Prediction method of intercept time and intercept point based on learning mid-course antimissile
-
摘要:
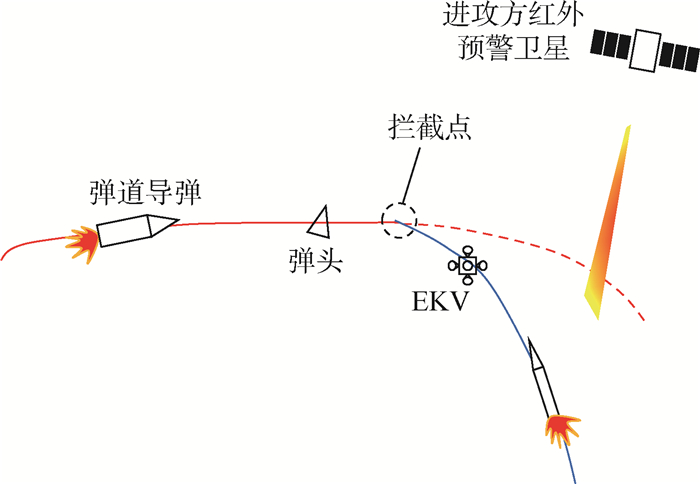
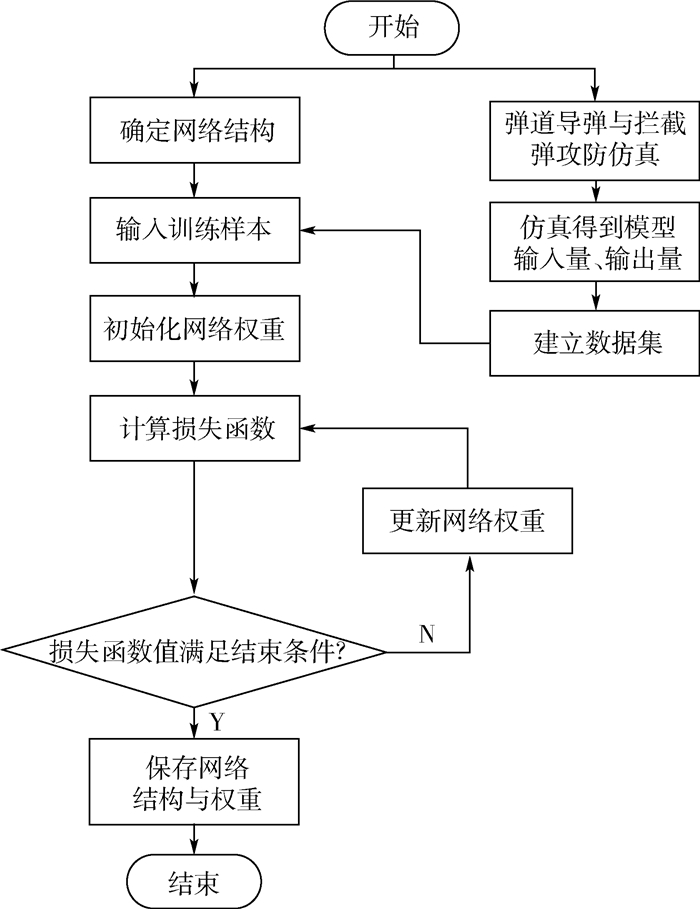
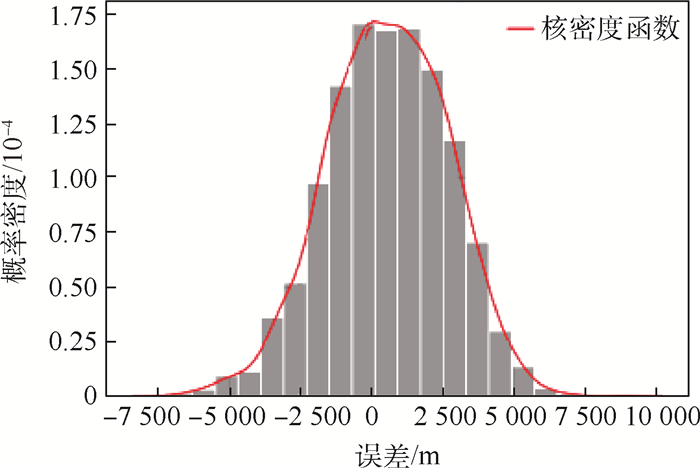
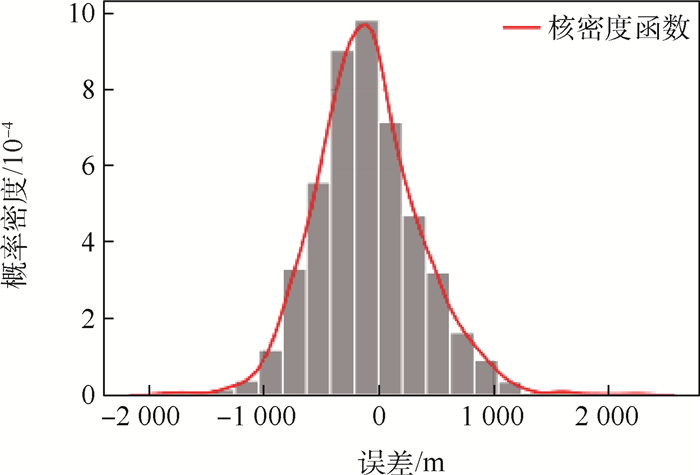
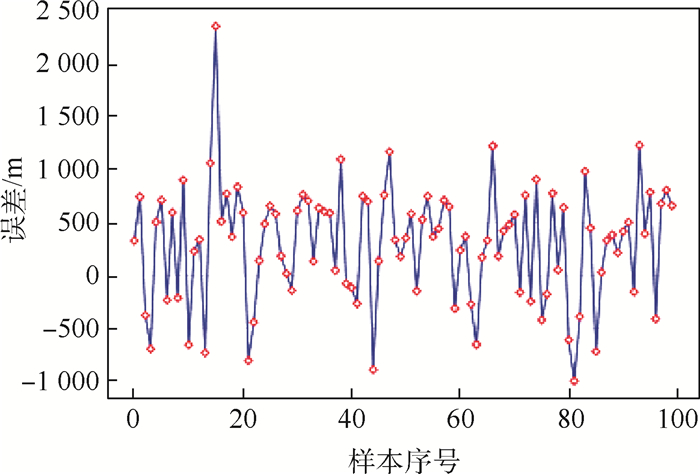
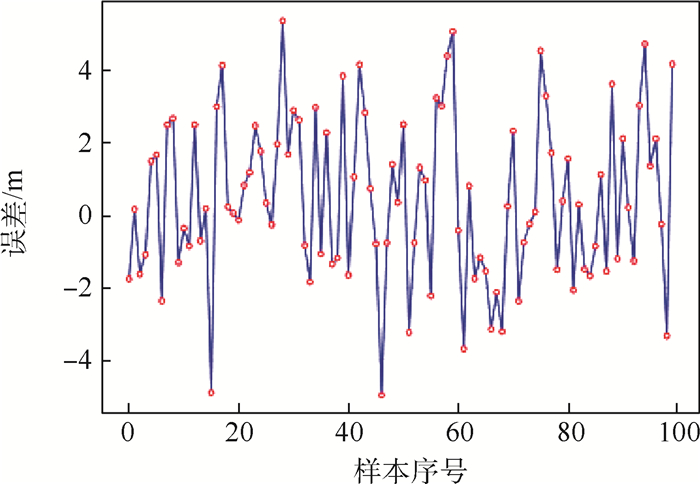
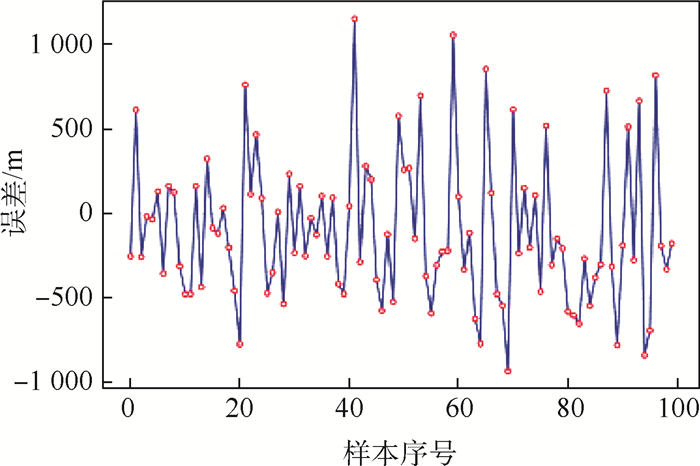
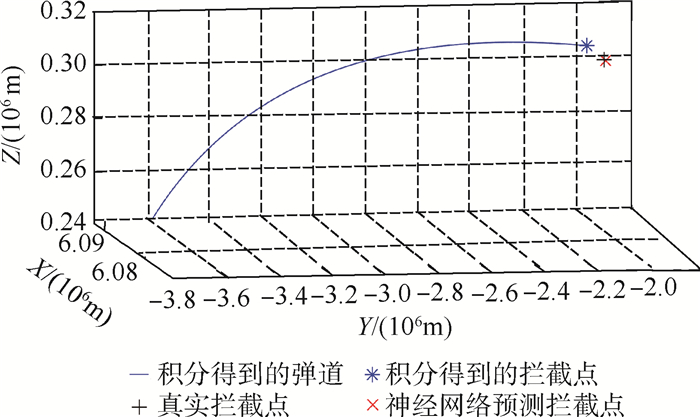
弹道导弹实时、准确地预测拦截弹的拦截点与拦截时间,是实现中段突防的有效手段。针对弹道导弹中段突防中的拦截点坐标及拦截时间的预测问题,提出了一种基于监督学习的在线预测方法。以拦截弹的主动段关机参数和关机时刻为输入量,建立拦截时间和拦截点预测模型。在多层感知机神经网络的基础上构建有监督学习算法,通过攻防仿真获取拦截弹的参数制作训练数据集,在线下完成网络训练。仿真结果表明:神经网络能够有效在线预测拦截时间和拦截点坐标,预测结果的相对误差分别为0.124 3%和0.128 5%,拦截时间预测结果误差的平均值为0.224 0 s,拦截点预测结果距离误差平均值为2 016.48 m,均满足精度要求。
Abstract:Accurately predicting the intercept point and intercept time of the interceptor in real time is an effective way to realize the mid-course penetration of ballistic missiles. In order to predict the intercept point coordinates and intercept time during the mid-course penetration process of ballistic missile, an online prediction method based on supervised learning is proposed in this paper. Using the shutdown parameters and the shutdown time of the boost stage of the interceptor as inputs, the prediction model of intercept time and intercept point was established. Based on the multi-layer perceptron neural network, a supervised learning algorithm was formulated, and the interceptor's parameters were obtained through the attack and defense simulation to make the set of training data. The network training was completed offline. The simulation results show that the neural network can effectively predict the interception time and the coordinates of interception point online, and the relative error of the prediction results is 0.124 3% and 0.128 5% respectively; the average error of the prediction results of intercept time is 0.224 0 s; the average distance error of the prediction results of intercept point is 2 016.48 m. They all meet the accuracy requirements.
-
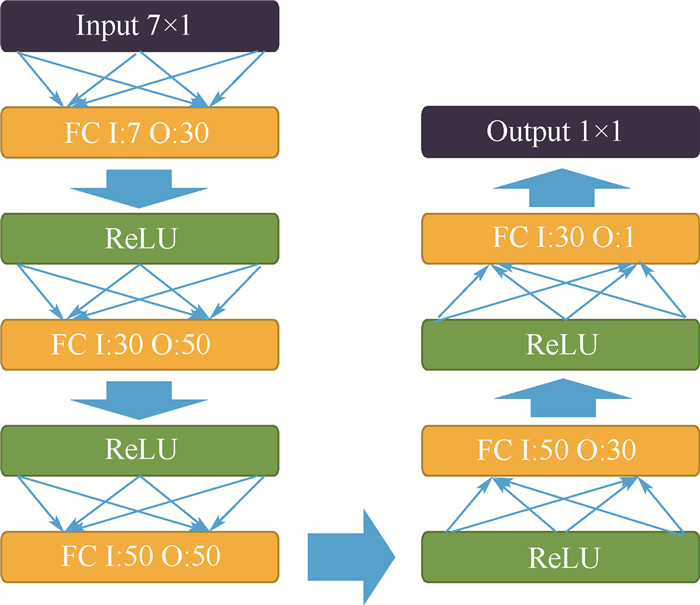
表 1 拦截时间预测网络结构
Table 1. Intercept time prediction network structure
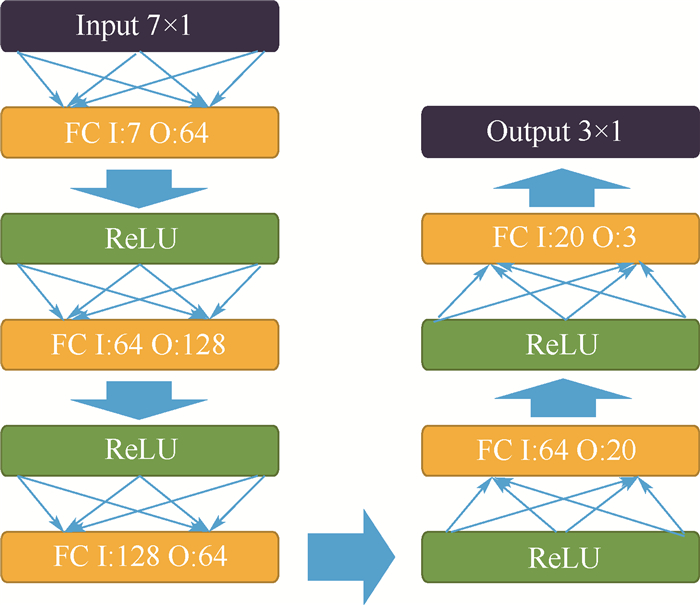
层名称 网络结构 输入层 7 全连接层1 I: 7 O: 30 激活函数1 ReLU 全连接层2 I: 30 O: 50 激活函数2 ReLU 全连接层3 I: 50 O: 50 激活函数3 ReLU 全连接层4 I: 50 O: 30 激活函数4 ReLU 全连接层5 I: 30 O: 1 输出层 1 表 2 拦截点预测网络结构
Table 2. Intercept point prediction network structure
层名称 网络结构 输入层 7 全连接层1 I: 7 O: 64 激活函数1 ReLU 全连接层2 I: 64 O: 128 激活函数2 ReLU 全连接层3 I: 128 O: 64 激活函数3 ReLU 全连接层4 I: 64 O: 20 激活函数4 ReLU 全连接层5 I: 20 O: 1 输出层 3 表 3 预测网络训练参数
Table 3. Prediction network training parameters
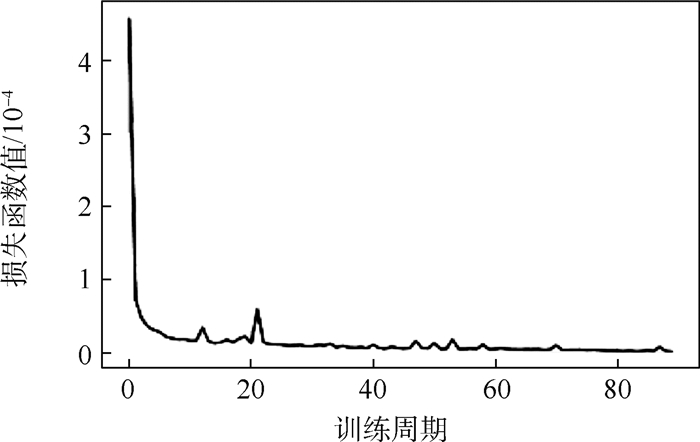
训练参数 拦截时间预测网络 拦截点预测网络 批尺寸 1 100 学习率 0.000 1 0.000 1 训练周期 94 54 表 4 拦截时间预测误差
Table 4. Prediction error of intercept time
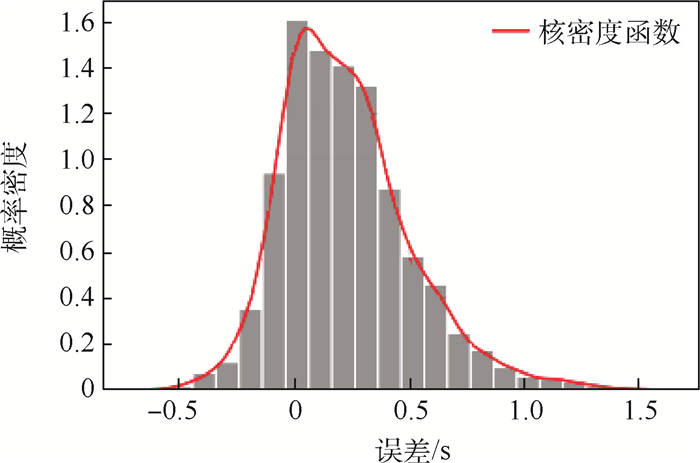
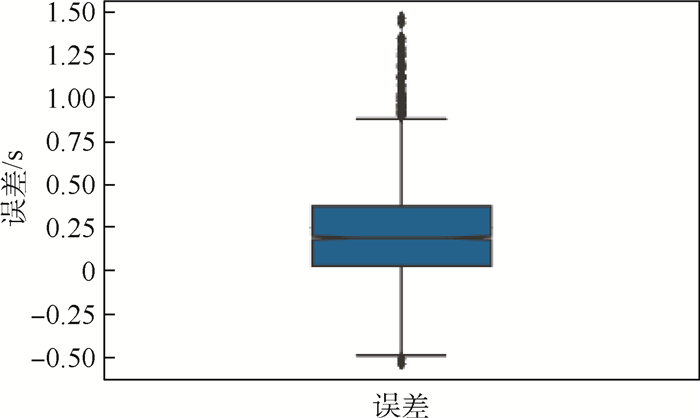
误差类型 平均值/s 最大值(绝对值) 标准差/s 相对误差 0.124 3% 误差 0.224 0 1.467 5 s 0.281 1 表 5 拦截点坐标预测误差
Table 5. Prediction error of intercept point's coordinates
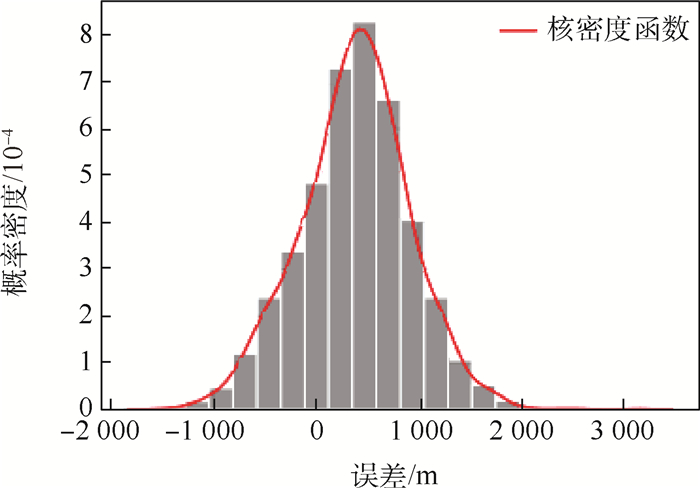
误差类型 平均值 最大值(绝对值) 标准差 相对误差/% 0.128 5 距离误差/m 2 016.48 9 255.64 1 223.14 X轴坐标误差/m 379.45 3 150.91 536.05 Y轴坐标误差/m 552.48 8 928.98 2 146.45 Z轴坐标误差/m 94.60 2 293.46 457.69 -
[1] 鲜勇, 郑晓龙. 弹道导弹攻防仿真系统建模[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2013: 14.XIAN Y, ZHENG X L. Modeling of ballistic missile attack and defense simulation system[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2013: 14(in Chinese). [2] THOMAS K, IAN W, WES R. Missile defense 2020: Next steps for defending the homeland[R]. Washington, D.C. : Center for Strategic International Studies, 2017. [3] 王虎, 邓大松. 地基拦截弹发展研究[J]. 战术导弹技术, 2019(3): 34-40.WANG H, DENG D S. Study on development of ground-based interceptor[J]. Tactical Missile Technology, 2019(3): 34-40(in Chinese). [4] 田宪科, 张科. 导弹拦截点计算及其仿真分析[J]. 飞行力学, 2011, 29(2): 93-97.TIAN X K, ZHANG K. Calculation and simulation analysis of missile intercept point[J]. Flight Dynamics, 2011, 29(2): 93-97(in Chinese). [5] 张华伟, 董茜, 王文灿, 等. 基于预测命中点的反弹道导弹拦截方法研究[J]. 弹箭与制导学报, 2007(2): 196-199. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9728.2007.02.062ZHANG H W, DONG Q, WANG W C, et al. Research way of intercepting ballistic missile based on the forecasting hitting position[J]. Journal of Projectiles, Rockets, Missiles and Guidance, 2007(2): 196-199(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9728.2007.02.062 [6] 王君, 周林, 雷虎民. 地空导弹与空中目标遭遇点预测模型和算法[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2009, 21(1): 80-83.WANG J, ZHOU L, LEI H M. Forecast model and arithmetic on hit point of ground-to-air missile and aerial target[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2009, 21(1): 80-83(in Chinese). [7] ZARCHAN P. Tactical and strategic missile guidance[M]. 6th ed. Reston: AIAA, 2012: 213-324, 715-862. [8] 谢经纬, 陈万春. 大气层外拦截弹建模与攻防效能分析[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2018, 44(9): 1826-1838. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0095XIE J W, CHEN W C. Exo-atmospheric interceptor modeling and penetration and defense effectiveness analysis[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018, 44(9): 1826-1838(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0095 [9] SONG E J, TAHK M J. Three-dimensional midcourse guidance using neural networks for interception of ballistic targets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2002, 38(2): 404-414. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2002.1008975 [10] SONG E J, LEE H, TAHK M. On-line suboptimal midcourse guidance using neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the 35th SICE Annual Conference International Session Papers. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 1996: 1313-1318. [11] SONG E J, TAHK M J. Real-time midcourse guidance with intercept point prediction[J]. Control Engineering Practice, 1998, 6(8): 957-967. doi: 10.1016/S0967-0661(98)00041-0 [12] 袁亚军. 中远程导弹防御指控系统设计与仿真评估研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2017: 11-13.YUAN Y J. The designation and research on middle-long range missile defense system command and control[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2017: 11-13(in Chinese). [13] CHIA H, TAN C, SUNG S. Enhancing knowledge discovery via association-based evolution of neural logic networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2006, 18(7): 889-901. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2006.111 [14] XU J X, HOU Z S. Notes on data-driven system approaches[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2009, 35(6): 668-675. [15] CHEN S, BILLINGS S A. Neural networks for nonlinear dynamic system modelling and identification[J]. International Journal of Control, 1991, 56(2): 319-346. [16] LESHNO M, LIN V Y, PINKUS A, et al. Multilayer feedforward networks with a nonpolynomial activation function can approximate any function[J]. Neural Networks, 1991, 6(6): 861-867. [17] GOLIK P, DOETSCH P, NEY H. Cross-entropy vs. squared error training: A theoretical and experimental comparison[C]//Interspeech, 2013: 1756-1760. [18] ALMÁSI A, WOZ'NIAK S, CRISTEA V, et al. Review of advances in neural networks: Neural design technology stack[J]. Neurocomputing, 2016, 174: 31-41. [19] GOODFELLOW I, BENGIO Y, COURVILLE A. Deep learning[M]. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2016. [20] 刘孝马. 大气层外动能拦截器中段制导相关问题研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学, 2015: 13.LIU X M. Research on the problems about midcourse guidance for exo-atmospheric kill vehicle[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2015: 13(in Chinese). 期刊类型引用(5)
1. 苗扬. 氢泄漏光学检测技术综述. 北京工业大学学报. 2022(03): 312-330 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 邓佳佳,陈星星,卢金树,薛大文,王恒远. 液舱旋转射流气体惰化特性分析. 煤气与热力. 2022(03): 19-25 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 王晨臣,潘俊,王洋洋,段伟杰. 抽吸气流量对催化惰化系统性能影响. 北京航空航天大学学报. 2022(07): 1183-1189 .  本站查看
本站查看4. 王立群,范菊莉,刘冠男,刘祎,潘俊,冯诗愚. 飞机燃油箱地面冷却惰化数值仿真. 海军航空大学学报. 2022(03): 242-248 .  百度学术
百度学术5. 彭孝天,冯诗愚,任童,张瑞华,潘俊,王洋洋. 飞行包线下燃油箱耗氧型催化惰化系统性能研究. 北京航空航天大学学报. 2021(08): 1565-1570 .  本站查看
本站查看其他类型引用(2)
-







 下载:
下载:






 百度学术
百度学术

