-
摘要:
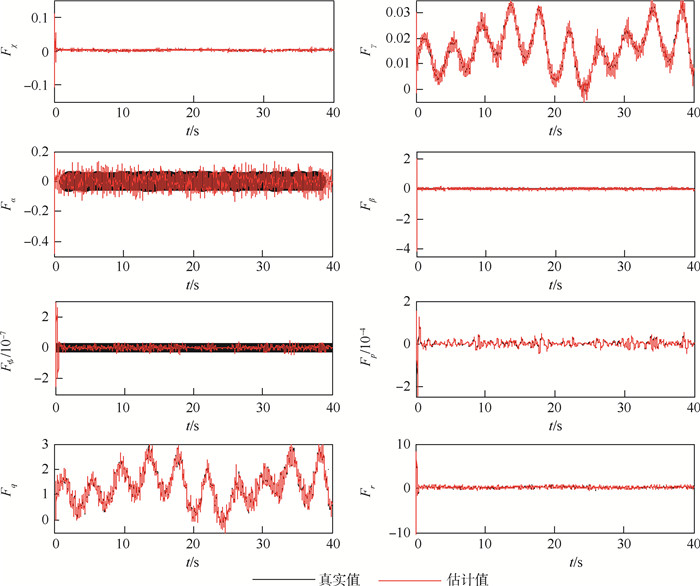
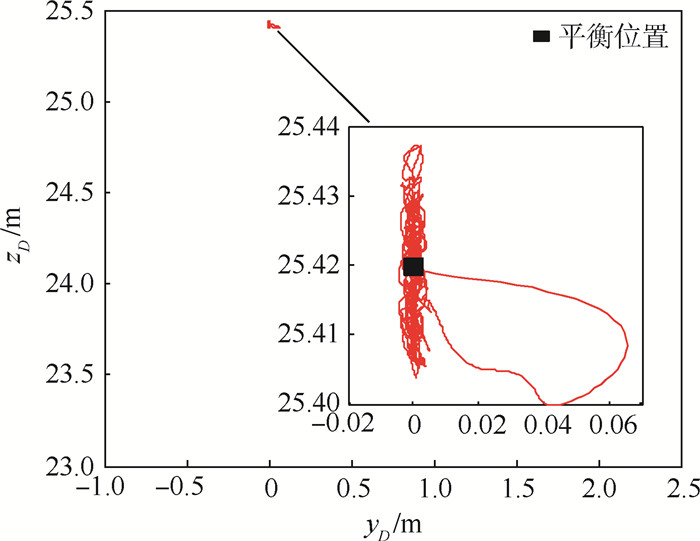
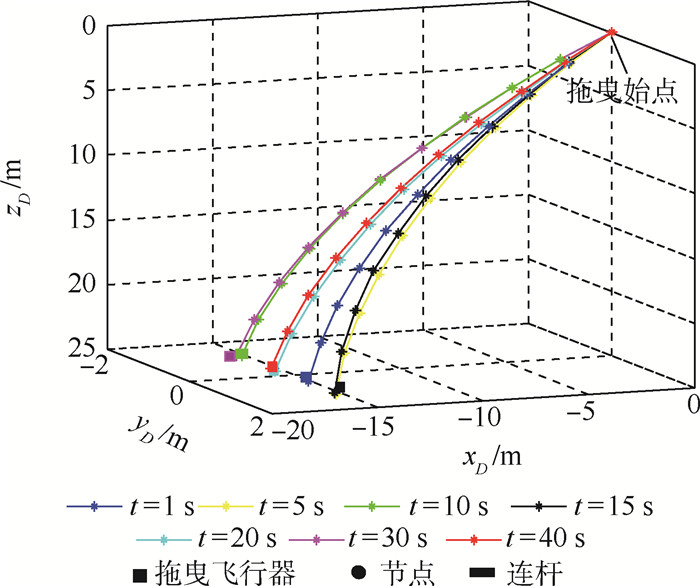
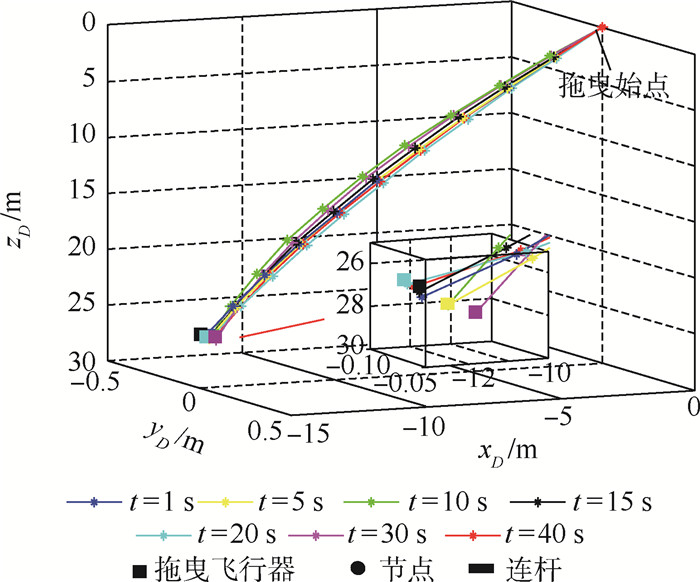
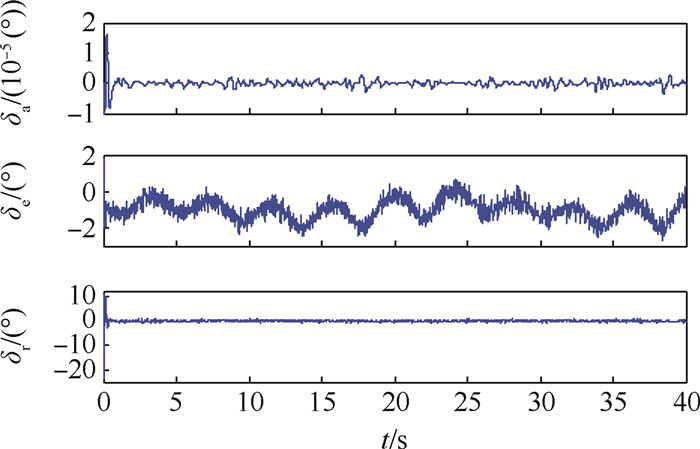
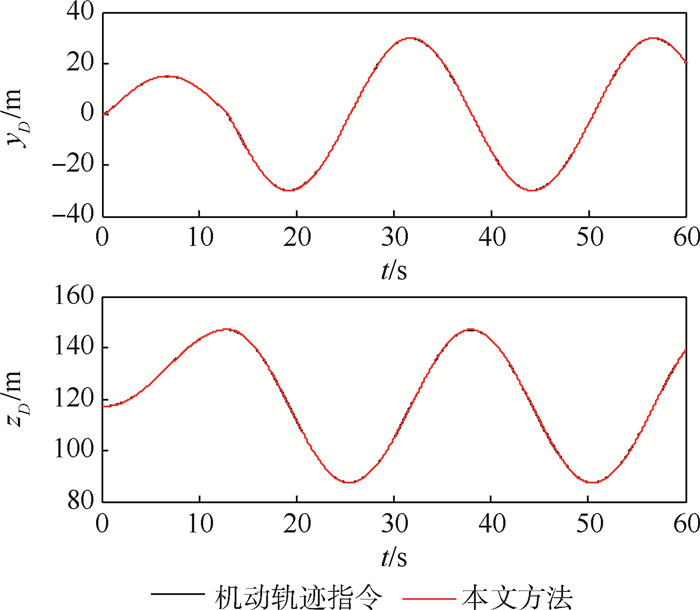
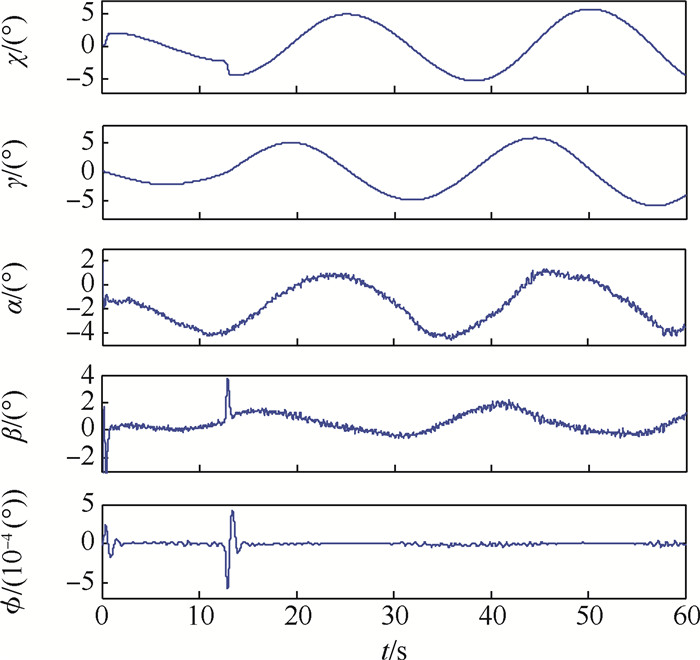
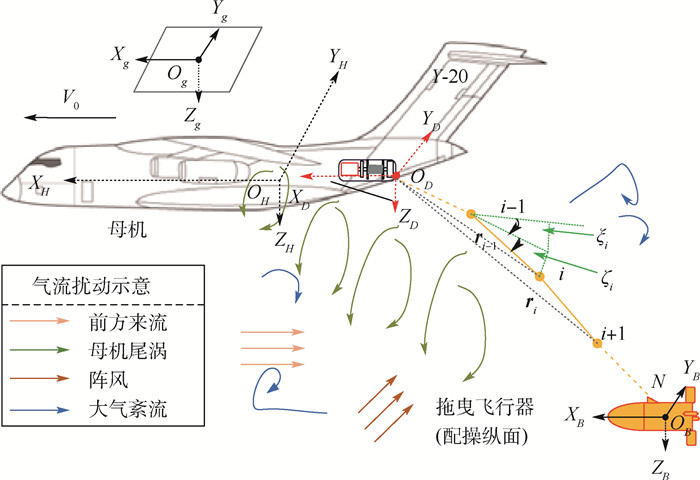
针对受未知风扰动作用下的绳系拖曳飞行器轨迹精确控制问题,设计了一种基于最小学习参数神经网络估计器的拖曳飞行器轨迹动态面控制方法。首先,结合绳系拖曳系统多刚体动力学模型,构建拖曳飞行器六自由度非线性模型,并完成其仿射非线性化处理。其次,考虑到拖曳飞行器可能受到前方飞机尾涡、紊流和阵风等未知气流及不可测量瞬变缆绳拉力等扰动的综合影响,构建了基于最小学习参数神经网络的拖曳飞行器状态/扰动在线估计器,以准确重构系统不可测量集总扰动。然后,基于所提状态/扰动在线估计器,设计了一种基于最小学习参数神经网络状态/扰动在线估计器的拖曳飞行器轨迹动态面控制方法,并分析了系统稳定性。最后,仿真表明,所提方法能够在多重气流扰动下实现拖曳飞行器位置稳定和机动轨迹跟踪。
Abstract:To handle the precise trajectory control problem of the cable towed vehicle under unknown airflow disturbances, the minimal learning parameter neural network estimator based dynamic surface trajectory control method is proposed for the towed vehicle. Firstly, combined with the multi-body dynamic model of the cable towed system, the towed vehicle's six-degree-of-freedom nonlinear model is established and then formulated in the affine nonlinear form. Secondly, considering the comprehensive influence on the towed vehicle by the unknown airflow disturbances (such as the trailing vortex, atmospheric turbulence, gust, etc.) and the variably unmeasurable cable tensions, the minimal learning parameter neural network based state/disturbance online estimators are established to accurately reconstitute the unmeasurable lumped disturbance of system. Thirdly, on the basis of the above state/disturbance online estimators, the minimal learning parameter neural network state/disturbance estimator based dynamic surface trajectory control method is proposed. Finally, the simulation results show that the proposed method can achieve the towed vehicle's trajectory stabilization and maneuvering trajectory tracking control.
-
-
[1] 刘钒. 飞行器拖曳系统气动特性数值模拟研究[D]. 绵阳: 中国空气动力研究与发展中心, 2014: 1-15.LIU F. Numerical simulation research on the aerodynamic characteristics of aerial towed cable system[D]. Mianyang: China Aerodynamics Research and Development Center, 2014: 1-15(in Chinese). [2] 王班, 郭吉丰, 易琳, 等. 空间绳系组合体拖曳动力学分析及振动控制[J]. 宇航学报, 2018, 9(2): 131-138.WANG B, GUO J F, YI L, et al. Dynamic analysis and vibration control of space towing tethered combination[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2018, 39(2): 131-138(in Chinese). [3] COCHRAN J E, INNOCENTI M, NO T S, et al. Dynamics and control of maneuverable towed flight vehicles[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 1992, 15(5): 1245-1252. doi: 10.2514/3.20975 [4] 郑小洪, 韩维, 贾忠湖. 风作用下机载拖曳天线的动力学建模与分析[J]. 航空学报, 2013, 34(11): 2565-2571.ZHENG X H, HAN W, JIA Z H. Modeling and simulation of trailing antennas on an aircraft under wind[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2013, 34(11): 2565-2571(in Chinese). [5] BOURMISTROV A S, HILL R D, RISEBOROUGH P. Nonlinear control law for aerial towed target[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 1995, 18(6): 1232-1238. doi: 10.2514/3.21535 [6] 方晓星, 王勇, 王英勋. 低空掠海飞行拖靶自抗扰高度控制律设计[J]. 南京理工大学学报, 2012, 36(5): 835-845. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9830.2012.05.019FANG X X, WANG Y, WANG Y X. Design of active disturbance rejection control law of low altitude sea skimming tow target[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2012, 36(5): 835-845(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9830.2012.05.019 [7] MA T L, WEI Z H, CHEN H B, et al. Simulation of the dynamic retrieval process of a towed target system under towing airplane's wake and atmospheric turbulence[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part G: Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2020, 234(9): 095441002091629. [8] 马东立, 刘亚枫, 林鹏. 绳系拖曳诱饵系统的动态特性研究[J]. 航空学报, 2014, 35(1): 161-170. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HKXB201401016.htmMA D L, LIU Y F, LIN P. Study of dynamic characteristics of aeronautic towed decoy system[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2014, 35(1): 161-170(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HKXB201401016.htm [9] 付孝龙, 白渭雄, 李欣, 等. 基于多普勒频率差的拖曳式诱饵干扰检测[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2017, 43(10): 2081-2088. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2016.0797FU X L, BAI W X, LI X, el al. Towed radar active decoy jamming detection based on Doppler frequency difference[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2017, 43(10): 2081-2088(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2016.0797 [10] 芦艳龙, 童中翔, 王超哲, 等. 绳系拖曳诱饵空气动力及动态特性[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2011, 37(4): 395-398.LU Y L, TONG Z X, WANG C Z, et al. Aerodynamic and dynamic characteristics of aeronautic towed decoy[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2011, 37(4): 395-398(in Chinese). [11] 张登成, 唐硕. 拖缆的弹簧柔性体模型在拖曳式空中发射系统中的应用研究[J]. 导弹与航天运载技术, 2005(4): 43-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7182.2005.04.009ZHANG D C, TANG S. Research on application of towline model in towed air-launch system[J]. Missile and Space Vehicles, 2005(4): 43-46(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-7182.2005.04.009 [12] MARTI S K, NESRIN S K. A study of air launch methods for RLVs: AIAA 2001-4619[R]. Reston: AIAA, 2001. [13] 王宏伦, 杜熠, 盖文东. 无人机自动空中加油精确对接控制[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2011, 37(7): 822-826. https://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/Y2011/V37/I7/822WANG H L, DU Y, GAI W D. Precise docking control in unmanned aircraft vehicle automated aerial refueling[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2011, 37(7): 822-826(in Chinese). https://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/Y2011/V37/I7/822 [14] 王海涛, 董新民, 郭军, 等. 空中加油软管锥套组合体甩鞭现象动力学建模与分析[J]. 航空学报, 2015, 36(9): 3116-3127.WANG H T, DONG X M, GUO J, et al. Dynamics modeling and analysis hos whipping phenomenon of aerial refueling hose-drogue assembly[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2015, 36(9): 3116-3127(in Chinese). [15] 张启钱, 许卫卫, 张洪海, 等. 复杂低空物流无人机路径规划[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(7): 1275-1286. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0455ZHANG Q Q, XU W W, ZHANG H H, et al. Path planning for logistics UAV in complex low-altitude airspace[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(7): 1275-1286(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0455 [16] HOCHSTELER R D, BOSMA J, CHACHAD G H, et al. Lighter-than-air (LTA) "AirStation" unmanned aircraft system (UAS) carrier concept: AIAA 2016-4223[R]. Reston: AIAA, 2016. [17] 陈唯实, 刘佳, 陈小龙, 等. 基于运动模型的低空非合作无人机目标识别[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2019, 45(4): 687-694. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0447CHEN W S, LIU J, CHEN X L, et al. Non-cooperative UAV target recognition in low-altitude airspace based on motion model[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2019, 45(4): 687-694(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0447 [18] SUN L, BEARD R W, COLTON M B. Motion planning and control for mothership-cable-drogue systems in aerial recovery of micro air vehicles[C]//Proceedings of the 2010 American Control Conference, 2010: 2101-2106. [19] NICHOLS J W, SUN L, BEARO R W, et al. Aerial rendezvous of small unmanned aircraft using a passive towed cable system[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2014, 37(4): 1131-1142. doi: 10.2514/1.62220 [20] MERZ M, JOHANSEN T A. Control of an end body towed by a circling unmanned aerial vehicle[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2019, 42(12): 2677-2686. doi: 10.2514/1.G004199 [21] WILLIAMSON W R, REED E, GLENN G J, et al. Controllable drogue for automated aerial refueling[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2010, 47(2): 515-527. doi: 10.2514/1.44758 [22] RO K, KUK T, KAMMAN J. Active control of aerial refueling hosedrogue systems: AIAA 2010-8400[R]. Reston: AIAA, 2010. [23] RO K, KUK T, KANMAN J. Dynamics and control of hose-drogue refueling systems during coupling[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2011, 34(6): 1694-1708. doi: 10.2514/1.53205 [24] SUN L, BEARD R W, COLTON M B, et al. Dynamics and control of cable-drogue system in aerial recovery of micro air vehicles based on Gauss's principle[C]//Proceedings of the 2009 American Control Conference, 2009: 4729-4734. [25] 肖业伦, 金长江. 大气扰动中的飞行原理[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 1993: 73-90.XIAO Y L, JIN C J. The rinciple of flight in atmospheric disturbance[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 1993: 73-90(in Chinese). [26] SU Z K, WANG H L, LI N, et al. Exact docking flight controller for autonomous aerial refueling with back-stepping based high order sliding mode[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2018, 101: 338-360. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2017.08.036 [27] SU Z K, LI C T, WANG H L. Barrier Lyapunov function-based robust flight control for the ultra-low altitude airdrop under airflow disturbances[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2019, 84: 375-386. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2018.10.008 [28] SANNER R M, SLOTINE J E. Gaussian networks for direct adaptive control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 1992, 3(36): 837-863. [29] BU X W, WU X Y, HUANG J Q, et al. Minimal-learning-parameter based simplified adaptive neural back-stepping control of flexible air-breathing hypersonic vehicles without virtual controllers[J]. Neurocomputing, 2016, 175: 816-825. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2015.10.116 [30] SHAO X L, LIU N, WANG Z Q, et al. Neuroadaptive integral robust control of visual quadrotor for tracking a moving object[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2020, 136: 106513. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2019.106513 [31] SHAO X L, LIU N, WANG Z Q, et al. Estimator-based MLP neuroadaptive dynamic surface containment control with prescribed performance for multiple quadrotors[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2020, 97: 105620. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2019.105620 [32] SU Z K, WANG H L, YAO P, et al. Back-stepping based anti-disturbance flight controller with preview methodology for autonomous aerial refueling[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2017, 61: 95-108. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2016.11.028 [33] DAVILA J. Exact tracking using backstepping control design and high-order sliding modes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2013, 58(8): 2077-2081. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2013.2246894 [34] SWAROOP D, HEDRICK J K, YIP P P, et al. Dynamic surface control for a class of nonlinear systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2000, 45(10): 1893-1899. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2000.880994 [35] CHEN M, YU J. Adaptive dynamic surface control of NSVs with input saturation using a disturbance observer[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2015, 28(3): 853-864. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2015.04.020 [36] SHAO X L, LIU N, LIU J, et al. Model-assisted extended state observer and dynamic surface control-based trajectory tracking for quadrotors via output-feedback mechanism[J]. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2018, 28(6): 2404-2423. doi: 10.1002/rnc.4023 -







 下载:
下载: