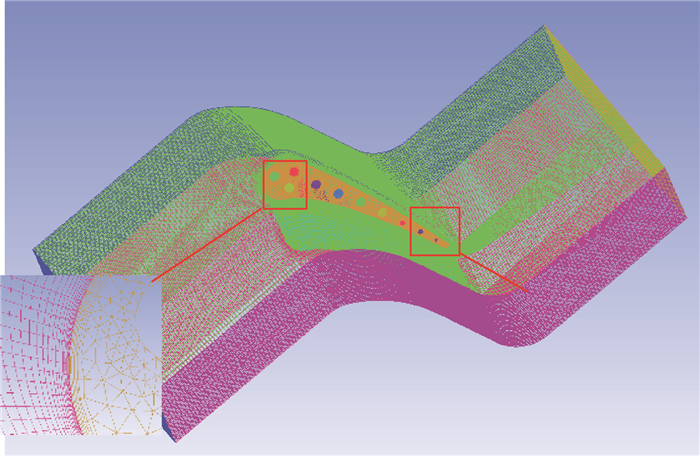
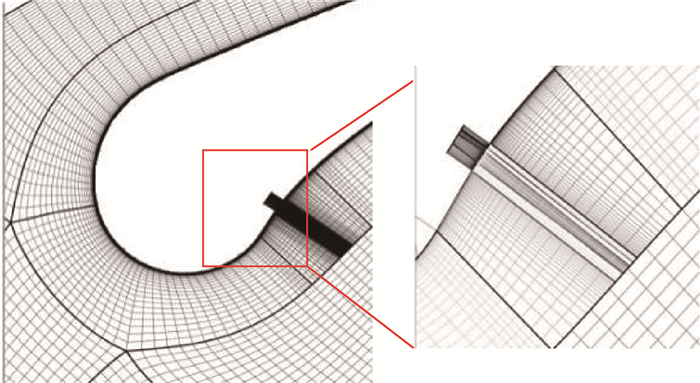
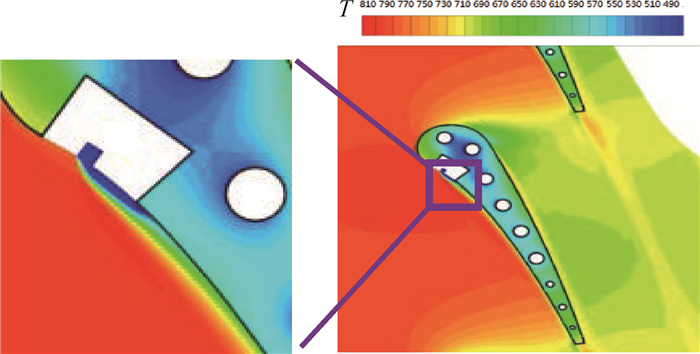
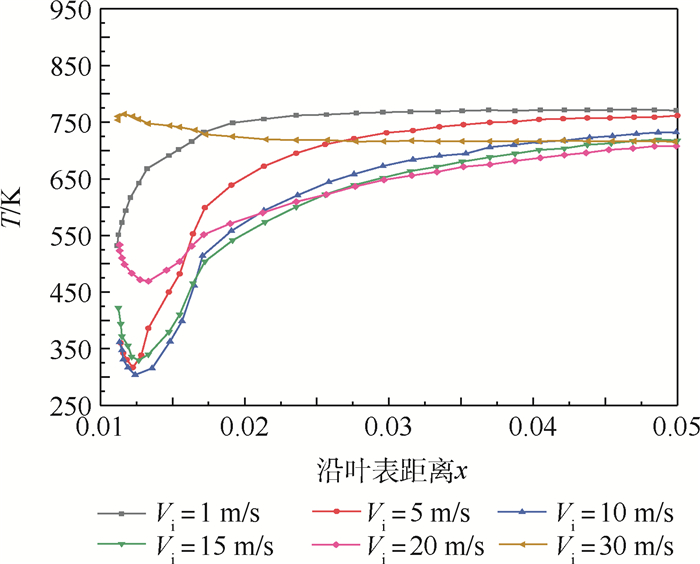
-
摘要:
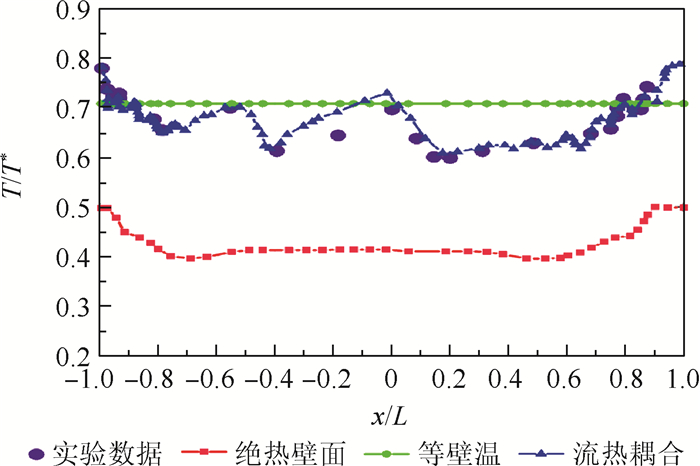
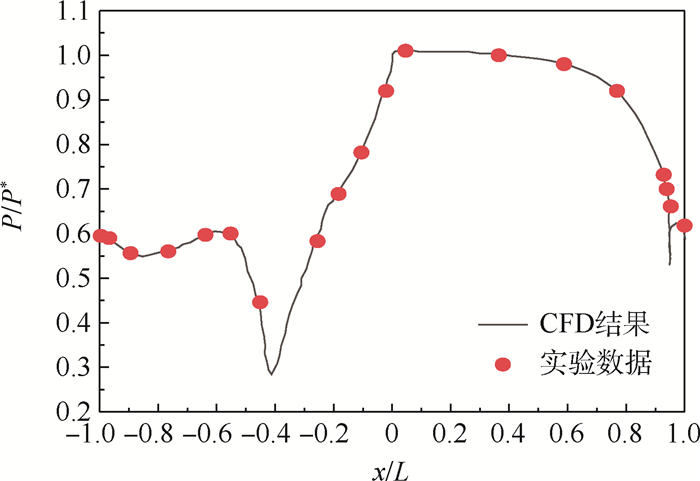
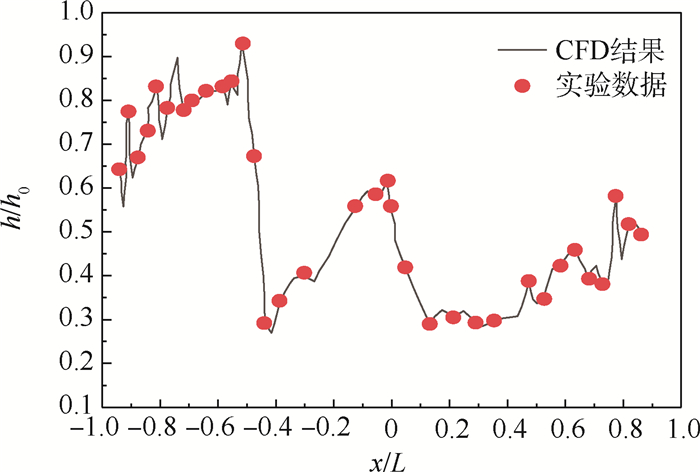
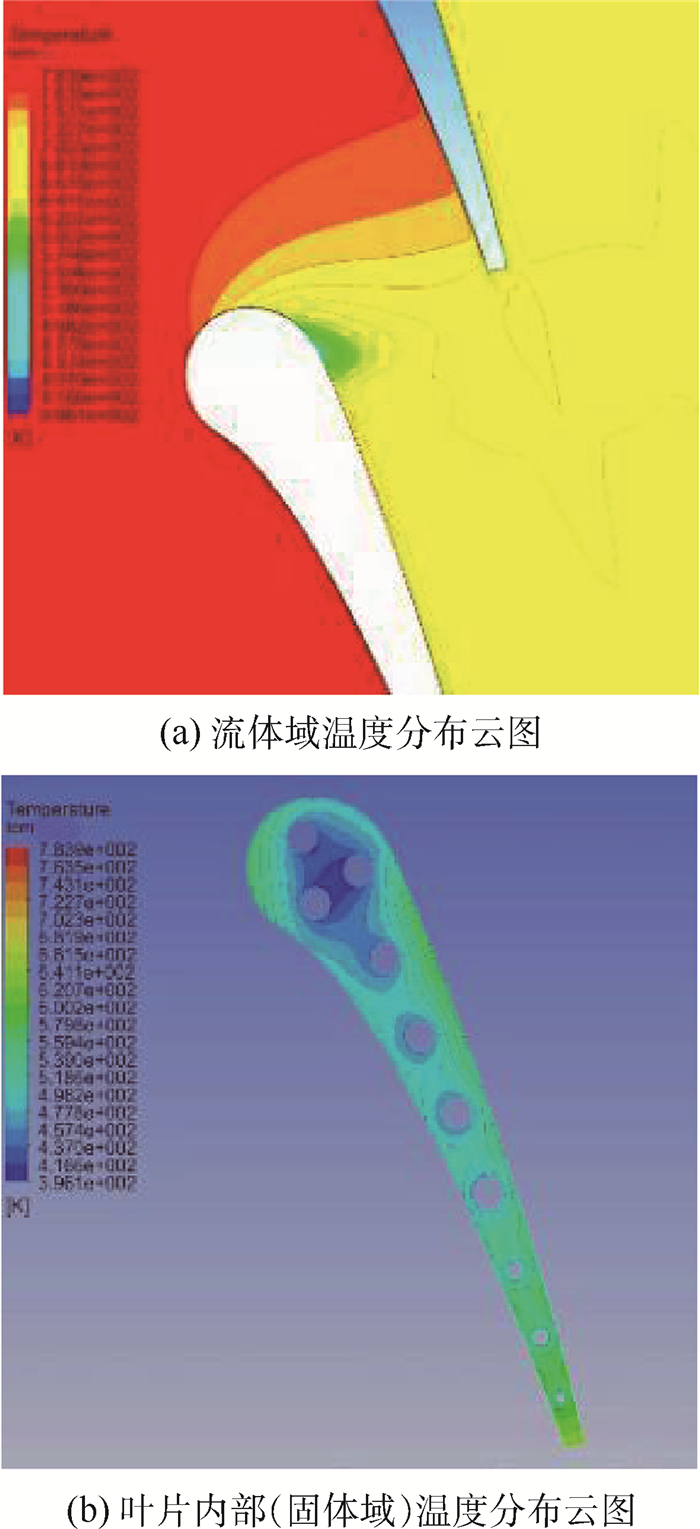
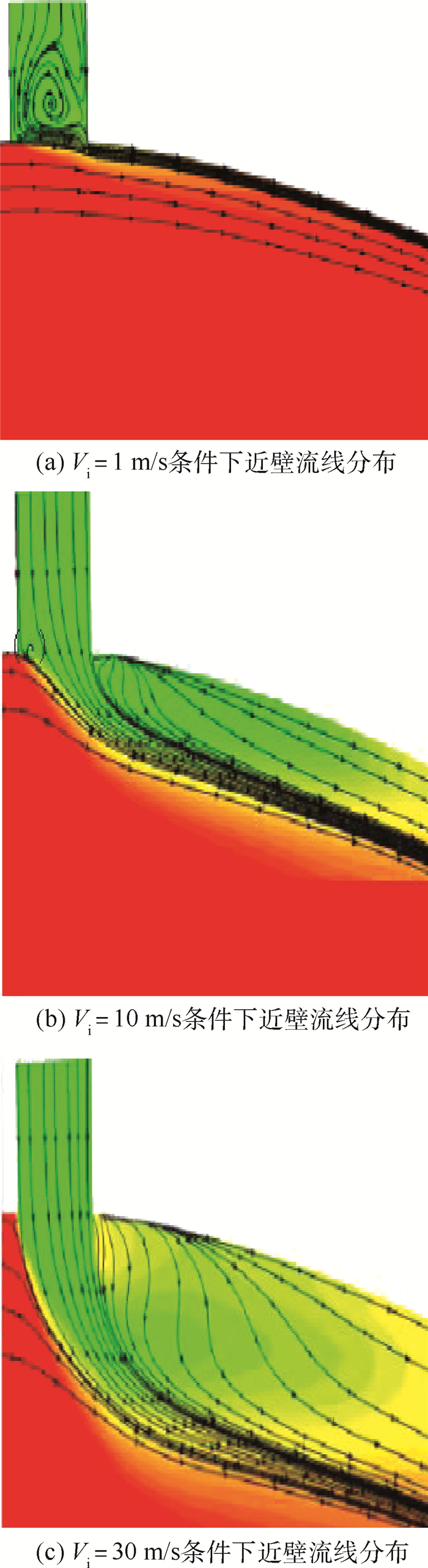
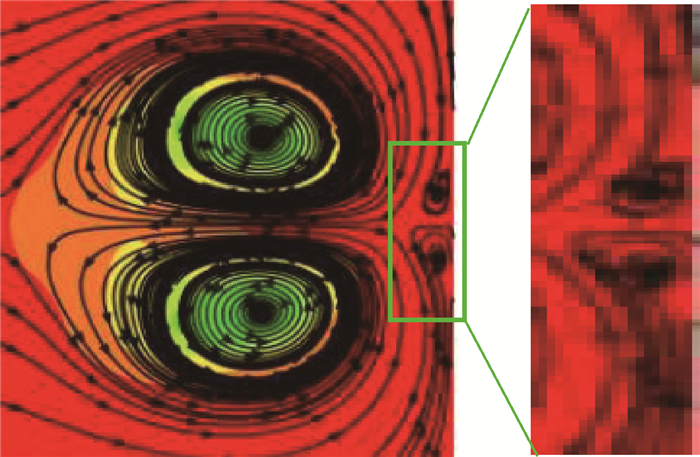
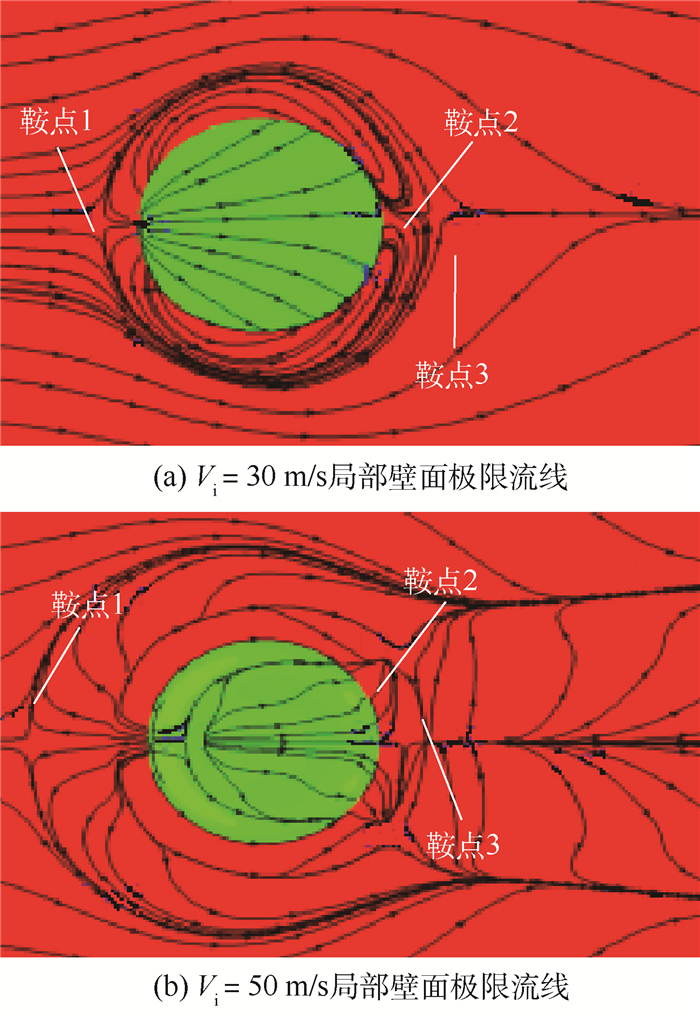
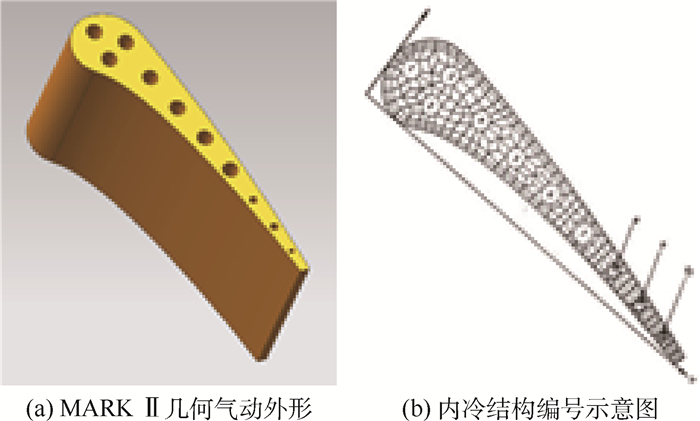
针对气冷涡轮叶片的多场耦合特性,利用流热耦合(CHT)方法,对采用不同气冷结构的高压涡轮导叶进行数值模拟。在内冷涡轮导叶算例中,对比实验数据选取精度较高的流热耦合计算方案,分析该内冷涡轮导叶的多场特性及耦合机理。在此基础上,以带有气膜冷却孔及内冷通道的气冷涡轮导叶为研究对象,重点围绕冷却射流与主流的相互作用,讨论近壁边界层中流热耦合关系及气冷效率影响因素等相关问题。结果表明:采用流热耦合计算方法及合适的湍流转捩模型有利于提高数值精度;气冷涡轮导叶的流场温度场密切耦合,流动换热特性互相影响;冷气射速低时,增加冷气流量可提高气膜冷却效率,冷气量达到一定值时,冷气流量增加将导致气膜冷却孔后上游冷却效果变差,下游冷却效果变好;冷气射速较高时,将与主流相互作用产生复杂流动结构(如肾形涡、马蹄涡等),对温度分布存在一定影响。
Abstract:According to the multi-field coupling characteristics of air-cooled turbine blades, numerical simulation of high-pressure turbine guide vanes with different air-cooling structures is carried out by the flow-heat coupling method. In internal cooling turbine blade example, by comparing the experimental data to select a higher-accuracy Conjugate Heat Transfer (CHT) calculation scheme, the multi-field characteristics and coupling mechanism of the internal cooling guide vane are analyzed. On this basis, the turbine guide vanes with film cooling holes and internal cooling channels are the research object, the interaction between cooling jet and main stream are focused on, and the fluid thermal coupling relationship in near wall boundary layer and related questions such as the factors affecting the air cooling efficiency are discussed. The results show that the use of flow-heat coupling calculation method and a suitable turbulent transition model is conducive to improving the simulation accuracy. Flow field and temperature field of the air-cooled guide vane are closely coupled, and the flow heat-transfer characteristics affect each other. In case of low speed rate, increased cool air flow can improve the cooling efficiency of the film, and if the flow of cold air is increased to a certain value, the increase in the cold flow will cause a poor upstream cooling effect behind the air-cooled hole and a better downstream cooling effect. High-speed cooling interacts with main stream, which will produce complex flow structures such as kidney-shaped vortices and horseshoe vortices that have certain influences on temperature distribution.
-
Key words:
- high-pressure turbine /
- Conjugate Heat Transfer (CHT) /
- film cooling /
- flow field structure /
- CFD
-
-
[1] 邹正平, 王松涛, 刘火星, 等. 航空燃气轮机涡轮气体动力学: 流动机理及气动设计[M]. 上海: 上海交通大学出版社, 2014: 101-102.ZOU Z P, WANG S T, LIU H X, et al. Turbine gas dynamics of air gas turbine: Flow mechanism and pneumatic design[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University Press, 2014: 101-102(in Chinese). [2] 安玉戈, 刘火星, 邹正平. 涡轮端区密封结构泄漏流动气热耦合研究[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2015, 36(12): 2579-2583.AN Y G, LIU H X, ZOU Z P. Aerothermal analysis of a turbine with endwall leakage flow[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2015, 36(12): 2579-2583(in Chinese). [3] 张红军. 多孔/流体/固体多区域流热耦合数值模拟方法以及耦合机制研究[D]. 北京: 北京航空航天大学, 2013: 26-29.ZHANG H J. Investigation of numerical conjugate heat transfer method and coupling mechanism for hybrid porous/fluid/solid domains[D]. Beijing: Beihang University, 2013: 26-29(in Chinese). [4] HEIDMANN J D, KASSAB A J, DIVO E A, et al. Conjugate heat transfer effects on a realistic film-cooled turbine vane: GT2003-38553[R]. New York: ASME, 2003. [5] BOHN D, BONHOFF B, SCHÖNENBORN H. Combined aerodynamic and thermal analysis of a turbine nozzle guide vane: IGTC-paper-108[R]. : IGTC, 1995. [6] 李宇. 三维流/热耦合数值模拟程序的发展及方法研究[D]. 北京: 北京航空航天大学, 2011: 33-36.LI Y. A 3-D conjugate heat transfer solver and methodology research[D]. Beijing: Beihang University, 2011: 33-36(in Chinese). [7] 苏欣荣, 袁新. 并行计算环境中的高效气热耦合方法[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2017, 38(1): 49-53.SU X R, YUAN X. Efficient gas-heat coupling method in parallel computing environment[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2017, 38(1): 49-53(in Chinese). [8] EIFEL M, CASPARY V, HONEN H, et al. Experimental and numerical analysis of gas turbine blades with different internal cooling geometries[J]. Journal of Turbomachinery, 2011, 133(1): 11018-11019. doi: 10.1115/1.4000541 [9] MAZUR Z, HERNANDEZ-ROSSETTE A, GARCIA-ILLESCAS R, et al. Analysis of conjugate heat transfer of a gas turbine first stage nozzle[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2006, 26(16): 1796-1806. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2006.01.025 [10] 董平. 航空发动机气冷涡轮叶片的气热耦合数值模拟研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2009: 10-11.DONG P. Research on conjugate heat transfer simulation of aero turbine engine air-cooled vane[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2009: 10-11(in Chinese). [11] HYLTON L D, MIHELC M S, TURNER E R, et al. Analytical and experiment evaluation of the heat transfer distribution over the surface of turbine vane: NASA-CR-168015[R]. Washington, D.C. : NASA, 1983. [12] LUO J, RAZINSKY E H. Conjugate heat transfer analysis of a cooled turbine vane using the V2F turbulence model: GT2006-91109[R]. New York: ASME, 2006. [13] 尚修宇. 高压涡轮多学科耦合机理及分析方法研究[D]. 北京: 北京航空航天大学, 2019: 10-12.SHANG X Y. Research on the multidisciplinary coupling mechanism and analysis method of HP turbine[D]. Beijing: Beihang University, 2019: 10-12(in Chinese). [14] KAYS W M, CRAWFORD M E. Convective heat and mass transfer[M]. 3rd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1993. [15] HISHIDA M, NAGANO Y, TAGAWA M. Transport processes of heat and momentum in the wall region//Proceedings of Eighth International Heat Transfer Conference, 1986: 925-930. [16] LIN Y, SPMG B, LI B, et al. Measured film cooling effectiveness of three multihole patterns[J]. Journal of Heat Transfer, 2006, 128(2): 192-197. doi: 10.1115/1.2137762 [17] MARGASON R J. Fifty years of jet in cross flow researeh[C]//Proceedings of the AGARD Symposium on Computational and Experimental Assessment of Jets in Cross Flow, 1983: 41. -







 下载:
下载: