-
摘要:
针对胶铆混合连接方式单面修补铝合金板的疲劳性能,设计了未修理、铆接修理、胶接修理和胶铆修理4种不同形式的试验件,对其进行了疲劳试验。建立了试验件的有限元模型,得到了结构应力分布,获得了裂纹长度-裂纹尖端应力强度因子(SIF)曲线,并与试验结果进行了对比。结果表明:胶接修理和胶铆修理能有效降低裂纹处应力水平及裂纹扩展速率,且相对于未修理试验件疲劳寿命分别提升184.3%和197.3%;胶铆修理中铆钉能抑制胶层脱黏,相比胶接修理方式修理质量更可靠有效;有限元分析(FEA)结果与试验数据吻合良好,SIF误差基本保持在8%以内。
-
关键词:
- 修补方式 /
- 疲劳性能 /
- 疲劳裂纹扩展 /
- 有限元分析(FEA) /
- 应力强度因子(SIF)
Abstract:Aimed at the fatigue performance of aluminum alloy plate with hybrid adhesive-rivet single-sided patch, specimens with four different methods including un-repair, riveted repair, adhesive repair and adhesive-rivet repair were designed and subjected to fatigue tests. The finite element models of specimens were established, and the structural stress distributions and the crack length-crack tip Stress Intensity Factor (SIF) curves were obtained and compared with the test results. The results show that adhesive repair and adhesive-rivet repair methods can effectively reduce the stress level at the crack and the crack growth rate. Compared with un-repair specimens, the fatigue life of adhesive repair and adhesive-rivet repair methods is increased by 184.3% and 197.3%, respectively. For the adhesive-rivet repair, the rivets can inhibit the debonding of the adhesive layer, and the repair quality of this method is more reliable and effective than that of the adhesive repair method. The Finite Element Analysis (FEA) results are in good agreement with the test results, and the SIF error of FEA is approximately within 8%.
-
飞机在服役过程中,机体结构在交变载荷的作用下容易产生疲劳裂纹损伤,据统计表明,机身蒙皮处产生疲劳裂纹现象最为严重,约占91.3%[1]。疲劳裂纹产生后若没有被及时发现及修理,将最终导致结构的破坏,严重威胁飞行安全[2]。因此,必须第一时间对产生疲劳裂纹的损伤部位进行更换或修理。目前,针对铝合金蒙皮结构出现的疲劳裂纹损伤,通常采用的修理方式为裂纹尖端钻止裂孔(裂纹长度小于15 mm)和补片补强方式修理(裂纹长度大于15 mm)[3]。
