Optimization method of multi-constellation GNSS vertical protection level based on particle swarm optimization algorithm
-
摘要:
针对传统的高级接收机自主完好性监测(ARAIM)算法中完好性风险和连续性风险分配存在保守的问题,提出了一种基于粒子群优化(PSO)算法的完好性风险和连续性风险分配方法。将不同的分配策略作为算法中不同的粒子,选取不同故障子集对应的垂直保护级的加权和为适应度函数,每个粒子基于粒子群优化寻优原理更新其位置及速度直至满足条件,进而得到优化后的分配策略和对应的垂直保护级。通过双星座对所提方法进行验证,并与传统方法进行对比分析,结果表明:基于PSO算法的完好性风险和连续性风险分配策略优化了垂直保护级,提高了ARAIM全球可用性。
-
关键词:
- GNSS /
- 垂直保护级 /
- 完好性风险 /
- 连续性风险 /
- 粒子群优化(PSO)算法
Abstract:Aimed at the conservative problem of integrity risk and continuity risk allocation in the traditional Advanced Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring (ARAIM) algorithm, a new integrity risk and continuity risk allocation method based on Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) algorithm is proposed. This method uses different allocation strategies as different particles in the algorithm, and selects the weighted sum of the vertical protection levels corresponding to different fault subsets as the fitness function. Each particle updates its position and speed based on the principle of particle swarm optimization until the conditions are met, and then the optimized allocation strategy and the corresponding vertical protection level are obtained. The algorithm is verified through dual constellations and compared with traditional methods. The results show that the integrity risk and continuity risk allocation strategy based on the particle swarm optimization algorithm optimizes the vertical protection level and improves the ARAIM global availability.
-
随着现代科学技术的发展,工程研究人员面临的工程系统日益庞大和复杂。考虑到对大型复杂系统进行物理实验的难度和实验所需的昂贵费用,工程研究人员试图通过建模与仿真技术来代替这些大型复杂系统的物理实验。通过对所建计算模型的分析来代替昂贵复杂的真实物理实验。但是,由于计算模型是由真实物理过程抽象近似而得到的,所以会存在一些模型信息与真实的物理过程不尽相同。模型和真实物理实验之间存在的差异使得工程研究人员对计算模型的准确性和可信度产生了质疑,在这种情况下,模型确认工作应运而生[1-3]。模型确认是指“从模型预期用途的角度客观评估模型在多大程度上反应真实物理的过程[4-7]”,简单来说就是要准确且定量地描述计算模型与实验结果之间的差异。
目前为止,已有的模型确认方法基本可分为四大类[8]:经典假设检验法[9-10]、贝叶斯因子法[11-13]、频率指标法[14-15]和面积指标法[16]。经典假设检验法主要关注于对原假设(H0:模型正确)和备择假设(H1:模型不正确)的接受或拒绝,没有定量地评估模型的准确性。贝叶斯因子法则是在考虑了先验信息后给出了模型正确的概率(置信度),但同样未能定量地评估模型的准确性。与前2种方法不同,频率指标法给出了模型与实验间的定量差异,但这一方法只考虑了均值这一特征量,对不确定情况下的离散程度等其他特征量没有考虑。基于以上问题,Ferson等通过对比计算模型输出量的累积分布函数与物理实验结果的经验分布函数,提出了面积指标法和u-pooling法[16]。该方法能够定量且客观地衡量模型与实验间的差异,但是该方法仅适用于一维或多维独立的模型。而工程中建立的模型常常是多维且相关的,此时上述方法就不再适合。所以,在此方法的基础上李维等又提出了基于概率积分转换(Probability Integral Transformation, PIT)的指标法和t-pooling法[17]。这二者分别用于解决相关多输出情况下的单个确认点和多个确认点的模型确认问题, 该方法的主要优点是在模型确认时考虑了多个输出的相关性,但PIT指标法和t-pooling法需要求解模型输出的联合累积分布函数,这在输出维度很高时是很难准确求得的。
对于以上模型确认方法所存在的各种问题,本文提出了一种新的模型确认方法。该方法使用核主成分分析(KPCA)的思想,并将其与面积指标方法相结合,给出了易于求解的模型确认指标,较好地解决了相关多输出情况下的模型确认问题。
本文首先回顾了面积指标和u-pooling指标,并指出了u-pooling法存在的问题;其次详细叙述本文所提出的新的模型确认方法;接着给出算例证明方法的正确性及有效性;最后对该方法的特点做出总结。
1. 面积指标法与u-pooling法
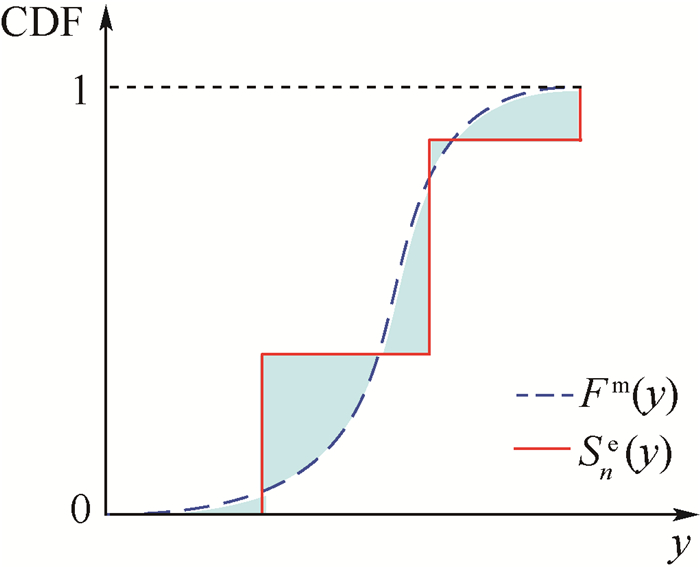
在文献[16]中,对于单输出的模型确认问题分别给出了用于单个确认点的面积指标法和用于多个确认点的u-pooling法,面积指标法是通过定量比较单个确认点处模型输出量y的累积分布函数(CDF)Fm(y)和实验观测值的经验分布函数Sne(y)的差异来评价模型与实验的一致性的,Fm(y)和Sne(y)的几何关系见图 1。
Fm(y)和Sne(y)的差异可以用数学表达式描述:

(1) 不同模型确认问题中面积指标的数值大小与所研究问题的输出量本身值的大小有关,但对于同一个确认问题,面积指标的大小则能较为准确且客观地反映出模型的好坏。由于Sne(y)依赖于实验样本,因此该方法的结果不可避免地会受到实验值样本量的影响[16]。
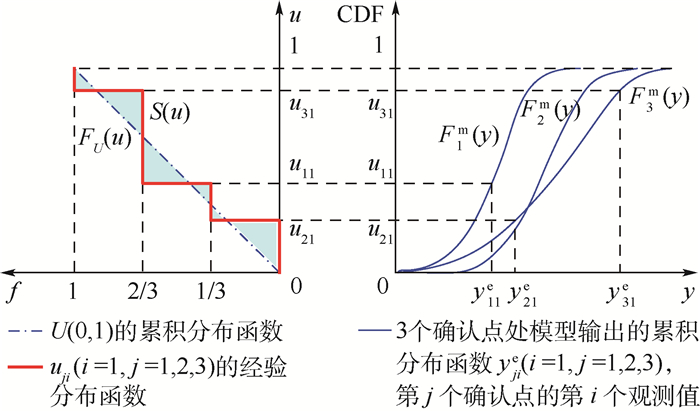
对于多个确认点,如果分别对每个确认点进行面积指标的求解,则会得到多个模型确认结果且不能合理地将这些结果进行统一,所以文献[16]提出了u-pooling法来解决多确认点问题。u-pooling法使用概率积分转换使得多个确认点的信息能够融合起来,从而得到一个合理的模型确认结果。将k个确认点处的模型输出量记作(y1, y2, …, yk),它们在各自确认点处的模型累积分布函数记为(F1m, F2m, …, Fkm)。k个确认点的实验观测值记为(y1e, y2e, …, yke),其中任意一个向量yje=(yj1e, yj2e, …, yjne)(j=1, 2, …, k)代表了第j个确认点处的n个实验观测值。u-pooling法首先将第j(j=1, 2, …, k)个确认点处的实验观测值yje通过对应的模型累积分布函数Fjm进行概率积分转换,从而由计算模型累积分布函数得到转换的概率值uji=Fjm(yjie)(i=1, 2, …, n;j=1, 2, …, k)。由实验样本yjie得到转换值uji后,就可以由uji得到其经验分布函数S(u)。由概率积分转换定理可知,单变量分布函数的概率分布为标准均匀分布U(0, 1),那么在模型输出分布与实验分布完全一致的假设条件下,每个确认点的实验观测值进行转化后的uji值均是服从标准均匀分布的,那么由所有确认点处得到的所有转换值也应该是服从标准均匀分布的,这也就意味着在模型与实验完全一致的条件下,S(u)应该是标准均匀分布的累积分布函数。则模型和真实物理过程的差异就可以用S(u)和标准均匀分布的累积分布函数FU(u)的面积差

u-pooling法将不同确认点处的实验观测信息通过相应确认点处的计算模型的累积分布函数进行融合,并且0≤q(FU, S)≤0.5。与面积指标相同,对于同一个确认问题,u-pooling指标的大小也能够直接反映出多个确认点的情况下计算模型的好坏。
在上述u-pooling法的实现过程中,可以看出该方法并没有考虑多个确认点处输出之间的相关性,而对于时间或空间上的多个确认点处的输出,它们之间往往具有非常强的相关性,因此u-pooling法这样处理多个确认点的模型确认是不合理的。本文将考虑多个确认点处输出间的相关性,并将多个确认点的模型确认与多输出的模型确认统一起来,将多确认点看作是多输出的一个特例,在这种情况下完成多输出模型确认工作。
2. 多输出模型的核主成分分析确认方法
2.1 主成分分析与核主成分分析
核主成分分析是在主成分分析的基础上发展起来的一种多元数据统计方法,为清晰起见,先对主成分分析进行简要说明,然后对核主成分分析与主成分分析进行对照,最后建立基于核主成分分析的多输出模型确认方法。
2.1.1 主成分分析
主成分分析(Principal Component Analysis,PCA)[18-20]的目的是将相关性较强的多维变量转化为彼此不相关的新变量。考虑一个相关d维输出模型y=[y1(x), y2(x), …, yd(x)],其中x为输入变量组成的向量。主成分分析能够将这些相关的多个输出y=[y1(x), y2(x), …, yd(x)]转化为线性不相关的主成分。其具体实现过程如下:
假设得到了N组上述d维模型y=[y1(x), y2(x), …, yd(x)]的输出实现值yj=[yj1, yj2, …, yjd](j=1, 2, …, N),将其记作一个N×d的矩阵Y=[y1, y2, …, yN]T。然后计算这一组数据Y的协方差矩阵,记作Σ,则Σ的表达式如下:

(2) 其中:yc是将矩阵Y的每一列进行中心化和标准化后得到的。主成分是通过对协方差矩阵Σ进行分解得到的。

(3) 式中:λk为矩阵Σ的第k个特征值,且λ1≥λ2≥…≥λd;φk为d×1维与λk对应的特征列向量,且(φ1, φ2, …, φd)为相互正交的单位向量。由向量(φ1, φ2, …, φd)构成了一个主成分空间,将原始数据投影到该主成分空间中得到的新数据就是所求的主成分:

(4) 这些主成分彼此间线性无关,且每一个主成分的方差等于其对应的特征值。第一主成分的方差最大,依次往后方差越来越小,所有主成分的方差之和与原始变量的方差之和相等。每一个主成分的方差占总方差的比例称为该主成分的贡献率ck(k=1, 2, …, d)如下:

(5) 在实际应用中,经过主成分提取后,前几个主成分已经包含了大部分原始变量的变异信息,所以选取累计贡献率达到85%(一般取85%,可根据具体问题而改变)的主成分进行分析,剩余贡献率很小的主成分可以忽略其影响,从而达到降维的效果。通过主成分提取不仅将原始的相关性问题转化为不相关问题,而且可以在降维的同时得到与分析原始变量相近的结果,所以这一方法很适合被用于相关多输出的模型确认问题。
2.1.2 核主成分分析
上述主成分分析是一种基于线性相关的转换方法[20-21],而相关多输出模型确认问题中多个输出之间一般不仅是简单的线性相关关系,此时主成分分析就不能完全提取模型中的非线性特征,而核主成分分析则可以弥补主成分分析的这种局限性。
核主成分分析[21-24]是指基于核函数的主成分分析,其本质是将原始数据通过某种非线性映射将其投影到高维特征空间,使其在高维特征空间中被线性化,然后在该高维特征空间中再使用主成分分析方法,从而达到提取具有复杂非线性相关性数据的主成分这一目的。
假设得到了N组上述d维模型y=[y1(x), y2(x), …, yd(x)]的输出实现值yj=[yj1, yj2, …, yjd](j=1, 2, …, N),将其记作一个N×d的矩阵Y=[y1, y2, …, yN]T。之后定义一个映射Φ:Yd→FD,其中Yd为原变量空间,FD为高维特征空间,D为高维特征空间的维数(D>d)。将原始空间的模型输出实现值[y1, y2, …, yN]T映射到高维特征空间后变为Φ(y)=[Φ(y1), Φ(y2), …, Φ(yN)]T,每一个映射后的Φ(yj)都是一个1×D维的行向量,再将每一个向量中心化记为Φc(yj)。这样在变化后的新空间中,协方差矩阵可表示为

(6) 与主成分分析类似,也对该协方差矩阵进行矩阵分解。

(7) 式中:λk为矩阵Σ的第k个特征值且λ1≥λ2≥…≥λD;Κφk为D×1维与λk对应的特征列向量,且(Κφ1, Κφ2, …, ΚφD)为相互正交的单位向量。由向量(Κφ1, Κφ2, …, ΚφD)构成了一个核主成分空间,将原始数据投影到该核主成分空间中得到的新数据就是所求的核主成分:

(8) 然而原始空间到高维特征空间的映射并非显式关系,而是需要通过核函数得到,所以需要通过以下推导将核函数引入上述过程从而求得核主成分,具体推导过程如下。
由式(7) 可知,Σ是一个D×D维的矩阵,对于其中每一个特征值λk和与之对应的特征向量Κφk式(9) 均成立:

(9) 同时,对于每一个特征向量Κφk又可以表示为[Φc(yj)]T的线性组合,αkj为对应的相关系数:

(10) 将式(6) 与式(10) 代入式(9) 中,则式(9) 等价于:

(11) 可以将(11) 式写成如下形式:

(12) 式(12) 中, Φc(yi)[Φc(yj)]T可看作是Φc(yi)与Φc(yj)的内积,可以用核函数K(yi, yj)来表示:K(yi, yj)=Φc(yi)·Φc(yj)。
式(12) 又可以写成如下核函数表达的形式:

(13) 定义一个N×N维的新矩阵K,称为核矩阵,核矩阵中的每一个元素可用核函数的形式表达如下:

(14) 则式(13) 等价于如下表达式:

(15) 其中:αk=(αk1, αk2, …, αkN)T为N×1维的列向量。通过求解式(15) 可以得出特征值λk和对应的特征向量αk,再结合式(10) 可以求出矩阵Σ的特征向量


(16) 上述推导过程均是基于将Φ(yj)进行中心化处理后而得到的,但实际应用中并不知道Φ(yj)的显式表达,也就无法对其中心化,此时要使用Kc来代替K进行上述求解过程,Kc的表达式如下[18]:

(17) 其中:1N为N×N的矩阵,每一个元素都是1/N。
通过以上核主成分分析后,就可以得到核主成分。与主成分分析相同,同样保留累计贡献率达到85%(一般取85%,可根据具体问题而改变)的核主成分进行之后的分析求解。
核主成分分析法是一种非线性主成分分析法,它将原始变量通过某种非线性映射转化为高维特征空间内的线性问题。这一非线性映射没有直接的表达式而是通过核函数完成的,因此称为核主成分分析。可以看出此分析方法考虑问题更为全面,比主成分分析所包含的原始变量信息更多, 而且同样能起到对原始数据的替代和简化作用。
2.2 多输出模型的核主成分分析确认方法具体流程
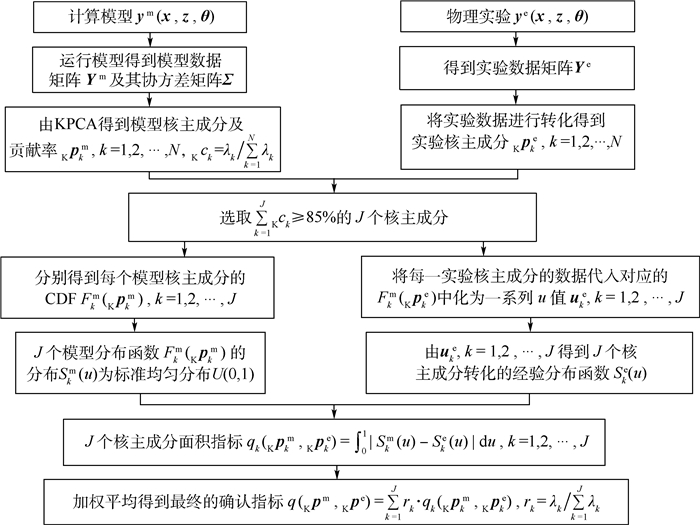
基于核主成分分析建立多输出模型确认方法的基本思想是:利用核主成分分析将相关的多输出问题转成不相关的核主成分,通过模型核主成分与实验核主成分的分布差异来识别模型与实验之间的一致性。具体的实现过程包括:① 模型输出数据核主成分分析; ② 实验数据在模型核主成分空间投影得到实验核主成分; ③ 模型、实验核主成分的差异求解。以下将对基于核主成分分析的模型确认方法进行详细说明。
设d维相关模型输出为ym(x, z, θ)=[y1m(x, z, θ), y2m(x, z, θ), …, ydm(x, z, θ)], 其中z为确认点变量,z=(z1, z2, …, zp)(p为确认点的数目,p≥1),θ为模型参数。对于具有p个确认点的问题,模型最终总的输出维数为dp。若该模型有N个输出样本yjm=[yj1m, yj2m, …, yj(dp)m](j=1, 2, …, N),则可以得到一个N×(dp)的模型输出矩阵Ym=[y1m, y2m, …, yNm]T。同样,设实验输出为ye(x, z, θ)=[y1e(x, z, θ), y2e(x, z, θ), …, yde(x, z, θ)],若实验有n个输出样本yje={yj1e, yj2e, …, yj(dp)e}(j=1, 2, …, n),则可以得到一个n×(dp)的实验输出矩阵Ye=[y1e, y2e, …, yne]T。得到了模型与实验的所有原始数据后,该方法的主要流程可用图 3描述。
1) 模拟产生N组模型数据
运行N次模型得到模型在给定的确认点z=(z1, z2, …, zp)处的N组输出数据,然后将数据记作一个N×(dp)的模型输出矩阵Ym。
2) 实验产生n组实测数据
重复n次实验得到和模型相同确认点处的n组实验数据,然后将数据记作一个n×(dp)的实验输出矩阵Ye。
3) 对Ym进行核主成分分析
对模型输出矩阵Ym进行核主成分分析,得到模型核主成分Κpkm(k=1, 2,…, N),和与之对应的特征值λ1≥λ2≥…≥λN,并计算每一核主成分的贡献率

4) 投影得到实验数据的核主成分
将实验输出数据投影到模型的核主成分空间,得到与模型核主成分Κpkm对应的实验核主成分Κpke。当模型与实验一致时,这二组数据应该也是一致的;反之,当模型与实验有差异时,这二者之间的差异则可以用来进行模型确认。
5) 选取贡献率大的J个核主成分进行降维
选取

6) J个模型核主成分分布函数的分布
由概率积分转换定理可知,所选取的J个模型核主成分Κpkm的分布函数Fkm(·)的分布为标准均匀分布,即Skm(u)=u。
7) 求得实验核主成分的转换样本的经验分布函数Ske(u)
将每一实验核主成分Κpke的n个数据代入对应的模型核主成分Κpkm的累积分布函数(CDF)Fkm(Κpke)中,得到这n个数据的概率值uke,计算uke的经验分布函数Ske(u)。
8) 求得每个核主成分模型与实验的差异
对选出的J个核主成分,可以得到转化后的J条经验分布函数Ske(u),将每一条分别和标准均匀分布U(0, 1) 进行对比,得到指标:

(18) 9) 基于核主成分分析的模型与实验的总差异
将这J个面积指标进行加权平均得到一个总的指标,加权系数


(19) 需要说明的是:在进行模型核主成分Κpkm与实验核主成分Κpke的对比时,没有直接使用面积指标而是将其做了类似u-pooling法中的转化,其目的是为了规范化差异的取值范围,避免不同输出模型量纲不同而造成的影响。转化后的指标具有明确的范围[0, 0.5],且该指标值越大,表示模型与实验之间的差异越大。最后对各个核主成分得到的指标进行汇总,该方法采用按照核主成分贡献率的大小加权平均,不同核主成分对指标的贡献可以通过加权系数体现。这一方法既解决了u-pooling法以及t-pooling法存在的多确认点间相关性的问题,也避免了求解多个输出间的联合概率分布函数,还具有降维的功能以便进一步简化分析过程,对于有多个确认点或多输出模型确认都可以使用,是对面积指标的延伸和拓展。
在上述基于核主成分分析的相关多输出模型确认方法的求解流程中,如果将数据的核主成分分析替换为主成分分析,其余步骤均保持不变,也是一种模型确认方法。但如同上述主成分分析所存在的问题,基于主成分分析的相关多输出模型确认方法对于非线性相关模型的确认效果则不如基于核主成分分析的确认方法好,在第3节的算例中会予以证实。
3. 算例分析
3.1 数值算例
将基于核主成分分析的相关多输出模型确认方法运用于一个数值算例中。假设该数值算例的实验输出如下:

(20) 式中:y1e和y2e代表 2个具有相关性的实验输出;z为模型确认点,在本算例中假设有20个不同的确认点,z分别取1, 2, …, 20;x1和x2为该算例的输入变量,均为服从标准正态分布N(0, 1) 的随机变量; (θ1, θ2)为该算例的参数,其真值均为1.5。最终该算例是一个含有随机变量的具有40维相关输出的模型确认问题,假设了3个备选的计算模型见表 1。
表 1 数值算例的3个备选的计算模型Table 1. Three alternative computational models of the numerical example模型 公式 模型1 y1m1=θ1cos(2πx1z)+zsin x2 θ1=1.5 y2m1=sin(0.5πx1+z)+zθ2cosx2 θ2=1.5 模型2 y1m2=θ1cos(2πx1z)+zsinx2 θ1=1.7 y2m2=sin(0.5πx1+z)+zθ2cosx2 θ2=1.5 模型3 y1m3=θ1cos(2πx1z)+zsinx2 θ1=1.7 y2m3=sin(0.5πx1+z)+zθ2cos x2 θ2=1.7 1) 方法的正确性验算
首先通过此算例验证所提方法的正确性。模型1与实验完全一致,是正确的模型,模型2和模型3与实验的差异依次增大。所以模型确认结果应是模型1优于模型2优于模型3。由式(20) 生成1 000组实验观测数据,表 1中的模型通过仿真分别得出10 000组模型响应数据,按照2.2节所提出的模型确认方法和步骤,得到每个模型的指标值,结果见表 2。
表 2 数值算例的模型确认结果Table 2. Model validation results of the numerical example模型 模型1 模型2 模型3 指标值 0.012 0 0.063 6 0.101 2 模型1的指标值小于模型2小于模型3,这一结果说明模型1优于模型2优于模型3,结论与定性分析相符,证明了该指标的正确性和有效性。
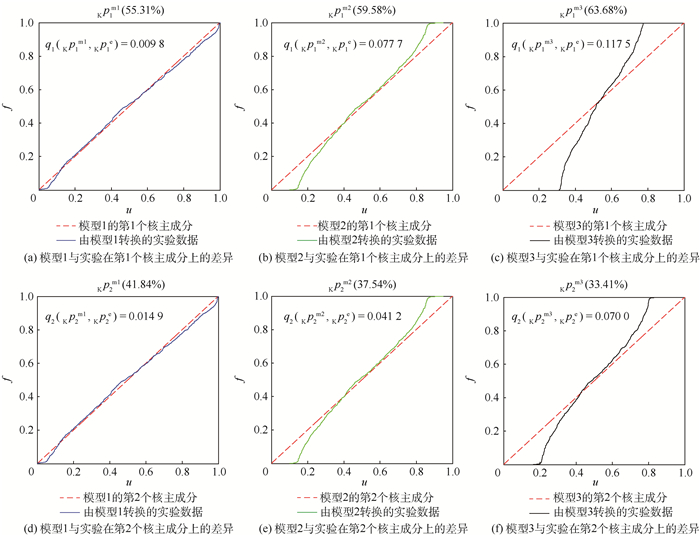
图 4给出了该数值算例确认结果的图形表示。从图中也可以直观地看出3个模型的优劣。在该算例中模型1、2和3分别使用核主成分分析得到了2个核主成分,每一个模型的每一个核主成分的贡献率以及对应的面积指标qk(Κpkm, Κpke)都标在图中。由于3个模型的累积分布函数的分布均为标准均匀分布,所以在3个图中表示相同。而实验数据经过不同模型转化则得到不同的经验分布函数,通过与标准均匀分布U(0, 1) 的对比就可以表示出不同模型与实验间的差异。对于模型1,由于它和实验完全一致,所以在图中可以看出,对于模型1的各个核主成分,实验数据转化后所得的经验分布曲线与由模型数据转化所得的标准均匀分布曲线几乎完全重合。而对于模型2和模型3,实验数据转化后所得的经验分布曲线与由模型数据转化所得的标准均匀分布曲线的差异则越来越大。
从表 2与图 4都可以看出,该方法可以给出实验与模型间的差异,并且能得到正确的模型确认结果,即模型1优于模型2优于模型3。
2) 方法的稳健性验算
证明了此方法的正确性后,再来分析此方法的稳健性,将该方法与基于主成分分析的模型确认方法进行对比,从指标的离散程度与错误率两方面对其进行比较。所谓离散程度是指多次计算模型确认指标后得到指标值的标准差,它能够从一定程度上描述指标的变异情况;而错误率则是指多次计算该指标后模型确认结果排序出现错误的频率。由式(20) 分别生成10、100、1 000组实验观测数据,由表 1中的模型通过仿真分别得出10 000组模型响应数据。按照2.2节所提出模型确认方法和步骤,在实验数据样本量不同的情况下,分别将2种方法求解指标的程序运行100次,计算这100个指标的标准差和错误率,计算结果见表 3。从表 3可以看出,随着实验数据样本量的增加,2种方法所求得的指标值的标准差和错误率都呈现下降趋势。但无论实验样本量为多少,基于核主成分分析的模型确认指标值的标准差和错误率总是低于基于主成分分析的。
表 3 数值算例的实验数据分别为10、100和1 000组时与10 000组模型数据确认结果对比Table 3. Validation results of the numerical example of comparing 10, 100, 1 000 experimental observations and 10 000 model responses指标类型 10组实验数据 100组实验数据 1 000组实验数据 标准差 错误率/% 标准差 错误率/% 标准差 错误率/% 模型1 模型2 模型3 模型1 模型2 模型3 模型1 模型2 模型3 基于PCA 0.027 9 0.025 1 0.023 4 35 0.012 7 0.014 7 0.013 5 18 0.004 4 0.006 8 0.006 6 2 基于KPCA 0.012 4 0.012 0 0.011 9 17 0.004 3 0.006 0 0.006 0 3 0.001 9 0.003 0 0.003 3 0 这一结果不难理解,由于核主成分分析比主成分分析多考虑了输出间的非线性相关性,所以获得原始数据的信息更为完整,最终使得基于核主成分分析的方法在结果中体现出一定的优势。由以上两部分说明本文所提出的基于核主成分分析的模型确认方法是正确且较为稳健的。
3.2 工程算例
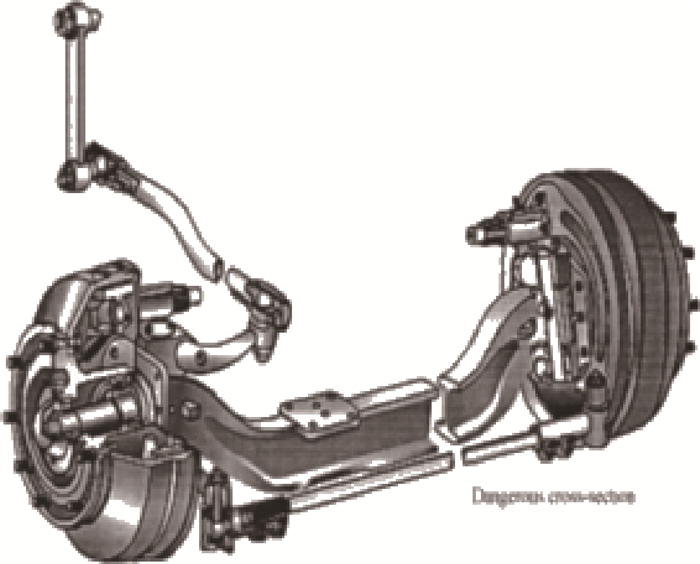
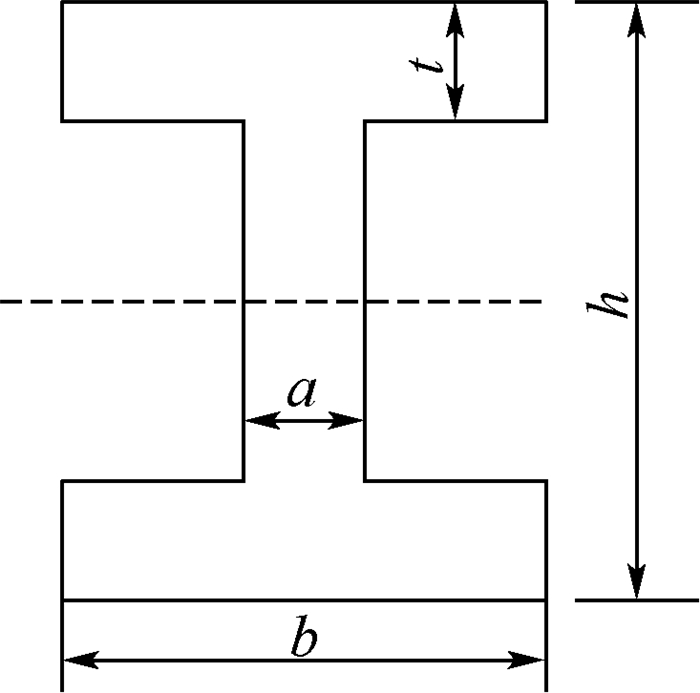
如图 5所示为一汽车前轴示意图,危险截面常发生在工字梁上,其截面形状如图 6所示。已知危险截面的最大正应力为σ和τ,其中M和T分别为前轴所受的弯矩和转矩, M~N(3 500 000, 175 0002), T~N(3 100 000, 155 0002), 二者均为正态分布, 单位为N·m。工字梁的几何参数为a、b、h、t,其中h服从正态分布h~N(85, 4.252) mm; a=12 mm, b=65 mm可以看作该算例的参数;t=14, 15, 16, 17, 18 mm,为该算例的确认点。则该工程问题的输出如下:

