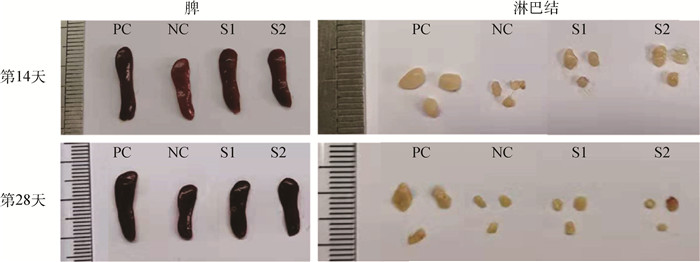
The dynamics modeling of the tilt-rotor aircraft is studied during dynamic transition process. Firstly, starting from the multibody dynamics, a box-wing tilt-rotor UAV is taken as an example, which is assumed as a multi-rigid-body system consisting of wings, a body, ducted fans, tilt rotors, etc. Secondly, the non-conservative force and moment matrix of the UAV system are established by the displacement constraints of different rigid body centroids, and the kinetic energy, potential energy, complementary virtual work and inverse potential energy of the UAV are established. Finally, based on the Lagrange equation in Hamilton system and the second Lagrange equation, the dynamics model of the box-wing tilt-rotor UAV is deduced and established. The simulation results show that the simulation results of the dynamics models established by the two types of Lagrange equations are consistent with the experimental data, which verifies the rationality of the proposed modeling method. In the case that the rotation speed of the tilt rotor is constant, the longer the transition process takes, the less the UAV is dropped, the smoother the trajectory is, but the more input energy is, and the design of the specific transition process should be determined according to the actual needs of the time that the transition process takes, input energy, etc.