止裂孔维修是通过消除裂纹尖端应力奇异性的方式降低应力集中,延缓裂纹扩展速率,属于临时性修理。而补片补强修理方案中,由于蒙皮结构内部不可达、不易操作等原因,一般采用金属补片通过铆接单面修补受损区域。铆接具有刚度高、抗剥离力强、可靠性高等优点,在航空行业中得到广泛应用。然而,由于铆钉的存在会增加结构质量,并且孔边区域会产生应力集中,使得结构受载情况更为恶劣,修理效果会大打折扣[4]。因此,新兴了另一种裂纹修补方式——复合材料胶接修补,由于胶接不需要开孔且具有连续的面连接,提高了结构强度和整体刚度,抗疲劳性能较传统铆接修理大幅提高[5-7]。但是,胶接也存在固有缺陷:抗剥离能力弱,易受湿热、腐蚀等外界环境因素影响而发生胶层老化,并且胶接的破坏形式是突然性开裂,瞬时连接强度降为零,大大限制了其在航空结构中的使用范围[8]。
基于此,有学者提出在机械连接中加入胶层进行混合连接以综合二者的优点[9-13],并且开始尝试在蒙皮结构修理中进行应用[14],发现混合连接方式具有更好的力学性能。库克超[11]提出在CFRP/铝合金异质材料之间采用胶铆混合方式进行连接的方法,分别通过有限元仿真和拉剪试验的方式对铆接、胶接和胶铆连接方式进行性能测试,并进行了对比分析,结果表明,胶铆混合连接接头的应力分布均匀,相比铆接方式降低了接头孔边应力集中水平,且铆钉的存在使得胶层所受剥离力与剪切力明显削弱,综合作用使得混合连接接头的力学性能显著提升。Sadowski等[12]对铆接、胶接和胶铆混合连接3种不同连接方式的双搭接结构进行静力拉伸测试和数值计算,结果表明,混合连接结构的拉伸强度最高,且比胶接结构和铆接结构分别高11%和130%。另外,相比纯胶接连接,加入紧固件进行混合连接一方面可以缓解胶层损伤扩展,但同时也可能带来应力集中的不利影响[13]。原志翔[14]采用胶接和胶铆混合2种不同连接方式对带圆形损伤孔的复合材料进行修补并开展静力拉伸测试,结果发现,胶铆混合修补方式承载能力更高。目前,对胶铆混合连接的研究大部分是针对胶铆接头的性能研究和理论分析,而对于胶铆混合连接在裂纹修理结构中的应用非常有限。
在补片铆接修理中,一般采用压铆连接,从而有效提升修理结构的强度和刚度。但是,压铆连接需要铆枪与顶铁在结构内外表面共同配合操作才能完成,对工艺要求较高且耗时较长,而且会受制于蒙皮结构的形状和空间位置。考虑到胶铆混合连接中高性能胶黏剂的承载能力较强,对起辅助连接作用的铆钉强度要求不需要太高[8],尝试在混合连接修理结构中采用单面特种铆接——拉铆工艺作为胶接的辅助工艺。与普通压铆连接相比,拉铆连接操作简单,由于不需要顶铁配合且可单面操作,效率更高,并且在与胶层配合的接头力学性能研究中表现良好[12, 15]。
基于此,本文尝试将胶铆混合连接方式应用到带中心裂纹铝合金板的单面修补中,开展与未修理、铆接修理和胶接修理试验件的疲劳性能对比试验。同时,建立了4种试验件的有限元仿真模型,分析了不同修理方式下结构应力分布和裂纹尖端应力强度因子(SIF)变化,并与试验结果进行了对比分析。
1. 试验设备、材料和方法
1.1 材料参数
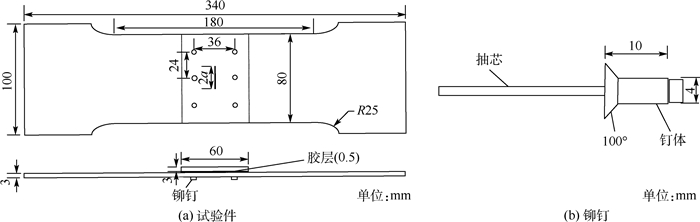
试验件采用3 mm厚度的2024铝合金板(材料参数参考文献[16])模拟蒙皮结构,使用相同材质和厚度的金属补片进行单面修补。铆钉选用CR3212沉头拉铆钉(钉体材质为5056铝合金),补片与基板之间采用双组分环氧树脂胶黏剂(Lord 320/322)进行黏接。材料的主要性能参数如表 1所示,其中铆钉与胶黏剂的参数由供应商提供。
表 1 材料性能参数Table 1. Parameters of material performance材料参数 2024 [16] CR3212 Lord 320/322 弹性模量/GPa 72 69 1.59 泊松比 0.33 0.33 0.35 屈服强度/MPa 371 326 拉伸强度/MPa 442 472 30.6 剪切强度/MPa 11.7 1.2 试验件制备
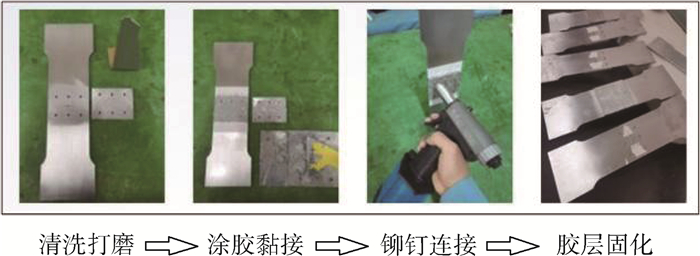
为了比对验证采用胶铆混合连接方式的修补效果,制备未修理、铆接修理、胶接修理和胶铆修理4种不同形式的试验件并分组(依次编组为第O、M、J和H组),每组4件,组内编号为O-1、O-2、O-3,…,依次类推。胶铆修理试验件和CR3212拉铆钉的尺寸示意图如图 1所示。铝合金基板的尺寸为340 mm×100 mm×3 mm,在中心处用线切割预制了半边长度a=10 mm的中心穿透裂纹,裂纹宽度为0.5 mm,裂纹方向与基板长度方向垂直。铝合金补片尺寸为80 mm×60 mm×3 mm,铆钉钉体直径为4 mm。其余3组试验件的尺寸参数与胶铆混合连接修理试验件一致,不同的是,铆接修理试验件不加入胶层黏接,胶接修理试验件不进行开孔和铆接。
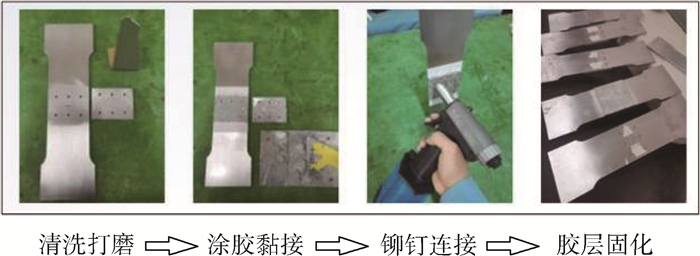
另外,如图 2所示,为了保证试验件的质量统一,规定胶铆修理试验件制作流程如下:
1) 清洗打磨。试验件上的油垢污渍等会影响胶层黏接效果,在黏接前使用砂纸打磨补片和基板黏接区域并使用丙酮清洗擦拭。清洗好的试验件置于洁净处干燥通风。
2) 涂胶黏接。对处理好的补片和基板黏接区域分别涂胶,为了控制胶层厚度统一,将少许0.5 mm直径的玻璃微珠均匀撒在胶层中,将补片与基板黏接并使用穿心夹定位夹紧。
3) 铆钉连接。补片与基板黏接后,立即使用气动铆枪将补片与基板进行拉铆连接。
4) 胶层固化。根据Lord 320/322胶黏剂给出的参数性能,将试验件置于洁净处静置24 h自然固化。
铆接、胶接修理试验件的加工方式参考胶铆修理试验件,在加工过程中发现,由于铆钉作用,胶铆混合连接对胶层厚度控制和固化时补片的加压固定都相比纯胶接更方便可靠,修理的效率更高。
1.3 疲劳性能测试
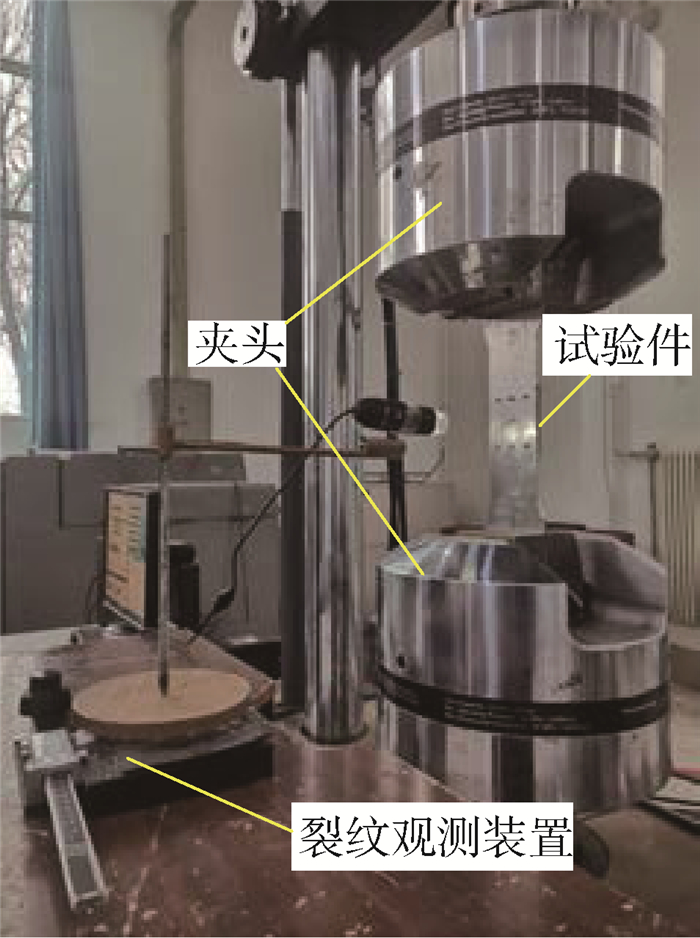
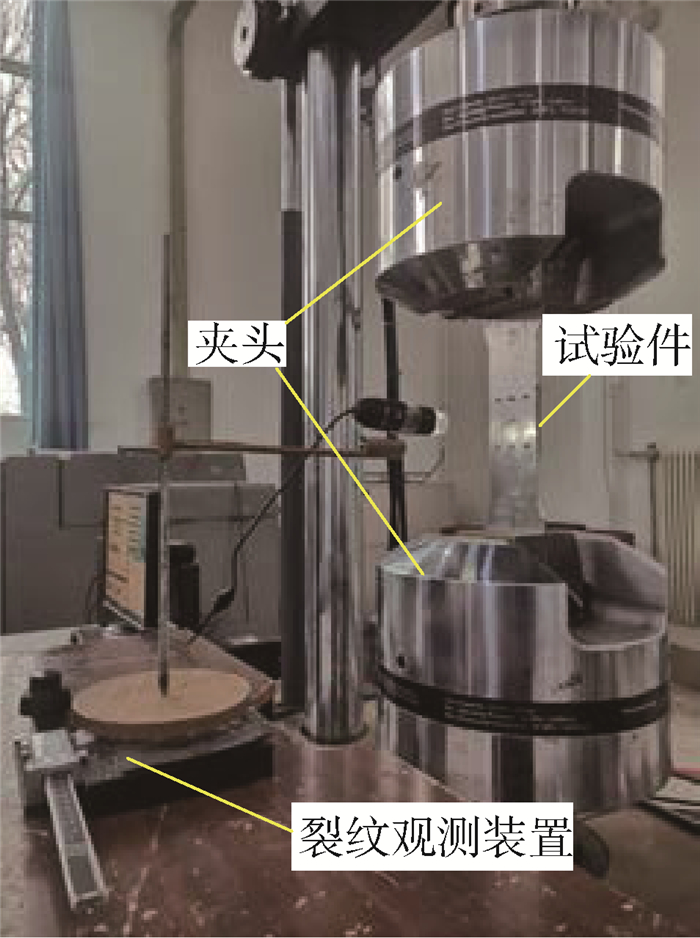
采用MTS 810-500 kN疲劳试验机对试验件进行疲劳性能测试,试验时参照GB/T 3075—2008[17]试验标准并设置加载参数如下:应力比R=0.1,频率10 Hz, 最大轴向载荷σmax=70 MPa,正弦波加载。试验过程中,通过裂纹观测装置定期对一定疲劳循环周次后的裂纹长度进行测量并记录(见图 3)。
2. 试验结果分析
2.1 试验结果
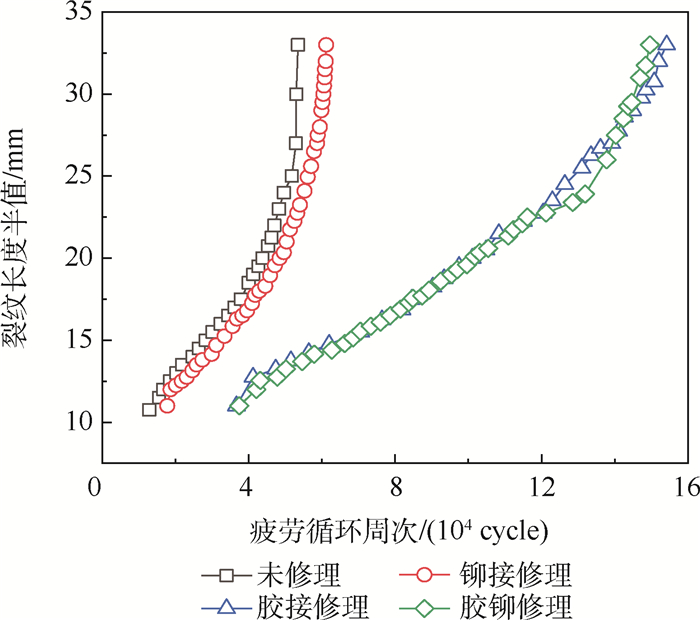
将4组试验件依次安装在疲劳试验机上进行疲劳加载测试,试验结果如表 2所示。为了比较不同修理方式下裂纹长度半值a与疲劳循环周次N的关系,分别取O-4、M-1、J-2和H-1这4件与所在组平均疲劳寿命较接近的试验数据作为各组样本,绘制a-N曲线,如图 4所示。试验结果表明,铆接修理小幅提升结构疲劳寿命,而胶接修理与胶铆修理修理效果接近,相比未修理方案疲劳寿命分别提高184.3%和197.3%。
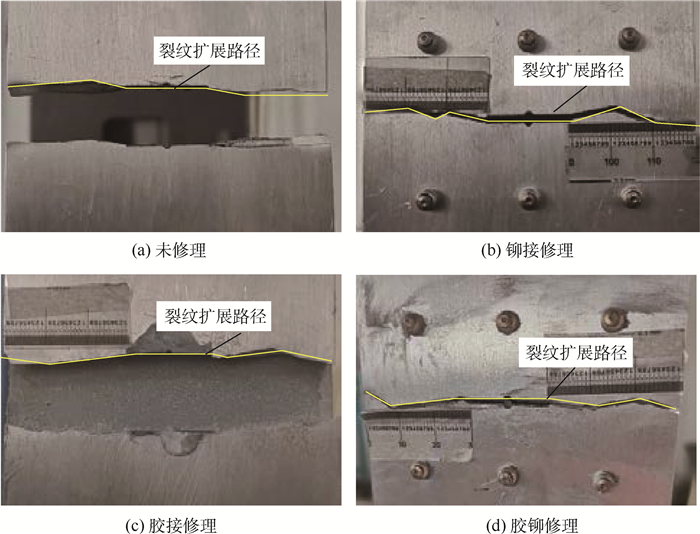
表 2 疲劳性能测试结果Table 2. Result of fatigue performance test组内编号 未修理/cycle 铆接修理/cycle 胶接修理/cycle 胶铆修理/cycle 1 61 104 61 360 102 619 151 651 2 53 884 62 289 158 308 151 748 3 42 907 73 430 183 402 162 088 4 44 579 62 396 131 294 136 537 平均寿命/cycle 50 619 64 869 143 906 150 506 离散度 0.145 3 0.076 4 0.209 4 0.060 5 寿命提高比例/% 28 184.3 197.3 图 5给出了4种不同形式试验件的失效模式。所有试验件的失效模式均为:基板沿着预制裂纹发生裂纹扩展并最终完全断裂,补片没有明显损伤。不同的是,铆接修理与胶铆修理的试验件由于铆钉作用,在基板完全失效后依然保持连接状态,而未修理与胶接修理试验件的上下端从失效断口完全分离脱开。因此,在修理结构中铆钉连接能增加结构的安全裕度。
分析胶接与胶铆混合连接2种连接形式胶层的失效模式,将胶接修理与胶铆修理试验件的胶层失效断面对比观察,如图 6所示。发现,胶接修理试验件中胶层以界面失效(脱黏)为主,而胶铆修理试验件则以内聚失效为主。
2.2 结果计算分析
为了研究比对不同方式的修理效果,需要计算分析4组试验件的裂纹扩展速率和裂纹尖端应力强度因子SIF的变化趋势。根据线弹性断裂力学理论,基于Paris公式计算裂纹扩展速率:

(1) 式中:da/dN为裂纹扩展速率;C和m为材料常数;ΔK为裂纹尖端SIF的增量,本试验中应力比等于0.1情况下:

(2) 其中:Kmax和Kmin分别为施加最大载荷与最小载荷时的裂纹尖端SIF。
含中心穿透裂纹的铝合金板裂纹尖端SIF计算公式为

(3) 式中:σ为试验件承受载荷应力值;w为试验件宽度。
通过对式(1)两边取自然对数,得到

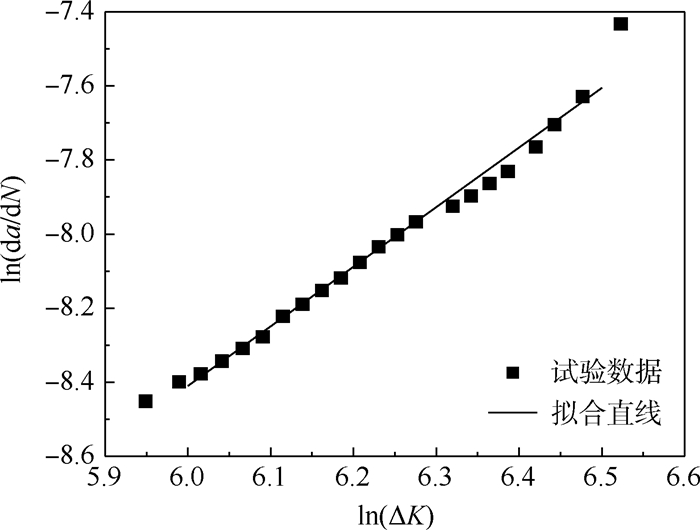
(4) 将O-4号试验件的试验数据代入计算,最终得到ln(da/dN)与ln(ΔK)之间的关系,如图 7所示。取置信水平α=0.05进行线性拟合,得到相关系数0.98,因此回归方程显著,表达式为

(5) 最终,得到铝合金材料参数C=1.42×10-8和m=1.61。采用应力强度因子修正法[18],假定修补试验件的材料参数与未修补试验件相同,即补片修补可以降低裂纹尖端应力强度因子但不改变材料参数。由此,可计算不同修理手段下的裂纹扩展速率,再由式(1)和式(2)得到4组试验件的裂纹尖端应力强度因子Kexp与a关系,如图 8所示。不难发现,胶接与胶铆混合连接修理试验件的Kexp-a曲线明显位于铆接修理和未修理试验件的下方,说明胶层作用能显著降低裂纹尖端SIF。在裂纹扩展初期,铆接修理、胶铆混合连接修理试验件的Kexp分别略低于未修理件和胶接修理件,而随着裂纹扩展(当a>20 mm之后),开始出现铆接修理、胶铆混合连接修理试验件的Kexp分别高于未修理和胶接修理试验件的现象。
进一步分析认为,造成该现象的原因如下:在铆接和胶铆混合连接试验件中,随着裂纹扩展,裂纹尖端所处位置不断偏离铆钉紧固力作用区域导致铆钉分载效果不断减弱。而铆钉孔的存在造成裂纹尖端应力集中现象比未开孔试验件更为严重。综合作用导致在裂纹扩展后期,铆接、胶铆混合连接修理试验件的Kexp分别高于未修理和胶接修理试验件。
3. 有限元分析
3.1 有限元模型
采用ABAQUS软件进行有限元仿真分析,由于试验件沿加载的长度方向呈中心对称,为减小运算负荷,建立中间试验段的1/2模型,图 9为胶铆混合连接修补试验件的有限元模型。采用扩展有限元方法XFEM(Extended Finite Element Method)模拟预制裂纹[19-21],为了提取裂纹尖端应力强度因子设置裂纹不扩展。基板与补片均采用C3D8R网格,采用三维实体模拟胶层,胶接面通过分别在补片与胶层、基板与胶层之间设置绑定约束(Tie)接触。为了提高计算精度,对基板中部裂纹所在区域进行局部网格细化,边界条件设置为一端固定约束,另一端施加最大轴向拉伸载荷70 MPa。
3.2 裂纹尖端应力分布及SIF预测
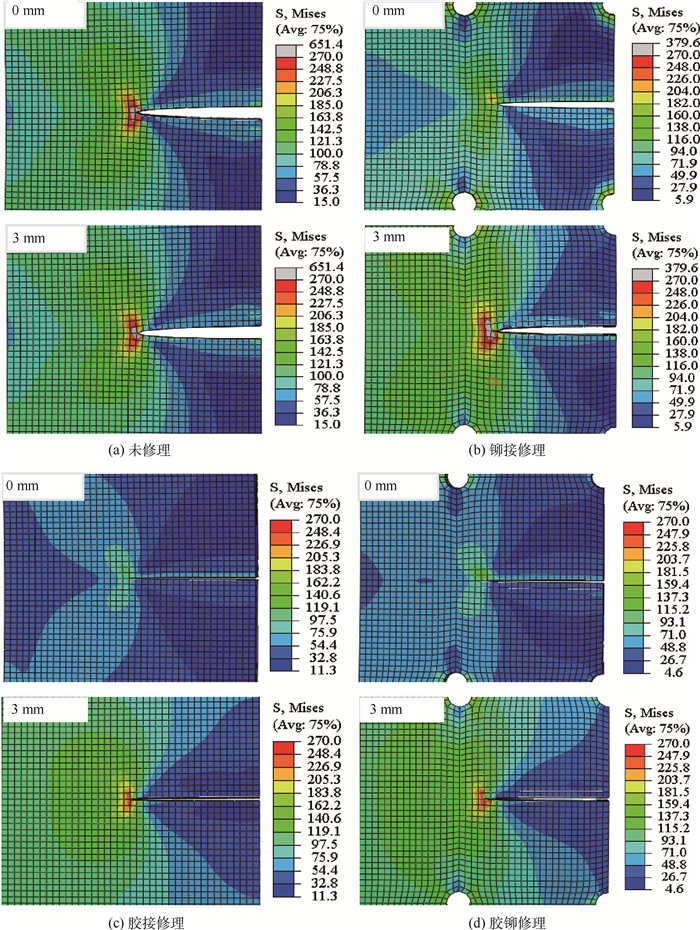
图 10为a=20 mm情况下,不同修理手段有限元模型的裂纹尖端Mises应力分布情况。其中,0 mm面为补片贴补的基板表面,厚度方向3 mm处则是对称的未贴补面。不难看出,由于补片的贴补使得修补面裂纹尖端附近的应力集中现象明显改善,且胶接修补与胶铆混合连接修补方式显著优于铆接修补。由于采取的是单面修补方式,修补面与未修补面应力分布不同,沿厚度方向裂纹尖端的SIF存在差异。设置有限元模型基板厚度方向网格尺寸为0.5 mm,得到a=20 mm情况下不同修理手段沿厚度方向裂纹尖端SIF值变化曲线,如图 11所示。修理结构中,未修补面较修补面裂纹尖端SIF高很多,胶接与胶铆混合连接方式修理结构沿厚度方向的裂纹尖端SIF基本一致且低于铆接修理试验件,这与裂纹尖端Mises应力分布情况基本相符。
建立a分别等于10 mm、12.5 mm、15 mm、17.5 mm、20 mm、22.5 mm、25 mm、27.5 mm、30 mm和32.5 mm时不同修理手段的有限元模型,绘制仿真预测的裂纹尖端SIF随a变化关系曲线及误差分析(见图 8)。所建立的模型能较好预测裂纹尖端SIF,大体上保持误差在8%以内,但在a较大时出现仿真结果明显低于Kexp现象,且胶接模型中最为显著。这可能是因为修理试验件在裂纹扩展后期,裂纹扩展路径带一定角度(见图 5)导致裂纹扩展速率加快,而有限元模型中采用的是垂直于加载方向的平直裂纹模拟,因此与实际产生偏离。另外,由图 6胶层失效模式结果,胶接修理试验件在疲劳试验过程中发生明显脱黏现象,而建立的有限元模型中未考虑脱黏因素影响。
4. 结论
通过对带中心裂纹的铝合金板开展胶铆混合连接修理,并与其他修理手段进行疲劳性能比对和有限元分析,得到以下结论:
1) 由于拉铆钉紧固力较小,铆接修理提升疲劳寿命有限,而胶接修理与胶铆修理能较好改善损伤结构的疲劳性能,疲劳寿命相比未修理试验件分别提升184.3%和197.3%。
2) 在胶接修理中,胶层可以有效传递载荷,降低裂纹尖端处的应力水平,减小裂纹尖端应力强度因子,但受拉剪力的作用易产生脱黏现象。胶接-拉铆混合连接修补中拉铆钉能抑制胶层剥离,提高修理结构的可靠性及安全裕度。
3) 建立的有限元仿真模型,能较好地模拟不同修理手段下裂纹处应力分布,预测的裂纹尖端SIF与试验结果吻合良好,误差基本保持在8%以内。
4) 提出的胶接-拉铆修理方案为蒙皮结构修补提供一定参考价值。
-
表 1 材料性能参数
Table 1. Parameters of material performance
材料参数 2024 [16] CR3212 Lord 320/322 弹性模量/GPa 72 69 1.59 泊松比 0.33 0.33 0.35 屈服强度/MPa 371 326 拉伸强度/MPa 442 472 30.6 剪切强度/MPa 11.7 表 2 疲劳性能测试结果
Table 2. Result of fatigue performance test
组内编号 未修理/cycle 铆接修理/cycle 胶接修理/cycle 胶铆修理/cycle 1 61 104 61 360 102 619 151 651 2 53 884 62 289 158 308 151 748 3 42 907 73 430 183 402 162 088 4 44 579 62 396 131 294 136 537 平均寿命/cycle 50 619 64 869 143 906 150 506 离散度 0.145 3 0.076 4 0.209 4 0.060 5 寿命提高比例/% 28 184.3 197.3 -
[1] 赵立涛, 王志瑾. 复合材料胶接修补金属裂纹板的应力强度因子研究[J]. 飞机设计, 2011, 31(2): 67-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4599.2011.02.016ZHAO L T, WANG Z J. The study of stress intensity factor of cracked metallic structure repaired with adhesive bonding composite patch[J]. Aircraft Design, 2011, 31(2): 67-70(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4599.2011.02.016 [2] 贺旺, 杜永华, 孙运刚, 等. 复合材料双面修理边缘裂纹铝合金厚板的静态和疲劳特性[J]. 南京理工大学学报, 2019, 43(4): 511-517.HE W, DU Y H, SUN Y G, et al. Static characteristics and fatigue behavior of edge-cracked thick aluminum plates double-side bonded with composite patches[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2019, 43(4): 511-517(in Chinese). [3] 何宇廷. 飞机结构寿命控制原理与技术[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2017: 346-356.HE Y T. Principle and technology of aircraft structure life control[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2017: 346-356(in Chinese). [4] CHEN Y W, YANG X J, LI M J, et al. Mechanical behavior and progressive failure analysis of riveted, bonded and hybrid joints with CFRP-aluminum dissimilar materials[J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2019, 139: 271-280. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2019.03.007 [5] BAKER A A. Bonded composite repair of fatigue-cracked primary aircraft structure[J]. Composite Structure, 1999, 47(1-4): 431-437. doi: 10.1016/S0263-8223(00)00011-8 [6] 董登科, 丁惠梁. 飞机金属结构复合材料修理技术[M]. 北京: 航空工业出版社, 2017: 5-13.DONG D K, DING H L. Advances in the bonded composite repair of metallic aircraft structure[M]. Beijing: Aviation Industry Press, 2017: 5-13(in Chinese). [7] 杨孚标. 复合材料修复含中心裂纹铝合金板的静态与疲劳特性研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科技大学, 2006: 46-60.YANG F B. The static characteristics and fatigue properties of the center-cracked aluminum plates bonded with composite patches[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2006: 46-60(in Chinese). [8] 王光建. 单面自冲铆-粘连接工艺的试验研究及数值模拟[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2008: 1-7.WANG G J. Experiment study and numerical simulation of single-sided rivet-bonding process[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2008: 1-7(in Chinese). [9] 刘璟琳. 胶铆复合接头力学性能及失效机理研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2019: 1-4.LIU J L. Study on mechanical properties and failure mechanism of hybrid bond-riveted joints[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2019: 1-4(in Chinese). [10] 乔海涛, 赖士洪, 邹贤武. 胶铆连接性能研究[J]. 中国胶粘剂, 2002(1): 52-53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2849.2002.01.018QIAO H T, LAI S H, ZOU X W. Study on properties of bond-riveted joint[J]. China Adhesives, 2002(1): 52-53(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2849.2002.01.018 [11] 库克超. CFRP/铝合金胶铆混合连接力学性能及疲劳强度分析[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2018: 67-68.KU K C. Analysis of mechanical properties and fatigue strength of CFRP/aluminum alloy adhesive-rivet hybrid jointing[D]. Xi'an: Xidian University, 2018: 67-68(in Chinese). [12] SADOWSKI T, GOLEWSKI P, ZARZEKA R. Damage and failure processes of hybrid joints: Adhesive bonded aluminium plates reinforced by rivets[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2011, 50(4): 1256-1262. doi: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2010.06.022 [13] 邹鹏, 倪迎鸽, 毕雪, 等. 胶螺混合连接在复合材料结构中的研究进展[J]. 航空工程进展, 2021, 12(1): 1-12.ZOU P, NI Y G, BI X, et al. Research development on bonded-bolted hybrid joint in composite structure[J]. Advances in Aeronautical Science and Engineering, 2021, 12(1): 1-12(in Chinese). [14] 原志翔. 复合材料胶铆混合修理损伤特性实验研究[D]. 天津: 中国民航大学, 2020: 44-51.YUAN Z X. Experimental study on damage properties of adhesive-rivet hybrid repair of composite materials[D]. Tianjin: Civil Aviation Universityof China, 2020: 44-51(in Chinese). [15] PIRONDI A, MORONI F. Clinch-bonded and rivet-bonded hybrid joints: Application of damage models for simulation of forming and failure[J]. Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology, 2009, 23(10-11): 1547-1574. doi: 10.1163/156856109X433063 [16] 肖群力, 黄其青, 殷之平. 典型机翼整体壁板止裂特性分析及优化设计[J]. 机械强度, 2012, 34(1): 92-96.XIAO Q L, HUANG Q Q, YIN Z P. Analysis of crack-arrest property and optimum design for typical integrally stiffened panel[J]. Journal of Mechanical Strength, 2012, 34(1): 92-96(in Chinese). [17] 全国钢标准化技术委员会. 金属材料疲劳试验轴向力控制方法: GB/T 3075-2008[S]. 北京: 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 2008: 1-13.National Technical Committee for Steel Standardization. Metallic materials, fatigue test, axial force control method: GB/T 3075-2008[S]. Beijing: General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, 2008: 1-13(in Chinese). [18] 王跃, 熊玉平, 赵霞, 等. 含裂纹铝合金板单面修补结构疲劳裂纹扩展分析[J]. 推进技术, 2018, 39(4): 865-871.WANG Y, XIONG Y P, ZHAO X, et al. Analysis of fatigue crack propagation for repaired aluminum alloy plate containing crack with single patch[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 2018, 39(4): 865-871(in Chinese). [19] BELYTSCHKO T, BLACK T. Elastic crack growth in finite elements with minimal remeshing[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 1999, 45(5): 601-620. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0207(19990620)45:5<601::AID-NME598>3.0.CO;2-S [20] 郭历伦, 陈忠富, 罗景润, 等. 扩展有限元方法及应用综述[J]. 力学季刊, 2011, 32(4): 612-625.GUO L L, CHEN Z F, LUO J R, et al. A review of the extended finite element method and its applications[J]. Chinese Quarterly of Mechanics, 2011, 32(4): 612-625(in Chinese). [21] 何龙龙, 刘志芳, 顾俊杰, 等. 基于XFEM的疲劳裂纹扩展路径和寿命预测[J]. 西北工业大学学报, 2019, 37(4): 737-743. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2758.2019.04.013HE L L, LIU Z F, GU J J, et al. Fatigue crack propagation path and life prediction based on XFEM[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2019, 37(4): 737-743(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2758.2019.04.013 期刊类型引用(5)
1. 冯蕴雯,宋祉岑,路成,陈晓宇. 基于跨尺度等效弹性的航空装备损修性能评估. 系统工程与电子技术. 2025(02): 508-517 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 王亚南,张广鑫,薛晓,宣善勇,符彬. 金属钉孔边裂纹复合材料修理方式研究. 化学与粘合. 2023(03): 275-279 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 张静,惠佳,李奇辉. 带闭合腔体金属胶接口盖成型工艺优化. 科技资讯. 2023(09): 60-64 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 刘礼平,齐雨阳,蔺越国,鲍蕊,徐建新,冯振宇,卿光辉. 碳纤维复合材料胶铆混合修理结构静载拉伸失效. 航空学报. 2023(24): 230-243 .  百度学术
百度学术5. 周庆祥,李刚卿,侯凯,肖君武,宋凯. 铝合金部件裂纹缺陷的多通道涡流检测仿真与试验研究. 电子测试. 2022(17): 34-38+87 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(2)
-







 下载:
下载:












 下载:
下载:





 百度学术
百度学术