(21) 同理,分别假设如下3个备选的计算模型如表 4所示,其中模型1与实验一致,是正确的模型,模型2和模型3与实验的差异依次增大。所以模型确认结果应是模型1优于模型2优于模型3。
表 4 工程算例的3个备选的计算模型Table 4. Three alternative computational models of the engineering example模型 公式 模型1 
a=12 mm b=65 mm模型2 
a=10 mm b=65 mm模型3 
a=10 mm b=63 mm由式(21) 生成1 000组实验观测数据,表 4中的模型通过仿真分别得出10 000组模型响应数据,按照2.2节所提出的模型确认方法和步骤,得到每个模型的指标值,结果见表 5。
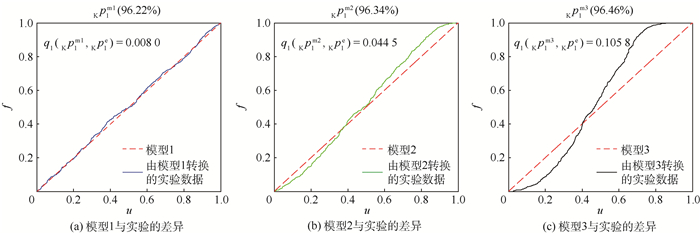
表 5 工程算例的模型确认结果Table 5. Model validation results of the engineering example模型 模型1 模型2 模型3 指标值 0.008 0 0.044 5 0.105 8 从表 5的结果可知,模型1的指标值小于模型2小于模型3,这一结果说明模型1优于模型2优于模型3,结论与定性分析相符, 再次证明了该指标的正确性和有效性。
图 7给出了这一确认结果的图形表示。从图中也可以直观地看出3个模型的优劣。在该算例中模型1、2和3分别使用核主成分分析得到了一个核主成分(因为第1个核主成分的贡献率已经高于85%),模型1的第1个核主成分的贡献率Kp1m1为96.22%,模型2的第1个核主成分的贡献率Kp1m2为96.34%,模型3的第1个核主成分的贡献率Kp1m3为96.46%,所以该算例中仅计算了模型与实验的第1个核主成分间的差异。由于核主成分分析结果只选择了第1个核主成分,所以加权系数为1,即第1个核主成分的指标值就是最终指标值。由于3个模型的累积分布函数的分布均为标准均匀分布,所以在图中三者表示相同。而实验数据经过不同模型转化则得到不同的经验分布函数,经过与标准均匀分布U(0, 1) 的对比就可以表示出不同模型与实验间的差异。从表 5和图 7都可以看出该方法可以给出实验与模型间的差异,并且能得到正确的模型确认结果,即模型1优于模型2优于模型3。
4. 结论
1) 方法将核主成分分析与面积法进行结合,将相关的模型输出与实验的输出通过核主成分分析变为不相关的核主成分,并用面积指标的思想定量描述二者间的差异。
2) 指标求解借鉴了u-pooling法的转化方法,将指标的范围规范在[0, 0.5]区间,避免了输出模型量纲不同所造成的影响。
3) 通过数值算例与工程算例证实了该方法的正确性和有效性,并与基于主成分的确认方法进行对比,证实了所提方法具有较好的稳健性。
4) 相比与多输出模型确认的PIT指标法和t-pooling法,该方法避免了求解多输出的联合分布函数,使得该方法在计算的难度上大大降低;同时该方法考虑了多个确认点间的相关性并使用核主成分分析处理了这一问题,使得该方法在理论上也更加完善。另外,该方法还利用核主成分分析对多个输出问题进行了降维,对于具有强相关性的高维输出模型确认问题,可以在保证分析精度的情况下大大降低分析的复杂度。
5) 本文提出的指标也有一定的局限性,首先,核主成分分析只是一种数学上处理问题的方法,它分析出的每一个核主成分物理意义不够明确,在工程使用中比较难理解。其次,虽然方法避免了求解多输出的联合分布函数,但是在核主成分分析中核函数构成的矩阵和样本量是成正比的,所以当样本量过大时,该方法的计算量较大。
处理具有相关性多输出模型的确认方法还有很多,可以进一步探索,提出更简洁高效的指标来解决工程中的模型确认问题。
-
表 1 ISM参数设置
Table 1. ISM parameter setting
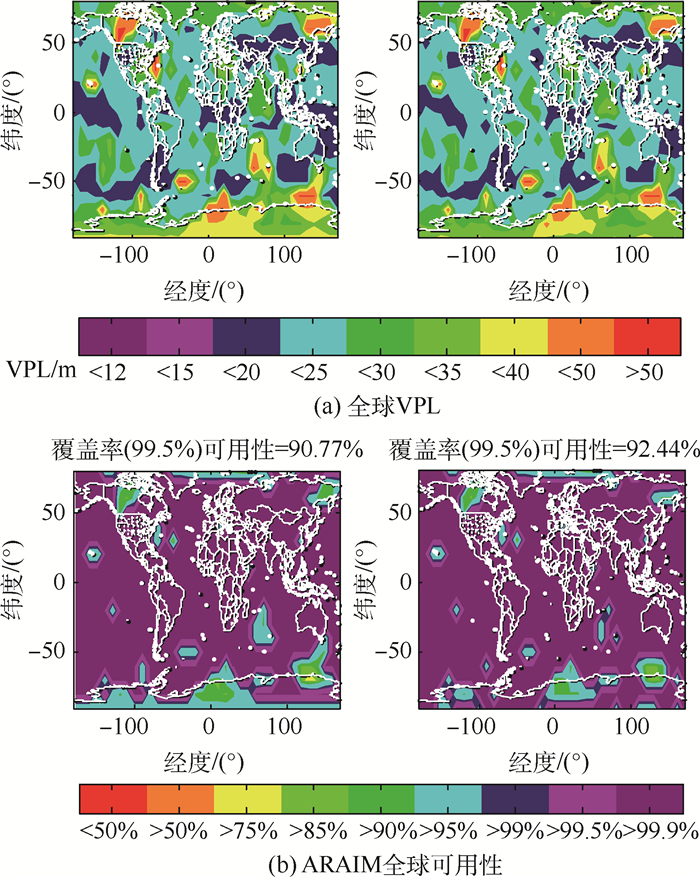
组号 星座 Psat Pconst bcont bnom σURA σURE 1 GPS 10-5 10-8 0 3/4 1 2/3 BDS 10-4 10-8 0 3/4 1 2/3 2 GPS 10-4 10-8 0 3/4 1 2/3 BDS 10-5 10-8 0 3/4 1 2/3 3 GPS 10-5 10-8 0 3/4 3/2 1 BDS 10-4 10-8 0 3/4 1 2/3 4 GPS 10-4 10-8 0 3/4 1 2/3 BDS 10-5 10-8 0 3/4 3/2 1 表 2 优化前后的ARAIM全球可用性对比
Table 2. Global availability comparison of ARAIM before and after optimization
组号 ARAIM全球可用性/% 传统分配方法 本文方法 1 90.77 92.44 2 92.10 93.49 3 77.62 79.40 4 79.23 81.01 -
[1] 刘金鑫, 滕继涛, 李锐, 等. 基于子集包含减少ARAIM子集数量的方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(8): 1592-1660. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0517LIU J X, TENG J T, LI R, et al. Method for reducing the number of ARAIM subsets[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(8): 1592-1660(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0517 [2] BLANCH J, WALTER T, ENGE P, et al. Advanced RAIM user algorithm description: Integrity support message processing, fault detection, exclusion, and protection level calculation[C]//ION Global Navigation Satellite Systems Conference, 2012: 2828-2849. [3] MENG Q, LIU J Y, ZENG Q H, et al. Improved ARAIM fault modes determination scheme based on feedback structure with probability accumulation[J]. GPS Solutions, 2019, 23(1): 16. doi: 10.1007/s10291-018-0809-8 [4] 王尔申, 杨迪, 宏晨, 等. ARAIM技术研究进展[J]. 电信科学, 2019, 35(8): 128-138.WANG E S, YANG D, HONG C, et al. Research progress of ARAIM technology[J]. Telecommunications Science, 2019, 35(8): 128-138(in Chinese). [5] JOERGER M, PERVAN B. Multi-constellation ARAIM exploiting satellite motion[J]. Navigation, 2020, 67(2): 235-253. doi: 10.1002/navi.334 [6] ZHAI Y W, ZHAN X Q, CHANG J, et al. ARAIM with more than two constellations[C]//ION 2019 Pacific PNT Meeting, 2019: 925-941. [7] LUO S L, WANG L, TU R, et al. Satellite selection methods for multi-constellation advanced RAIM[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2020, 65(5): 1503-1517. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2019.12.015 [8] BANG E, MILNER C, MACABIAU C, et al. ARAIM temporal correlation effect on PHMI[C]//International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation, 2018: 2682-2694. [9] SUN X, XU L, JI Y, et al. An extremum approximation ARAIM algorithm based on GPS and BDS[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 30027-30036. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2972766 [10] SUN Y, WANG T S, WANG Z P, et al. Optimal risk allocation for BDS/GPS advanced receiver autonomous integrity monitoring[C]//Proceedings of the 2015 International Technical Meeting of the Institute of Navigation, 2015: 687-695. [11] BLANCH J, WALTER T, ENGE P. RAIM with optimal integrity and continuity allocations under multiple failures[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2010, 46(3): 1235-1247. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2010.5545186 [12] EL-MOWAFY A, YANG C. Limited sensitivity analysis of ARAIM availability for LPV-200 over Australia using real data[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2016, 57(2): 659-670. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2015.10.046 [13] Working Group C, EU-U.S. ARAIM technical subgroup milestone 3 report[EB/OL]. (2016-02-25)[2019-09-20]. [14] Working Group C, EU-U.S. ARAIM concept of operation[EB/OL]. [2019-09-20]. [15] 刘若辰, 李建霞, 刘静, 等. 动态多目标优化研究综述[J]. 计算机学报, 2020, 43(7): 1246-1278.LIU R C, LI J X, LIU J, et al. A survey on dynamic multi-objective optimization[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2020, 43(7): 1246-1278(in Chinese). [16] RUSSELL C E, SHI Y. Particle swarm optimization: Developments, applications and resources[C]//Congress on Evolutionary Computation, 2002: 81-86. 期刊类型引用(16)
1. 陈宝,谢光毅,黄春,付江华. 基于改进K均值和马尔科夫链的公交车行驶工况构建. 重庆工商大学学报(自然科学版). 2024(03): 18-25 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 阴艳超,施成娟,邹朝普,刘孝保. 基于深度时间卷积神经网络与迁移学习的流程制造工艺过程质量时序关联预测. 中国机械工程. 2023(14): 1659-1671 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 夏侯唐凡,陈江涛,邵志栋,吴晓军,刘宇. 随机和认知不确定性框架下的CFD模型确认度量综述. 航空学报. 2022(08): 180-196 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 林楠,刘翰霖,孟祥发,刘海琪,杨佳佳. 基于高光谱的黑土区土壤重金属含量估测. 农业机械学报. 2021(03): 218-225 .  百度学术
百度学术5. 詹文仲,何建宗,郑风雷,夏云峰. 基于主成分分析和模糊综合评价的架空线路状态评估研究. 电子设计工程. 2021(12): 117-120+127 .  百度学术
百度学术6. 宋学朋,柯愈贤,魏美亮,石海天,廖宝泉. 基于多维云模型的充填管道堵塞风险评估. 煤炭科学技术. 2021(09): 95-102 .  百度学术
百度学术7. 王石,宋学朋,石海天. 基于云模型和改进CRITIC的深井垂直充填管道磨损风险评估. 重庆大学学报. 2020(04): 73-84 .  百度学术
百度学术8. 李丹,黄钰辉,孙中宇,张卫强,甘先华,王佐霖,孙红斌,杨龙. 不同树种叶片养分含量提取的高光谱方法及精度评价. 热带地理. 2020(02): 175-183 .  百度学术
百度学术9. 王彦岩,马腾飞,沈义涛,张正兴,郝宝玉. 基于KPCA与KFDA的国六柴油机EGR系统故障诊断. 车用发动机. 2020(04): 31-35 .  百度学术
百度学术10. 张文,夏怀健,林海英,贾素锦,贺新房,袁葆. 面向用户侧的电能替代实施效果评估模型研究. 供用电. 2019(03): 27-31+43 .  百度学术
百度学术11. 任嘉骏,李心怡,薛凯琳. 基于数据挖掘的医院综合评价量化建模方法研究. 计算机应用与软件. 2019(02): 289-293+307 .  百度学术
百度学术12. 孙曙光,纪学玲,杜太行,郝立林,王锐雄. 机械振动下交流接触器电寿命预测失效特征量提取. 仪器仪表学报. 2019(03): 114-125 .  百度学术
百度学术13. 周游,张广智,高刚,赵威,易院平,魏红梅. 核主成分分析法在测井浊积岩岩性识别中的应用. 石油地球物理勘探. 2019(03): 667-675+490 .  百度学术
百度学术14. 张保强,苏国强,展铭,郭勤涛. 概率盒框架下多响应模型确认度量方法. 控制与决策. 2019(12): 2642-2648 .  百度学术
百度学术15. 赵录峰,吕震宙,阚丽娟. 随机和区间变量共存条件下的模型确认指标. 北京航空航天大学学报. 2018(05): 967-974 .  本站查看
本站查看16. 万青玲. 基于KPCA-GWO-SVR组合模型的股票价格预测. 中南财经政法大学研究生学报. 2018(01): 32-39 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(11)
-








 下载:
下载:






 下载:
下载:



 百度学术
百度学术