出一种神经网络与极限梯度提升(XGBoost)集成的遥测数据互相关结构知识发现方法。在对遥测时间序列进行线性、单调性、序对一致性、散点图形状4个维度相关结构信息标注的基础上,将混合采样、代价矩阵、神经网络、XGBoost算法相结合,直接对遥测数据进行分类得到其相关结构类别或相关关系有无的知识。采用量子卫星任务数据进行实验的结果表明:较之于原始XGBoost模型、融合混合采样与代价矩阵的XGBoost模型,所提方法在受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线、F1-score等性能指标方面具有更高的分类精度,且对类别不平衡数据不敏感,是一种适用于遥测数据互相关结构知识发现的有效方法。
Abstract:Aimed at the problem that traditional telemetry data correlation analysis methods can only discover relevant degree knowledge and cannot provide relevant structural information, an extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) and neural network ensemble learning method is proposed to discover the cross-correlation structural knowledge of telemetry data. Based on the dimension related structural information annotated by linearity, monotony, order pair consistency and scatter diagram shape, an algorithm combining hybrid sampling, cost sensitive matrix, neural network and XGBoost is developed to directly measure the telemetry data. The data is classified to obtain knowledge of relevant structural categories or related relationships. The results of experiments using quantum satellite mission data indicate that compared with the original XGBoost model, and the fusion-mixed sampling and cost-sensitive XGBoost model, the XGBoost model with neural network ensemble has higher classification accuracy on the performance indicators such as receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and F1-score. The proposed method is not sensitive to categorially imbalanced data, making it an effective method for the discovery of cross-correlation structural knowledge of telemetry data.
-
表 1 分类准则
Table 1. Classification criteria
相关维度 相关系数阈值区间 相关结构类别 线性维度
Pearson[0.7, 0.9) 线性正相关 [0.9, 1] 线性完全正相关 (-0.9, -0.7] 线性负相关 [-1, -0.9] 线性完全负相关 (-0.7, 0.7) 无线性相关 单调性维度Spearman [0.7, 0.9) 单调增相关 (-0.9, -0.7] 单调减相关 [-1, -0.9] 完全单调减相关 [0.9, 1] 完全单调增相关 (-0.7, 0.7) 无单调相关 序对一致性维度
Kendall[0.9, 1] 序对一致负相关 (-0.9, -0.7] 序对一致正相关 [0.7, 0.9) 序对一致完全负相关 [-1, -0.9] 序对一致完全正相关 (-0.7, 0.7) 无序对一致性 散点图形状维度MIC ≥0.8 
正弦波相关 
距离聚类 
密度聚类 [0, 0.8) 无散点图形状相关 表 2 代价矩阵
Table 2. Cost sensitive matrix
类别 1 … m 1 1 … c(1, m) ⋮ ⋮ ⋮ m c(m, 1) … 1 表 3 3种模型对比实验所得F1-score
Table 3. F1-score obtained from contrast test of three models
相关结构类别 F1 F2 F3 无线性相关 0.97 0.97 1.00 线性正相关 0.83 0.93 0.99 线性完全正相关 0.74 0.97 0.99 线性负相关 0.44 0.92 1.00 线性完全负相关 0 0.84 1.00 无单调相关 0.98 0.91 0.97 单调增相关 0.71 0.86 0.95 完全单调增相关 0.81 0.95 0.95 单调减相关 0.50 1.00 0.99 完全单调减相关 0 1.00 1.00 无序对一致性 0.98 0.89 0.99 序对一致正相关 0 1.00 0.99 序对一致完全正相关 0.85 0.97 0.99 序对一致负相关 0 0.33 1.00 序对一致完全负相关 0.67 0.88 0.99 无散点图形状相关 0.97 0.93 0.98 密度聚类 0.73 0.94 0.98 正弦波相关 0.95 0.98 1.00 距离聚类 0.62 0.97 0.99 表 4 原始数据测试集分类性能
Table 4. Raw data test set classification performance
相关结构类别 P R F1 无线性相关 1.00 0.50 0.67 线性正相关 0.67 1.00 0.80 线性完全正相关 1.00 0.50 0.67 线性负相关 0.67 1.00 0.80 线性完全负相关 1.00 1.00 1.00 无序对一致性 1.00 1.00 1.00 序对一致正相关 1.00 1.00 1.00 序对一致完全正相关 1.00 1.00 1.00 序对一致负相关 0.67 1.00 0.80 序对一致完全负相关 1.00 0.50 0.67 无单调相关 1.00 0.50 0.67 单调增相关 1.00 0.50 0.67 完全单调增相关 1.00 1.00 1.00 单调减相关 1.00 1.00 1.00 完全单调减相关 1.00 1.00 1.00 无散点图形状相关 1.00 0.50 0.67 密度聚类 1.00 1.00 1.00 正弦波相关 1.00 1.00 1.00 距离聚类 0.67 1.00 0.80 -
[1] FAYYAD U, PIAETSKYSHAPIRO G, SMYTH P.The KDD process for extracting useful knowledge from volumes of data[J].Communications of the ACM, 1996, 39(11):27-34. doi: 10.1145/240455.240464 [2] 钱宇华, 成红红, 梁新彦, 等.大数据关联关系度量研究综述[J].数据采集与处理, 2015, 30(6):1147-1159.QIAN Y H, CHENG H H, LIANG X Y, et al.Review for variable association measuring big data[J].Journal of Data Acquisition and Processing, 2015, 30(6):1147-1159(in Chinese). [3] MOON Y I, RAJAGOPALAN B, LALL U.Estimation of mutual information using kernel density estimators[J].Physical Review E, 1995, 52(3):2318-2321. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.52.2318 [4] RESHEF D N, RESHEF Y A, FINUCANE H K, et al.Detecting novel associations in large data sets[J].Science, 2011, 334(6062):1518-1524. doi: 10.1126/science.1205438 [5] 魏邦友.载人航天器综合测试数据评估方法的研究[J].电子质量, 2017(7):28-30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0107.2017.07.008WEI B Y.Research on evaluation method of comprehensive test data for manned spacecraft[J].Electronics Quality, 2017(7):28-30(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0107.2017.07.008 [6] 陆兵焱, 陈友龙, 李映颖.基于SPSS对试飞数据进行的相关性分析[J].科技信息, 2009(15):95.LU B Y, CHEN Y L, LI Y Y.Correlation analysis of flight test data based on SPSS[J].Science & Technology Information, 2009(15):95(in Chinese). [7] 任国恒.同步卫星遥测数据相关性分析与研究[D].西安: 西安工业大学, 2011.REN G H.Correlation analysis and research on the telemetry data of synchronous satellite[D].Xi'an: Xi'an Technological University, 2011(in Chinese). [8] 王鹏, 张善从.基于最大信息系数的时延数据相关性分析方法[J].电子测量技术, 2015, 38(9):112-115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7300.2015.09.026WANG P, ZHANG S C.Method for the correlation analysis of data with time delay based on maximum information coefficient[J].Electronic Measurement Technology, 2015, 38(9):112-115(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7300.2015.09.026 [9] XIN D, DE C P.An effective method for mining quantitative association rules with clustering partition in satellite telemetry data[C]//Proceedings of the 2014 2nd International Conference on Advanced Cloud and Big Data (CBD'14).Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2014: 26-33. [10] FOSLIEN W, GURALNIK V, HAIGH K Z.Data mining for space applications[C]//8th International Conference on Space Operations.Reston: AIAA, 2004. [11] 唐明珠.类别不平衡和误分类代价不等的数据集分类方法及应用[D].长沙: 中南大学, 2012.TANG M Z.Classification methods for class-imbalanced datasets of unequal misclassification costs and their applications[D].Changsha: Central South University, 2012(in Chinese). [12] 李军.不平衡数据学习的研究[D].长春: 吉林大学, 2011.LI J.Research on the imbalanced data learning[D].Changchun: Jilin University, 2011(in Chinese). [13] 李朋丽, 田伟平, 李家春.基于BP神经网络的滑坡稳定性分析[J].广西大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 38(4):905-911. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7445.2013.04.018LI P L, TIAN W P, LI J C.Analysis of landslide stability based on BP neural network[J].Journal of Guangxi University(Natural Science Edition), 2013, 38(4):905-911(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7445.2013.04.018 [14] 王嘉强, 范延滨.基于LSTM模型的人体情景多标签识别研究[J].青岛大学学报(工程技术版), 2018, 33(4):44-48.WANG J Q, FAN Y B.Research on multi-label recognition of human scene based on LSTM model[J].Journal of Qingdao University(E & T), 2018, 33(4):44-48(in Chinese). [15] 陈志仁, 顾红.基于注水原理的雷达目标多分类器集成算法[J].南京理工大学学报, 2018, 42(3):380-384.CHEN Z R, GU H.Radar target multi-classifier integration algorithm based on water-filling theory[J].Journal of Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2018, 42(3):380-384(in Chinese). [16] 乐明明.数据挖掘分类算法的研究和应用[D].西安: 电子科技大学, 2017.LE M M.Research and application of data mining classification algorithm[D].Xi'an: University of Electronic Science and Technology, 2017(in Chinese). [17] 毛文斌.基于人工神经网络的高维遥感数据分类研究[D].杭州: 杭州电子科技大学, 2013.MAO W B.A study on high-dimensional remote sensing data classification based on artificial neural networks[D].Hangzhou: Hangzhou Dianzi University, 2013(in Chinese). [18] 李廷伟, 梁甸农, 黄海风, 等.一种基于BP神经网络的极化干涉SAR植被高度反演方法[J].国防科技大学学报, 2010, 32(3):60-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2010.03.012LI T W, LIANG D N, HUANG H F, et al.A BP neural-network based method for vegetation height inversion of the polarimetric interferometric SAR[J].Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2010, 32(3):60-64(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2010.03.012 [19] 王桂兰, 赵洪山, 米增强.XGBoost算法在风机主轴承故障预测中的应用[J].电力自动化设备, 2019, 39(1):73-77.WANG G L, ZHAO H S, MI Z Q.Application of XGBoost algorithm in fault prediction of main bearing of wind turbine[J].Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2019, 39(1):73-77(in Chinese). [20] 王思晨, 丁家满.一种不平衡数据集成分类方法[J].软件导刊, 2018, 17(8):76-80.WANG S C, DING J M.An integrated classification method for imbalanced data[J].Software Guide, 2018, 17(8):76-80(in Chinese). [21] 张明, 胡晓辉, 吴嘉昕.基于混合采样的不平衡数据集算法研究[J].计算机工程与应用, 2019, 55(17):68-75. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1804-0307ZHANG M, HU X H, WU J X.Imbalanced data processing algorithm based on mixed sampling[J].Computer Engineering and Applications, 2019, 55(17):68-75(in Chinese). doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1804-0307 [22] 王璐林.面向不平衡样本的Boosting分类算法研究[D].哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2013.WANG L L.Research of Boosting classification algorithm for imbalanced data[D].Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2013(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: