Scheduling algorithm of TTE network based on greedy randomized adaptive search procedure
-
摘要:
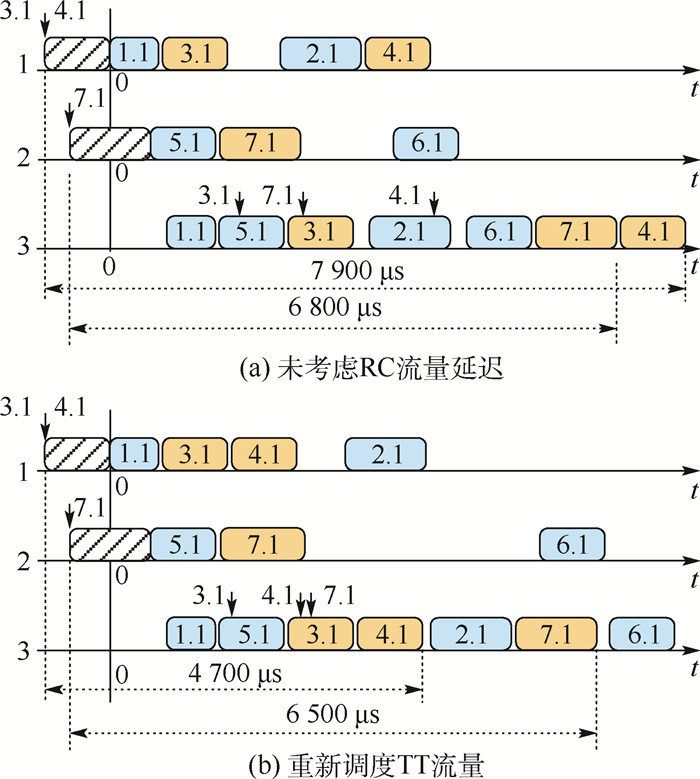
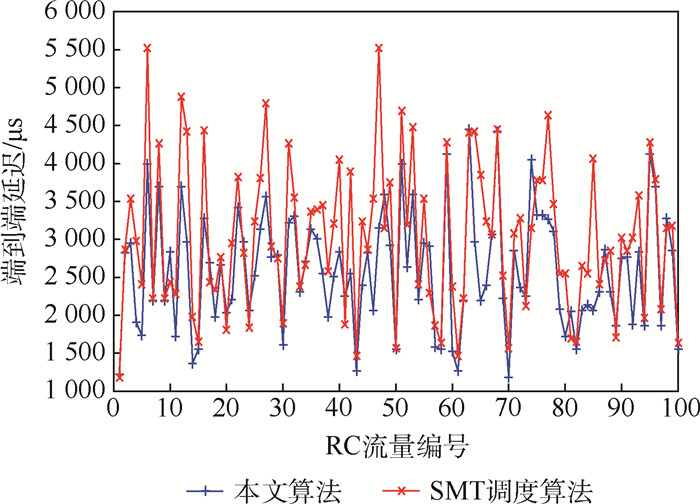
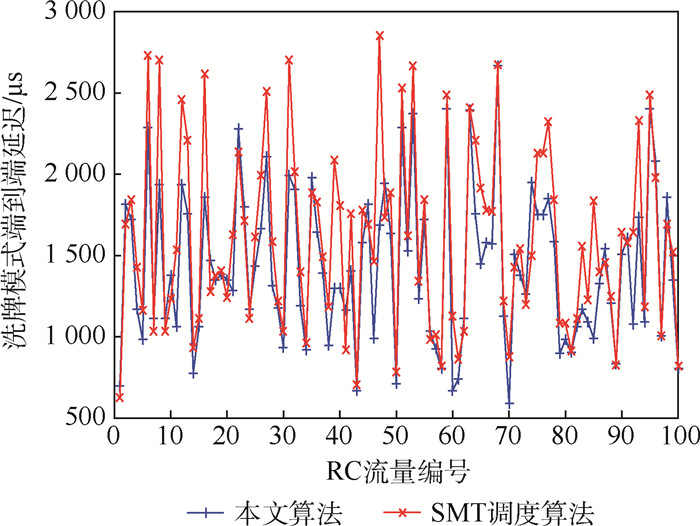
时间触发以太网(TTE)采用全局时间触发机制,使通信任务传输具有严格的时间确定性和无冲突性,适用于航空电子等混合关键应用领域。TTE网络提供3种不同的流量类型:具有低抖动和有界端到端延迟的时间触发(TT)流量,有限制端到端延迟的速率约束(RC)流量和无实时性保证"尽力传"(BE)流量。针对可满足性模理论(SMT)等调度算法在生成TT流量离线时刻调度表的过程中,未综合考虑TT流量路由和时刻调度表对RC流量延迟产生影响的问题,为了优化TTE网络实时性能,提出了一种基于贪婪随机自适应搜索算法的TTE通信任务调度算法。在TT流量离线调度表的生成过程中考虑了RC流量的最坏端到端延迟(WCD),在保证TT流量满足可调度性的前提下,通过路由规划和调度时刻表规划降低了RC流量的WCD。对比实验结果表明:所提算法可以有效的提升整网的实时性能,通过A380拓扑组网案例的对比分析,RC流量的平均延迟减少了14.34%。网络中流量规模越大,所提算法的收益越大。
-
关键词:
- 时间触发以太网(TTE) /
- 贪婪随机自适应搜索 /
- 调度算法 /
- 优化设计 /
- 实时性分析
Abstract:Time-Triggered Ethernet (TTE) makes communication tasks have strict determinacy and conflict free by global time-triggered mechanism, which is suitable for mixed critical application fields such as avionics. TTE network provides three different traffic types: Time-Triggered (TT) traffic with low jitter and bounded end-to-end delay, Rate Constrained (RC) traffic with limited end-to-end delay, and no real-time guaranteed "Best Effort" (BE) traffic. Aiming at the problem that Satisfiability Modulo Theories (SMT) and other methods do not consider the influence of TT traffic routing and scheduling on RC traffic delay in the process of generating the TT traffic scheduling timetable, in order to optimize the real-time performance of TTE network, this paper proposes a scheduling algorithm based on greedy randomized adaptive search procedure. The Worst-Case end-to-end Delay (WCD) of RC traffic is considered in the generation process of TT traffic offline scheduling timetable. Under the premise of ensuring the schedulability of TT traffic, the WCD of RC traffic is reduced by routing strategy and scheduling strategy. The comparative experimental results show that the proposed method can effectively improve the real-time performance of the network. Through the comparative analysis of A380 topology networking cases, the average delay of RC traffic is reduced by 14.34%. Also, the larger the network traffic scale, the greater the income of this method.
-
表 1 网络流量参数
Table 1. Network traffic parameters
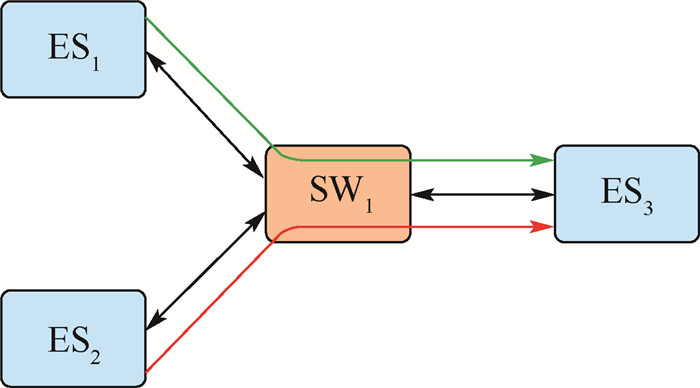
流量编号 周期/ms 帧长/bit 路由 f1∈FTT 40 750 {[ES1, SW1], [SW1, ES3]} f2∈FTT 20 1 250 {[ES1, SW1], [SW1, ES3]} f3∈FRC 10 1 000 {[ES1, SW1], [SW1, ES3]} f4∈FRC 20 1 000 {[ES1, SW1], [SW1, ES3]} f5∈FTT 40 1 000 {[ES2, SW1], [SW1, ES3]} f6∈FTT 80 750 {[ES2, SW1], [SW1, ES3]} f7∈FRC 20 1 250 {[ES2, SW1], [SW1, ES3]} 表 2 TC2用例实验结果对比
Table 2. Comparison of experimental results in TC2
TC2 TT流量/条 RC流量平均延迟/μs 平均延迟优化比例/% 本文算法 SMT调度算法 1 90 1 811.184 1 939.503 6.62 2 120 2 120.23 2 302.004 7.9 3 150 2 343.516 2 582.929 9.27 4 180 2 520.142 2 875.879 11.82 5 210 2 690.12 3 140.462 14.34 表 3 TC3用例实验结果对比
Table 3. Comparison of experimental results in TC3
TC3 TT流量/条 RC流量平均延迟/μs 平均延迟优化比例/% 本文算法 SMT调度算法 1 90 1 212.797 1 274.539 4.84 2 120 1 299.493 1 385.83 6.23 3 150 1 328.248 1 435.529 7.47 4 180 1 390.14 1 523.595 8.76 5 210 1 430.422 1 600.63 10.63 -
[1] Aerospace. SAE AS6802: Time-Triggered Ethernet[S]. [S. l. ]: SAE International, 2011: 8-21. [2] ARINC. Aircraft data network, Part 7, Avionics full-duplex switched ethernet network: ARINC 664P7[S]. [S. l. ]: Aeronautical Radio INC, 2009: 9-18. [3] KOPETZ H. Real-time systems: Design principles for distributed embedded applications[M]. Berlin: Springer Science and Business Media, 2011: 79-109. [4] KOPETZ H, ADEMAJ A, GRILLINGER P, et al. The time-triggered ethernet (TTE) design[C]//Eighth IEEE International Symposium on Object-Oriented Real-Time Distributed Computing (ISORC'05). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2005: 22-33. [5] 刘成, 李航, 何锋, 等. 基于轨迹方法的AFDX网络路由配置算法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2012, 38(12): 1587-1590. https://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/Y2012/V38/I12/1587LIU C, LI H, HE F, et al. Routing algorithm of AFDX network based on trajectory approach[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2012, 38(12): 1587-1590(in Chinese). https://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/Y2012/V38/I12/1587 [6] Al S A, BRUN O, CHERAMY M, et al. Optimal design of virtual links in AFDX networks[J]. Real-Time Systems, 2013, 49(3): 308-336. doi: 10.1007/s11241-012-9171-z [7] 代真, 何锋, 张宇静, 等. AFDX虚拟链路路径实时寻优算法[J]. 航空学报, 2015, 36(6): 1924-1932.DAI Z, HE F, ZHANG Y J, et al. Real-time path optimization algorithm of AFDX virtual link[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2015, 36(6): 1924-1932(in Chinese). [8] STEINER W. An evaluation of SMT-based schedule synthesis for time-triggered multi-hop networks[C]//201031st IEEE Real-Time Systems Symposium. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2010: 375-384. [9] STEINER W. Synthesis of static communication schedules for mixed-criticality systems[C]//201114th IEEE International Symposium on Object/Component/Service-Oriented Real-Time Distributed Computing Workshops. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011: 11-18. [10] CRACIUNAS S S, OLIVER R S. Combined task- and network-level scheduling for distributed time-triggered systems[J]. Real-Time Systems, 2016, 52(2): 161-200. doi: 10.1007/s11241-015-9244-x [11] 宋梓旭, 李峭, 汪晶晶, 等. 基于可调度性排序的时间触发调度表生成方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2018, 44(11): 145-152. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0043SONG Z X, LI Q, WANG J J, et al. Time-triggered scheduling table generation method based on schedulability ranking[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018, 44(11): 145-152(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0043 [12] SUETHANUWONG E. Scheduling time-triggered traffic in TTEthernet systems[C]//Proceedings of 2012 IEEE 17th International Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation (ETFA 2012). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2012: 1-4. [13] SCHWEISSGUTH E, DANIELIS P, TIMMERMANN D, et al. ILP-based joint routing and scheduling for time-triggered networks[C]//Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Real-Time Networks and Systems. New York: ACM, 2017: 8-17. [14] 李浩若, 何锋, 郑重, 等. 基于强化学习的时间触发通信调度方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2019, 45(9): 1894-1901. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0789LI H R, HE F, ZHENG Z, et al. Time-triggered communication scheduling method based on reinforcement learning[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2019, 45(9): 1894-1901(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0789 [15] TÃMAŞ-SELICEAN D, POP P, STEINER W. Design optimization of TTE thernet-based distributed real-time systems[J]. Real-Time Systems, 2015, 51(1): 1-35. doi: 10.1007/s11241-014-9214-8 [16] ZHAO L, XIONG H, ZHENG Z, et al. Improving worst-case latency analysis for rate-constrained traffic in the time-triggered ethernet network[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2014, 18(11): 1927-1930. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2014.2358233 [17] ZHAO L, POP P, LI Q, et al. Timing analysis of rate-constrained traffic in TTEthernet using network calculus[J]. Real-Time Systems, 2017, 53(2): 254-287. doi: 10.1007/s11241-016-9265-0 [18] GAREY M R, JOHNSON D S, SETHI R, et al. The complexity of flowshop and jobshop scheduling[J]. Mathematics of Operations Research, 1976, 1(2): 117-129. doi: 10.1287/moor.1.2.117 [19] YEN J Y. Finding the k shortest loopless paths in a network[J]. Management Science, 1971, 17(11): 712-716. doi: 10.1287/mnsc.17.11.712 [20] RESENDE M G C, RIBEIRO C C. GRASP: Greedy randomized adaptive search procedures[M]//BURKE E K, KENDALL G. Search methodologies. Berlin: Springer, 2014: 287-312. -







 下载:
下载: