-
摘要:
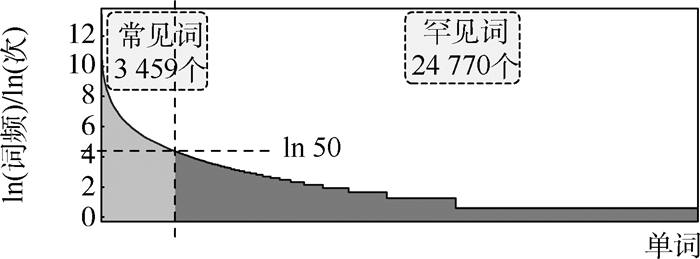
图像描述生成任务旨在基于输入图像生成对应的自然语言描述。现有任务数据集中大部分图像的描述语句通常包含少量常见词和大量罕见词,呈现出长尾分布。已有研究专注于提升模型在整个数据集上的描述语句准确性,忽视了对大量罕见词的准确描述,限制了在实际场景中的应用。针对这一问题,提出了基于动态语义记忆网络(DSMN)的长尾图像描述生成模型,旨在保证模型对常见名词准确描述的同时,提升模型对罕见名词的描述效果。DSMN模型能够动态挖掘罕见词与常见词的全局语义关系,实现从常见词到罕见词的语义知识迁移,通过协同考虑全局单词语义关系信息及当前输入图像和已生成单词的局部语义信息提升罕见词的语义特征表示能力和预测性能。为了有效评价长尾图像描述生成方法,基于MS COCO Captioning数据集定义了长尾图像描述生成任务专用测试集Few-COCO。在MS COCO Captioning和Few-COCO数据集上的多个量化实验表明,DSMN模型在Few-COCO数据集上的罕见词描述准确率为0.602 8%,召回率为0.323 4%,F-1值为0.356 7%,相较于基准方法提升明显。
Abstract:Image captioning takes image as input and outputs a text sequence. Nowadays, most images included in image captioning datasets are captured from daily life of internet users. Captions of these images are consequently composed of a few common words and many rare words. Most existing studies focus on improving performance of captioning in the whole dataset, regardless of captioning performance among rare words. To solve this problem, we introduce long-tail image captioning with dynamic semantic memory network (DSMN). Long-tail image captioning requires model improving performance of rare words generation, while maintaining good performance of common words generation. DSMN model dynamically mining the global semantic relationship between rare words and common words, enabling knowledge transfer from common words to rare words. Result shows DSMN improves performance of semantic representation of rare words by collaborating global words semantic relation and local semantic information of the input picture and generated words. For better evaluation on long-tail image captioning, we organized a task-specified test split Few-COCO from original MS COCO Captioning dataset. By conducting quantitative and qualitative experiments, the rare words description precision of DSMN model on Few-COCO dataset is 0.602 8%, the recall is 0.323 4%, and the F-1 value is 0.356 7%, showing significant improvement compared with baseline methods.
-
Key words:
- deep learning /
- image understanding /
- image captioning /
- long-tail distribution /
- memory network
-
表 1 MS COCO Captioning数据集的词频分布
Table 1. Word frequency distribution of MS COCO Captioning dataset
统计项 统计值 全部词汇 9 487 全部名词 7 669 出现100次以下名词 6 089 出现80次以下名词 5 859 出现50次以下名词 5 420 出现20次以下名词 4 156 出现10次以下名词 2 888 表 2 MS COCO Captioning Karpathy测试集上的生成文本相似性指标结果
Table 2. Results of similarity metrics of generated captions in MS COCO Captioning Karpathy test split
表 3 Few-COCO测试集上的生成文本相似性指标结果
Table 3. Results of similarity metrics for generated captions in Few-COCO test split
表 4 Few-COCO测试集上的罕见词描述准确性结果
Table 4. Results of rare word accuracy metrics for generated captions in Few-COCO test split
表 5 Few-COCO测试集上的罕见词描述准确性消融实验结果
Table 5. Ablation results of rare word accuracy metrics for generated captions in Few-COCO test split
模型 精确率/% 召回率/% F-1值/% DSMN-Base 0.373 3 0.129 2 0.166 2 DSMN-w/o MEM 0.535 6 0.224 5 0.266 2 DSMN 0.602 8 0.323 4 0.356 7 表 6 Few-COCO测试集上融合参数K的分析结果
Table 6. Results of analyzing combination coefficient K in Few-COCO test split
K 精确率/% 召回率/% F-1值/% 0.50 0.424 3 0.137 9 0.180 8 0.25 0.602 8 0.323 4 0.356 7 0 0.400 1 0.169 8 0.201 4 -
[1] HOSSAIN M Z, SOHEL F, SHIRATUDDIN M F, et al. A comprehensive survey of deep learning for image captioning[EB/OL]. (2018-10-14)[2021-09-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.04020. [2] CORNIA M, STEFANINI M, BARALDI L, et al. Meshed-memory transformer for image captioning[C]//2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 10575-10584. [3] XU K, BA J, KIROS R, et al. Show, attend and tell: Neural image caption generation with visual attention[C]//International Conference on Machine Learning, 2015: 2048-2057. [4] ANDERSON P, HE X, BUEHLER C, et al. Bottom-up and top-down attention for image captioning and visual question answering[C]//2018 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 6077-6086. [5] LU J S, XIONG C M, PARIKH D, et al. Knowing when to look: Adaptive attention via a visual sentinel for image captioning[C]// 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 3242-3250. [6] LU D, WHITEHEAD S, HUANG L F, et al. Entity-aware image caption generation[EB/OL]. (2018-11-07)[2021-09-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1804.07889. [7] YANG X, TANG K H, ZHANG H W, et al. Auto-encoding scene graphs for image captioning[C]//2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 10677-10686. [8] CHEN X L, FANG H, LIN T Y, et al. Microsoft COCO captions: Data collection and evaluation server[EB/OL]. (2015-04-03)[2021-09-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1504.00325. [9] LI Y H, YAO T, PAN Y W, et al. Pointing novel objects in image captioning[C]//2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 12489-12498. [10] ANDERSON P, FERNANDO B, JOHNSON M, et al. SPICE: Semantic propositional image caption evaluation[C]// European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 382-398. [11] VINYALS O, TOSHEV A, BENGIO S, et al. Show and tell: A neural image caption generator[C]//2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 3156-3164. [12] YOU Q Z, JIN H L, WANG Z W, et al. Image captioning with semantic attention[C]//2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 4651-4659. [13] VEDANTAM R, ZITNICK C L, PARIKH D. CIDEr: Consensus-based image description evaluation[C]//2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 4566-4575. [14] LIN C Y. ROUGE: A package for automatic evaluation of summaries[C]//Proceedings of the Workshop on Text Summarization Branches Out, 2004: 74-81. [15] BANERJEE S, LAVIE A. METEOR: An automatic metric for MT evaluation with improved correlation with human judgments[C]//Proceedings of the ACL Workshop on Intrinsic and Extrinsic Evaluation Measures for Machine Translation and/or Summarization, 2005: 65-72. [16] PAPINENI K, ROUKOS S, WARD T, et al. BLEU: A method for automatic evaluation of machine translation[C]//Proceedings of the 40th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. New York: ACM, 2002: 311-318. [17] DEVLIN J, CHENG H, FANG H, et al. Language models for image captioning: The quirks and what works[EB/OL]. (2015-10-14)[2021-09-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1505.01809v2. [18] KULKARNI G, PREMRAJ V, DHAR S, et al. Baby talk: Understanding and generating image descriptions[C]//2011 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011: 1601-1608. [19] LI S, KULKARNI G, BERG T, et al. Composing simple image descriptions using web-scale n-grams[C]//Proceedings of the Fifteenth Conference on Computational Natural Language Learning. New York: ACM, 2011: 220-228. [20] GONG Y C, WANG L W, HODOSH M, et al. Improving image-sentence embeddings using large weakly annotated photo collections[C]// European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2014: 529-545. [21] ORDONEZ V, KULKARNI G, BERG T. Im2Text: Describing images using 1 million captioned photographs[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2011, 24: 1143-1151. [22] HODOSH M, YOUNG P, HOCKENMAIER J. Framing image description as a ranking task: Data, models and evaluation metrics (extended abstract)[J]. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, 2013, 47: 853-899. doi: 10.1613/jair.3994 [23] REN S Q, HE K M, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137-1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 [24] GERS F A, SCHMIDHUBER J, CUMMINS F. Learning to forget: Continual prediction with LSTM[J]. Neural Computation, 2000, 12(10): 2451-2471. doi: 10.1162/089976600300015015 [25] RENNIE S J, MARCHERET E, MROUEH Y, et al. Self-critical sequence training for image captioning[C]//2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1179-1195. [26] HERDADE S, KAPPELER A, BOAKYE K, et al. Image captioning: Transforming objects into words[EB/OL]. (2020-01-11)[2021-09-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1906.05963v1. [27] GUO L T, LIU J, ZHU X X, et al. Normalized and geometry-aware self-attention network for image captioning[C]//2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 10324-10333. [28] HE S, LIAO W, TAVAKOLI H R, et al. Image captioning through image transformer[C]//Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision, 2020. [29] YAN C G, HAO Y M, LI L, et al. Task-adaptive attention for image captioning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2022, 32(1): 43-51. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2021.3067449 [30] JI J Y, LUO Y P, SUN X S, et al. Improving image captioning by leveraging intra- and inter-layer global representation in transformer network[C]//Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto: AAAI, 2021, 35(2): 1655-1663. [31] LU J S, BATRA D, PARIKH D, et al. ViLBERT: Pretraining task-agnostic visiolinguistic representations for vision-and-language tasks[EB/OL]. (2019-08-06)[2021-09-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.02265. [32] SUN Y, WANG S H, LI Y K, et al. ERNIE: Enhanced representation through knowledge integration[EB/OL]. (2019-04-19)[2021-09-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.09223. [33] VENUGOPALAN S, HENDRICKS L A, ROHRBACH M, et al. Captioning images with diverse objects[C]//2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1170-1178. [34] CHEN S Z, JIN Q, WANG P, et al. Say as you wish: Fine-grained control of image caption generation with abstract scene graphs[C]//2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 9959-9968. [35] CHEN T L, ZHANG Z P, YOU Q Z, et al. "Factual" or "emotional": Stylized image captioning with adaptive learning and attention[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 527-543. [36] ZHAO W T, WU X X, ZHANG X X. MemCap: Memorizing style knowledge for image captioning[C]//Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto: AAAI, 2020, 34(7): 12984-12992. [37] AGRAWAL H, DESAI K R, WANG Y F, et al. Nocaps: Novel object captioning at scale[C]//2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 8947-8956. [38] WU Y, ZHU L, JIANG L, et al. Decoupled novel object captioner[C]//Proceedings of the 26th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. New York: ACM, 2018: 1029-1037. [39] YAO T, PAN Y W, LI Y H, et al. Incorporating copying mechanism in image captioning for learning novel objects[C]//2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 5263-5271. [40] SUKHBAATAR S, SZLAM A, WESTON J, et al. End-to-end memory networks[EB/OL]. (2015-11-24)[2021-09-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1503.08895v5. [41] CHEN H, REN Z, TANG J, et al. Hierarchical variational memory network for dialogue generation[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 World Wide Web Conference, 2018: 1653-1662. [42] HUANG Y, WANG L. ACMM: Aligned cross-modal memory for few-shot image and sentence matching[C]//2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision(ICCV). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 5773-5782. [43] HAN J W, NGAN K N, LI M J, et al. A memory learning framework for effective image retrieval[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image, 2005, 14(4): 511-524. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2004.841205 [44] JOHNSON J, KARPATHY A, LI F F. DenseCap: Fully convolutional localization networks for dense captioning[C]//2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 4565-4574. [45] LOPER E, BIRD S. NLTK: The natural language toolkit[C]//Proceedings of the COLING/ACL on Interactive Presentation Sessions, 2006: 69-72. [46] KINGMA D P, BA J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization[EB/OL]. (2017-01-30)[2021-09-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6980v8?hl:ja. [47] BENGIO S, VINYALS O, JAITLY N, et al. Scheduled sampling for sequence prediction with recurrent neural networks[EB/OL]. (2015-09-23)[2021-09-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1506.03099v3. -







 下载:
下载: