-
摘要:
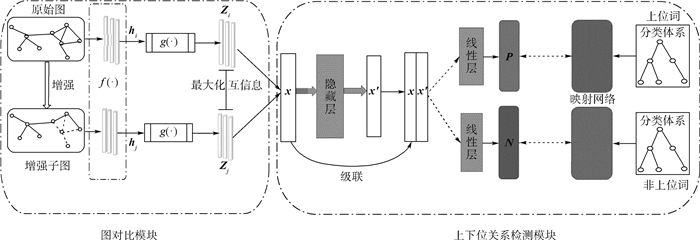
上下位关系是自然语言处理(NLP)下游任务的基础,因此上下位关系检测是自然语言处理领域备受关注的问题。针对现有词嵌入方法采用随机初始化词向量,不能很好地捕获上下位关系不对称和可传递的特性,且现有模型没有充分利用预测向量与真实投影之间关系的局限性,提出了一种基于图对比学习的上下位关系检测(HyperCL)方法。引入图对比学习进行数据增强,基于最大化局部和全局表示的互信息,学习具有鲁棒性的词特征表示。所提方法学习了将下位词的词向量投影到上位词和非上位词,同时能够更好地区分嵌入空间中的上位词和非上位词,从而提高了检测精度。在2个基准数据集上的实验结果表明,所提模型比现有方法在准确率上提升了0.03以上。
-
关键词:
- 自然语言处理(NLP) /
- 上下位关系检测 /
- 图对比学习 /
- 数据增强 /
- 词嵌入
Abstract:Hypernymy is the foundation of many downstream tasks in natural language processing (NLP), so hypernymy detection has received considerable attention in the field of NLP. Adopting random initialization word vectors, existing word embedding methods cannot well capture the asymmetry and transferability of hypernymy, or make full use of the relationship between the prediction vector and the real projection. To address these problems, a novel method is proposed for detecting hypernymy based on graph contrastive learning (HyperCL). Firstly, HyperCL is introduced for data enhancement, and robust word feature representations are learned based on maximizing mutual information between local and global representations. Secondly, the proposed method learns how to project the hyponym vector to its hypernym and non-hypernym, and better distinguish the hypernym and non-hypernym in the embedded space, thus improving the detection accuracy. Experimental results on two benchmark datasets show that the proposed model increases the accuracy by more than 0.03, compared with the existing methods.
-
表 1 不同方法的AP值比较
Table 1. Comparison of AP with different methods
表 2 不同词嵌入下的检测性能比较
Table 2. Comparison of detection performance under different word embeddings
输入 AP BLESS WBLESS HyperCL-no 0.987 0.922 HyperCL 0.992 0.961 表 3 不同损失函数下的检测性能比较
Table 3. Comparison of detection performance with different loss functions
输入 AP BLESS WBLESS Baseline-no 0.964 0.887 HyperCL-no 0.987 0.922 Baseline 0.945 0.870 HyperCL 0.992 0.961 -
[1] ZHANG Y C, AHMED A, JOSIFOVSKI V, et al. Taxonomy discovery for personalized recommendation[C]//Proceedings of the 7th ACM International Recommendation on Web Search and Data Mining. New York: ACM, 2014: 243-252. [2] VULIC I, GERZ D, KIELA D, et al. HyperLex: A large-scale evaluation of graded lexical entailment[J]. Computational Linguistics, 2017, 43(4): 781-835. doi: 10.1162/COLI_a_00301 [3] WANG Z Y, ZHAO K, WANG H X, et al. Query understanding through knowledge-based conceptualization[C]//Proceedings of the International Joint Conferences on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto: AAAI, 2015: 3264-3270. [4] WANG C Y, YAN J C, ZHOU A, et al. Transductive non-linear learning for Chinese hypernym prediction[C]//Proceedings of the 55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, 2017: 1394-1404. [5] HEARST M. Automatic acquisition of hyponyms from large text corpora[C]//Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Computational Linguistics, 1992: 539-545. [6] ROLLER S, KIELA D, NICKEL M. Hearst patterns revisited: Automatic hypernym detection from large text corpora[C]//Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, 2018: 358-363. [7] GEFFET M, DAGAN I. The distributional inclusion hypotheses and lexical entailment[C]//Proceedings of the 43rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, 2015: 107-114. [8] SANTUS E, LENCI A, LU Q, et al. Chasing hypernyms in vector spaces with entropy[C]//Proceedings of the 14th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, 2014: 38-42. [9] KIELA D, RIMELL L, VULIC I, et al. Exploiting image generality for lexical entailment detection[C]//Proceedings of the 53rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 7th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing, 2015: 119-124. [10] NGUYEN K A, KOPER M, WALDE S S I, et al. Hierarchical embeddings for hypernymy detection and directionality[C]//Proceedings of the 2017 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, 2017: 233-243. [11] ROLLER S, ERK K, BOLEDA G. Inclusive yet selective: Supervised distributional hypernymy detection[C]//Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Computational Linguistics, 2014: 1025-1036. [12] WEEDS J, CLARKE D, REFFIFIN J, et al. Learning to distinguish hypernyms and co-hyponyms[C]//Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Computational Linguistics, 2014: 2249-2259. [13] SHWARTZ V, GOLDBERG Y, DAGAN I. Improving hypernymy detection with an integrated path-based and distributional method[C]//Proceedings of the 54th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, 2016: 2389-2398. [14] YU Z, WANG H, LIN X, et al. Learning term embeddings for hypernymy identification[C]//Proceedings of the International Joint Conferences on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto: AAAI, 2015: 1390-1397. [15] LUU A T, TAY Y, HUI S C, et al. Learning term embeddings for taxonomic relation identification using dynamic weighting neural network[C]//Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, 2016: 403-413. [16] 汪诚愚, 何晓丰, 宫学庆, 等. 面向上下位关系预测的词嵌入投影模型[J]. 计算机学报, 2020, 43(5): 869-883. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJX202005007.htmWANG C Y, HE X F, GONG X Q, et al. Word embedding projection models for hypernymy[J]. Journal of Computers, 2020, 43(5): 869-883(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJX202005007.htm [17] FU R J, GUO J, QIN B, et al. Learning semantic hierarchies via word embeddings[C]//Proceedings of the 52nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, 2014: 1199-1209. [18] VELICKOVIC P, FEDUS W, HAMILTON W L, et al. Deep graph infomax[C]//ICLR 2019, 2019: 1-17. [19] REN Y X, LIU B, HUANG C, et al. Heterogeneous deep graph infomax[EB/OL]. (2020-11-13)[2021-09-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.08538. [20] SUN F Y, HOFFMANN J, VERMA V, et al. InfoGraph: Unsupervised and semi-supervised graph-level representation learning via mutual information maximization[EB/OL]. (2020-01-17)[2021-09-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.01000. [21] WANG C Y, HE X F, ZHOU A Y. Improving hypernymy prediction via taxonomy enhanced adversarial learning[C]//Proceedings of the 33rd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto: AAAI, 2019: 7128-7135. [22] WANG C Y, FAN Y, HE X F, et al. A family of fuzzy orthogonal projection models for monolingual and cross-lingual hypernymy prediction[C]//The World Wide Web Conference. New York: ACM, 2019: 1965-1976. [23] PHAM N, LAZARIDOU A, BARONI M. A multitask objective to inject lexical contrast into distributional semantics[C]//Proceedings of the 53rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 7th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing, 2015: 21-26. -







 下载:
下载: